* adding first version of new knative sample + small fix to knative distributed calculator Signed-off-by: TenSt <stepan.maks@gmail.com> * adding second part + grammar fixes Signed-off-by: TenSt <stepan.maks@gmail.com> * adding deploy and react form folders; small fixes Signed-off-by: TenSt <stepan.maks@gmail.com> * adding reference to React Form source files Signed-off-by: TenSt <stepan.maks@gmail.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| deploy | ||
| img | ||
| react-form | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
Darp Binding + Knative Serving and Eventing
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Dapr runtime version | v1.5.0 |
| Knative Serving version | v1.0 |
| Language | Javascript, Python, Go, C# |
| Environment | Kubernetes > v1.20 |
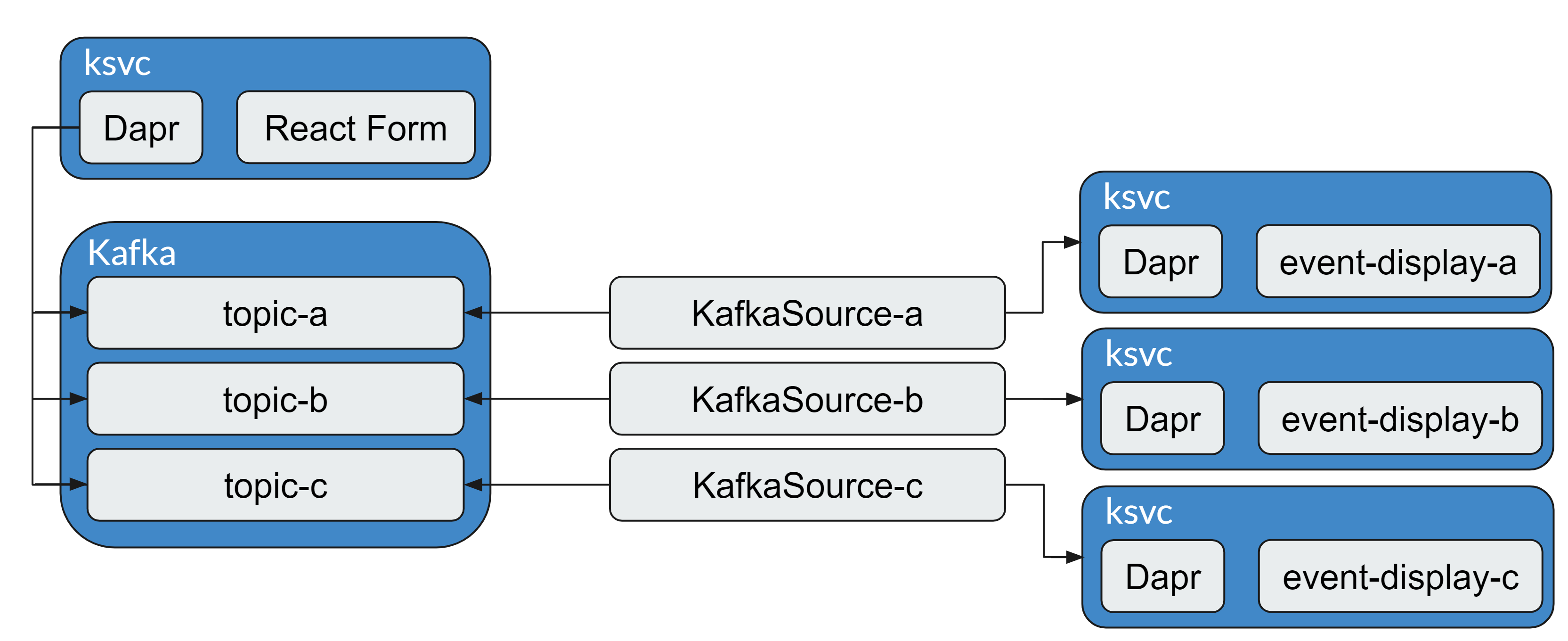
This is a sample application based on Dapr bindings quickstart using:
- Knative Serving (with Kourier) to host React Form and backend applications
- Dapr Bindings to put events into the Kafka topics
- Knative Eventing to read events from Kafka topics and distribute them to backend applications
This is built as a proof-of-concept to show how to use Knative and Dapr.
Prerequisites
This sample requires you to have the following installed on your machine:
- Dapr CLI v1.5.0
- kubectl
- An online hoster Kubernetes cluster, such as AKS or GKE
- React Form that will be used to send events to Dapr. The image is hosted under my Docker Hub account, but you can change it to your own. Source files can be found here and here.
Also, unless you have already done so, clone the repository with the samples and cd into the right directory:
git clone https://github.com/dapr/samples.git
cd samples/bindings-knative-eventing
Step 1 - Make sure that your kubectl client is working
The first thing you need is an enabled Kubernetes cluster. This sample was tested on a fully-fledged cluster.
Once you have that make sure you get a positive response from the following kubectl command
kubectl get pods
This should either have output as No resources found in default namespace. or should list the pods running the default namesapce.
Step 2 - Setup Dapr
Follow instructions to download and install the Dapr CLI and initialize Dapr.
Step 3 - Setup Knative Serving and Eventing
Note: Here you can find full instruction of how to install and configure Knative Serving. All the information below in steps 3 and 4 is an excerpt from it which was used and tested.
Install Knative Serving CRDs
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative/serving/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/serving-crds.yaml
Install Knative Serving Core
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative/serving/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/serving-core.yaml
Install Knative Kourier - networking layer
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative/net-kourier/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/kourier.yaml
Configure Knative to use Kourier
kubectl patch configmap/config-network \
--namespace knative-serving \
--type merge \
--patch '{"data":{"ingress.class":"kourier.ingress.networking.knative.dev"}}'
Verify installation
kubectl get pods -n knative-serving
All pods inside knative-serving namespace should have Running or Completed status.
Step 3 - Configure DNS for Knative
Fetch the External IP address by running the command
kubectl --namespace kourier-system get service kourier
Configure DNS
This sample was tested with real DNS. In this case, you need to take the External IP address from the previous step and add it to your DNS wildcard A record (e.g. *.knative.example.com).
Direct Knative to use that domain
Please change knative.example.com below to your domain.
kubectl patch configmap/config-domain \
--namespace knative-serving \
--type merge \
--patch '{"data":{"knative.example.com":""}}'
Install Knative Eventing CRDs
kubectl apply -f kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative/eventing/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/eventing-crds.yaml
Install Knative Eventing Core
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative/eventing/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/eventing-core.yaml
Install Knative Extention - Kafka Source
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/knative-sandbox/eventing-kafka/releases/download/knative-v1.0.0/source.yaml
Step 4 - Install Kafka cluster
As a part of this sample, I'm using Strimzi to create and install Kafka clusters. Here is the instruction of how to do that.
Here is a quick excerpt from it:
Create a namespace for Kafka
kubectl create namespace kafka
Apply all installation files (this will also create Strimzi operator)
kubectl create -f 'https://strimzi.io/install/latest?namespace=kafka' -n kafka
Wait until Strimzi operator is up and running
kubectl get pod -n kafka
Create new Kafka cluster
kubectl apply -f https://strimzi.io/examples/latest/kafka/kafka-persistent-single.yaml -n kafka
Wait until Kafka cluster is up and running
kubectl wait kafka/my-cluster --for=condition=Ready --timeout=300s -n kafka
Step 5 - Setup Sample
Apply Knative part
kubectl apply -f knative/.
Apply Dapr part
kubectl apply -f dapr/.
Verification
Verify that there are 3 pods from KafkaSource in default namespace:
kubectl get pods
Example output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kafkasource-a-26f8b1a8-519a-4717-bdf2-e49bacb5dc9d-898bdff676s2 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-b-297a7da3-9503-4685-9f02-4745f412af5f-7cbbdfc998n7 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-c-c31fa8d2-51a5-482e-91cd-071ef4b52221-5cbd795mckpz 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
Verify that there are 4 Knative Services created. Make sure that READY is set to True. Otherwise, please wait until all the necessary components are configured by Knative.
kubectl get ksvc
Example output:
NAME URL LATESTCREATED LATESTREADY READY REASON
event-display-a http://event-display-a.default.svc.cluster.local event-display-a-rev1 event-display-a-rev1 True
event-display-b http://event-display-b.default.svc.cluster.local event-display-b-rev1 event-display-b-rev1 True
event-display-c http://event-display-c.default.svc.cluster.local event-display-c-rev1 event-display-c-rev1 True
react-form http://react-form.default.knative.example.com react-form-rev1 react-form-rev1 True
Step 6 - How it works
Deploy files
In the deploy folder we have two folders: knative and dapr which holds respective items.
Knative folder contain 3 types of resources: Knative service, Kafka Source, and Kafka Topic. Dapr folder contain 2 types of resources: Knative service and Dapr Binding component.
Knative Service
By default, Knative Serving will scale to zero its workloads if there is no traffic to them. Wait for a couple of minutes and run the next command to list all pods in the default namespace:
kubectl get pods
Example output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kafkasource-a-26f8b1a8-519a-4717-bdf2-e49bacb5dc9d-898bdff676s2 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-b-297a7da3-9503-4685-9f02-4745f412af5f-7cbbdfc998n7 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-c-c31fa8d2-51a5-482e-91cd-071ef4b52221-5cbd795mckpz 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
As you can see, there are only pods from KafkaSource and there are no pods of React Form and Event Display applications. Here you can find all details about Knative Services.
Kafka Source
The KafkaSource reads all the messages, from all partitions, and sends those messages as CloudEvents through HTTP to its configured sink. If the sink is not available, no pods will be created. Here is the detailed instruction.
Let's have a look at the yaml file of kafkasource-a:
apiVersion: sources.knative.dev/v1beta1
kind: KafkaSource
metadata:
name: a
spec:
consumerGroup: knative-group
bootstrapServers:
- my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.kafka:9092 # note the kafka namespace
topics:
- topic-a
sink:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: event-display-a
Necessary items ouf of it:
bootstrapServers - this is the address of your Kafka server
topics - list of topics from which we will read events
sink - the reference to the service which should receive events
List all Kafka Sources:
kubectl get kafkasource
Example output:
NAME TOPICS BOOTSTRAPSERVERS READY REASON AGE
a ["topic-a"] ["my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.kafka:9092"] True 3d5h
b ["topic-b"] ["my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.kafka:9092"] True 3d3h
c ["topic-c"] ["my-cluster-kafka-bootstrap.kafka:9092"] True 3d3h
Kafka Topic
This is an optional resource that is used if you use Strimzi. It is used by the Topic operator to keep topics in sync with the Kafka cluster. Here is detailed instruction.
List all Kafka Topics:
kubectl get kafkatopics -n kafka
Example output:
NAME CLUSTER PARTITIONS REPLICATION FACTOR READY
consumer-offsets---84e7a678d08f4bd226872e5cdd4eb527fadc1c6a my-cluster 50 1 True
strimzi-store-topic---effb8e3e057afce1ecf67c3f5d8e4e3ff177fc55 my-cluster 1 1 True
strimzi-topic-operator-kstreams-topic-store-changelog---b75e702040b99be8a9263134de3507fc0cc4017b my-cluster 1 1 True
topic-a my-cluster 3 1 True
topic-b my-cluster 3 1 True
topic-c my-cluster 3 1 True
Dapr Binding component
This component allows you to bind your apps with external systems using events. In this particular case, we use Output bindings to send events to our Kafka topics. Here you can find details about Kafka binding component.
List all Dapr components:
kubectl get components
Example output:
NAME AGE
topic-a 3d4h
topic-b 3d3h
topic-c 3d3h
We use a separate component for each external topic to which we will send events.
Sample in action
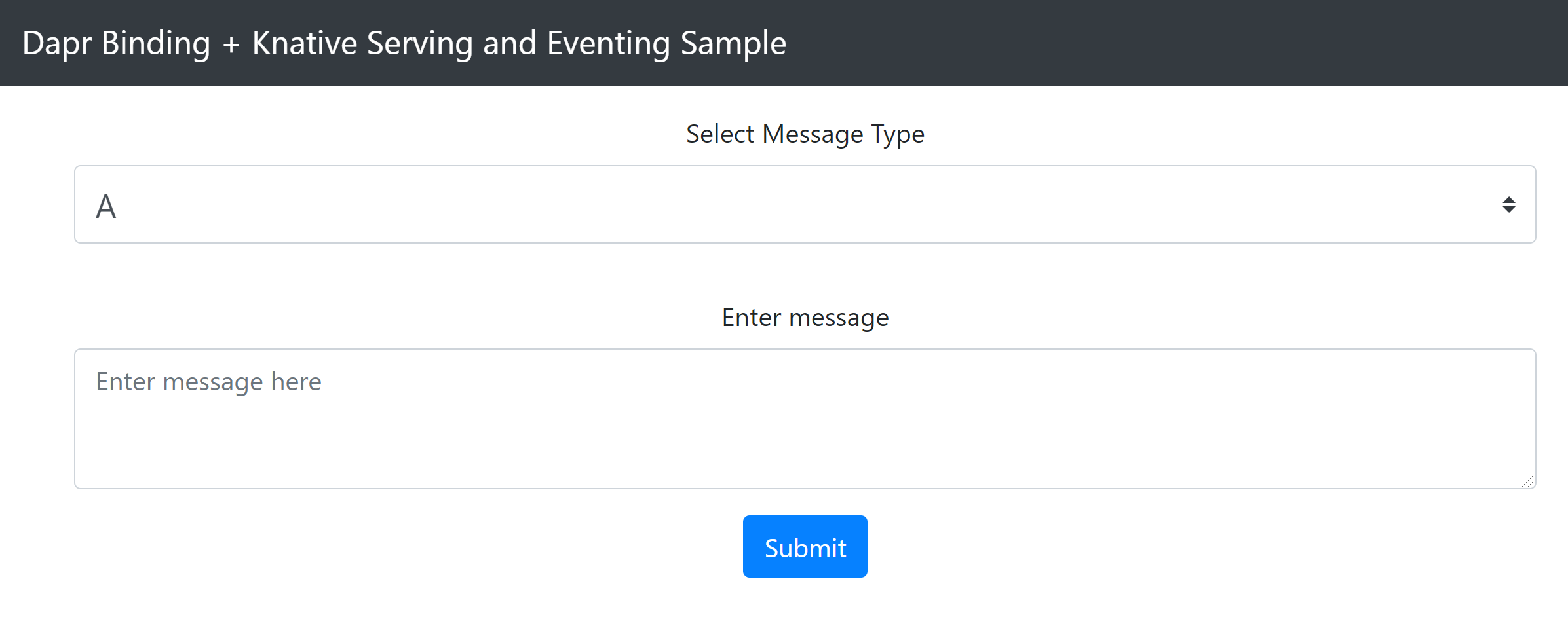
Navigate to the address of your React Form Knative service (http://react-form.default.knative.example.com) with your browser and you should see the React Form.
Using drop-down menu send some messages to the A, B and C. Then go back to your console and list all pods:
kubectl get pods
You should see that now we have pods running for our React Form and 3 backend Event Display applications:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
event-display-a-rev1-deployment-84b98798d8-dgdt5 3/3 Running 0 14s
event-display-b-rev1-deployment-7445b94cbb-mwfdg 3/3 Running 0 11s
event-display-c-rev1-deployment-786c7bcbbb-gc9jn 2/3 Running 0 6s
kafkasource-a-26f8b1a8-519a-4717-bdf2-e49bacb5dc9d-898bdff676s2 1/1 Running 0 3d4h
kafkasource-b-297a7da3-9503-4685-9f02-4745f412af5f-7cbbdfc998n7 1/1 Running 0 3d4h
kafkasource-c-c31fa8d2-51a5-482e-91cd-071ef4b52221-5cbd795mckpz 1/1 Running 0 3d4h
react-form-rev1-deployment-849ddfb5cd-86jxs 3/3 Running 0 29s
Take a look at logs of each backend Event Display application and you should see an event with a message that you've sent:
☁️ cloudevents.Event
Context Attributes,
specversion: 1.0
type: dev.knative.kafka.event
source: /apis/v1/namespaces/default/kafkasources/a#topic-a
subject: partition:1#1
id: partition:1/offset:1
time: 2021-12-16T22:16:31.497Z
Data,
{"message":"test A"}
Wait a minute and you will see that Knative Serving will scale our apps back to zero:
kubectl get pods
Example output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kafkasource-a-26f8b1a8-519a-4717-bdf2-e49bacb5dc9d-898bdff676s2 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-b-297a7da3-9503-4685-9f02-4745f412af5f-7cbbdfc998n7 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
kafkasource-c-c31fa8d2-51a5-482e-91cd-071ef4b52221-5cbd795mckpz 1/1 Running 0 3d3h
Conclustion
Knative is a powerful platform that provides different tools to deploy and manage modern serverless workloads. Combining it with Dapr opens up a lot of different scenarios which can help developers to implement their solutions.