mirror of https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger.git
Add configs track changes to docs
This commit is contained in:
parent
0830abd51d
commit
e9cd7afc8a
16
README.md
16
README.md
|
|
@ -38,6 +38,9 @@ ClusterIP [services](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ser
|
|||
Istio [virtual services](https://istio.io/docs/reference/config/istio.networking.v1alpha3/#VirtualService))
|
||||
to drive the canary analysis and promotion.
|
||||
|
||||
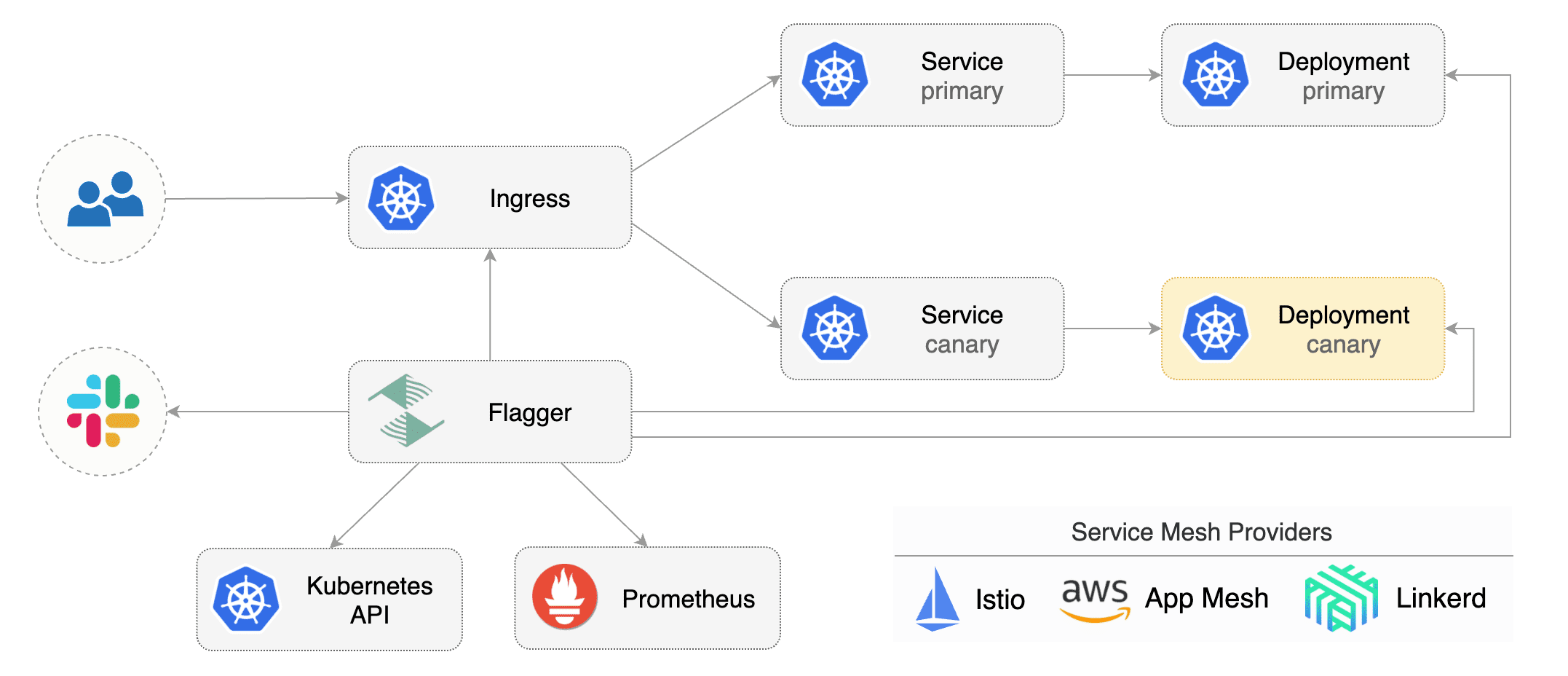
Flagger keeps track of ConfigMaps and Secrets referenced by a Kubernetes Deployment and triggers a canary analysis if any of those objects change.
|
||||
When promoting a workload in production, both code (container images) and configuration (config maps and secrets) are being synchronised.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Gated canary promotion stages:
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,28 +51,28 @@ Gated canary promotion stages:
|
|||
* halt advancement if a rolling update is underway
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight percentage from 0% to 5% (step weight)
|
||||
* call webhooks and check results
|
||||
* check canary HTTP request success rate and latency
|
||||
* halt advancement if any metric is under the specified threshold
|
||||
* increment the failed checks counter
|
||||
* check if the number of failed checks reached the threshold
|
||||
* route all traffic to primary
|
||||
* scale to zero the canary deployment and mark it as failed
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated (revision bump) and start over
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated and start over
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight by 5% (step weight) till it reaches 50% (max weight)
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request success rate is under the threshold
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request duration P99 is over the threshold
|
||||
* halt advancement if the primary or canary deployment becomes unhealthy
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary deployment is being scaled up/down by HPA
|
||||
* promote canary to primary
|
||||
* copy ConfigMaps and Secrets from canary to primary
|
||||
* copy canary deployment spec template over primary
|
||||
* wait for primary rolling update to finish
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* route all traffic to primary
|
||||
* scale to zero the canary deployment
|
||||
* mark rollout as finished
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated (revision bump) and start over
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the canary analysis _max weight_ and the _step weight_ percentage in the Flagger's custom resource.
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated and start over
|
||||
|
||||
For a deployment named _podinfo_, a canary promotion can be defined using Flagger's custom resource:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -248,6 +251,9 @@ kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
|
|||
podinfod=quay.io/stefanprodan/podinfo:1.4.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** that Flagger tracks changes in the deployment `PodSpec` but also in `ConfigMaps` and `Secrets`
|
||||
that are referenced in the pod's volumes and containers environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new canary analysis:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -336,6 +342,8 @@ Events:
|
|||
Warning Synced 1m flagger Canary failed! Scaling down podinfo.test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitoring
|
||||
|
||||
Flagger comes with a Grafana dashboard made for canary analysis.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -97,38 +97,42 @@ the Istio Virtual Service. The container port from the target deployment should
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
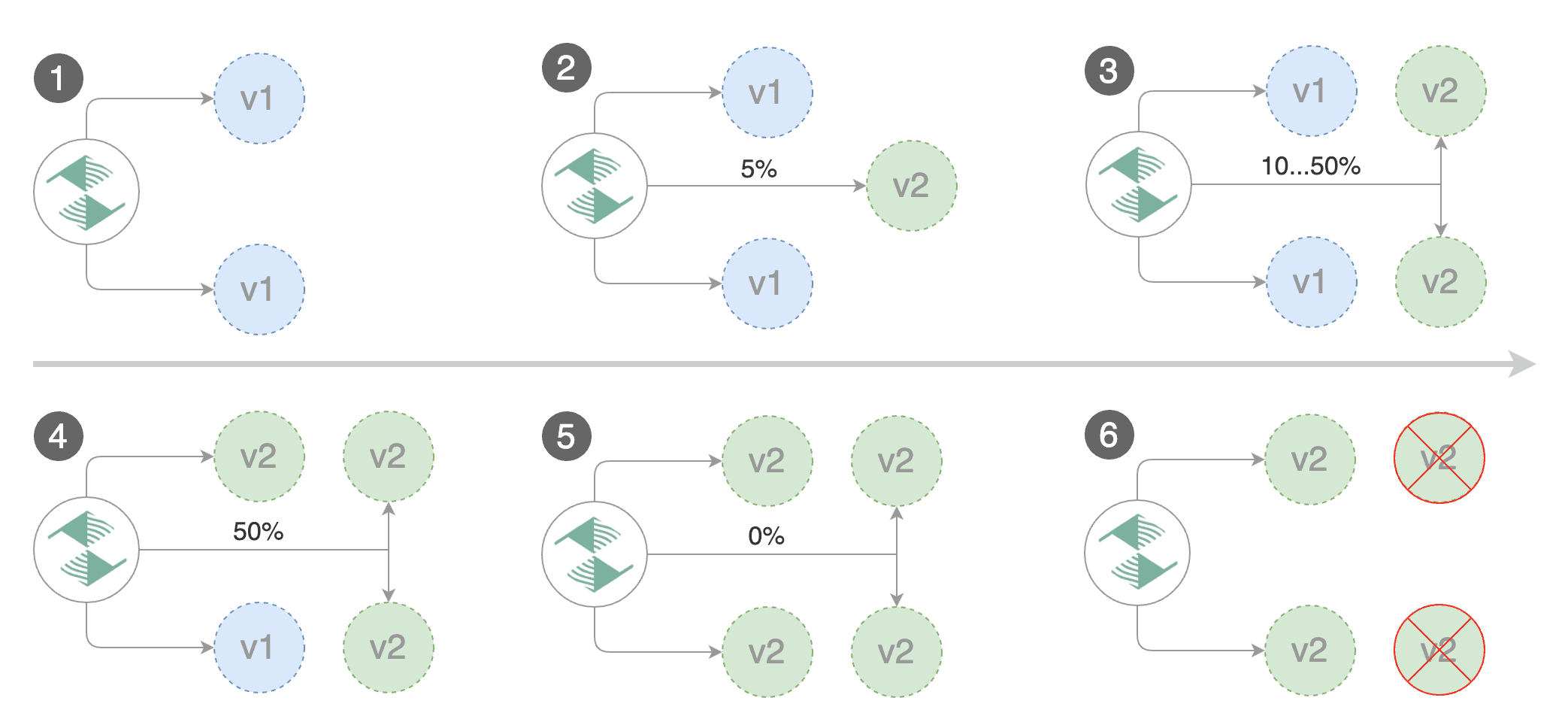
A canary deployment is triggered by changes in any of the following objects:
|
||||
|
||||
* Deployment PodSpec (container image, command, ports, env, resources, etc)
|
||||
* ConfigMaps mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
|
||||
* Secrets mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
Gated canary promotion stages:
|
||||
|
||||
* scan for canary deployments
|
||||
* creates the primary deployment if needed
|
||||
* check Istio virtual service routes are mapped to primary and canary ClusterIP services
|
||||
* check primary and canary deployments status
|
||||
* halt advancement if a rolling update is underway
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight percentage from 0% to 5% \(step weight\)
|
||||
* halt advancement if a rolling update is underway
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight percentage from 0% to 5% (step weight)
|
||||
* call webhooks and check results
|
||||
* check canary HTTP request success rate and latency
|
||||
* halt advancement if any metric is under the specified threshold
|
||||
* increment the failed checks counter
|
||||
* halt advancement if any metric is under the specified threshold
|
||||
* increment the failed checks counter
|
||||
* check if the number of failed checks reached the threshold
|
||||
* route all traffic to primary
|
||||
* scale to zero the canary deployment and mark it as failed
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated \(revision bump\) and start over
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight by 5% \(step weight\) till it reaches 50% \(max weight\)
|
||||
* halt advancement if the primary or canary deployment becomes unhealthy
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary deployment is being scaled up/down by HPA
|
||||
* halt advancement if any of the webhook calls are failing
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request success rate is under the threshold
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request duration P99 is over the threshold
|
||||
* route all traffic to primary
|
||||
* scale to zero the canary deployment and mark it as failed
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated and start over
|
||||
* increase canary traffic weight by 5% (step weight) till it reaches 50% (max weight)
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request success rate is under the threshold
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary request duration P99 is over the threshold
|
||||
* halt advancement if the primary or canary deployment becomes unhealthy
|
||||
* halt advancement while canary deployment is being scaled up/down by HPA
|
||||
* promote canary to primary
|
||||
* copy canary deployment spec template over primary
|
||||
* copy ConfigMaps and Secrets from canary to primary
|
||||
* copy canary deployment spec template over primary
|
||||
* wait for primary rolling update to finish
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* halt advancement if pods are unhealthy
|
||||
* route all traffic to primary
|
||||
* scale to zero the canary deployment
|
||||
* mark the canary deployment as finished
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated \(revision bump\) and start over
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the canary analysis _max weight_ and the _step weight_ percentage in the Flagger's custom resource.
|
||||
* mark rollout as finished
|
||||
* wait for the canary deployment to be updated and start over
|
||||
|
||||
### Canary Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ kubectl -n test apply -f ${REPO}/artifacts/loadtester/deployment.yaml
|
|||
kubectl -n test apply -f ${REPO}/artifacts/loadtester/service.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a canary custom resource \(replace example.com with your own domain\):
|
||||
Create a canary custom resource (replace example.com with your own domain):
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1alpha3
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,6 +146,8 @@ Events:
|
|||
Normal Synced 5s flagger Promotion completed! Scaling down podinfo.test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
You can monitor all canaries with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,7 +183,8 @@ Generate latency:
|
|||
watch curl http://podinfo-canary:9898/delay/1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary, the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
|
||||
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary,
|
||||
the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
kubectl -n test describe canary/podinfo
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue