mirror of https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger.git
Add Flagger install guide for GKE
This commit is contained in:
parent
9c77c0d69c
commit
f7a7963dcf
|
|
@ -1,16 +1,15 @@
|
|||
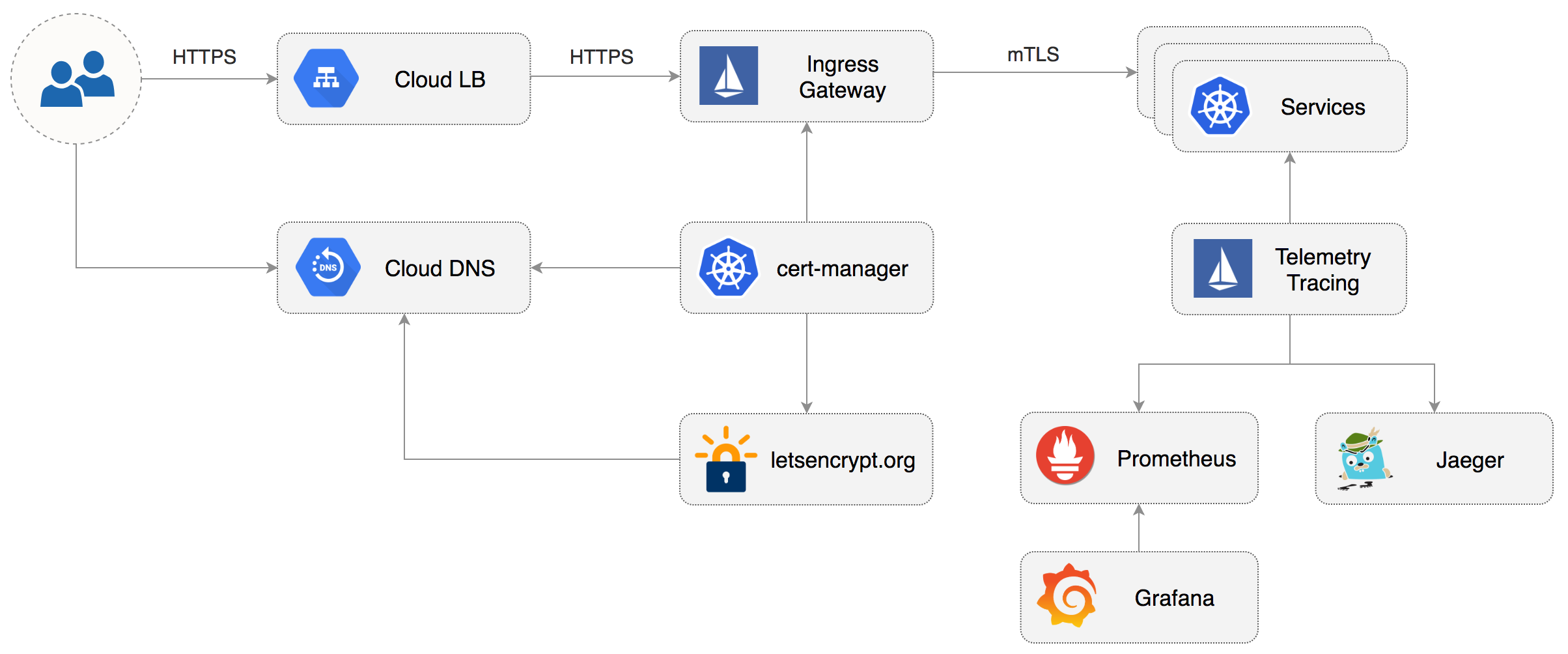
# Install Istio
|
||||
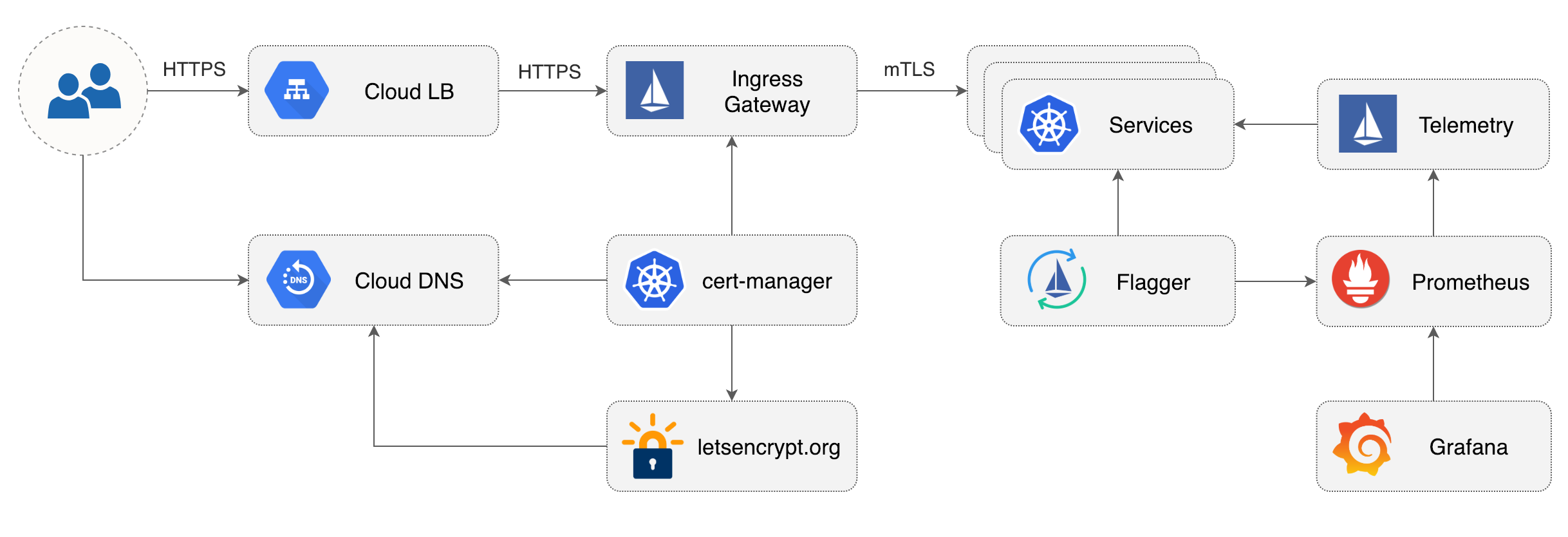
# Flagger install on Google Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
This guide walks you through setting up Istio with Jaeger, Prometheus, Grafana and
|
||||
Let’s Encrypt TLS for ingress gateway on Google Kubernetes Engine.
|
||||
This guide walks you through setting up Flagger and Istio on Google Kubernetes Engine.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
You will be creating a cluster on Google’s Kubernetes Engine \(GKE\),
|
||||
if you don’t have an account you can sign up [here](https://cloud.google.com/free/) for free credits.
|
||||
|
||||
Login into GCP, create a project and enable billing for it.
|
||||
Login into Google Cloud, create a project and enable billing for it.
|
||||
|
||||
Install the [gcloud](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/) command line utility and configure your project with `gcloud init`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,8 +22,8 @@ gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
|
|||
Set the default compute region and zone:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
gcloud config set compute/region europe-west3
|
||||
gcloud config set compute/zone europe-west3-a
|
||||
gcloud config set compute/region us-central1
|
||||
gcloud config set compute/zone us-central1-a
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Enable the Kubernetes and Cloud DNS services for your project:
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,32 +47,33 @@ brew install kubernetes-helm
|
|||
|
||||
### GKE cluster setup
|
||||
|
||||
Create a cluster with three nodes using the latest Kubernetes version:
|
||||
Create a cluster with the Istio add-on:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
k8s_version=$(gcloud container get-server-config --format=json \
|
||||
| jq -r '.validNodeVersions[0]')
|
||||
K8S_VERSION=$(gcloud container get-server-config --format=json \
|
||||
| jq -r '.validMasterVersions[0]')
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud container clusters create istio \
|
||||
--cluster-version=${k8s_version} \
|
||||
--zone=europe-west3-a \
|
||||
--num-nodes=3 \
|
||||
gcloud beta container clusters create istio \
|
||||
--cluster-version=${K8S_VERSION} \
|
||||
--zone=us-central1-a \
|
||||
--num-nodes=2 \
|
||||
--machine-type=n1-highcpu-4 \
|
||||
--preemptible \
|
||||
--no-enable-cloud-logging \
|
||||
--disk-size=30 \
|
||||
--enable-autorepair \
|
||||
--scopes=gke-default,compute-rw,storage-rw
|
||||
--addons=Istio \
|
||||
--istio-config=auth=MTLS_PERMISSIVE
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will create a default node pool consisting of `n1-highcpu-4` \(vCPU: 4, RAM 3.60GB, DISK: 30GB\)
|
||||
The above command will create a default node pool consisting of two `n1-highcpu-4` \(vCPU: 4, RAM 3.60GB, DISK: 30GB\)
|
||||
preemptible VMs. Preemptible VMs are up to 80% cheaper than regular instances and are terminated and replaced
|
||||
after a maximum of 24 hours.
|
||||
|
||||
Set up credentials for `kubectl`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
gcloud container clusters get-credentials istio -z=europe-west3-a
|
||||
gcloud container clusters get-credentials istio
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a cluster admin role binding:
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,9 +87,11 @@ kubectl create clusterrolebinding "cluster-admin-$(whoami)" \
|
|||
Validate your setup with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl get nodes -o wide
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system get svc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In a couple of seconds GCP should allocate an external IP to the `istio-ingressgateway` service.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud DNS setup
|
||||
|
||||
You will need an internet domain and access to the registrar to change the name servers to Google Cloud DNS.
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,34 +118,30 @@ Wait for the name servers to change \(replace `example.com` with your domain\):
|
|||
watch dig +short NS example.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a static IP address named `istio-gateway-ip` in the same region as your GKE cluster:
|
||||
Create a static IP address named `istio-gateway` using the Istio ingress IP:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
gcloud compute addresses create istio-gateway-ip --region europe-west3
|
||||
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get svc/istio-ingressgateway -ojson \
|
||||
| jq -r .status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip)
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud compute addresses create istio-gateway --addresses ${GATEWAY_IP} --region us-central1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Find the static IP address:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
gcloud compute addresses describe istio-gateway-ip --region europe-west3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create the following DNS records \(replace `example.com` with your domain and set your Istio Gateway IP\):
|
||||
Create the following DNS records \(replace `example.com` with your domain\):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
DOMAIN="example.com"
|
||||
GATEWAYIP="35.198.98.90"
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud dns record-sets transaction start --zone=istio
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
|
||||
--name="${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
|
||||
--name="${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAY_IP}
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
|
||||
--name="www.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
|
||||
--name="www.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAY_IP}
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
|
||||
--name="*.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
|
||||
--name="*.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAY_IP}
|
||||
|
||||
gcloud dns record-sets transaction execute --zone istio
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,31 +152,16 @@ Verify that the wildcard DNS is working \(replace `example.com` with your domain
|
|||
watch host test.example.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Istio with Helm
|
||||
|
||||
Download the latest Istio release:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -L https://git.io/getLatestIstio | sh -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to `istio-x.x.x` dir and copy the Istio CLI in your bin:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd istio-x.x.x/
|
||||
sudo cp ./bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the Istio CRDs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ./install/kubernetes/helm/istio/templates/crds.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Install cert-manager
|
||||
|
||||
Create a service account and a cluster role binding for Tiller:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ./install/kubernetes/helm/helm-service-account.yaml
|
||||
kubectl -n kube-system create sa tiller
|
||||
|
||||
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule \
|
||||
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
|
||||
--serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Deploy Tiller in the `kube-system` namespace:
|
||||
|
|
@ -187,125 +170,42 @@ Deploy Tiller in the `kube-system` namespace:
|
|||
helm init --service-account tiller
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Find the GKE IP ranges:
|
||||
Install cert-manager's CRDs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
gcloud container clusters describe istio --zone=europe-west3-a \
|
||||
| grep -e clusterIpv4Cidr -e servicesIpv4Cidr
|
||||
CM_REPO=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jetstack/cert-manager
|
||||
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ${CM_REPO}/release-0.6/deploy/manifests/00-crds.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll be using the IP ranges to allow unrestricted egress traffic for services running inside the service mesh.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure Istio with Prometheus, Jaeger, and cert-manager:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
global:
|
||||
nodePort: false
|
||||
proxy:
|
||||
# replace with your GKE IP ranges
|
||||
includeIPRanges: "10.28.0.0/14,10.7.240.0/20"
|
||||
|
||||
sidecarInjectorWebhook:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
enableNamespacesByDefault: false
|
||||
|
||||
gateways:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
istio-ingressgateway:
|
||||
replicaCount: 2
|
||||
autoscaleMin: 2
|
||||
autoscaleMax: 3
|
||||
# replace with your Istio Gateway IP
|
||||
loadBalancerIP: "35.198.98.90"
|
||||
type: LoadBalancer
|
||||
|
||||
pilot:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
replicaCount: 1
|
||||
autoscaleMin: 1
|
||||
autoscaleMax: 1
|
||||
resources:
|
||||
requests:
|
||||
cpu: 500m
|
||||
memory: 1024Mi
|
||||
|
||||
grafana:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
security:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
adminUser: admin
|
||||
# change the password
|
||||
adminPassword: admin
|
||||
|
||||
prometheus:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
|
||||
servicegraph:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
|
||||
tracing:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
jaeger:
|
||||
tag: 1.7
|
||||
|
||||
certmanager:
|
||||
enabled: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the above file as `my-istio.yaml` and install Istio with Helm:
|
||||
Create the cert-manager namespace and disable resource validation:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm upgrade --install istio ./install/kubernetes/helm/istio \
|
||||
--namespace=istio-system \
|
||||
-f ./my-istio.yaml
|
||||
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
|
||||
|
||||
kubectl label namespace cert-manager certmanager.k8s.io/disable-validation=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verify that Istio workloads are running:
|
||||
Install cert-manager:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system get pods
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm repo update && helm install \
|
||||
--name cert-manager \
|
||||
--namespace cert-manager \
|
||||
--version v0.6.0 \
|
||||
stable/cert-manager
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
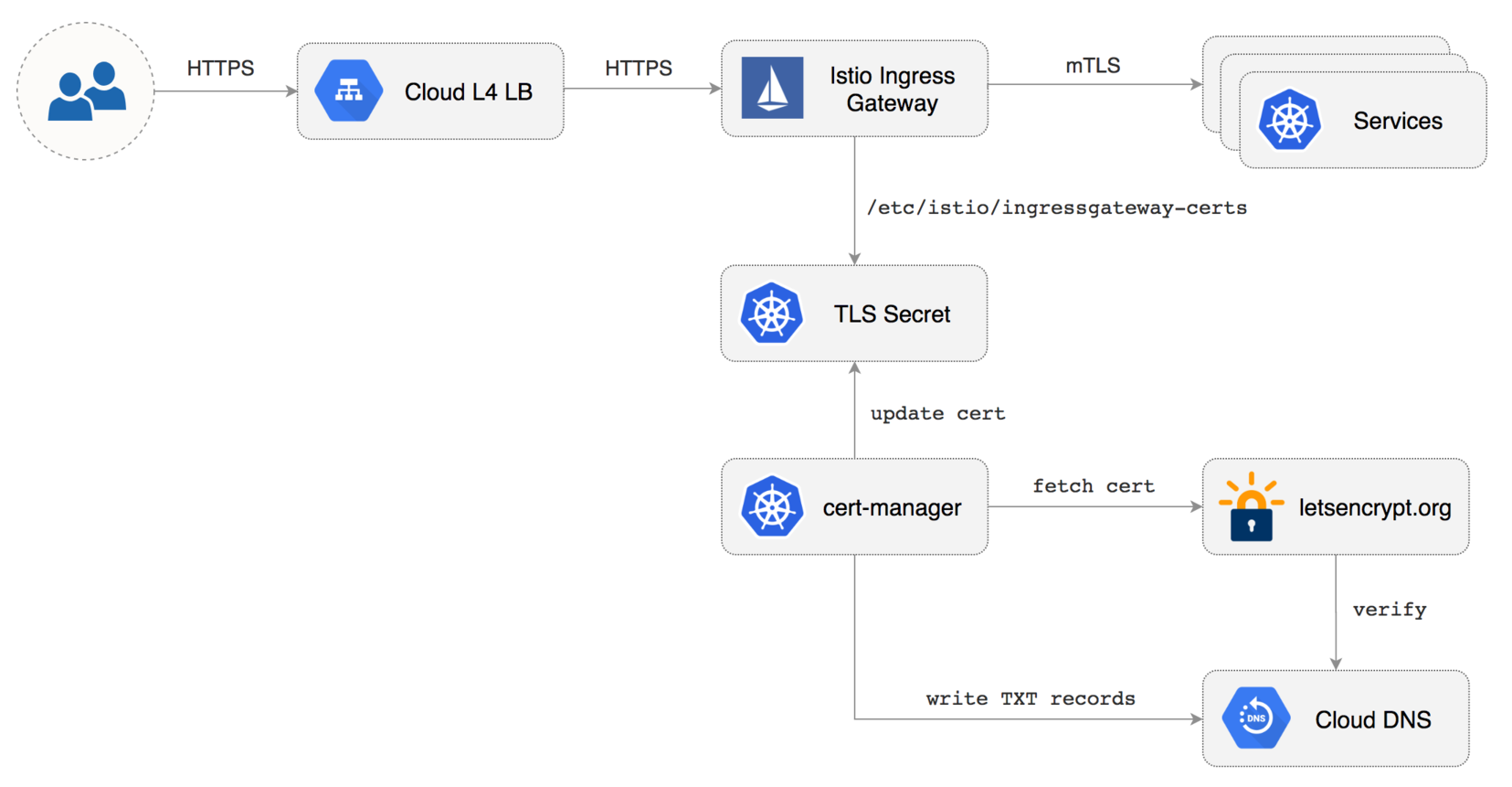
### Configure Istio Gateway with LE TLS
|
||||
### Istio Gateway TLS setup
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create a Istio Gateway in istio-system namespace with HTTPS redirect:
|
||||
Create a generic Istio Gateway to expose services outside the mesh on HTTPS:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
|
||||
kind: Gateway
|
||||
metadata:
|
||||
name: public-gateway
|
||||
namespace: istio-system
|
||||
spec:
|
||||
selector:
|
||||
istio: ingressgateway
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- port:
|
||||
number: 80
|
||||
name: http
|
||||
protocol: HTTP
|
||||
hosts:
|
||||
- "*"
|
||||
tls:
|
||||
httpsRedirect: true
|
||||
- port:
|
||||
number: 443
|
||||
name: https
|
||||
protocol: HTTPS
|
||||
hosts:
|
||||
- "*"
|
||||
tls:
|
||||
mode: SIMPLE
|
||||
privateKey: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.key
|
||||
serverCertificate: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
REPO=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stefanprodan/flagger/master
|
||||
|
||||
Save the above resource as istio-gateway.yaml and then apply it:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ./istio-gateway.yaml
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ${REPO}/artifacts/gke/istio-gateway.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a service account with Cloud DNS admin role \(replace `my-gcp-project` with your project ID\):
|
||||
|
|
@ -387,37 +287,76 @@ spec:
|
|||
- "example.com"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the above resource as of-cert.yaml and then apply it:
|
||||
Save the above resource as istio-gateway-cert.yaml and then apply it:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ./of-cert.yaml
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ./istio-gateway-cert.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In a couple of seconds cert-manager should fetch a wildcard certificate from letsencrypt.org:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system logs deployment/certmanager -f
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system describe certificate istio-gateway
|
||||
|
||||
Certificate issued successfully
|
||||
Certificate istio-system/istio-gateway scheduled for renewal in 1438 hours
|
||||
Events:
|
||||
Type Reason Age From Message
|
||||
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
|
||||
Normal CertIssued 1m52s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Recreate Istio ingress gateway pods:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system delete pods -l istio=ingressgateway
|
||||
kubectl -n istio-system get pods -l istio=ingressgateway
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that Istio gateway doesn't reload the certificates from the TLS secret on cert-manager renewal.
|
||||
Since the GKE cluster is made out of preemptible VMs the gateway pods will be replaced once every 24h,
|
||||
if your not using preemptible nodes then you need to manually kill the gateway pods every two months
|
||||
if your not using preemptible nodes then you need to manually delete the gateway pods every two months
|
||||
before the certificate expires.
|
||||
|
||||
### Expose services outside the service mesh
|
||||
### Install Prometheus
|
||||
|
||||
In order to expose services via the Istio Gateway you have to create a Virtual Service attached to Istio Gateway.
|
||||
The GKE Istio add-on does not include a Prometheus instance that scraps the Istio telemetry service.
|
||||
Because Flagger uses the Istio HTTP metrics to run the canary analysis you have to
|
||||
deploy the following Prometheus configuration that's similar to the one that comes with the official Istio Helm chart.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a virtual service in `istio-system` namespace for Grafana \(replace `example.com` with your domain\):
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
REPO=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stefanprodan/flagger/master
|
||||
|
||||
kubectl apply -f ${REPO}/artifacts/gke/istio-prometheus.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Flagger and Grafana
|
||||
|
||||
Add Flagger Helm repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm repo add flagger https://flagger.app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Deploy Flagger in the `istio-system` namespace with Slack notifications enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm upgrade -i flagger flagger/flagger \
|
||||
--namespace=istio-system \
|
||||
--set metricsServer=http://prometheus.istio-system:9090 \
|
||||
--set slack.url=https://hooks.slack.com/services/YOUR/SLACK/WEBHOOK \
|
||||
--set slack.channel=general \
|
||||
--set slack.user=flagger
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Deploy Grafana in the `istio-system` namespace:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
helm upgrade -i flagger-grafana flagger/grafana \
|
||||
--namespace=istio-system \
|
||||
--set url=http://prometheus.istio-system:9090 \
|
||||
--set user=admin \
|
||||
--set password=replace-me
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Expose Grafana through the public gateway by creating a virtual service \(replace `example.com` with your domain\):
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
|
||||
|
|
@ -433,8 +372,7 @@ spec:
|
|||
http:
|
||||
- route:
|
||||
- destination:
|
||||
host: grafana
|
||||
timeout: 30s
|
||||
host: flagger-grafana
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the above resource as grafana-virtual-service.yaml and then apply it:
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,17 +382,3 @@ kubectl apply -f ./grafana-virtual-service.yaml
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to `http://grafana.example.com` in your browser and you should be redirected to the HTTPS version.
|
||||
|
||||
Check that HTTP2 is enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -I --http2 https://grafana.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/2 200
|
||||
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
|
||||
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3
|
||||
server: envoy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue