更新图床
This commit is contained in:
parent
2a9b627a90
commit
17cb4b45c7
|
|
@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ dp[i][j]可以初始化为true么? 当然不行,怎能刚开始就全都匹
|
|||
|
||||
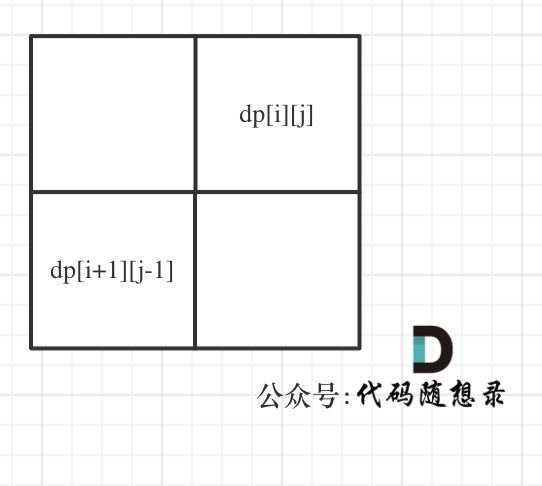
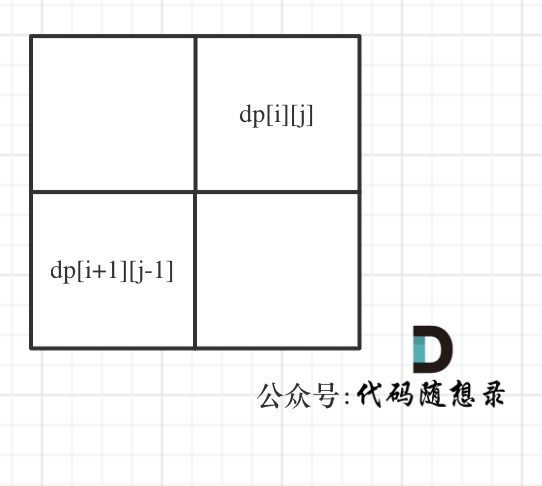
dp[i + 1][j - 1] 在 dp[i][j]的左下角,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果这矩阵是从上到下,从左到右遍历,那么会用到没有计算过的dp[i + 1][j - 1],也就是根据不确定是不是回文的区间[i+1,j-1],来判断了[i,j]是不是回文,那结果一定是不对的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 注意遍历顺序
|
|||
|
||||
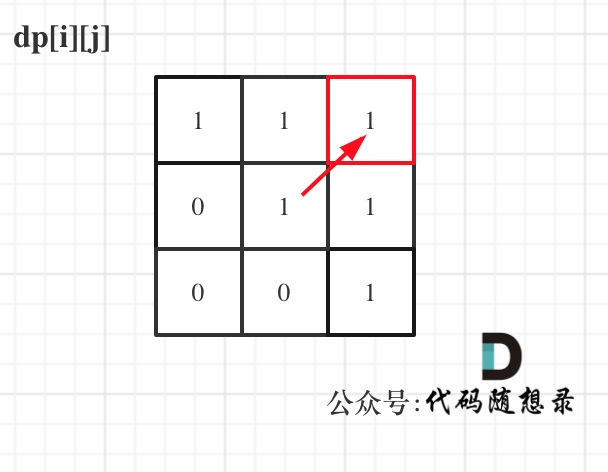
举例,输入:"aaa",dp[i][j]状态如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**注意因为dp[i][j]的定义,所以j一定是大于等于i的,那么在填充dp[i][j]的时候一定是只填充右上半部分**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
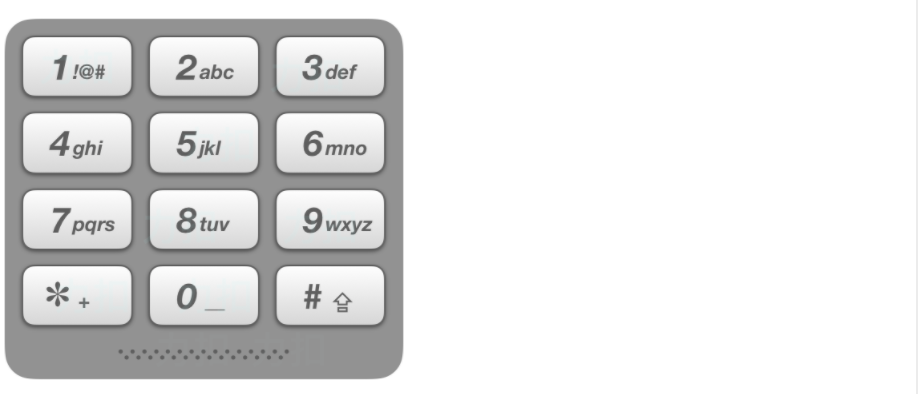
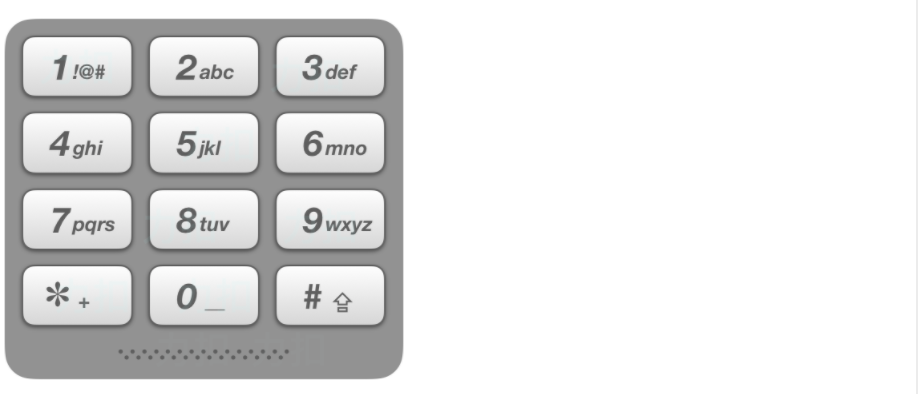
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
* 输入:"23"
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ const string letterMap[10] = {
|
|||
|
||||
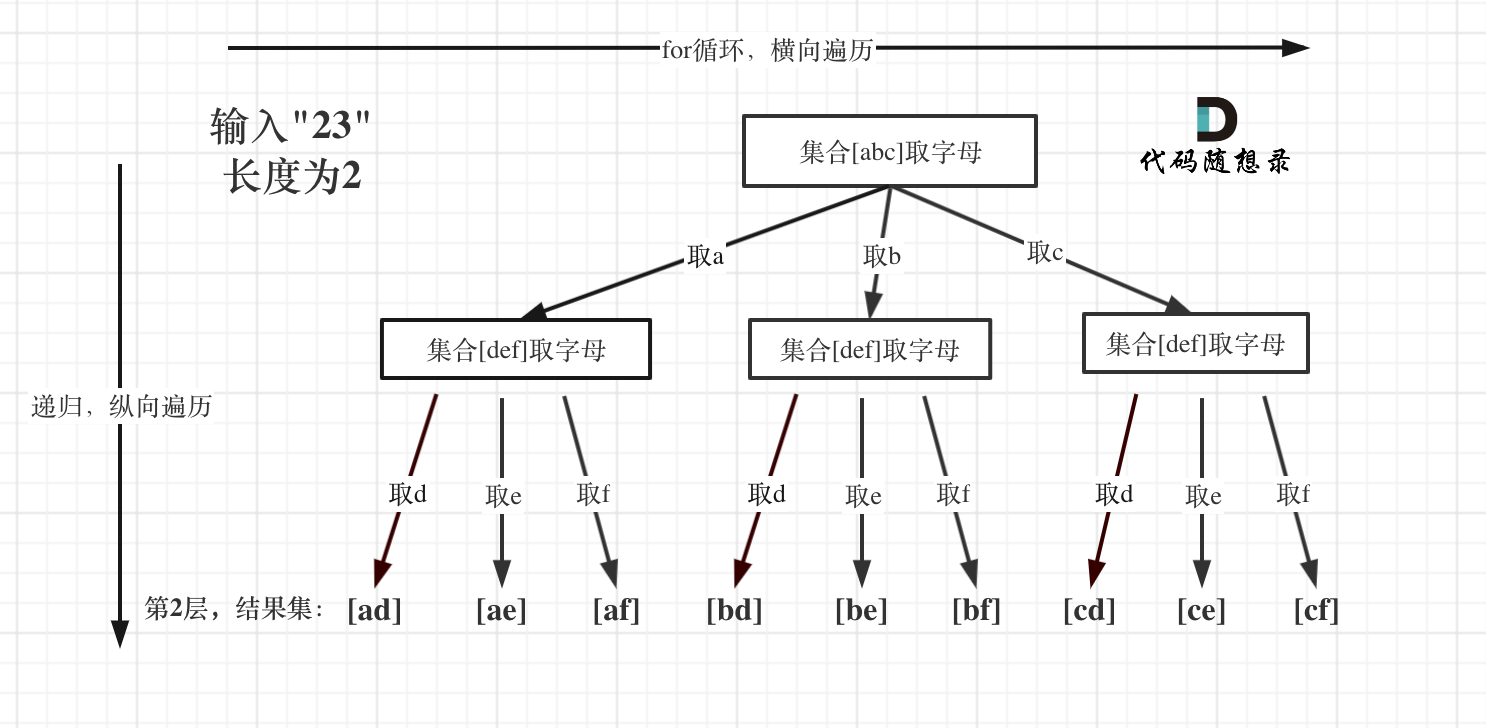
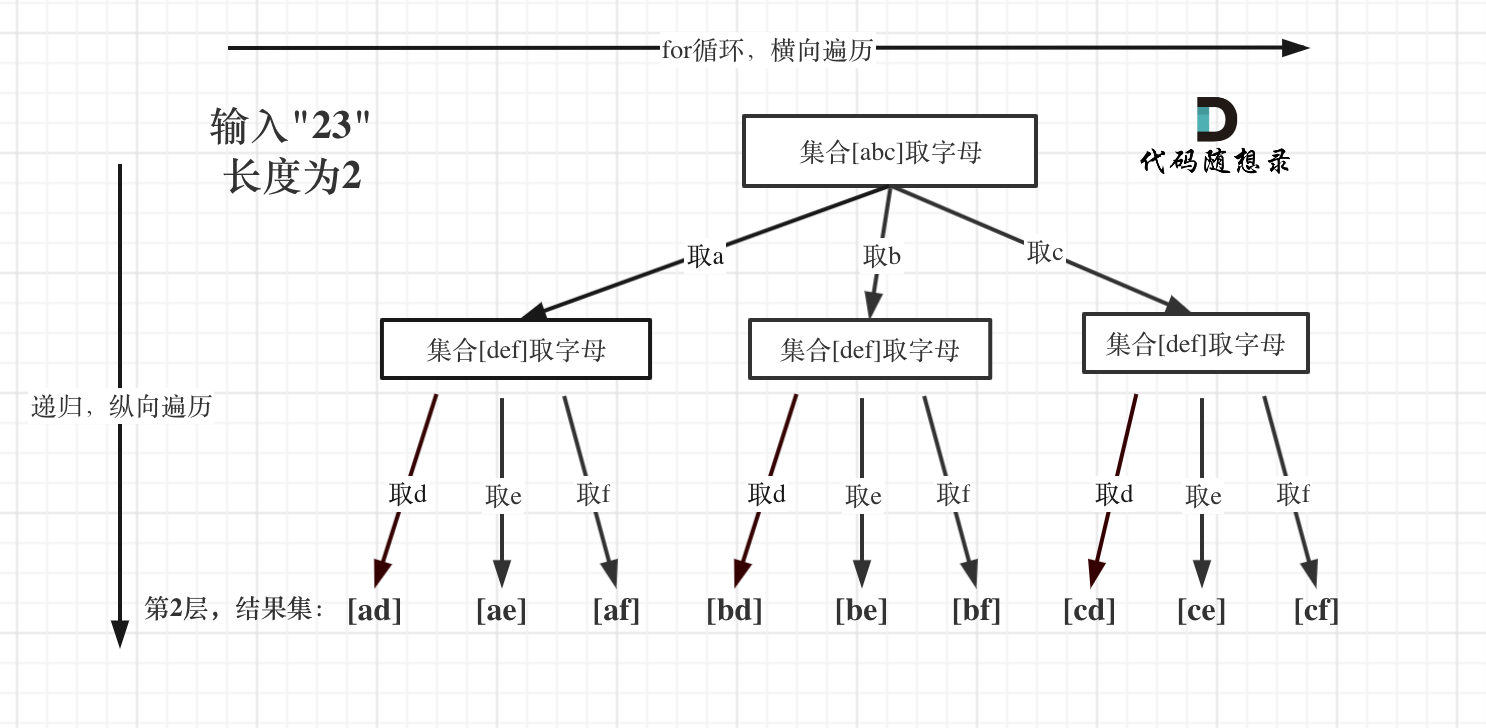
例如:输入:"23",抽象为树形结构,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
图中可以看出遍历的深度,就是输入"23"的长度,而叶子节点就是我们要收集的结果,输出["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
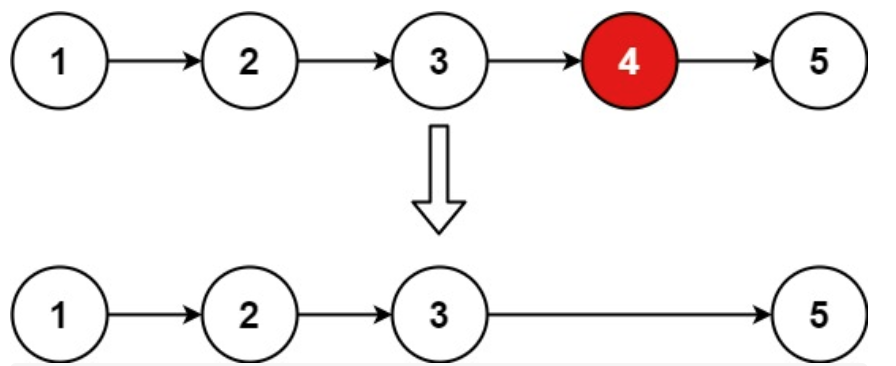
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
|
||||
输出:[1,2,3,5]
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -80,14 +80,17 @@ cd a/b/c/../../
|
|||
|
||||
先来分析一下 这里有三种不匹配的情况,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. 第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了 ,所以不匹配。
|
||||
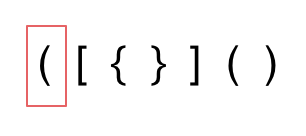
|
||||
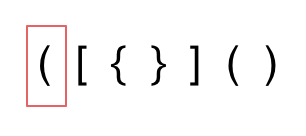
|
||||
|
||||
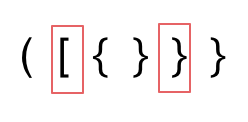
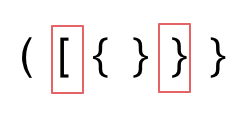
2. 第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. 第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
|
||||
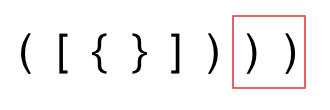
|
||||
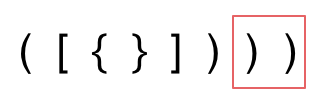
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们的代码只要覆盖了这三种不匹配的情况,就不会出问题,可以看出 动手之前分析好题目的重要性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -7,6 +8,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 35.搜索插入位置
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,18 +18,22 @@
|
|||
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 5
|
||||
* 输出: 2
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 2
|
||||
* 输出: 1
|
||||
|
||||
示例 3:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 7
|
||||
* 输出: 4
|
||||
|
||||
示例 4:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入: [1,3,5,6], 0
|
||||
* 输出: 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -37,7 +43,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
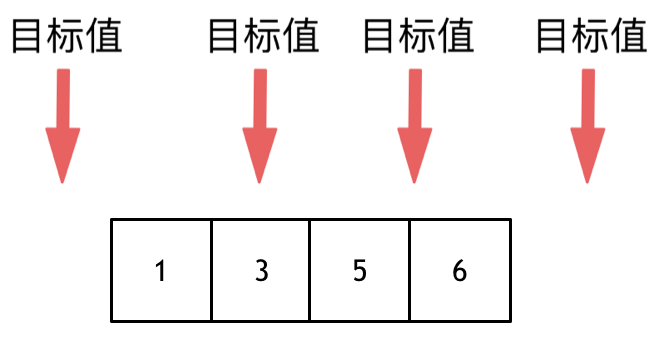
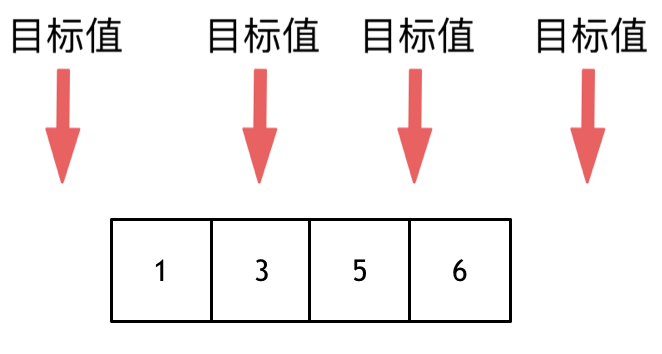
这道题目,要在数组中插入目标值,无非是这四种情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 目标值在数组所有元素之前
|
||||
* 目标值等于数组中某一个元素
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,13 +84,14 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
效率如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 二分法
|
||||
|
||||
既然暴力解法的时间复杂度是$O(n)$,就要尝试一下使用二分查找法。
|
||||
既然暴力解法的时间复杂度是O(n),就要尝试一下使用二分查找法。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
大家注意这道题目的前提是数组是有序数组,这也是使用二分查找的基础条件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,7 +101,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
大体讲解一下二分法的思路,这里来举一个例子,例如在这个数组中,使用二分法寻找元素为5的位置,并返回其下标。
|
||||
|
||||
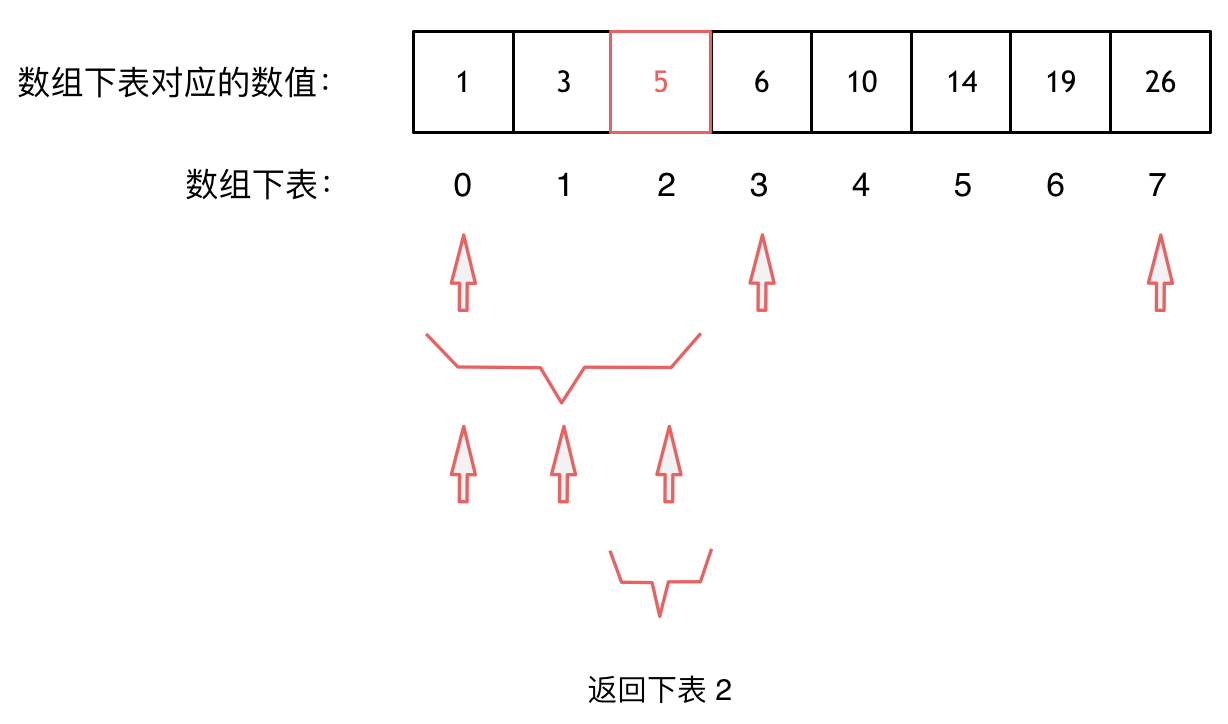
|
||||
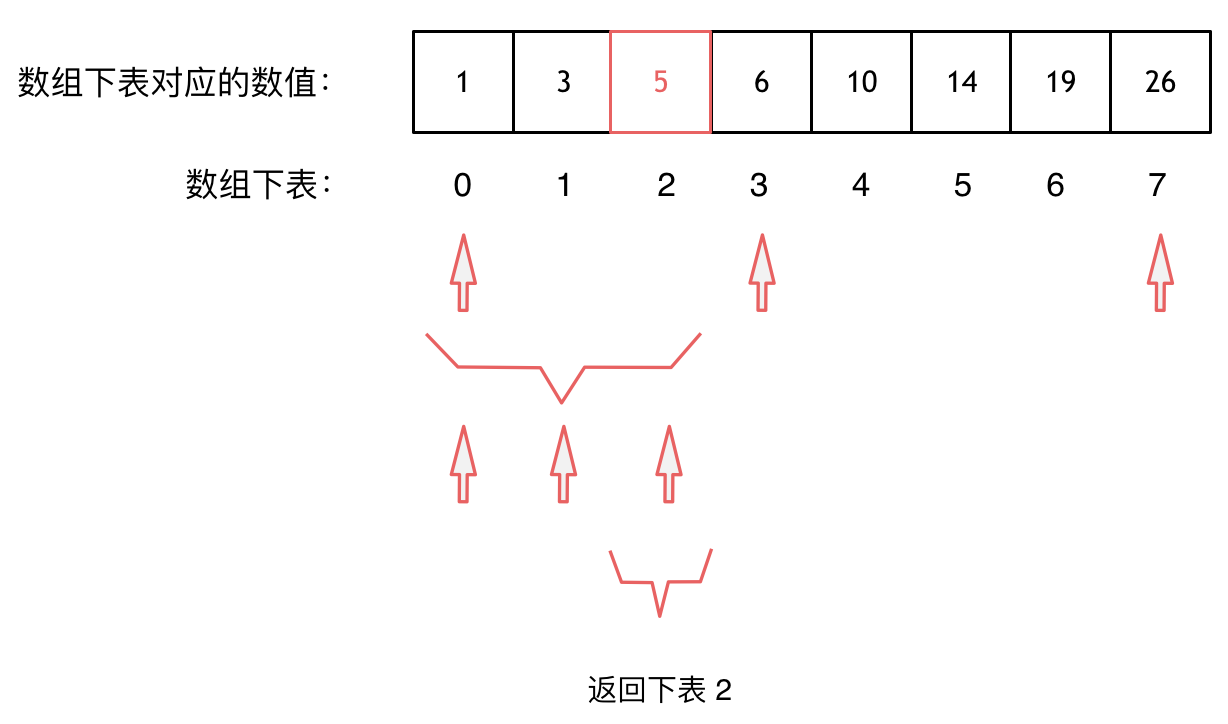
|
||||
|
||||
二分查找涉及的很多的边界条件,逻辑比较简单,就是写不好。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,7 +152,7 @@ public:
|
|||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||||
|
||||
效率如下:
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 二分法第二种写法
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -199,7 +206,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,11 +233,12 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//第二种二分法:左闭右开
|
||||
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
|
||||
int left = 0;
|
||||
int right = nums.length;
|
||||
int right = nums.length;
|
||||
while (left < right) { //左闭右开 [left, right)
|
||||
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
|
||||
if (nums[middle] > target) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -290,7 +298,8 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -308,7 +317,8 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return right + 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var searchInsert = function (nums, target) {
|
||||
let l = 0, r = nums.length - 1, ans = nums.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -350,7 +360,7 @@ function searchInsert(nums: number[], target: number): number {
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
### Swift
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
// 暴力法
|
||||
|
|
@ -383,7 +393,9 @@ func searchInsert(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> Int {
|
|||
return right + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def searchInsert(nums: Array[Int], target: Int): Int = {
|
||||
|
|
@ -404,7 +416,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PHP
|
||||
### PHP
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
// 二分法(1):[左闭右闭]
|
||||
|
|
@ -429,11 +441,13 @@ function searchInsert($nums, $target)
|
|||
return $r + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//版本一 [left, right]左闭右闭区间
|
||||
int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
|
||||
//左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize-1]
|
||||
//左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize-1]
|
||||
int left =0;
|
||||
int mid =0;
|
||||
int right = numsSize - 1;
|
||||
|
|
@ -451,14 +465,15 @@ int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//数组中未找到target元素
|
||||
//target在数组所有元素之后,[left, right]是右闭区间,需要返回 right +1
|
||||
//target在数组所有元素之后,[left, right]是右闭区间,需要返回 right +1
|
||||
return right + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//版本二 [left, right]左闭右开区间
|
||||
int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
|
||||
//左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize)
|
||||
//左闭右开区间 [0 , numsSize)
|
||||
int left =0;
|
||||
int mid =0;
|
||||
int right = numsSize;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果对回溯法理论还不清楚的同学,可以先看这个视频[视频来了!!带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wDd5azGIYWjbU0fdua_qBg)
|
||||
|
||||
# 37. 解数独
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,20 +16,21 @@
|
|||
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
|
||||
|
||||
一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则:
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
|
||||
空白格用 '.' 表示。
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
|
||||
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
|
||||
空白格用 '.' 表示。
|
||||
|
||||
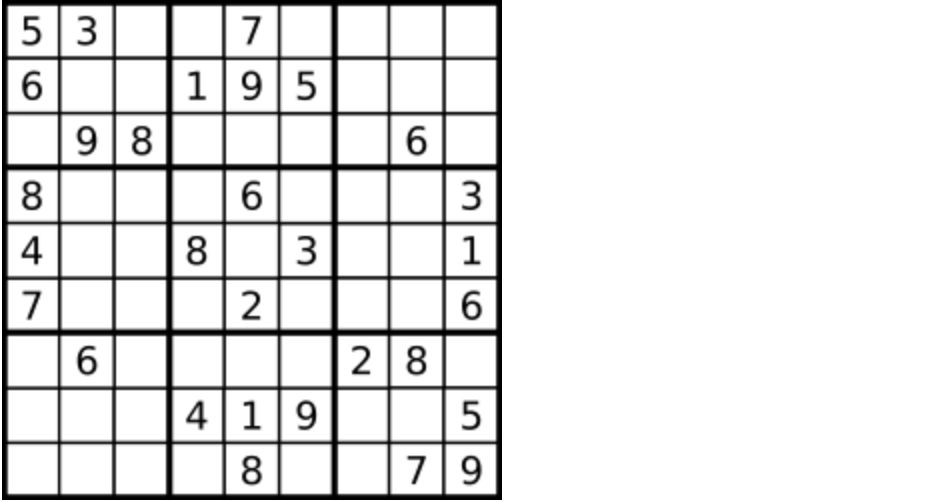
|
||||
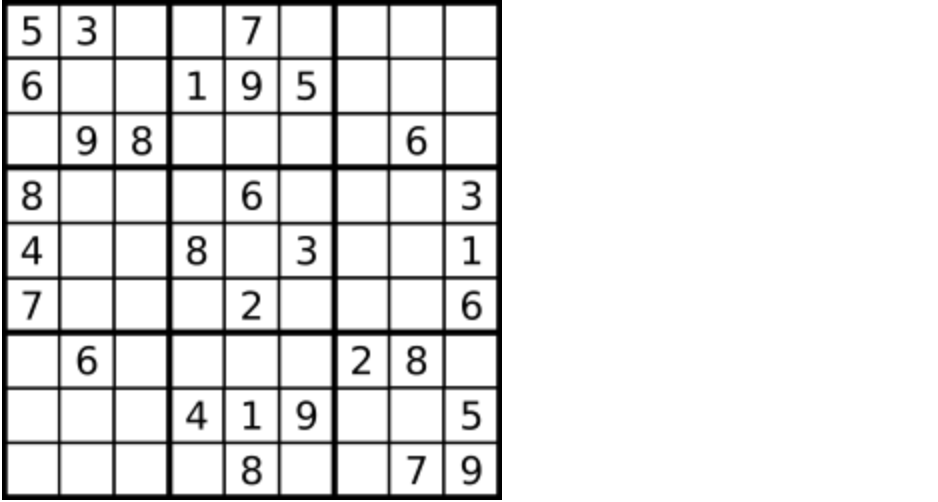
|
||||
|
||||
一个数独。
|
||||
|
||||
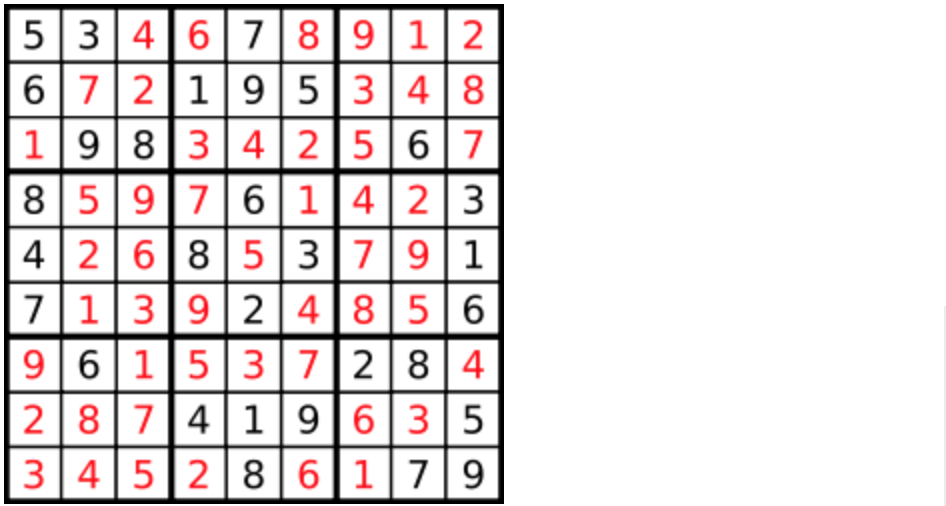
|
||||
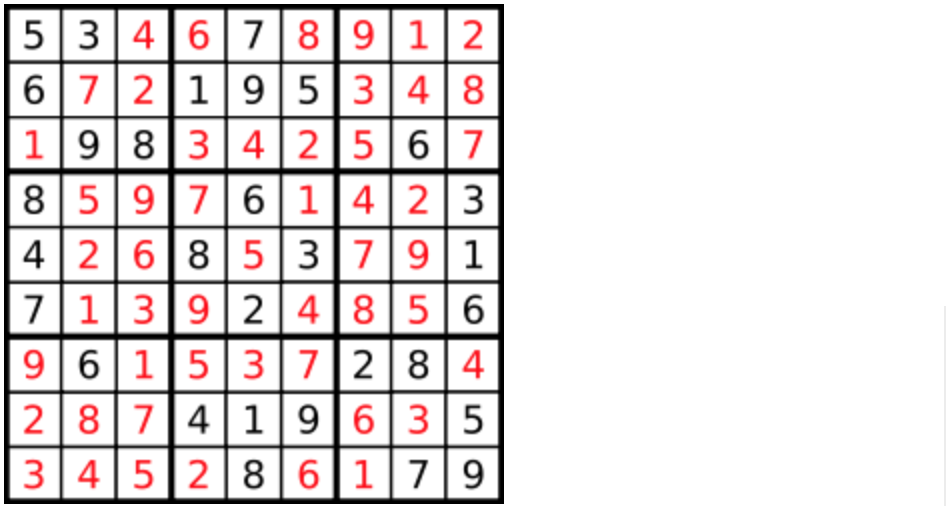
|
||||
|
||||
答案被标成红色。
|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
* 给定的数独序列只包含数字 1-9 和字符 '.' 。
|
||||
* 你可以假设给定的数独只有唯一解。
|
||||
* 给定数独永远是 9x9 形式的。
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +57,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
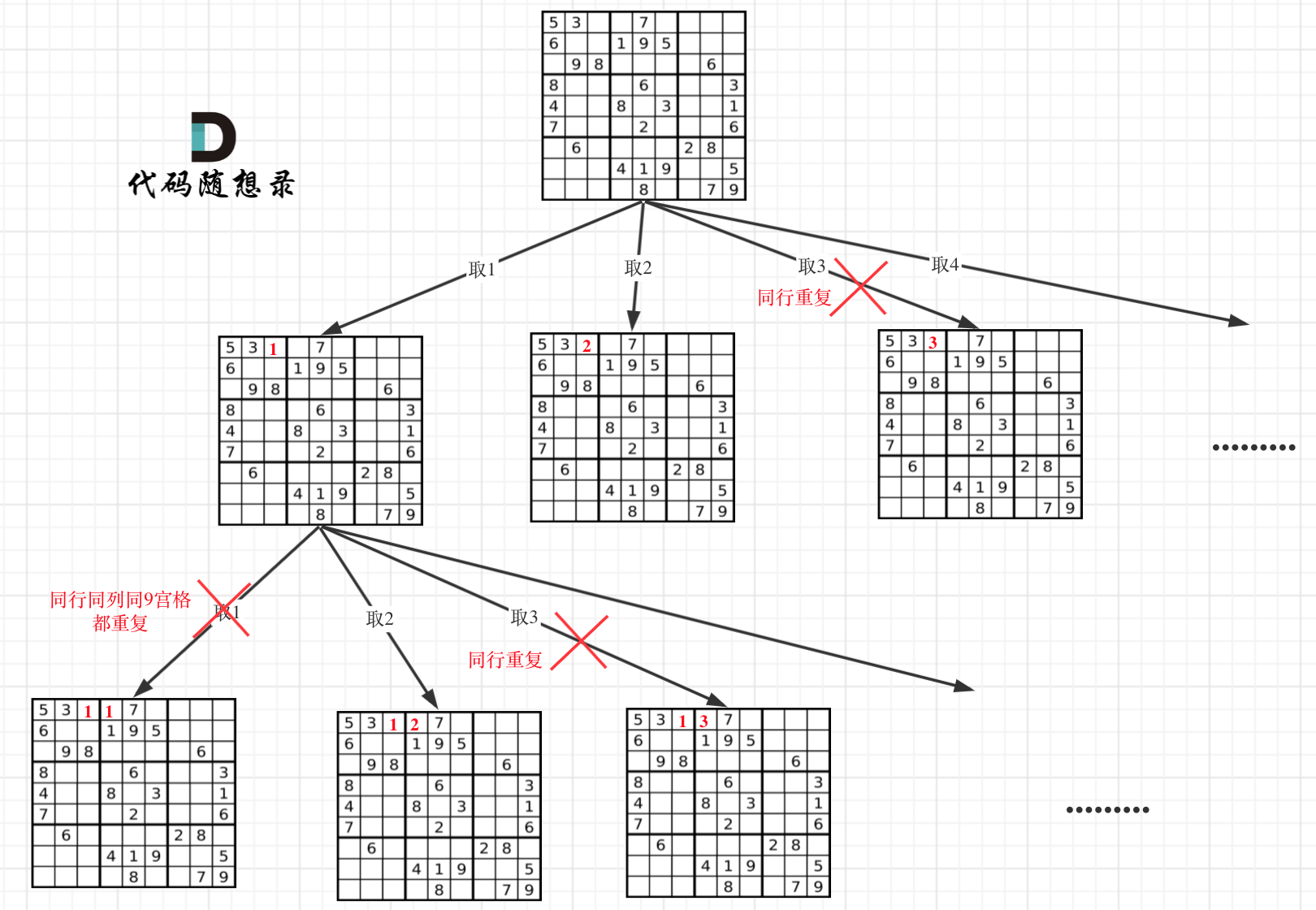
因为这个树形结构太大了,我抽取一部分,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
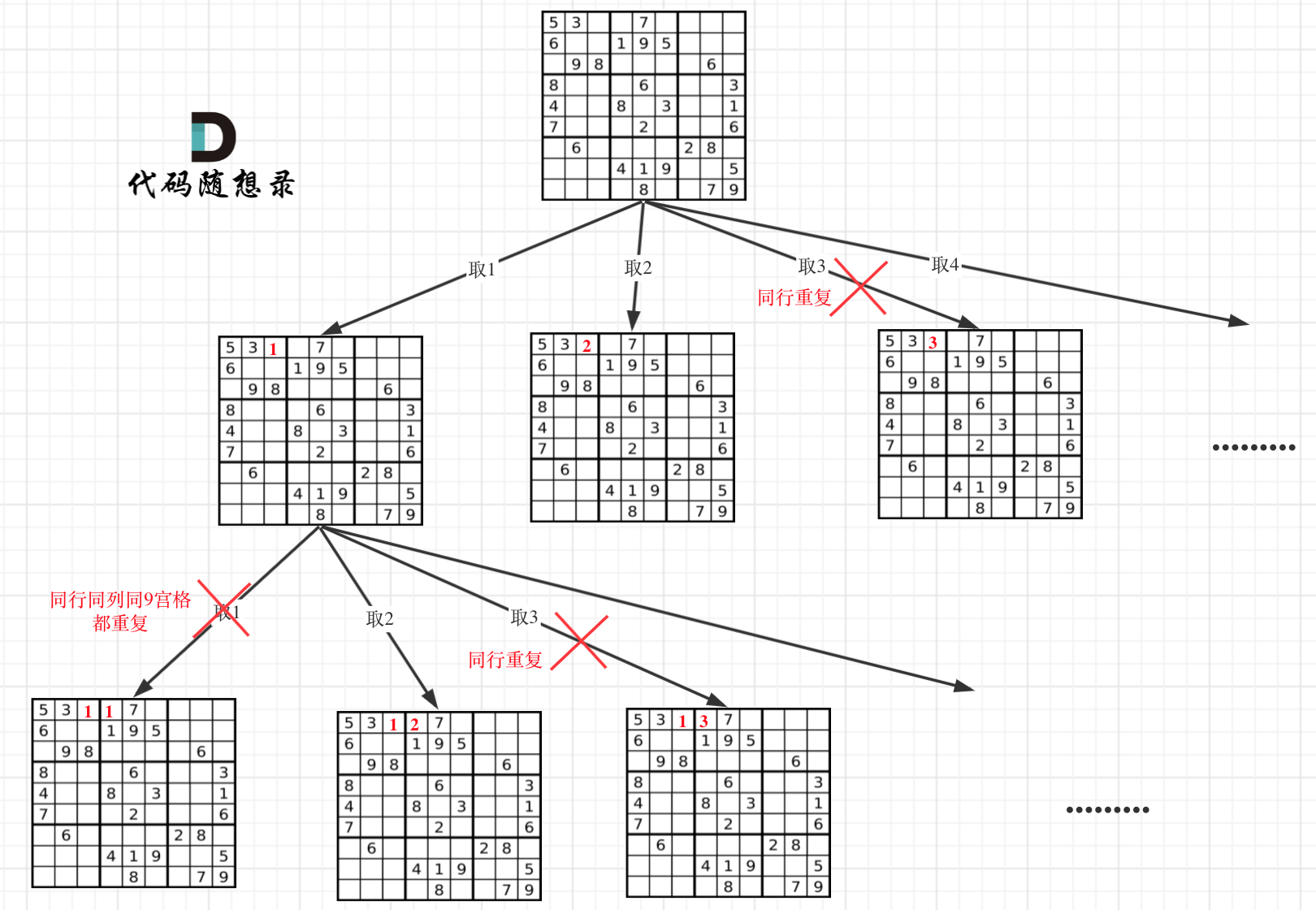
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 回溯三部曲
|
||||
|
|
@ -85,7 +88,7 @@ bool backtracking(vector<vector<char>>& board)
|
|||
|
||||
* 递归单层搜索逻辑
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
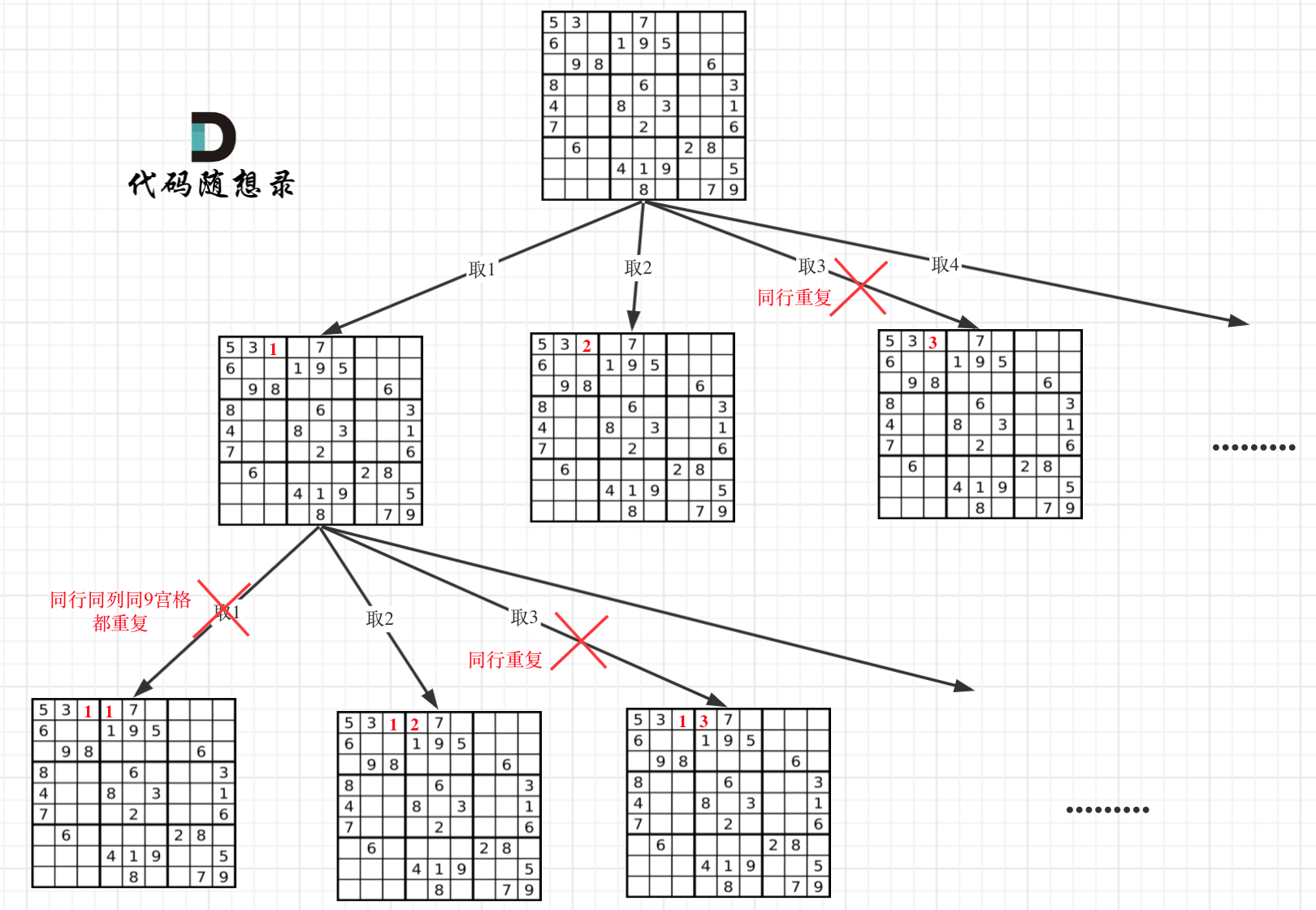
|
||||
|
||||
在树形图中可以看出我们需要的是一个二维的递归(也就是两个for循环嵌套着递归)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -171,8 +174,8 @@ bool backtracking(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
|
|||
board[i][j] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销k
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false; // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false; // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true; // 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了
|
||||
|
|
@ -223,7 +226,8 @@ public:
|
|||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -291,7 +295,8 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def solveSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
|
||||
|
|
@ -306,7 +311,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
for j in range(len(board[0])): # 遍历列
|
||||
# 若空格内已有数字,跳过
|
||||
if board[i][j] != '.': continue
|
||||
for k in range(1, 10):
|
||||
for k in range(1, 10):
|
||||
if self.is_valid(i, j, k, board):
|
||||
board[i][j] = str(k)
|
||||
if self.backtracking(board): return True
|
||||
|
|
@ -334,7 +339,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func solveSudoku(board [][]byte) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -392,7 +397,8 @@ func isvalid(row, col int, k byte, board [][]byte) bool {
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var solveSudoku = function(board) {
|
||||
function isValid(row, col, val, board) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -433,7 +439,7 @@ var solveSudoku = function(board) {
|
|||
if (backTracking()) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
board[i][j] = `.`
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -444,7 +450,7 @@ var solveSudoku = function(board) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
backTracking(board)
|
||||
return board
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -543,7 +549,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
bool isValid(char** board, int row, int col, int k) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -660,9 +666,10 @@ func solveSudoku(_ board: inout [[Character]]) {
|
|||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
详细写法:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
|
||||
backtracking(board)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -692,7 +699,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 列
|
||||
for (j <- 0 until 9) {
|
||||
if (board(x)(j) == value) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -717,9 +724,10 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
遵循Scala至简原则写法:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def solveSudoku(board: Array[Array[Char]]): Unit = {
|
||||
backtracking(board)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,40 +6,43 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 39. 组合总和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
|
||||
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
|
||||
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
|
||||
|
||||
说明:
|
||||
|
||||
* 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
|
||||
* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
|
||||
* 所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
|
||||
* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
|
||||
* 所求解集为:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[
|
||||
[7],
|
||||
[2,2,3]
|
||||
]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
* 输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
|
||||
* 所求解集为:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[2,2,2,2],
|
||||
[2,3,3],
|
||||
[3,5]
|
||||
]
|
||||
[
|
||||
[2,2,2,2],
|
||||
[2,3,3],
|
||||
[3,5]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[Leetcode:39. 组合总和讲解](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ),相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +52,7 @@ candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
|
|||
|
||||
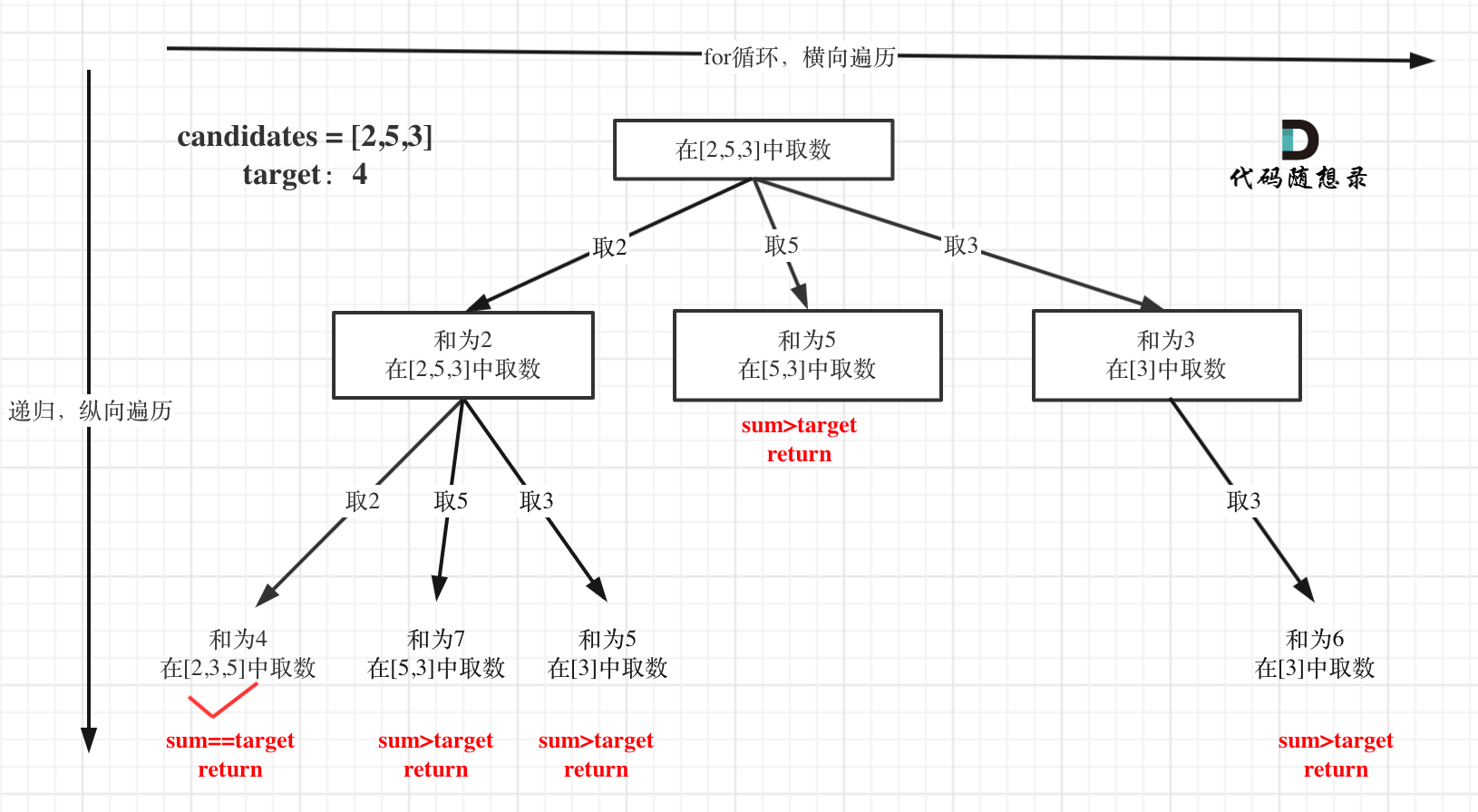
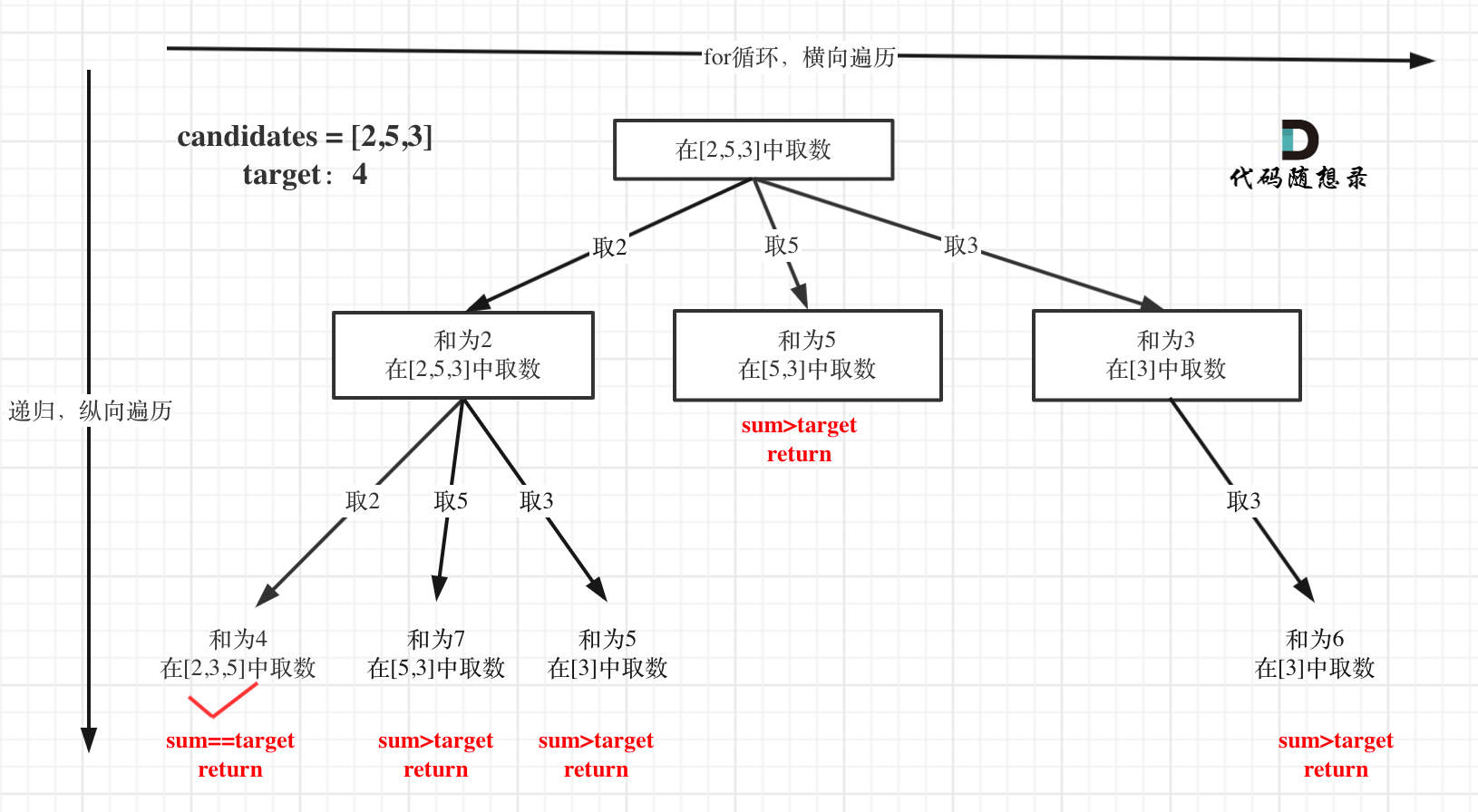
本题搜索的过程抽象成树形结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意图中叶子节点的返回条件,因为本题没有组合数量要求,仅仅是总和的限制,所以递归没有层数的限制,只要选取的元素总和超过target,就返回!
|
||||
|
||||
而在[77.组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)和[216.组合总和III](https://programmercarl.com/0216.组合总和III.html) 中都可以知道要递归K层,因为要取k个元素的组合。
|
||||
|
|
@ -83,7 +87,7 @@ void backtracking(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex)
|
|||
|
||||
在如下树形结构中:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
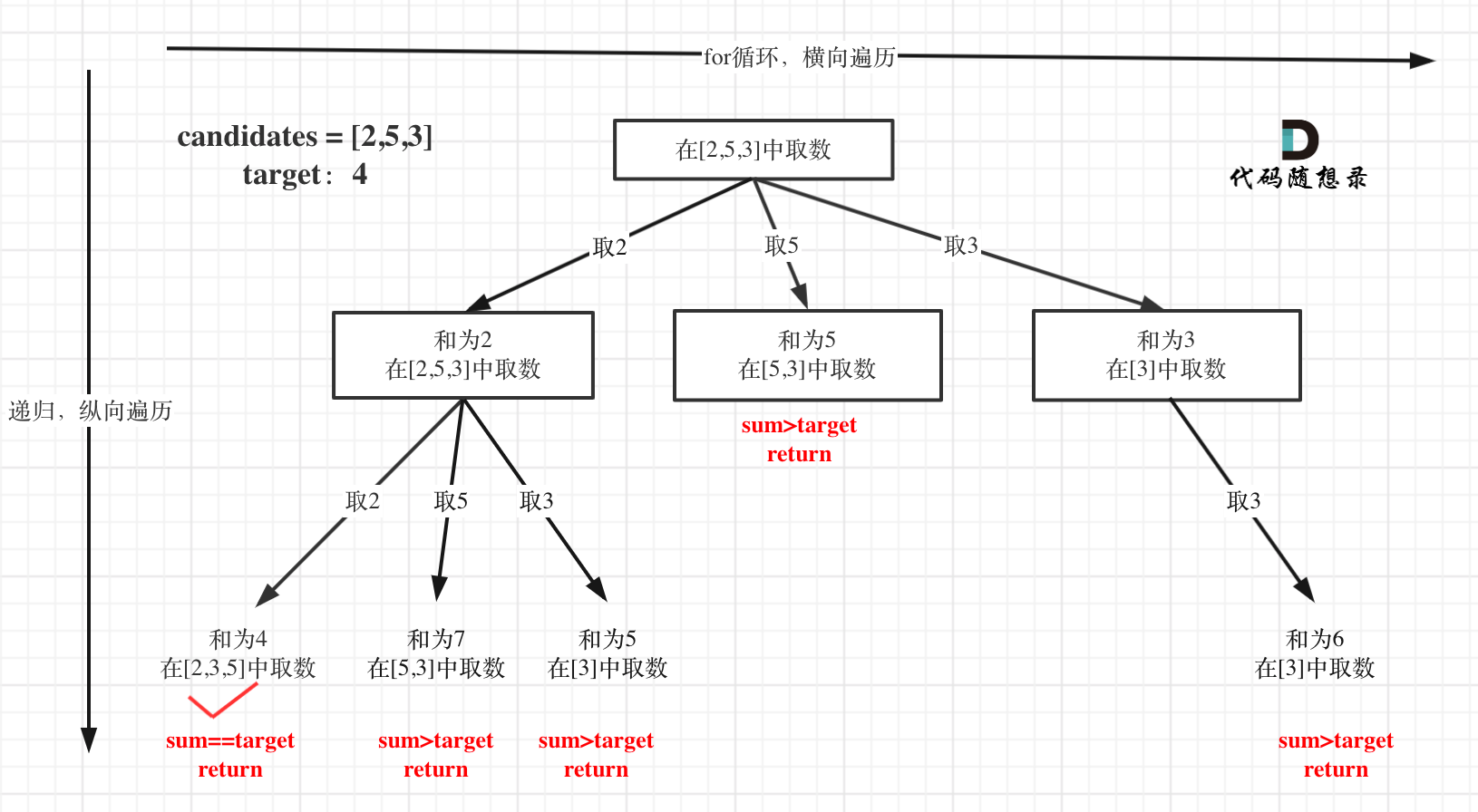
|
||||
|
||||
从叶子节点可以清晰看到,终止只有两种情况,sum大于target和sum等于target。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -156,7 +160,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在这个树形结构中:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
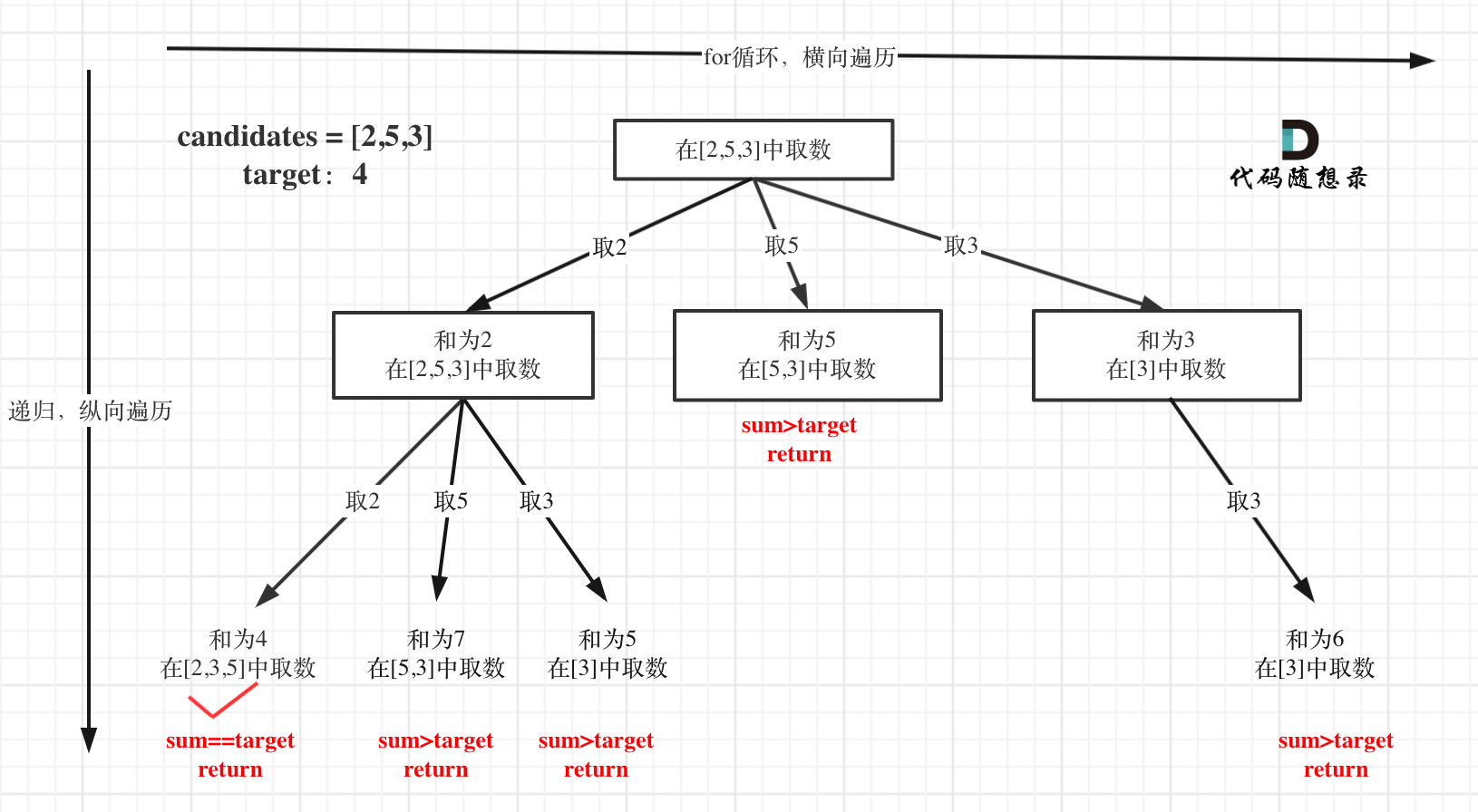
|
||||
|
||||
以及上面的版本一的代码大家可以看到,对于sum已经大于target的情况,其实是依然进入了下一层递归,只是下一层递归结束判断的时候,会判断sum > target的话就返回。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,7 +173,7 @@ public:
|
|||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
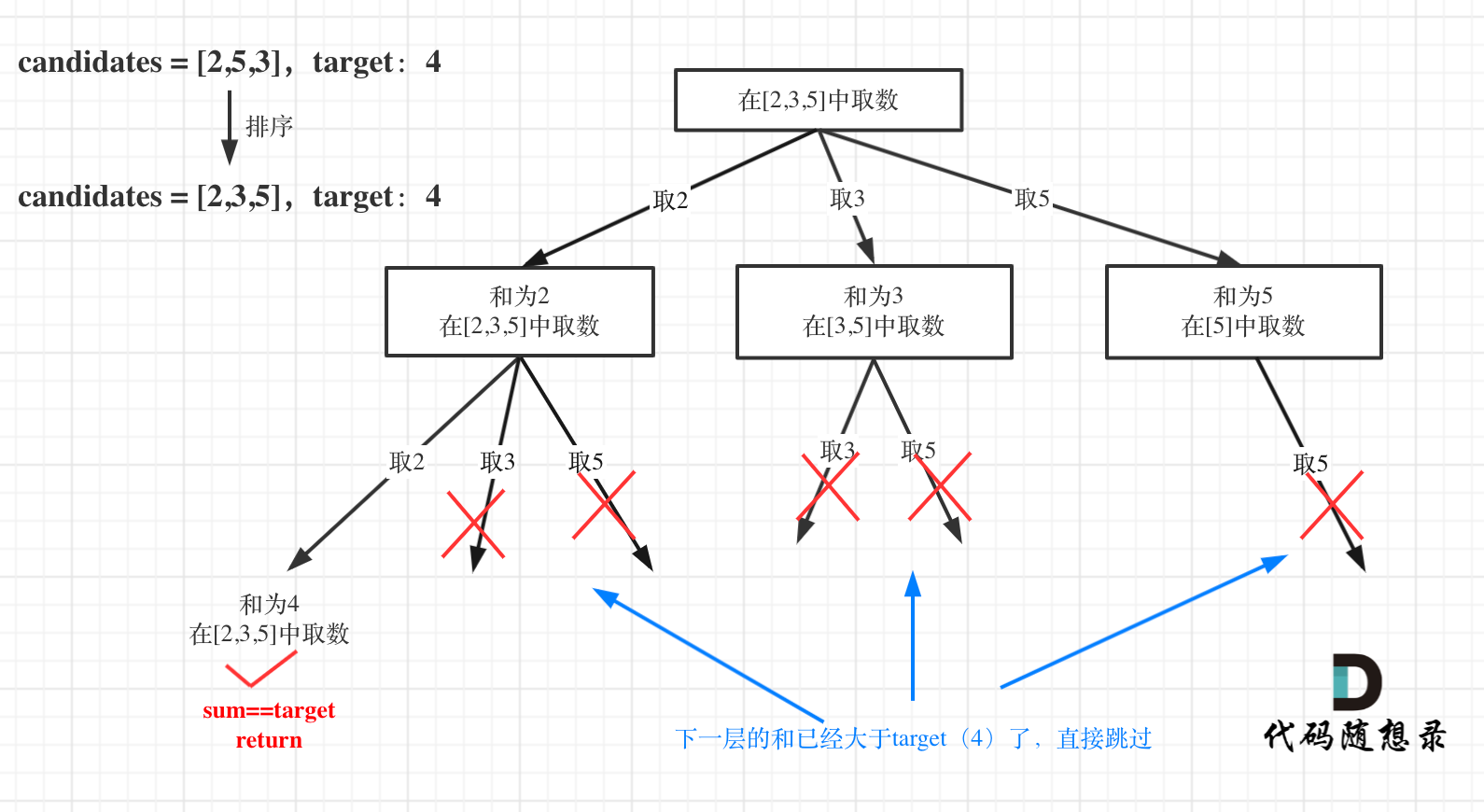
|
||||
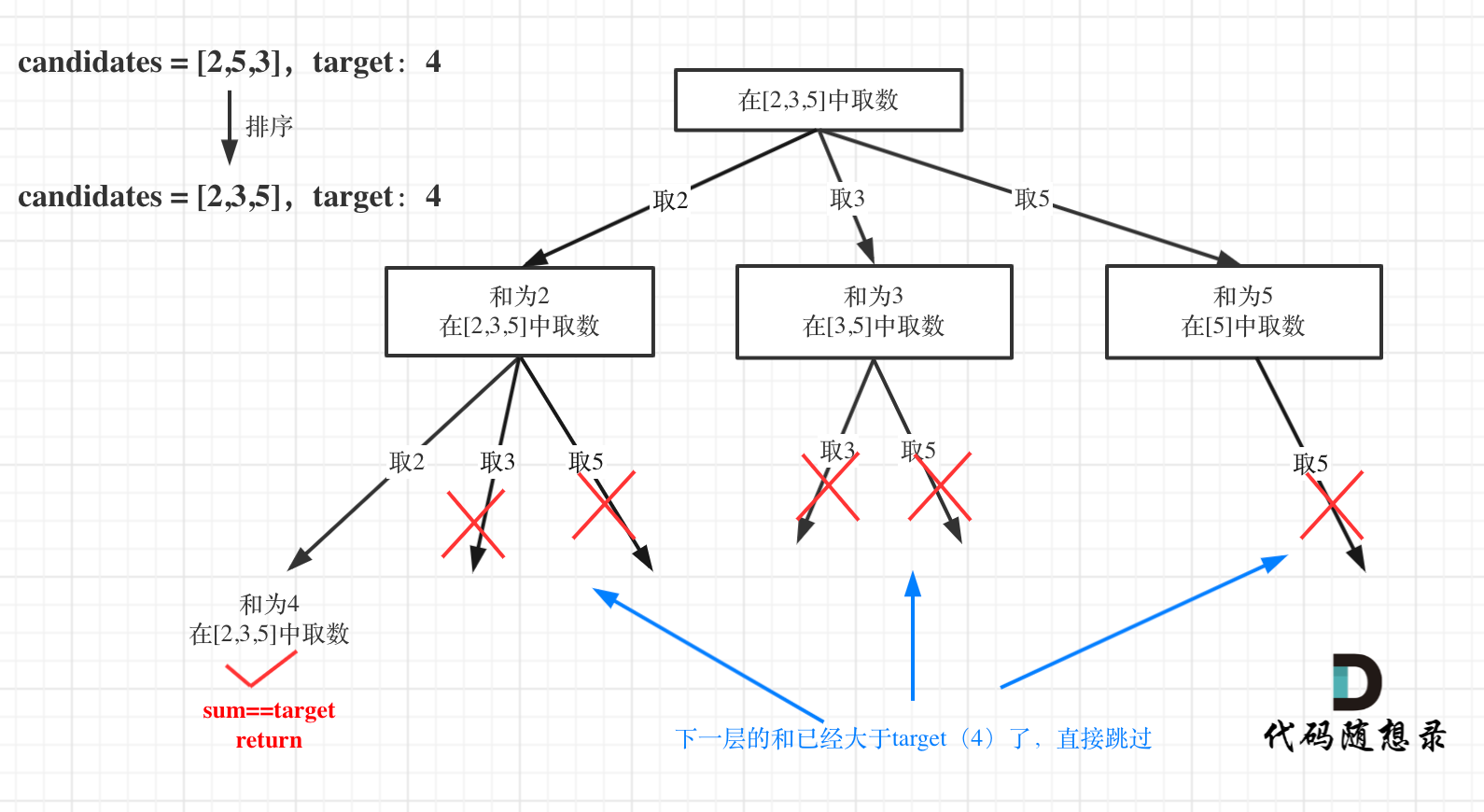
|
||||
|
||||
for循环剪枝代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -235,7 +239,8 @@ public:
|
|||
# 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Java
|
||||
## Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
// 剪枝优化
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,8 +269,10 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
**回溯**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
|
|
@ -287,9 +294,9 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
self.paths.append(self.path[:]) # 因为是shallow copy,所以不能直接传入self.path
|
||||
return
|
||||
if sum_ > target:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# 单层递归逻辑
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# 单层递归逻辑
|
||||
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
|
||||
sum_ += candidates[i]
|
||||
self.path.append(candidates[i])
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,7 +304,9 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
sum_ -= candidates[i] # 回溯
|
||||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**剪枝回溯**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
|
|
@ -321,11 +330,11 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
if sum_ == target:
|
||||
self.paths.append(self.path[:]) # 因为是shallow copy,所以不能直接传入self.path
|
||||
return
|
||||
# 单层递归逻辑
|
||||
# 单层递归逻辑
|
||||
# 如果本层 sum + condidates[i] > target,就提前结束遍历,剪枝
|
||||
for i in range(start_index, len(candidates)):
|
||||
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
|
||||
return
|
||||
if sum_ + candidates[i] > target:
|
||||
return
|
||||
sum_ += candidates[i]
|
||||
self.path.append(candidates[i])
|
||||
self.backtracking(candidates, target, sum_, i) # 因为无限制重复选取,所以不是i-1
|
||||
|
|
@ -333,7 +342,8 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
主要在于递归中传递下一个数字
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
|
@ -423,7 +433,7 @@ function combinationSum(candidates: number[], target: number): number[][] {
|
|||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, candidates: &Vec<i32>, target: i32, mut sum: i32, start_index: usize) {
|
||||
if sum == target {
|
||||
if sum == target {
|
||||
result.push(path.to_vec());
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -447,7 +457,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
|
|||
|
||||
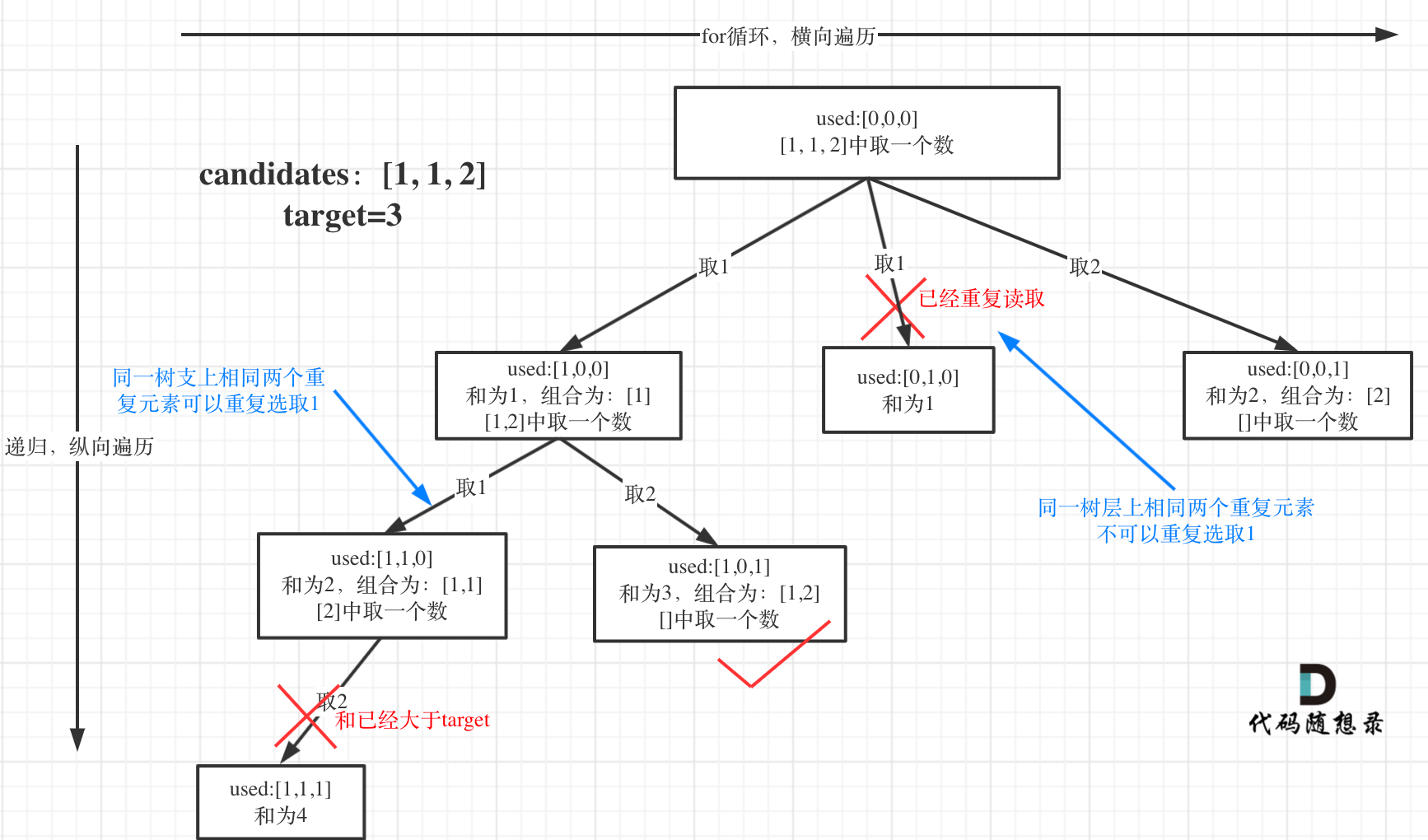
选择过程树形结构如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
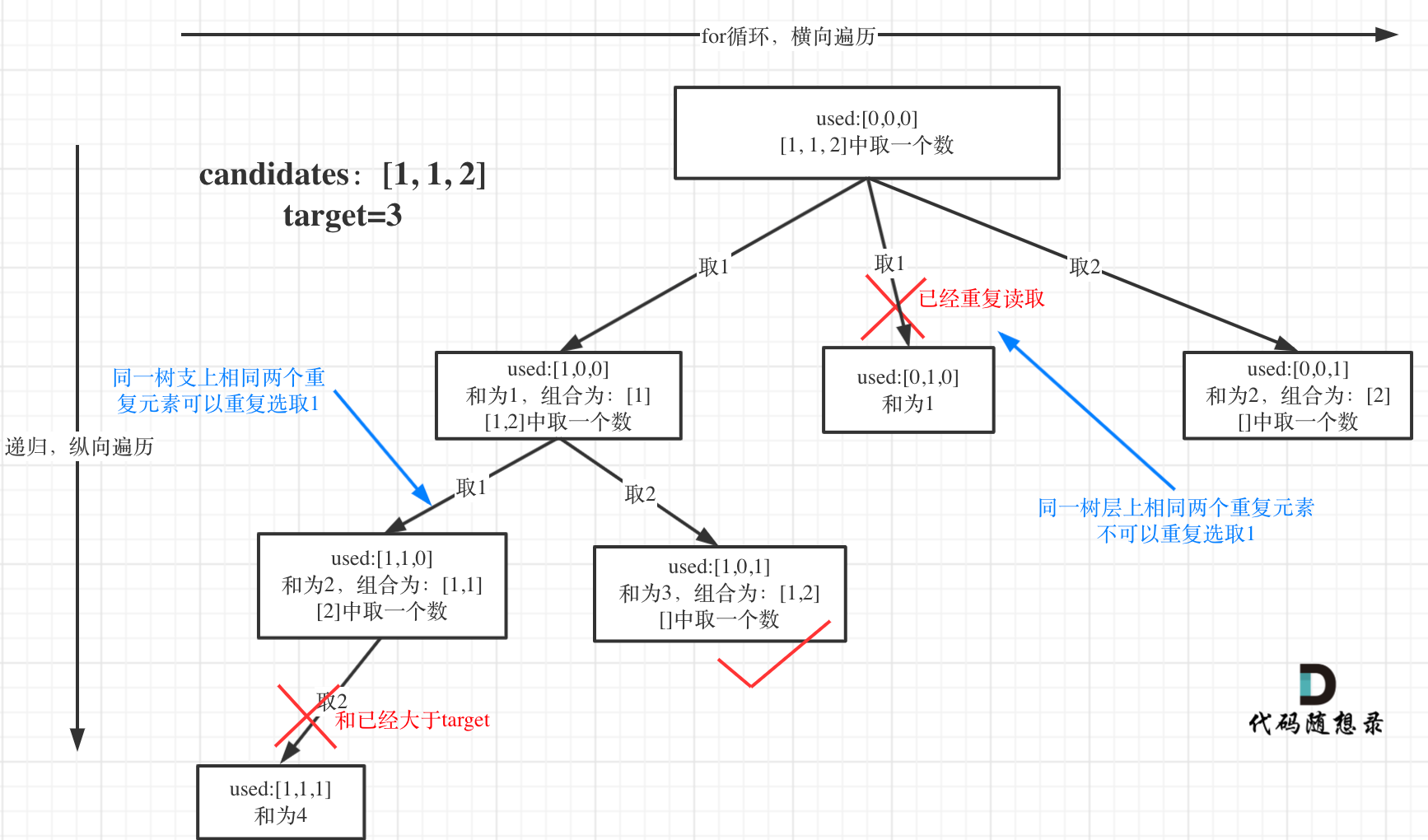
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到图中,每个节点相对于 [39.组合总和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FLg8G6EjVcxBjwCbzpACPw)我多加了used数组,这个used数组下面会重点介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ if (sum == target) {
|
|||
|
||||
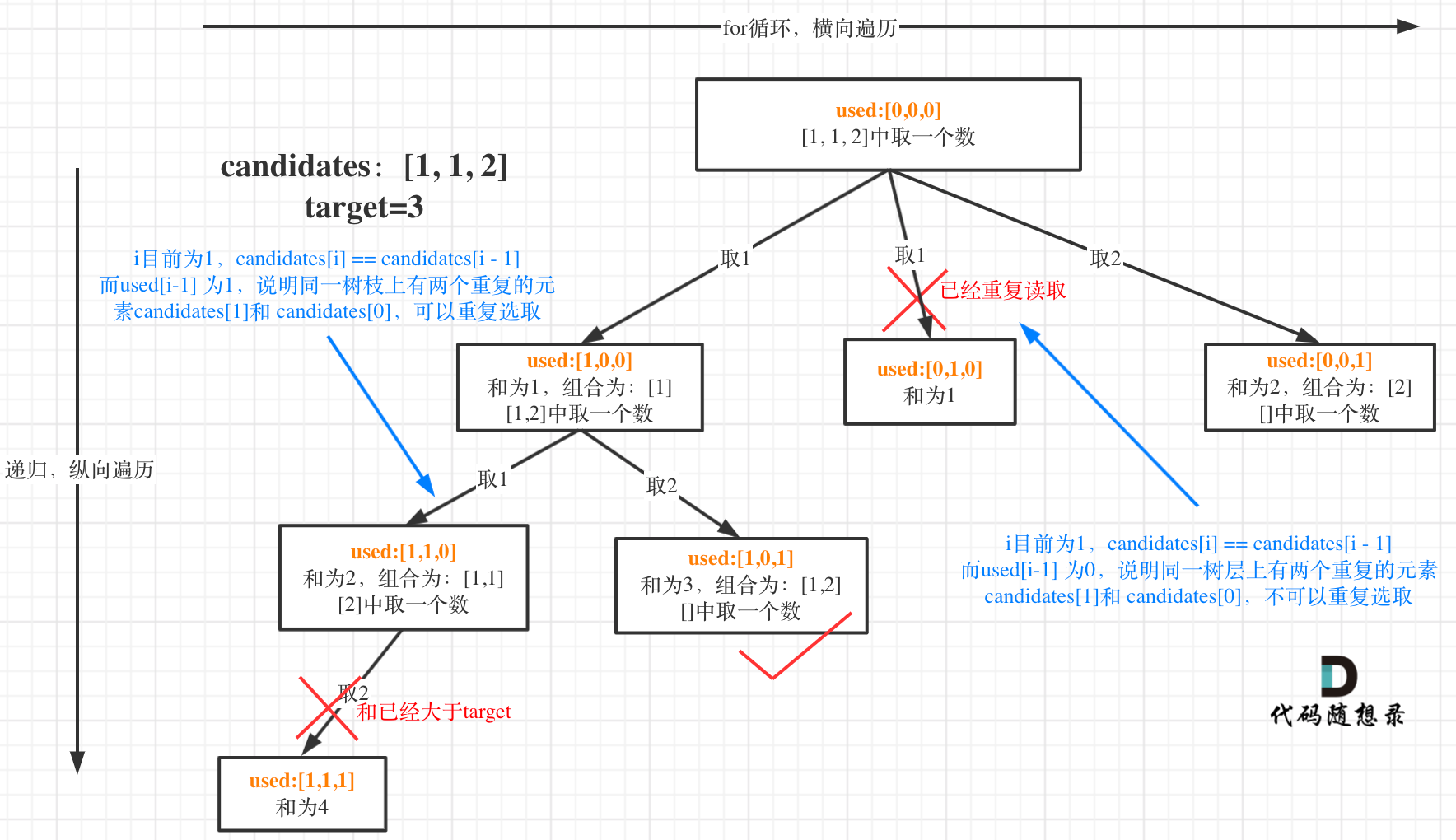
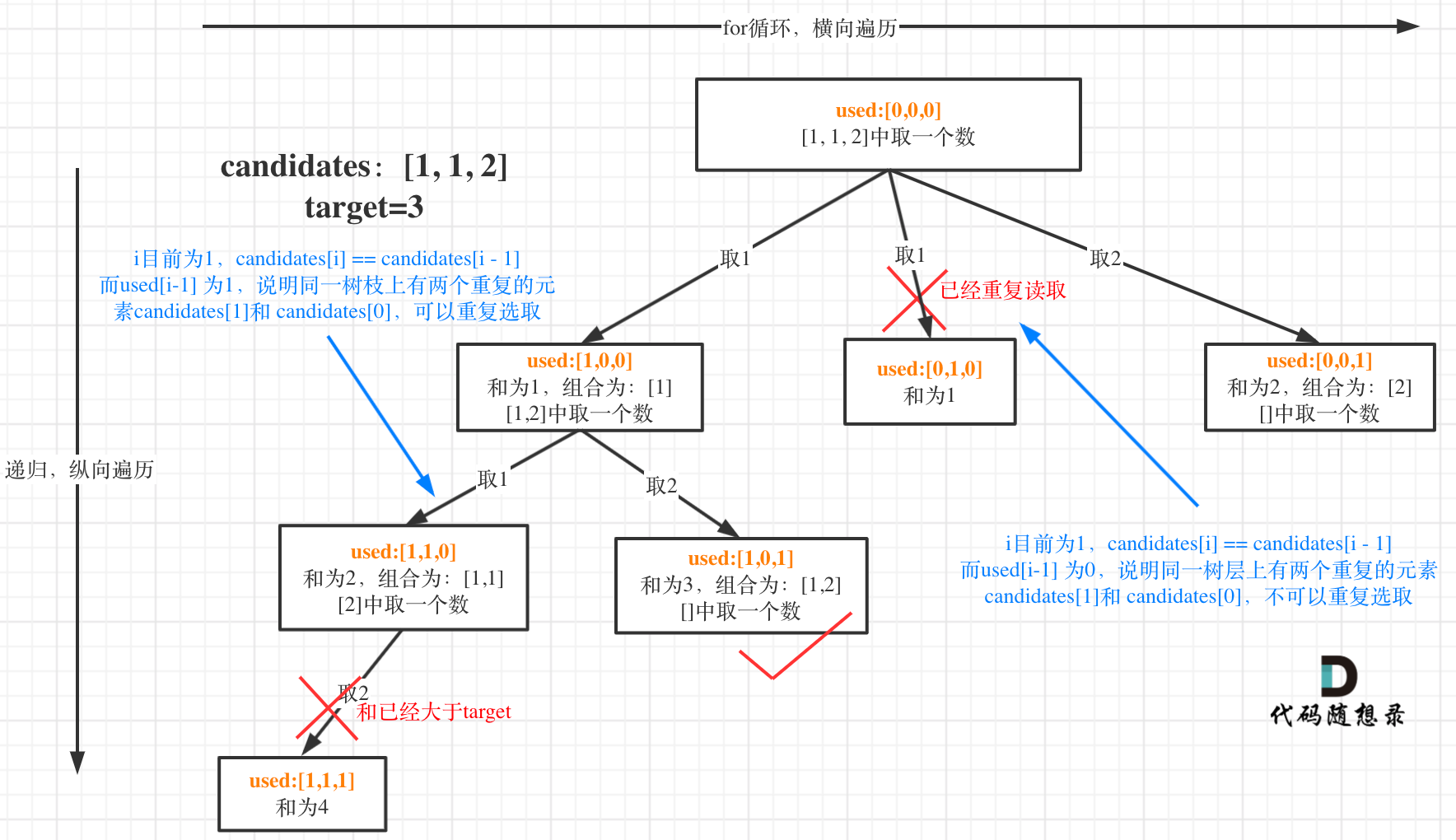
这块比较抽象,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我在图中将used的变化用橘黄色标注上,可以看出在candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]相同的情况下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,9 +6,10 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 这个图就是大厂面试经典题目,接雨水! 最常青藤的一道题,面试官百出不厌!
|
||||
|
||||
# 42. 接雨水
|
||||
# 42. 接雨水
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -15,7 +17,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
|
||||
* 输出:6
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,26 +29,27 @@
|
|||
* 输出:9
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
接雨水问题在面试中还是常见题目的,有必要好好讲一讲。
|
||||
|
||||
本文深度讲解如下三种方法:
|
||||
|
||||
* 双指针法
|
||||
* 动态规划
|
||||
* 单调栈
|
||||
|
||||
## 暴力解法
|
||||
## 暴力解法
|
||||
|
||||
本题暴力解法也是也是使用双指针。
|
||||
|
||||
首先要明确,要按照行来计算,还是按照列来计算。
|
||||
|
||||
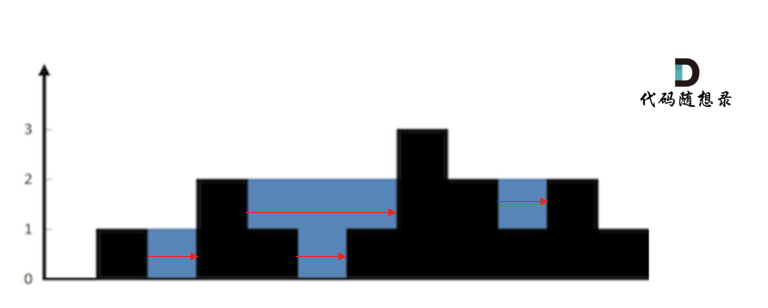
按照行来计算如图:
|
||||
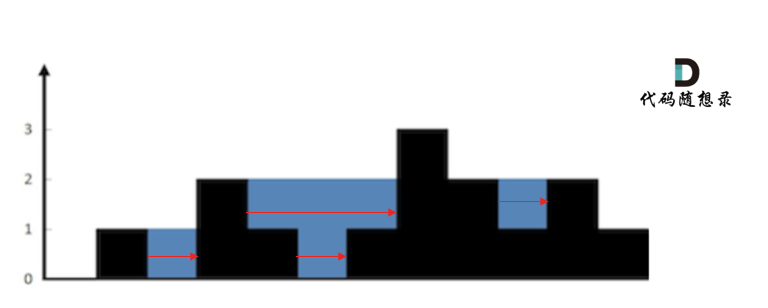
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
按照列来计算如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学在实现的时候,很容易一会按照行来计算一会按照列来计算,这样就会越写越乱。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,7 +61,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
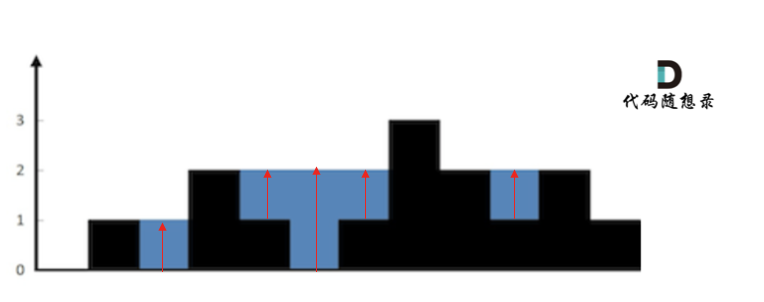
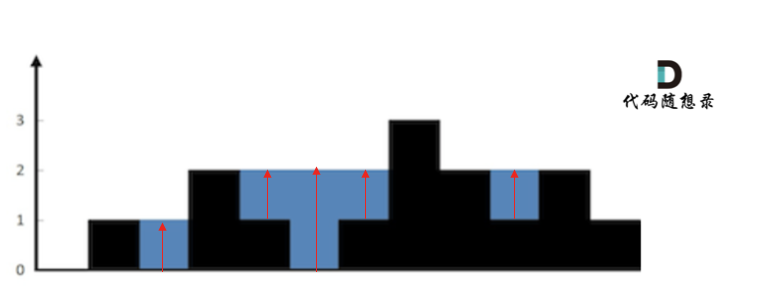
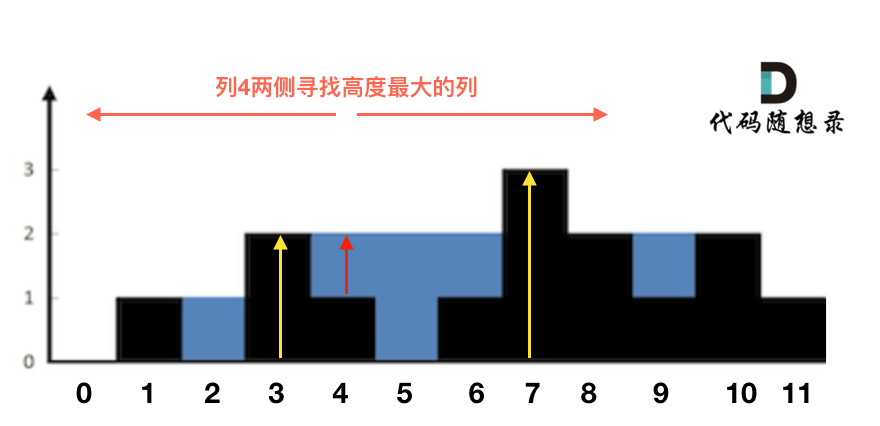
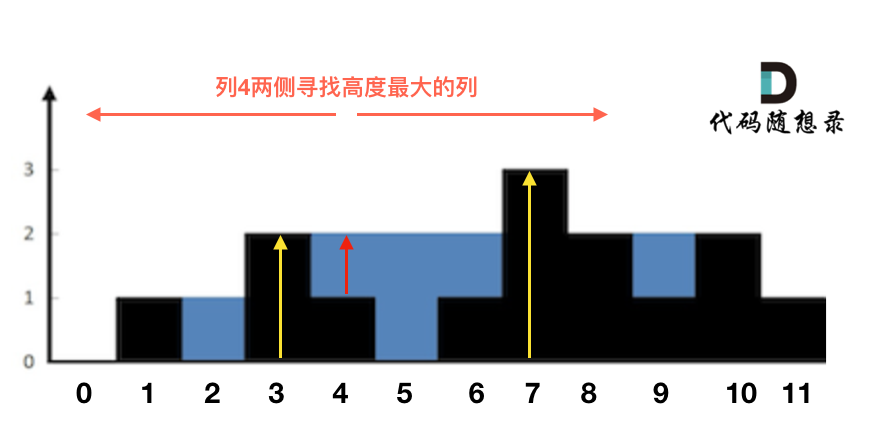
这句话可以有点绕,来举一个理解,例如求列4的雨水高度,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
列4 左侧最高的柱子是列3,高度为2(以下用lHeight表示)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +75,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
此时求出了列4的雨水体积。
|
||||
|
||||
一样的方法,只要从头遍历一遍所有的列,然后求出每一列雨水的体积,相加之后就是总雨水的体积了。
|
||||
一样的方法,只要从头遍历一遍所有的列,然后求出每一列雨水的体积,相加之后就是总雨水的体积了。
|
||||
|
||||
首先从头遍历所有的列,并且**要注意第一个柱子和最后一个柱子不接雨水**,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +135,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
因为每次遍历列的时候,还要向两边寻找最高的列,所以时间复杂度为O(n^2),空间复杂度为O(1)。
|
||||
|
||||
力扣后面修改了后台测试数据,所以以上暴力解法超时了。
|
||||
力扣后面修改了后台测试数据,所以以上暴力解法超时了。
|
||||
|
||||
## 双指针优化
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,9 +184,9 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 单调栈解法
|
||||
## 单调栈解法
|
||||
|
||||
关于单调栈的理论基础,单调栈适合解决什么问题,单调栈的工作过程,大家可以先看这题讲解 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
|
||||
关于单调栈的理论基础,单调栈适合解决什么问题,单调栈的工作过程,大家可以先看这题讲解 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈就是保持栈内元素有序。和[栈与队列:单调队列](https://programmercarl.com/0239.滑动窗口最大值.html)一样,需要我们自己维持顺序,没有现成的容器可以用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -197,7 +200,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
1. 首先单调栈是按照行方向来计算雨水,如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
知道这一点,后面的就可以理解了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -211,11 +214,11 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
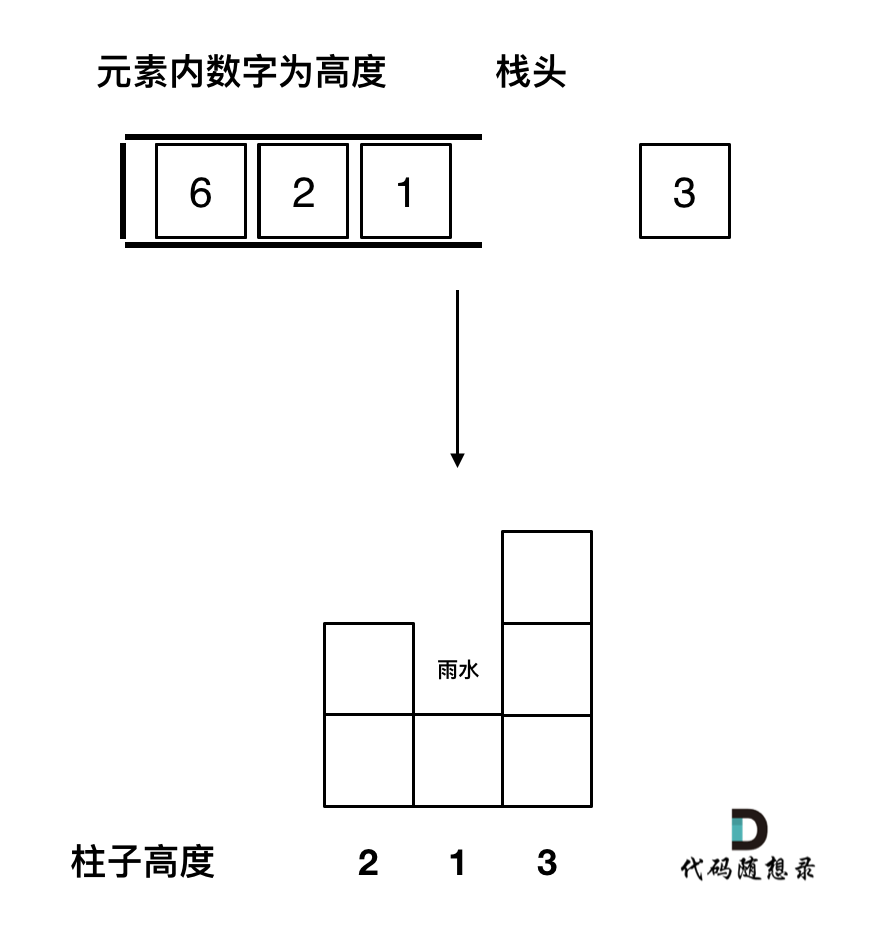
|
||||
|
||||
关于单调栈的顺序给大家一个总结: [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 中求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的,[84.柱状图中最大的矩形](https://programmercarl.com/0084.柱状图中最大的矩形.html)求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 遇到相同高度的柱子怎么办。
|
||||
3. 遇到相同高度的柱子怎么办。
|
||||
|
||||
遇到相同的元素,更新栈内下标,就是将栈里元素(旧下标)弹出,将新元素(新下标)加入栈中。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -225,7 +228,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
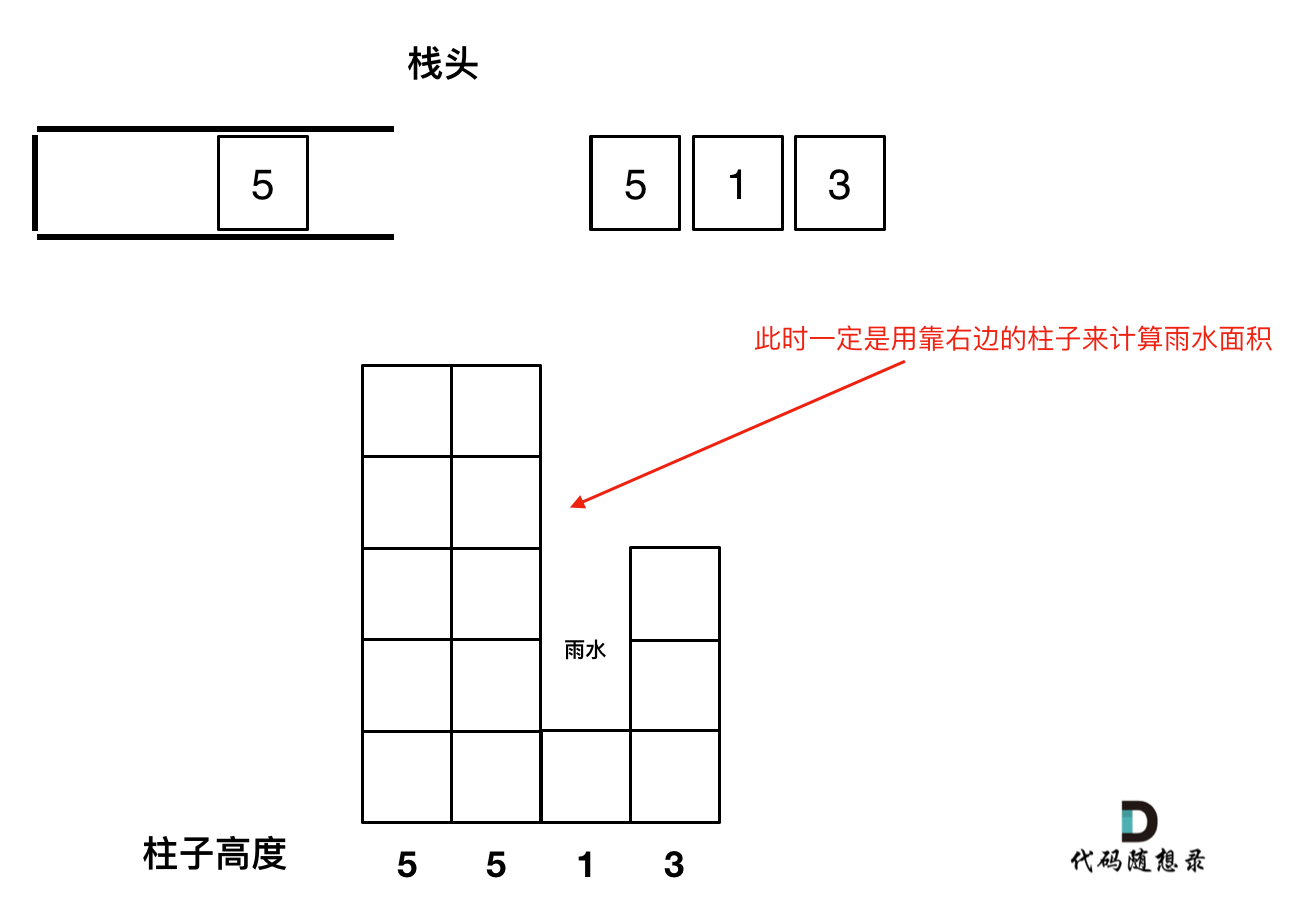
|
||||
|
||||
4. 栈里要保存什么数值
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -233,7 +236,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
长就是通过柱子的高度来计算,宽是通过柱子之间的下标来计算,
|
||||
|
||||
那么栈里有没有必要存一个pair<int, int>类型的元素,保存柱子的高度和下标呢。
|
||||
那么栈里有没有必要存一个pair<int, int>类型的元素,保存柱子的高度和下标呢。
|
||||
|
||||
其实不用,栈里就存放下标就行,想要知道对应的高度,通过height[stack.top()] 就知道弹出的下标对应的高度了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,17 +248,17 @@ stack<int> st; // 存着下标,计算的时候用下标对应的柱子高度
|
|||
|
||||
明确了如上几点,我们再来看处理逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
### 单调栈处理逻辑
|
||||
### 单调栈处理逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
以下操作过程其实和 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 也是一样的,建议先做 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
|
||||
以下操作过程其实和 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html) 也是一样的,建议先做 [739. 每日温度](https://programmercarl.com/0739.每日温度.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
以下逻辑主要就是三种情况
|
||||
以下逻辑主要就是三种情况
|
||||
|
||||
* 情况一:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度小于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] < height[st.top()]
|
||||
* 情况二:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度等于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] == height[st.top()]
|
||||
* 情况三:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] > height[st.top()]
|
||||
* 情况一:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度小于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] < height[st.top()]
|
||||
* 情况二:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度等于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] == height[st.top()]
|
||||
* 情况三:当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度 height[i] > height[st.top()]
|
||||
|
||||
先将下标0的柱子加入到栈中,`st.push(0);`。 栈中存放我们遍历过的元素,所以先将下标0加进来。
|
||||
先将下标0的柱子加入到栈中,`st.push(0);`。 栈中存放我们遍历过的元素,所以先将下标0加进来。
|
||||
|
||||
然后开始从下标1开始遍历所有的柱子,`for (int i = 1; i < height.size(); i++)`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -278,9 +281,9 @@ if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 例如 5 5 1 7 这种情况
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度,此时就出现凹槽了,如图所示:
|
||||
如果当前遍历的元素(柱子)高度大于栈顶元素的高度,此时就出现凹槽了,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
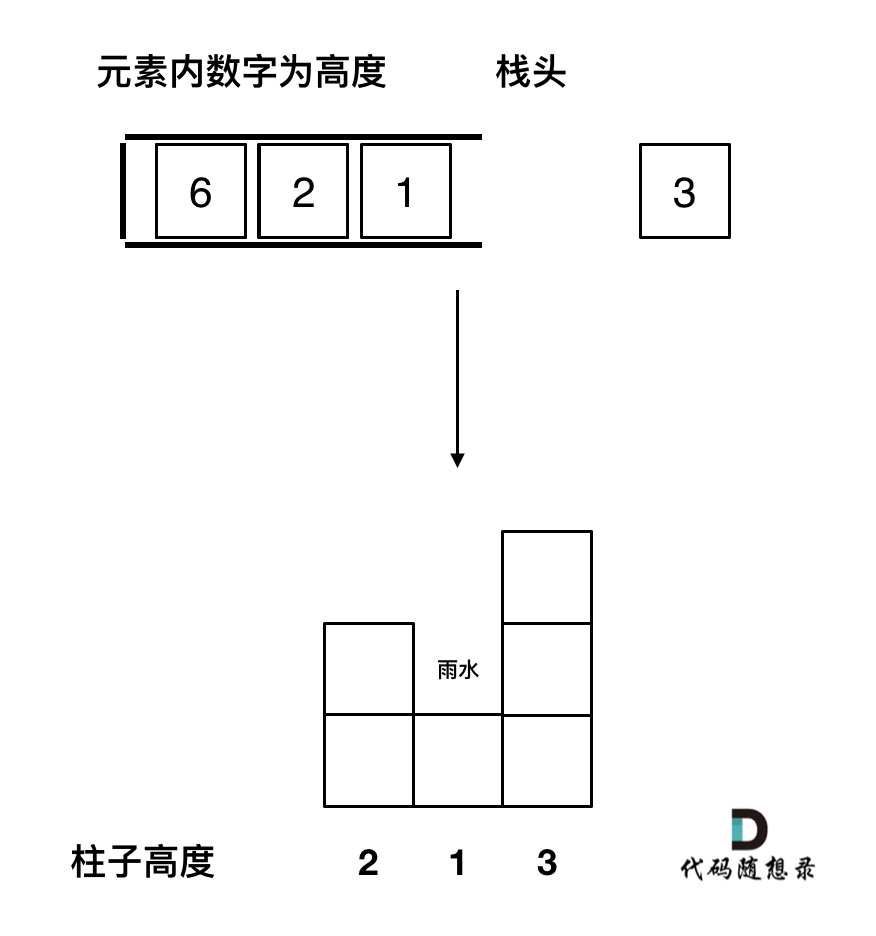
|
||||
|
||||
取栈顶元素,将栈顶元素弹出,这个就是凹槽的底部,也就是中间位置,下标记为mid,对应的高度为height[mid](就是图中的高度1)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -290,7 +293,7 @@ if (height[i] == height[st.top()]) { // 例如 5 5 1 7 这种情况
|
|||
|
||||
此时大家应该可以发现其实就是**栈顶和栈顶的下一个元素以及要入栈的元素,三个元素来接水!**
|
||||
|
||||
那么雨水高度是 min(凹槽左边高度, 凹槽右边高度) - 凹槽底部高度,代码为:`int h = min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[mid];`
|
||||
那么雨水高度是 min(凹槽左边高度, 凹槽右边高度) - 凹槽底部高度,代码为:`int h = min(height[st.top()], height[i]) - height[mid];`
|
||||
|
||||
雨水的宽度是 凹槽右边的下标 - 凹槽左边的下标 - 1(因为只求中间宽度),代码为:`int w = i - st.top() - 1 ;`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -373,11 +376,12 @@ public:
|
|||
精简之后的代码,大家就看不出去三种情况的处理了,貌似好像只处理的情况三,其实是把情况一和情况二融合了。 这样的代码不太利于理解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Java:
|
||||
### Java:
|
||||
|
||||
暴力解法:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int trap(int[] height) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -385,7 +389,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
|
||||
// 第一个柱子和最后一个柱子不接雨水
|
||||
if (i==0 || i== height.length - 1) continue;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int rHeight = height[i]; // 记录右边柱子的最高高度
|
||||
int lHeight = height[i]; // 记录左边柱子的最高高度
|
||||
for (int r = i+1; r < height.length; r++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -404,6 +408,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
双指针:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int trap(int[] height) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,15 +416,15 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
if (length <= 2) return 0;
|
||||
int[] maxLeft = new int[length];
|
||||
int[] maxRight = new int[length];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录每个柱子左边柱子最大高度
|
||||
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i< length; i++) maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i-1]);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 记录每个柱子右边柱子最大高度
|
||||
maxRight[length - 1] = height[length - 1];
|
||||
for(int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxRight[i+1]);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 求和
|
||||
int sum = 0;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -432,13 +437,14 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈法
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int trap(int[] height){
|
||||
int size = height.length;
|
||||
|
||||
if (size <= 2) return 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// in the stack, we push the index of array
|
||||
// using height[] to access the real height
|
||||
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
|
||||
|
|
@ -458,7 +464,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
int heightAtIdx = height[index];
|
||||
while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIdx > height[stackTop])){
|
||||
int mid = stack.pop();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (!stack.isEmpty()){
|
||||
int left = stack.peek();
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -472,7 +478,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
stack.push(index);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return sum;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -481,6 +487,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
### Python:
|
||||
|
||||
暴力解法:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -495,32 +502,35 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
for k in range(i+2,len(height)):
|
||||
if height[k] > rHight:
|
||||
rHight = height[k]
|
||||
res1 = min(lHight,rHight) - height[i]
|
||||
res1 = min(lHight,rHight) - height[i]
|
||||
if res1 > 0:
|
||||
res += res1
|
||||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
双指针:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
leftheight, rightheight = [0]*len(height), [0]*len(height)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
leftheight[0]=height[0]
|
||||
for i in range(1,len(height)):
|
||||
leftheight[i]=max(leftheight[i-1],height[i])
|
||||
rightheight[-1]=height[-1]
|
||||
for i in range(len(height)-2,-1,-1):
|
||||
rightheight[i]=max(rightheight[i+1],height[i])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
for i in range(0,len(height)):
|
||||
summ = min(leftheight[i],rightheight[i])-height[i]
|
||||
result += summ
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -565,8 +575,8 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
result += h * w
|
||||
stack.append(i)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
# 单调栈压缩版
|
||||
|
||||
# 单调栈压缩版
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
|
||||
stack = [0]
|
||||
|
|
@ -586,7 +596,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func trap(height []int) int {
|
||||
|
|
@ -601,7 +611,7 @@ func trap(height []int) int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
left++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if height[right] > rightMax {
|
||||
if height[right] > rightMax {
|
||||
rightMax = height[right] // //设置右边最高柱子
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res += rightMax - height[right] // //左边必定有柱子挡水,所以,遇到所有值小于等于rightMax的,全部加入水池
|
||||
|
|
@ -652,6 +662,7 @@ func min(a,b int)int{
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
单调栈解法
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func trap(height []int) int {
|
||||
if len(height) <= 2 {
|
||||
|
|
@ -896,12 +907,12 @@ int trap(int* height, int heightSize) {
|
|||
while (left < right) { //两个指针重合就结束
|
||||
leftMax = fmax(leftMax, height[left]);
|
||||
rightMax = fmax(rightMax, height[right]);
|
||||
if (leftMax < rightMax) {
|
||||
if (leftMax < rightMax) {
|
||||
ans += leftMax - height[left]; //这里考虑的是下标为left的“底”能装多少水
|
||||
++left;//指针的移动次序是这个方法的关键
|
||||
//这里左指针右移是因为左“墙”较矮,左边这一片实际情况下的盛水量是受制于这个矮的左“墙”的
|
||||
//而较高的右边在实际情况下的限制条件可能不是当前的左“墙”,比如限制条件可能是右“墙”,就能装更高的水,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
ans += rightMax - height[right]; //同理,考虑下标为right的元素
|
||||
--right;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
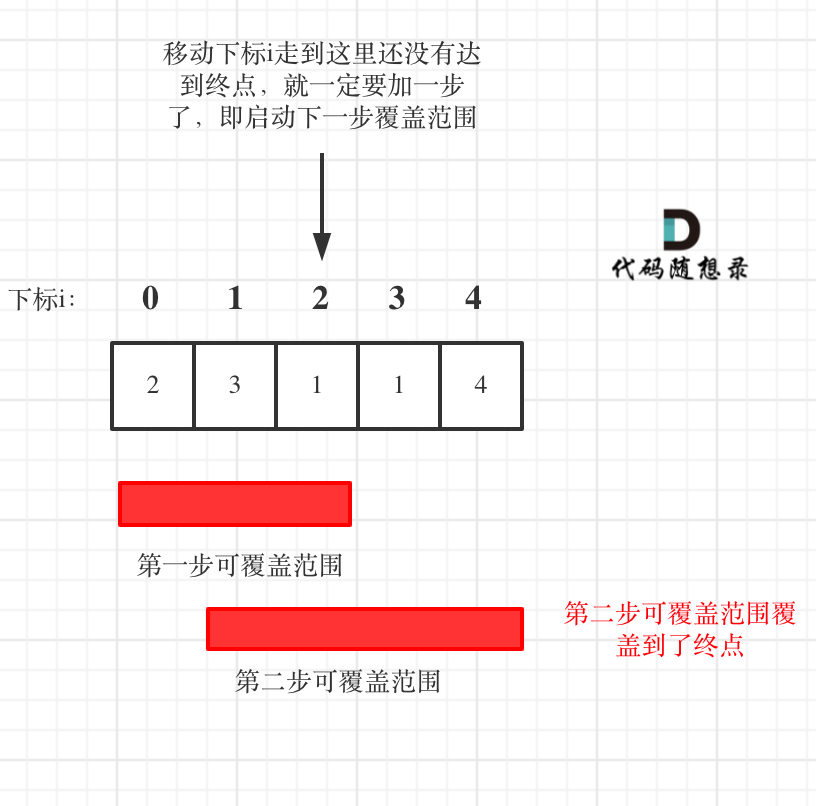
|
||||
|
||||
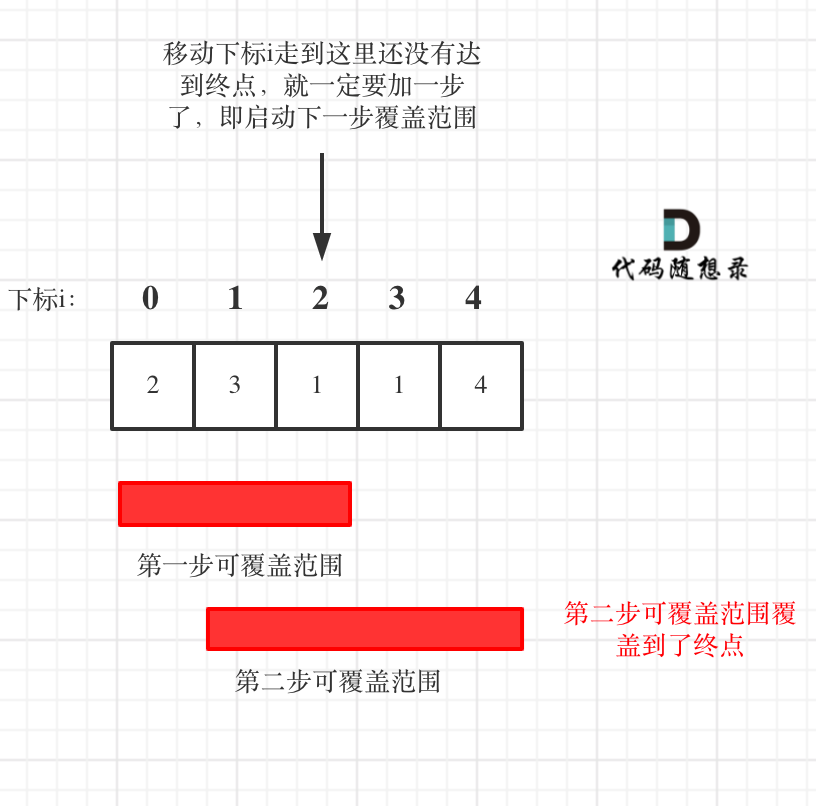
|
||||
|
||||
**图中覆盖范围的意义在于,只要红色的区域,最多两步一定可以到!(不用管具体怎么跳,反正一定可以跳到)**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,11 +97,11 @@ public:
|
|||
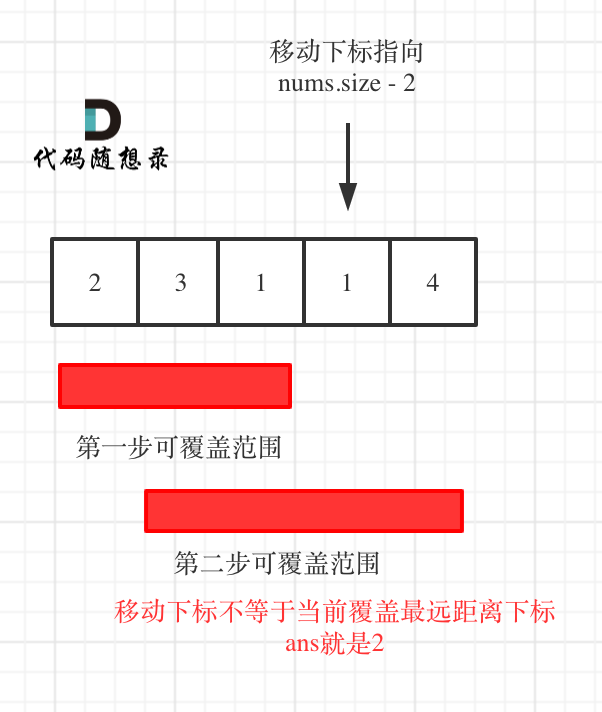
因为当移动下标指向nums.size - 2时:
|
||||
|
||||
* 如果移动下标等于当前覆盖最大距离下标, 需要再走一步(即ans++),因为最后一步一定是可以到的终点。(题目假设总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置),如图:
|
||||
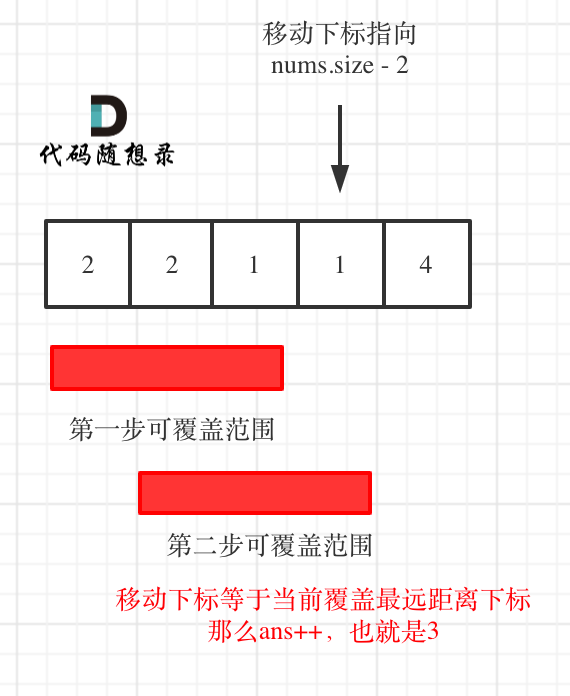
|
||||
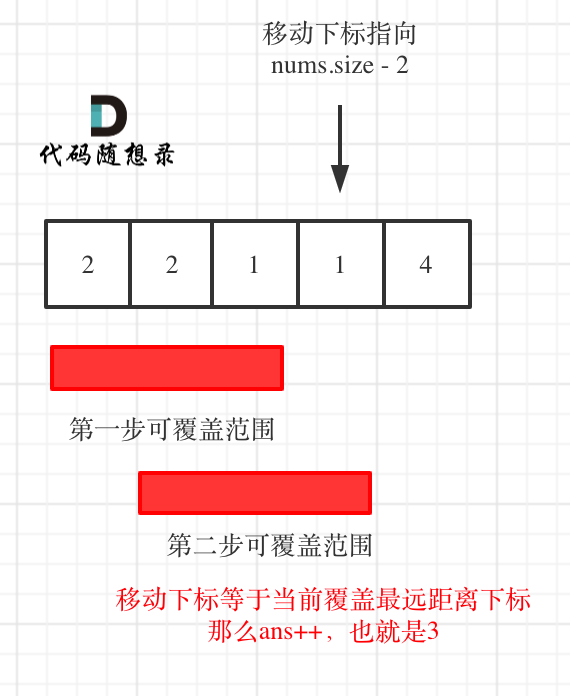
|
||||
|
||||
* 如果移动下标不等于当前覆盖最大距离下标,说明当前覆盖最远距离就可以直接达到终点了,不需要再走一步。如图:
|
||||
|
||||
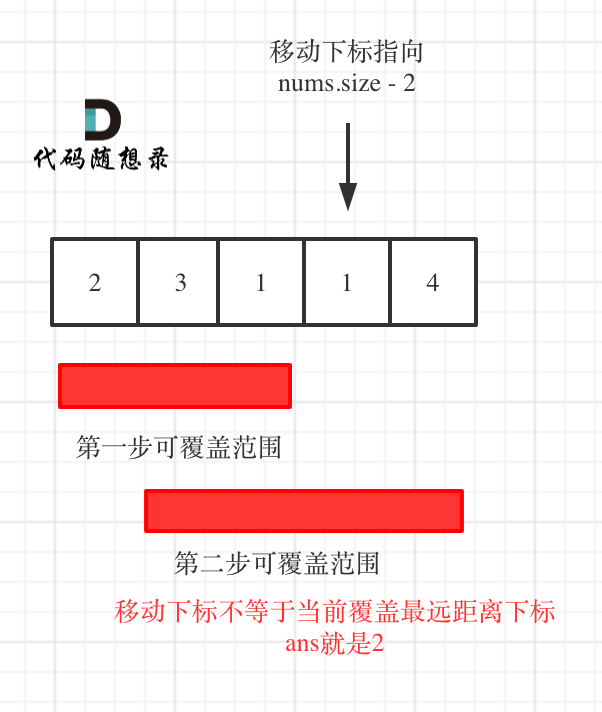
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ void backtracking (vector<int>& nums, vector<bool>& used)
|
|||
|
||||
* 递归终止条件
|
||||
|
||||
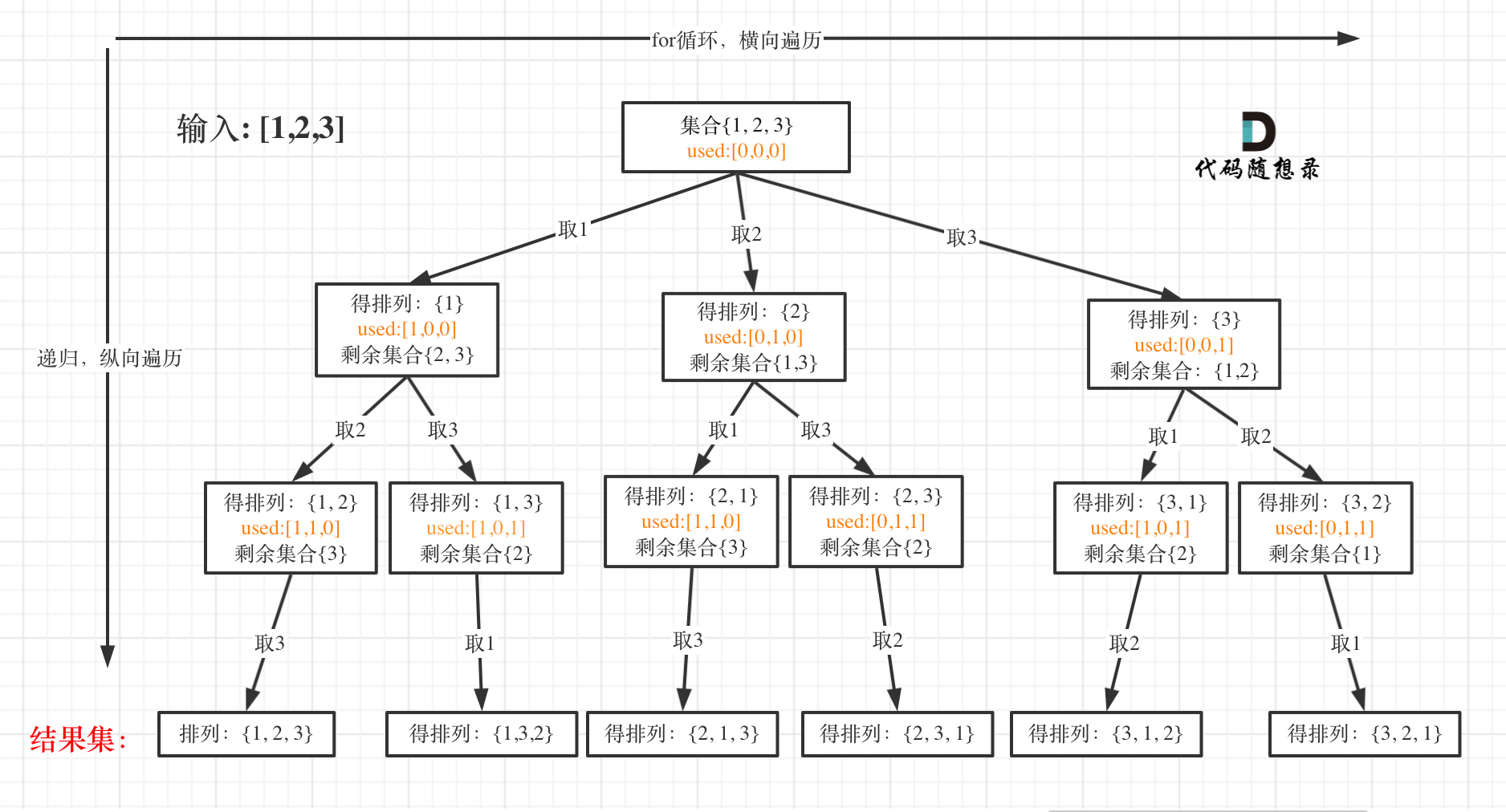
|
||||
|
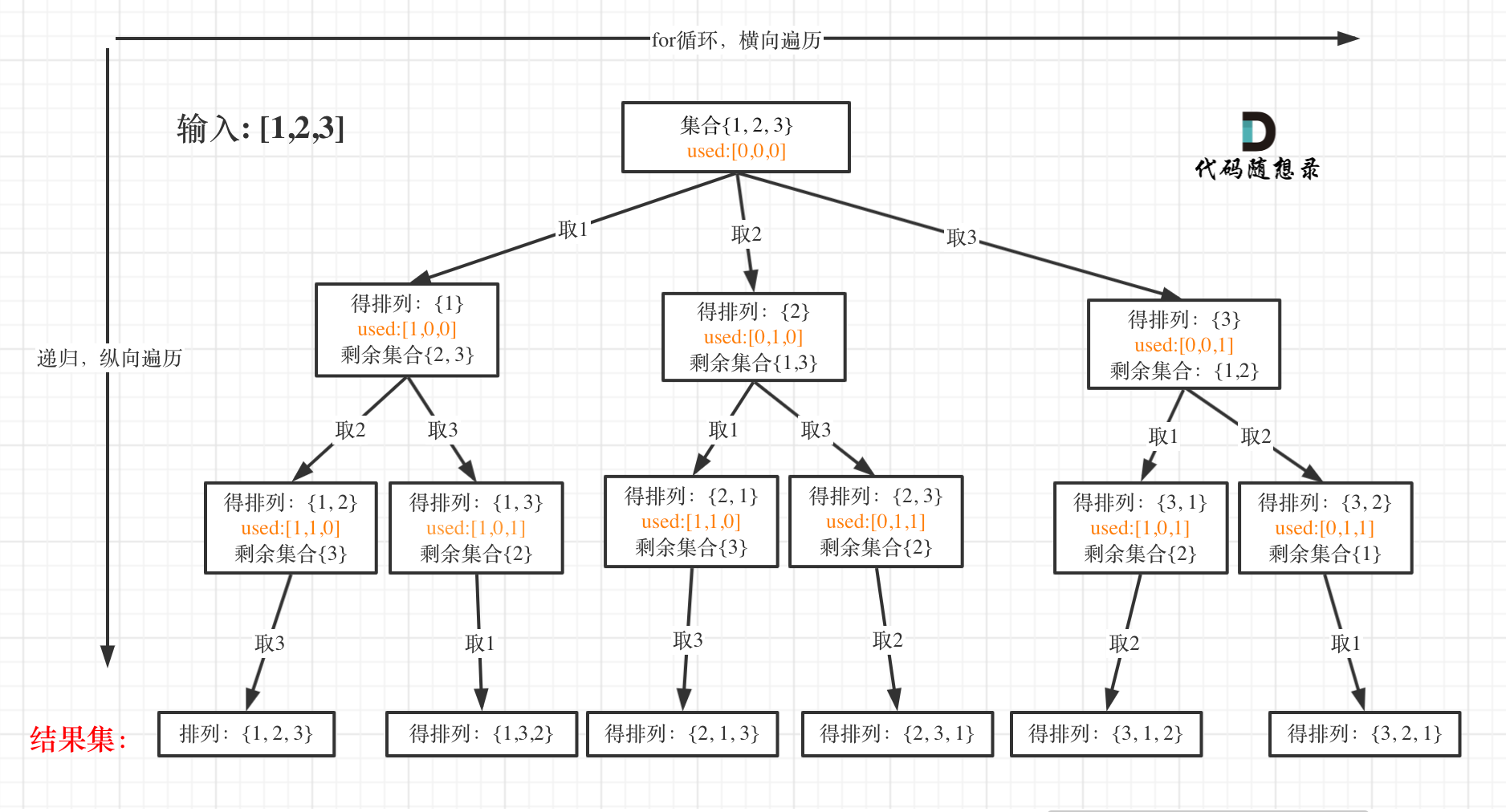
||||
|
||||
可以看出叶子节点,就是收割结果的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 47.全排列 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,17 +14,20 @@
|
|||
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:nums = [1,1,2]
|
||||
* 输出:
|
||||
[[1,1,2],
|
||||
[1,2,1],
|
||||
[2,1,1]]
|
||||
[[1,1,2],
|
||||
[1,2,1],
|
||||
[2,1,1]]
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:nums = [1,2,3]
|
||||
* 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
* 1 <= nums.length <= 8
|
||||
* -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +50,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
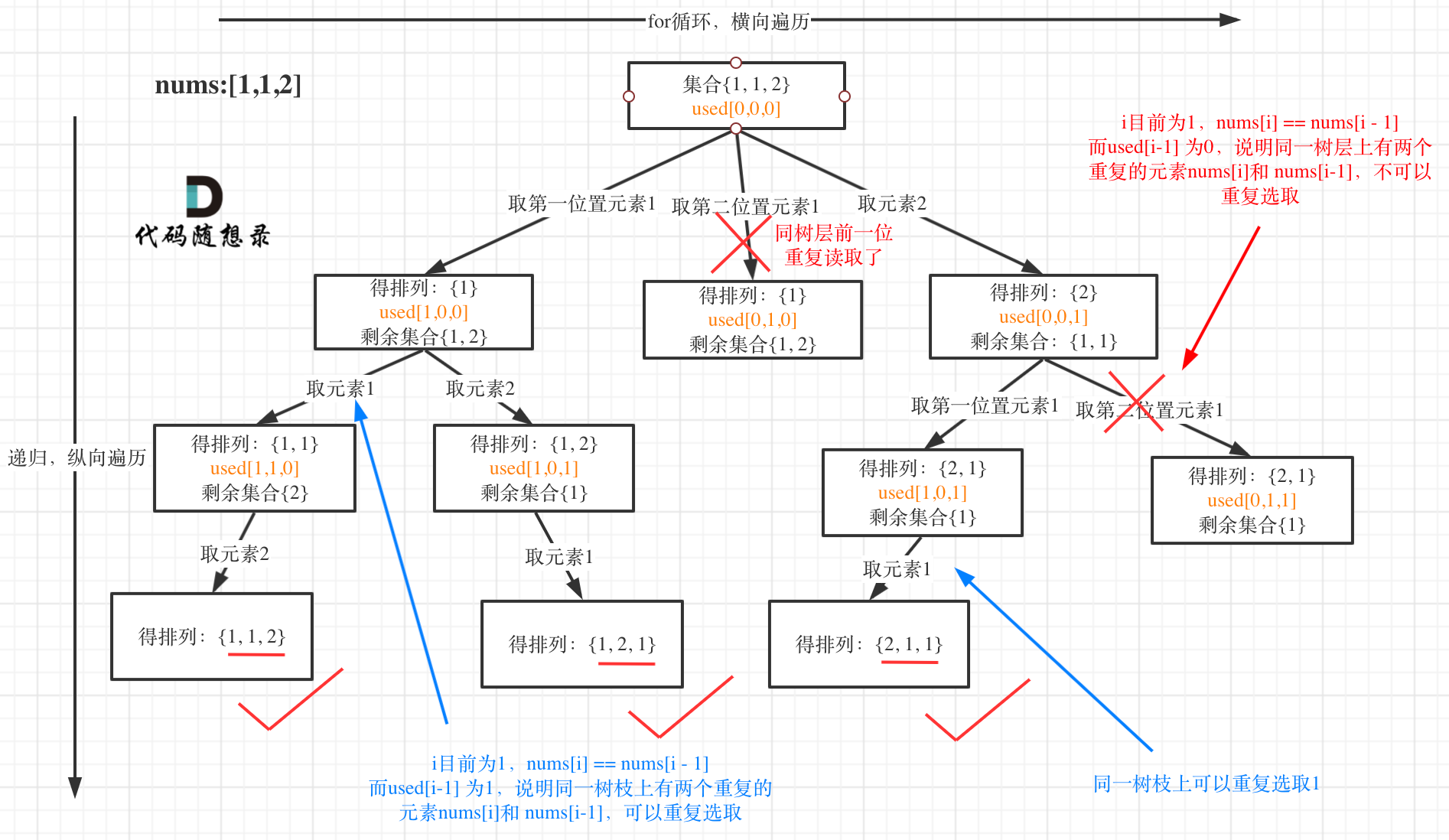
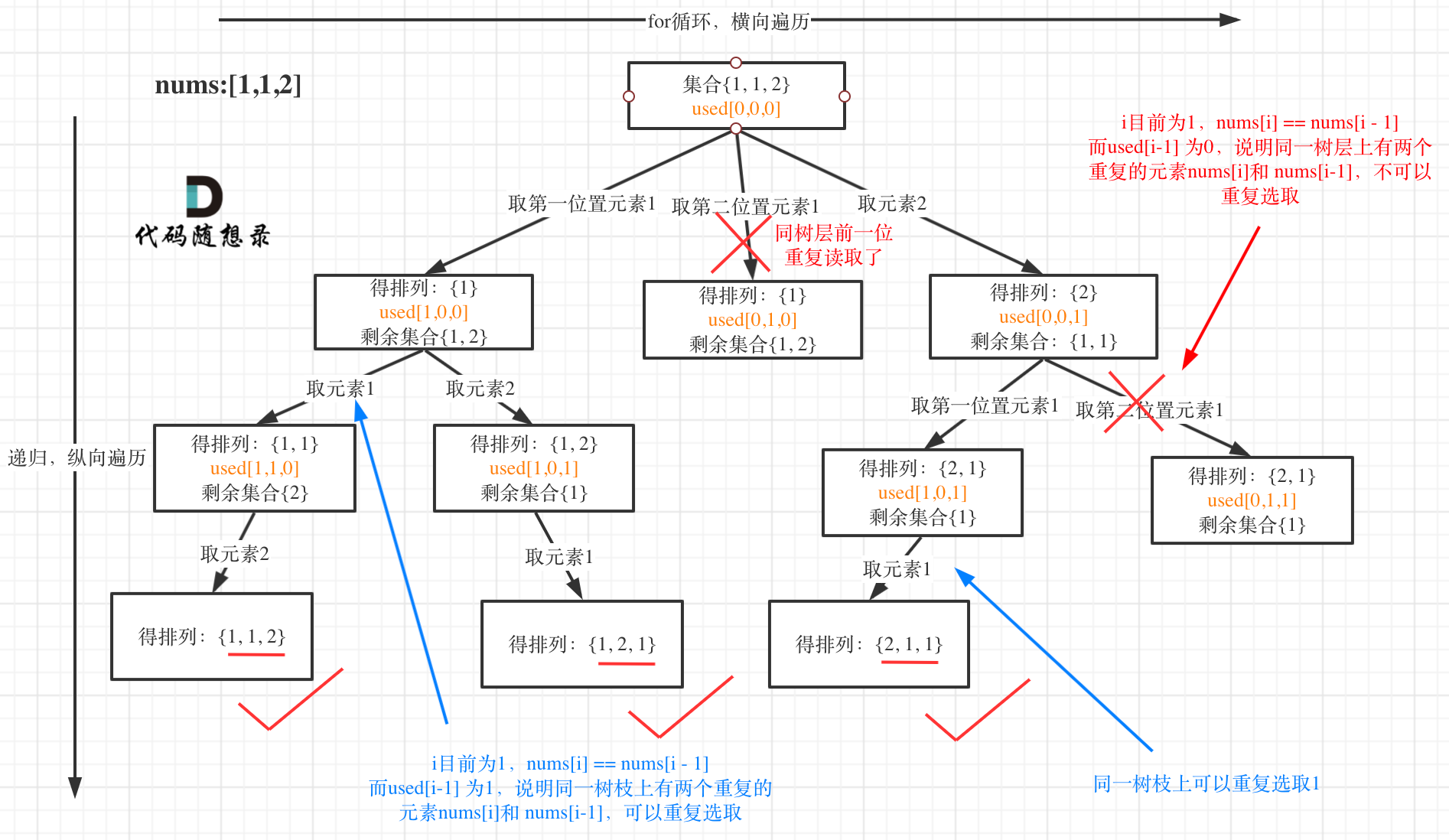
我以示例中的 [1,1,2]为例 (为了方便举例,已经排序)抽象为一棵树,去重过程如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
图中我们对同一树层,前一位(也就是nums[i-1])如果使用过,那么就进行去重。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,7 +73,7 @@ private:
|
|||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
||||
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝nums[i - 1]使用过
|
||||
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过
|
||||
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过
|
||||
// 如果同一树层nums[i - 1]使用过则直接跳过
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
|
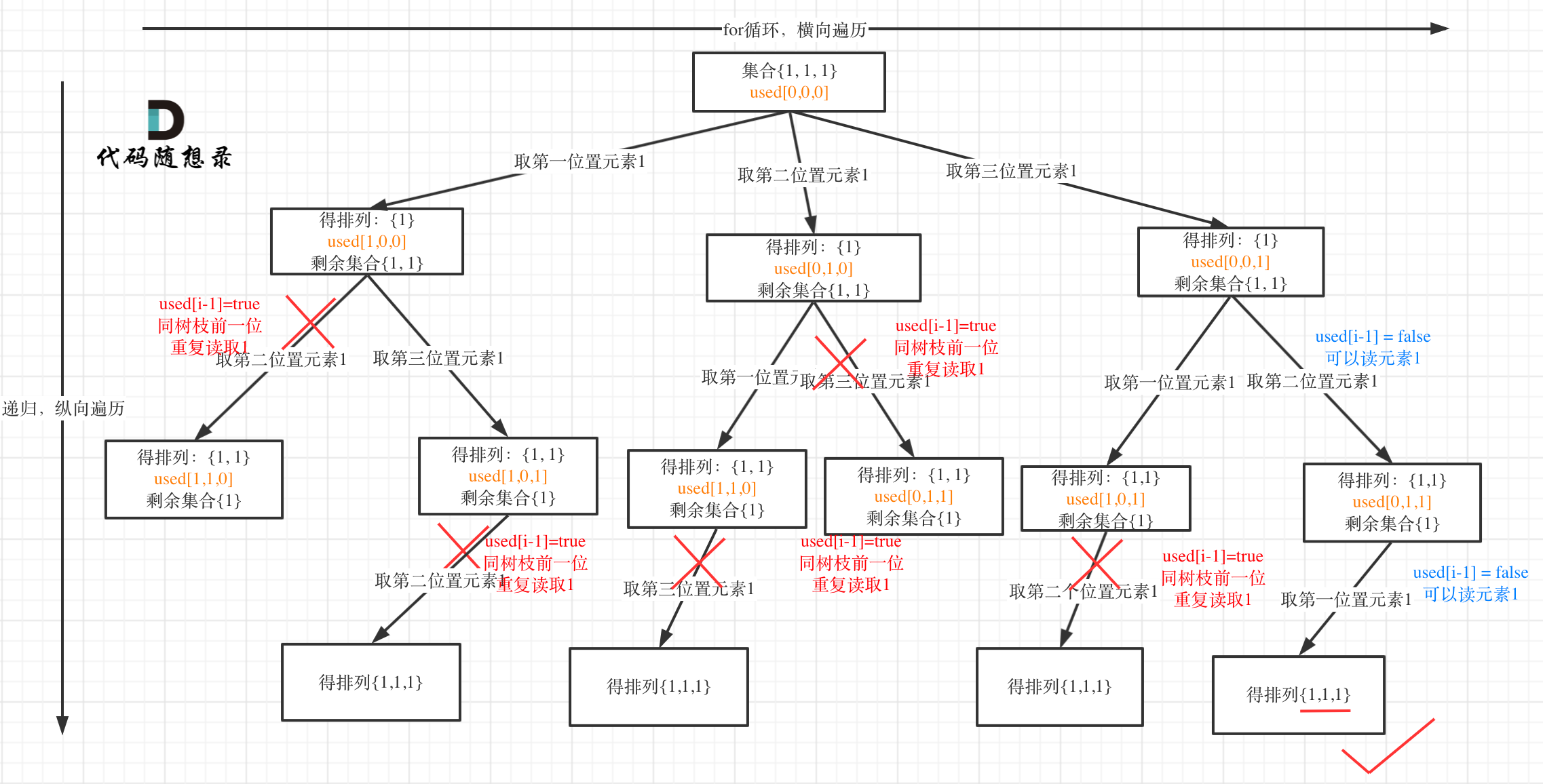
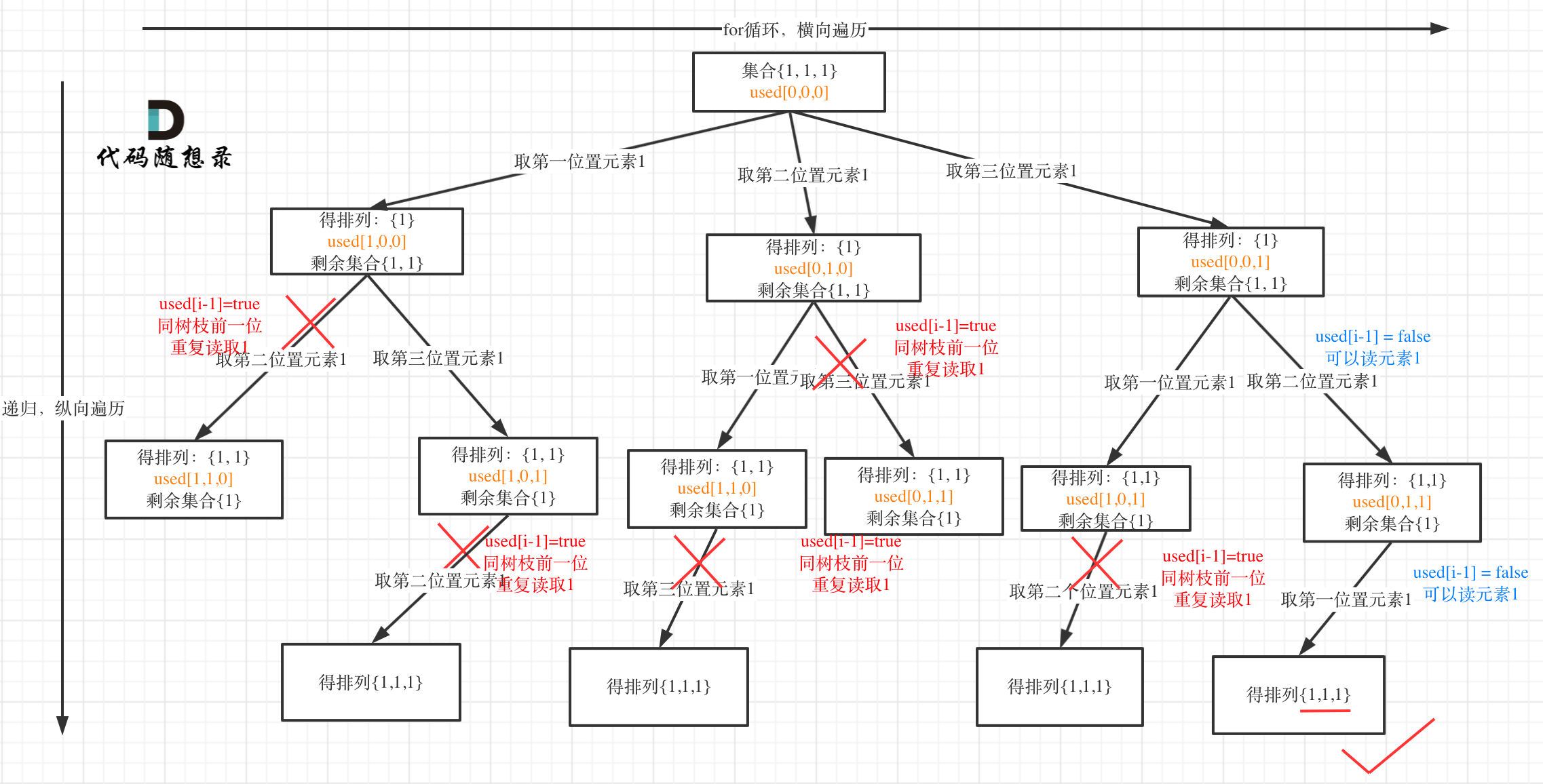
@ -123,23 +128,26 @@ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
|
|||
|
||||
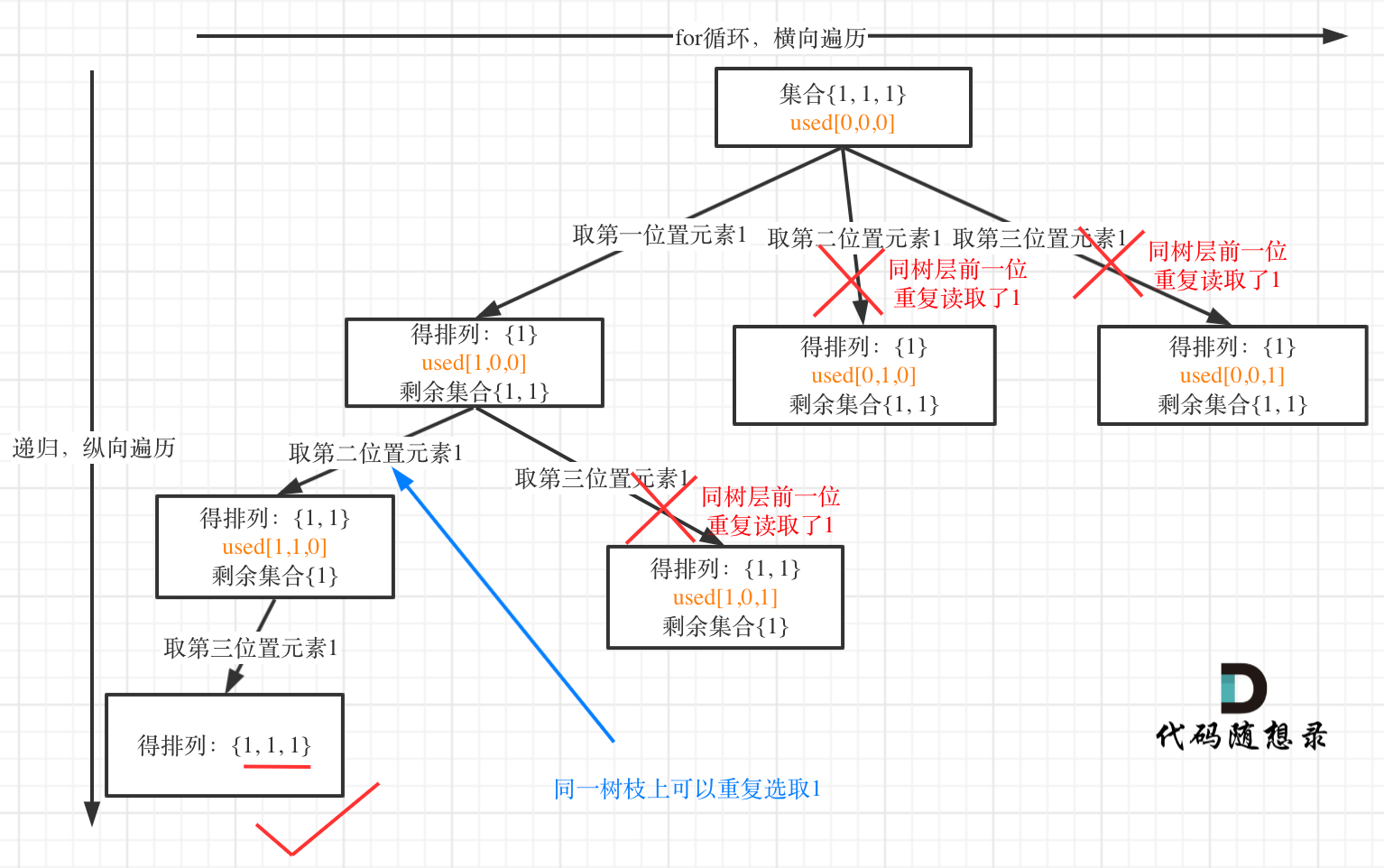
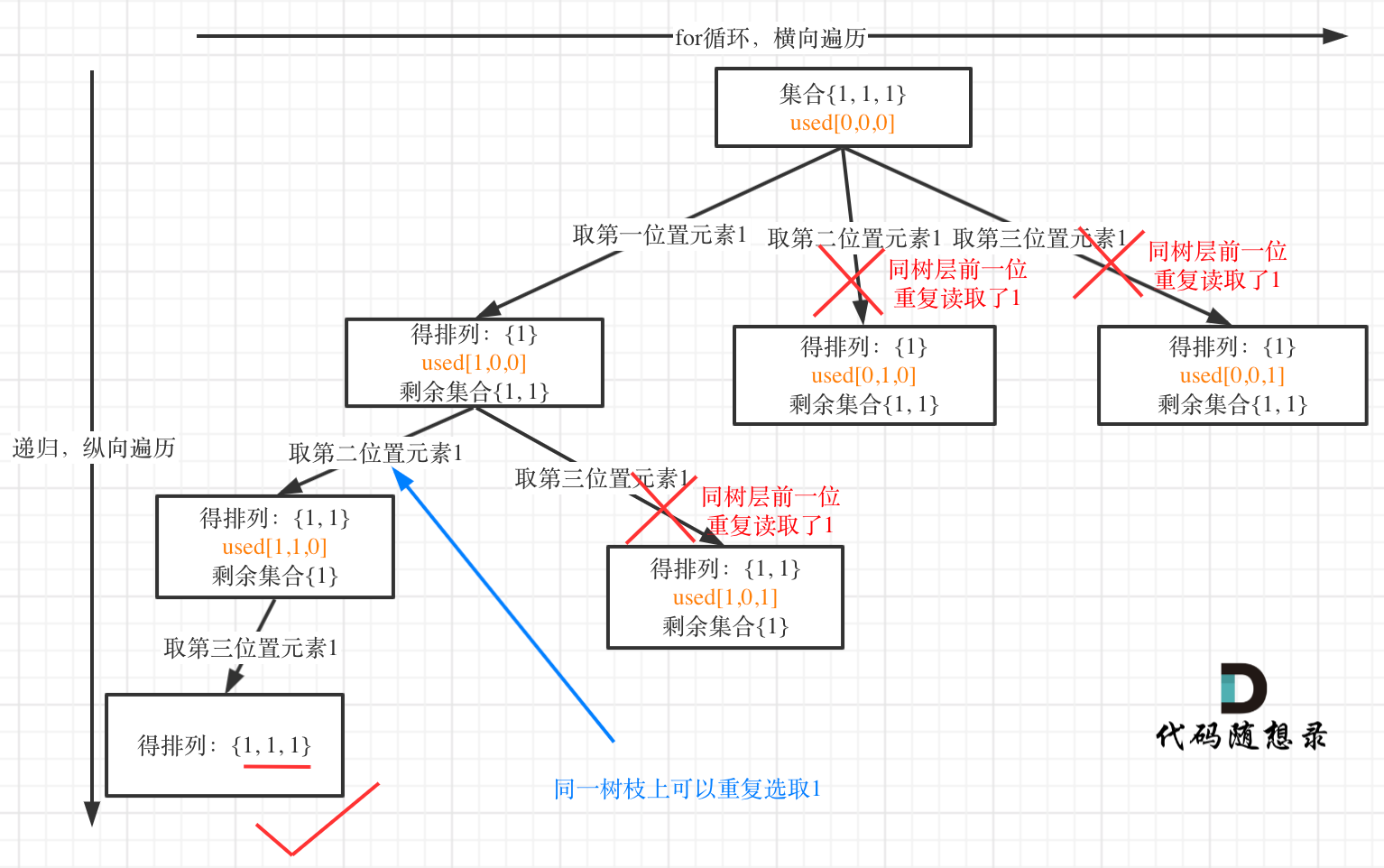
树层上去重(used[i - 1] == false),的树形结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
树枝上去重(used[i - 1] == true)的树型结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
大家应该很清晰的看到,树层上对前一位去重非常彻底,效率很高,树枝上对前一位去重虽然最后可以得到答案,但是做了很多无用搜索。
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
这道题其实还是用了我们之前讲过的去重思路,但有意思的是,去重的代码中,这么写:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
和这么写:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +162,7 @@ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == true) {
|
|||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### java
|
||||
### java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -196,7 +204,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### python
|
||||
### python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
|
|
@ -224,7 +232,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var (
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,7 +272,6 @@ func dfs(nums []int, cur int) {
|
|||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
|
||||
var permuteUnique = function (nums) {
|
||||
nums.sort((a, b) => {
|
||||
return a - b
|
||||
|
|
@ -392,6 +399,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//临时数组
|
||||
int *path;
|
||||
|
|
@ -483,7 +491,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
// 当前索引为0,不存在和前一个数字相等可以进入回溯
|
||||
// 当前索引值和上一个索引不相等,可以回溯
|
||||
// 前一个索引对应的值没有被选,可以回溯
|
||||
// 因为Scala没有continue,只能将逻辑反过来写
|
||||
// 因为Scala没有continue,只能将逻辑反过来写
|
||||
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && num(i) != num(i - 1)) || used(i-1) == false) {
|
||||
used(i) = true
|
||||
path.append(num(i))
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,
|
|||
|
||||
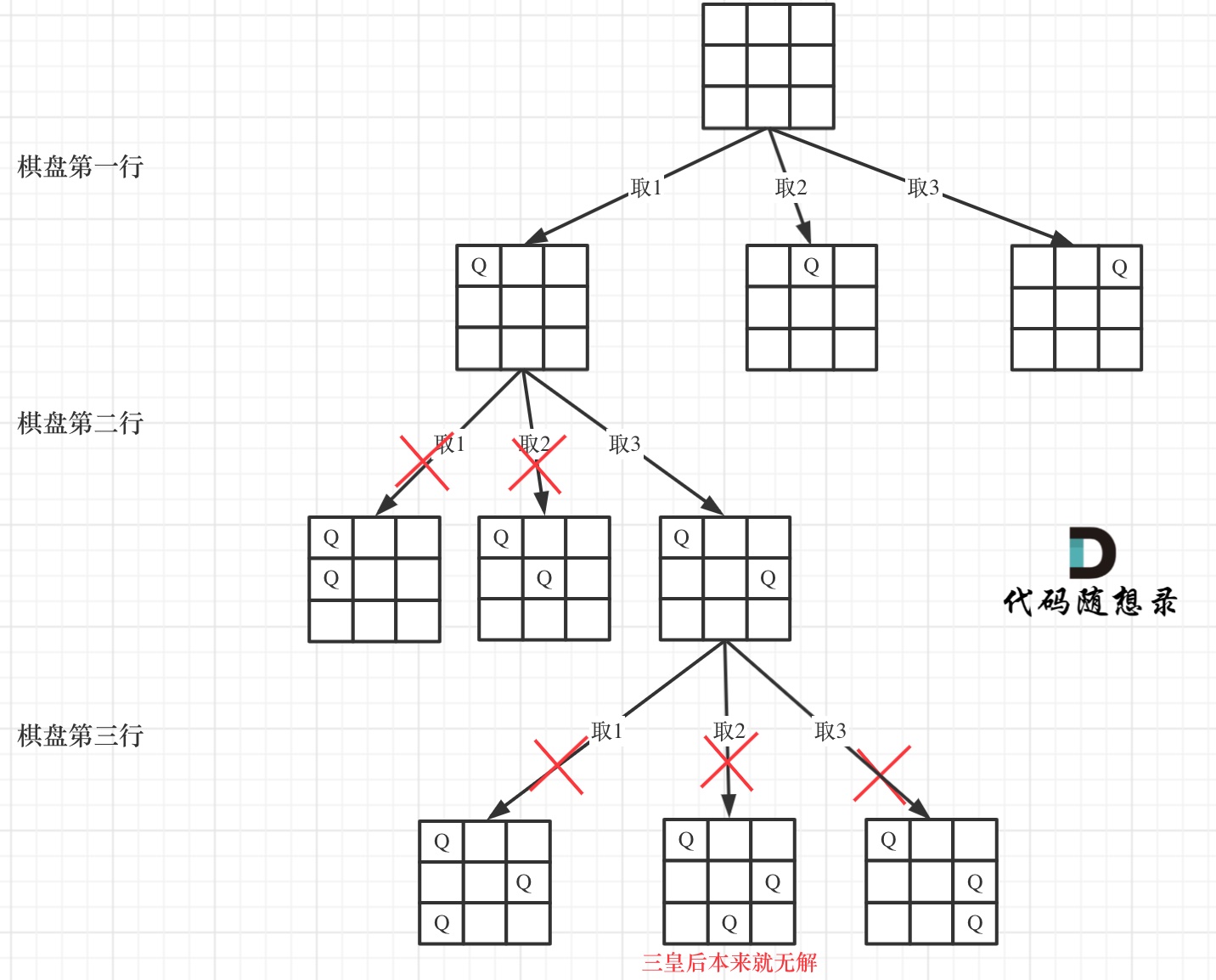
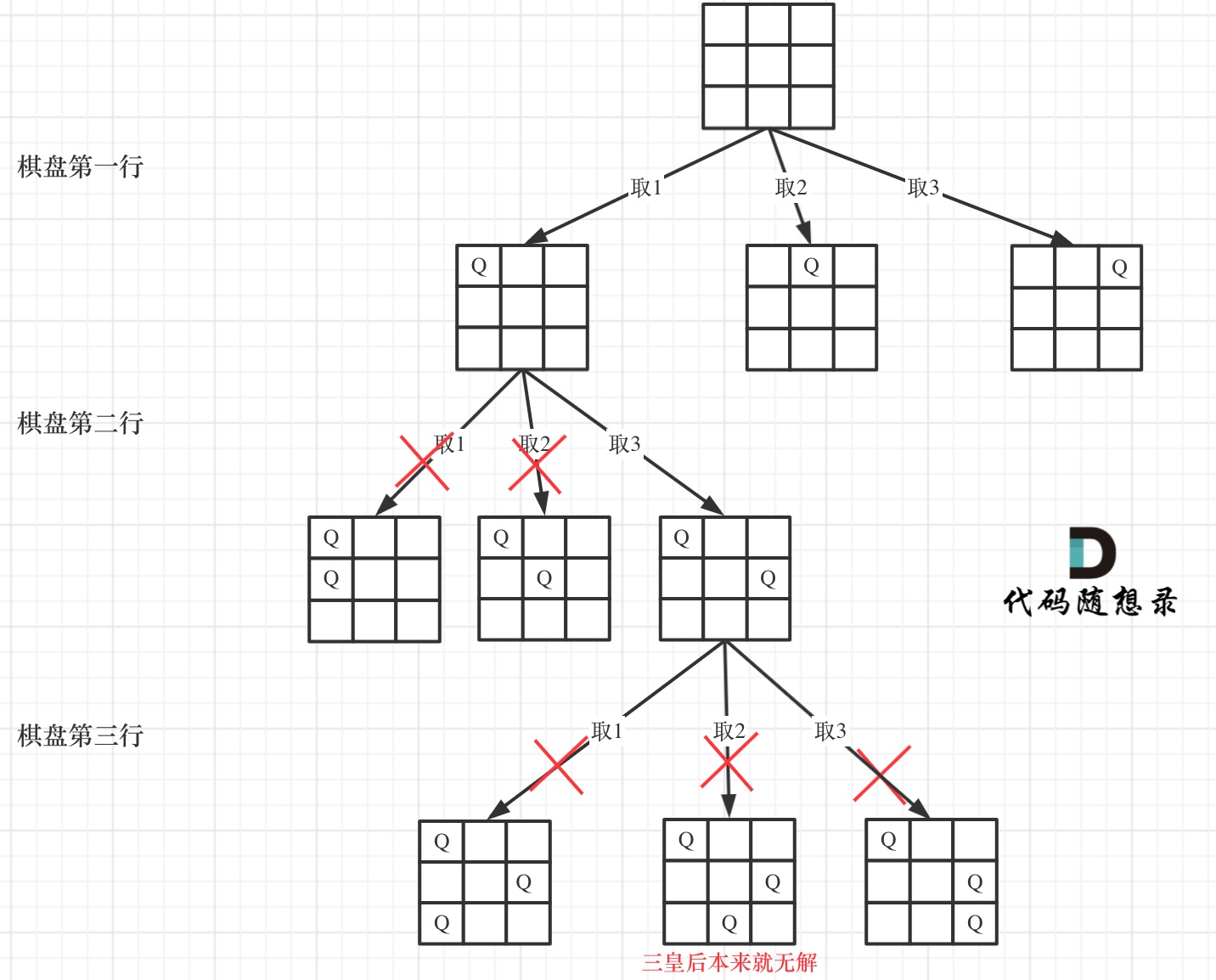
下面我用一个 3 * 3 的棋盘,将搜索过程抽象为一棵树,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这棵树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
|
|||
* 递归终止条件
|
||||
|
||||
在如下树形结构中:
|
||||

|
||||
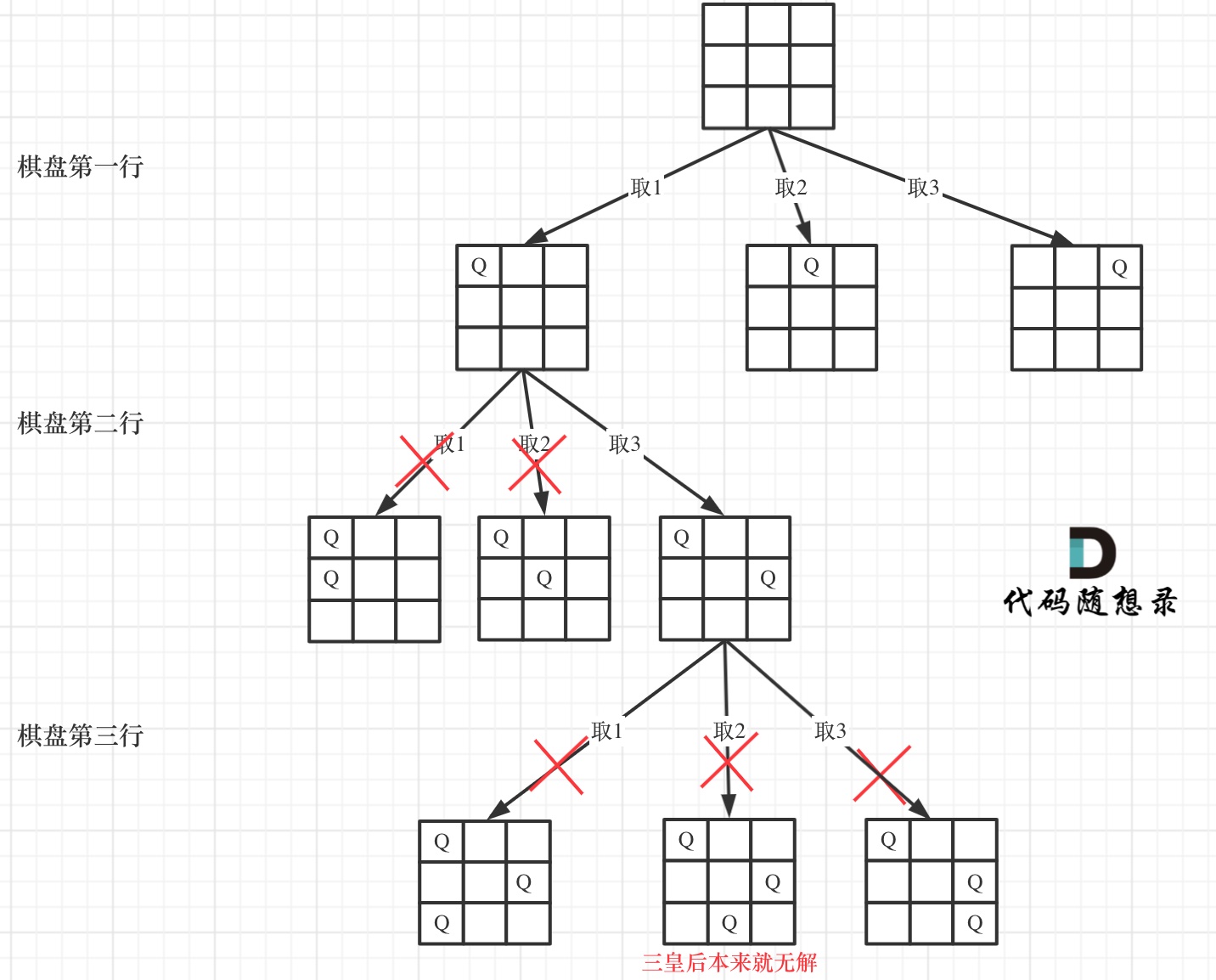
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出,当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,9 @@
|
|||
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
|
||||
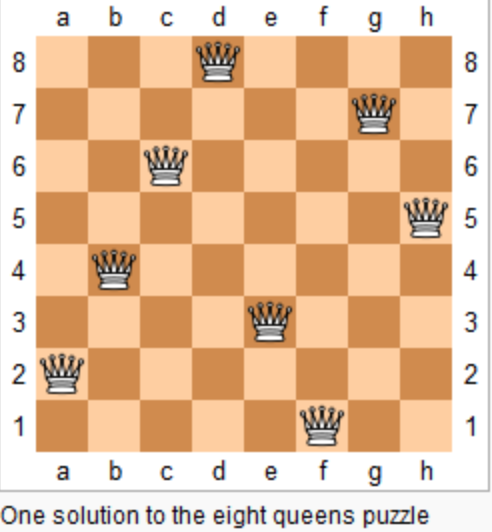
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个整数 n,返回 n 皇后不同的解决方案的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ dp[0]应该是多少呢?
|
|||
5. 举例推导dp数组
|
||||
|
||||
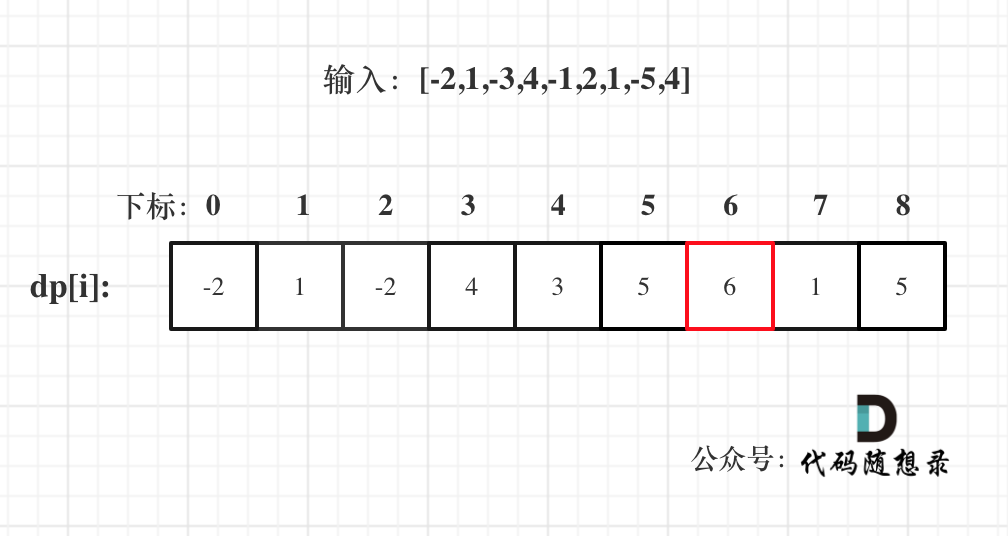
以示例一为例,输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],对应的dp状态如下:
|
||||
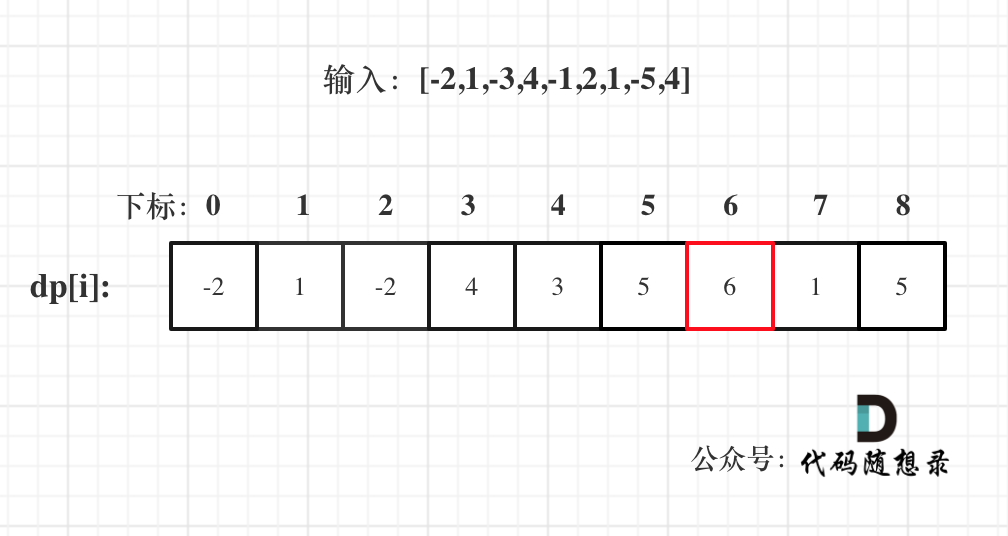
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**注意最后的结果可不是dp[nums.size() - 1]!** ,而是dp[6]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
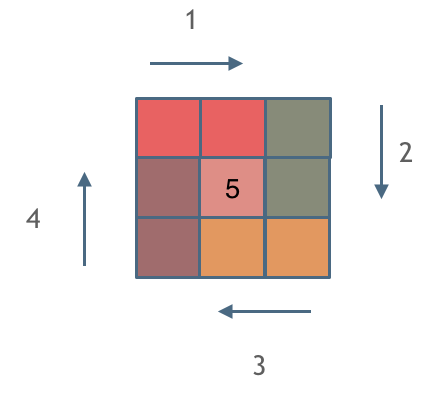
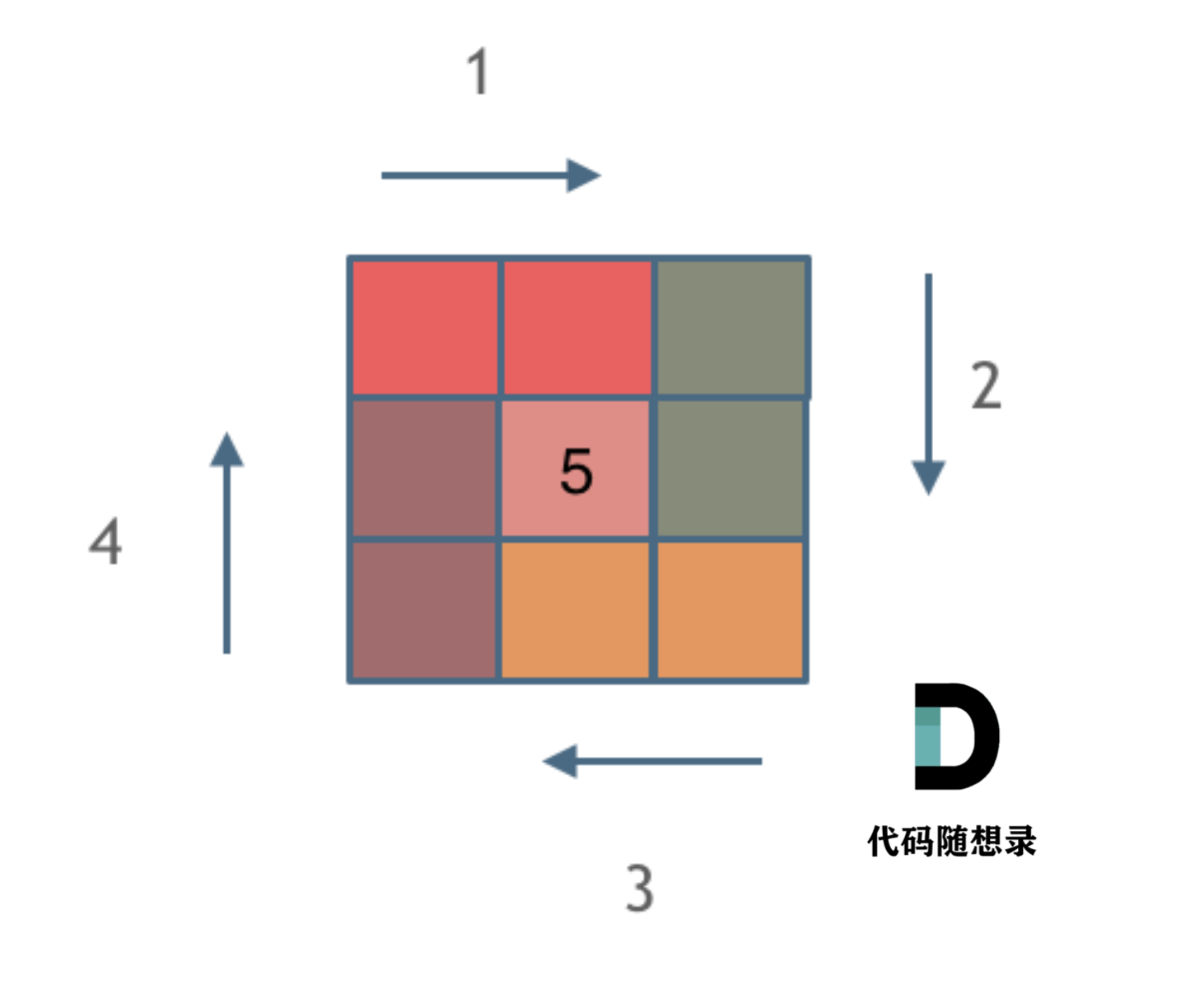
由外向内一圈一圈这么画下去,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这里每一种颜色,代表一条边,我们遍历的长度,可以看出每一个拐角处的处理规则,拐角处让给新的一条边来继续画。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
i每次移动只能在cover的范围内移动,每移动一个元素,cover得到该元素数值(新的覆盖范围)的补充,让i继续移动下去。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
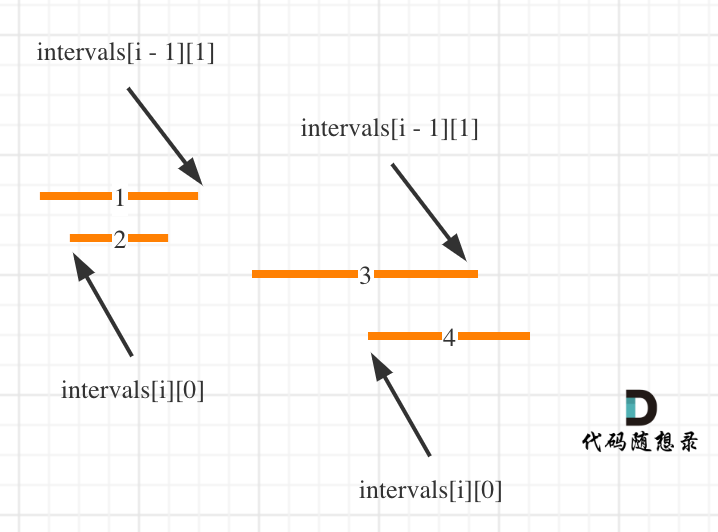
这么说有点抽象,看图:(**注意图中区间都是按照左边界排序之后了**)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
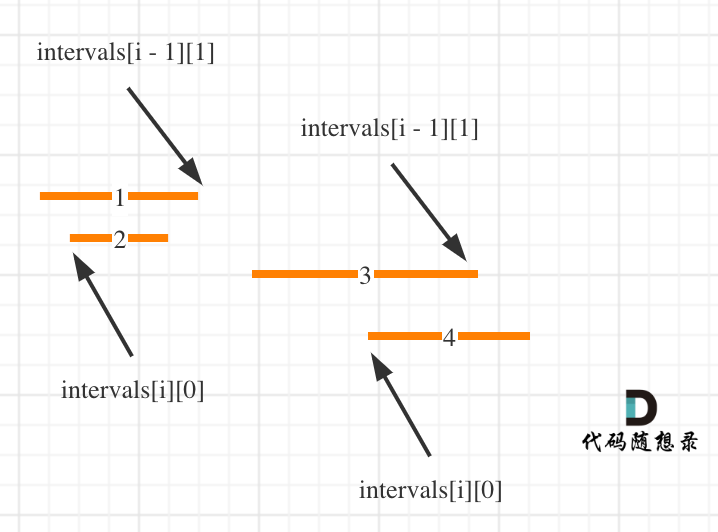
|
||||
|
||||
知道如何判断重复之后,剩下的就是合并了,如何去模拟合并区间呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,14 +1,16 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 62.不同路径
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths/)
|
||||
|
||||
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
|
||||
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
|
||||
|
||||
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish” )。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,30 +18,35 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
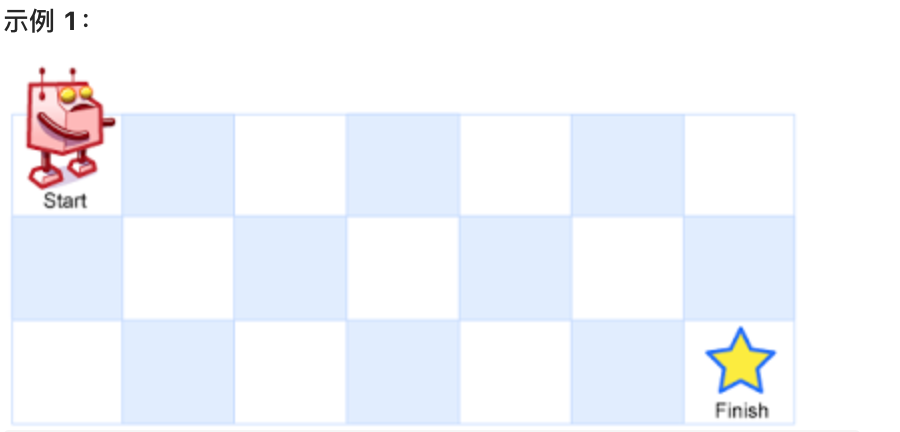
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:m = 3, n = 7
|
||||
* 输出:28
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:m = 2, n = 3
|
||||
* 输出:3
|
||||
|
||||
解释: 从左上角开始,总共有 3 条路径可以到达右下角。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下
|
||||
2. 向右 -> 向下 -> 向右
|
||||
3. 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
示例 3:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:m = 7, n = 3
|
||||
* 输出:28
|
||||
|
||||
示例 4:
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:m = 3, n = 3
|
||||
* 输出:6
|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
* 1 <= m, n <= 100
|
||||
* 题目数据保证答案小于等于 2 * 10^9
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +64,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图举例:
|
||||
|
||||
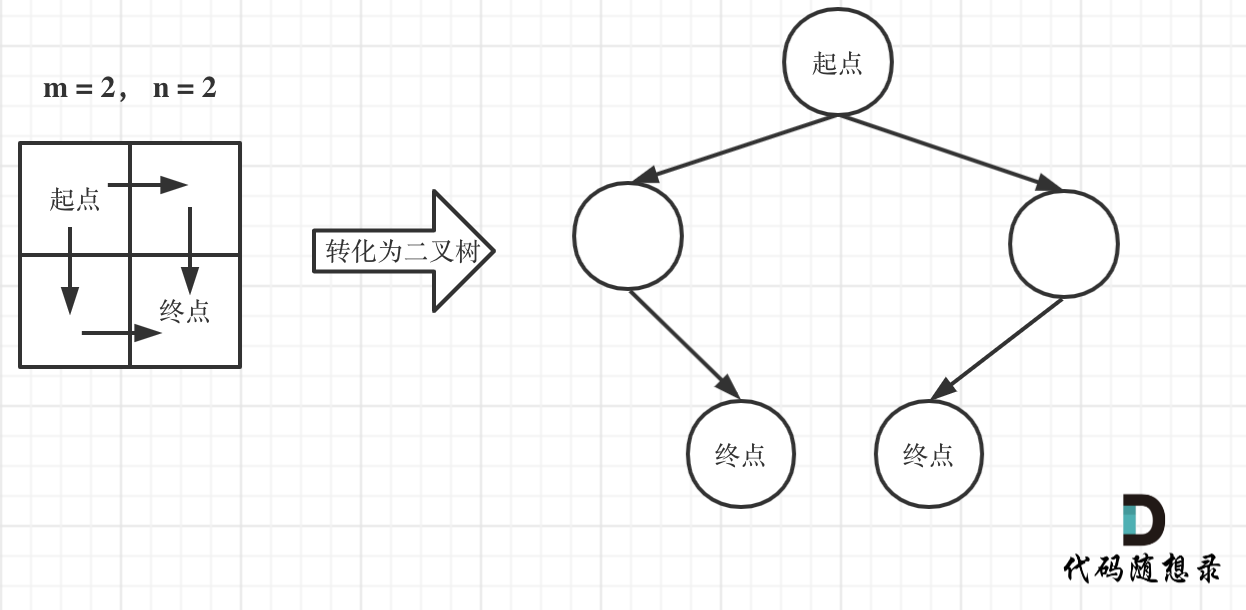
|
||||
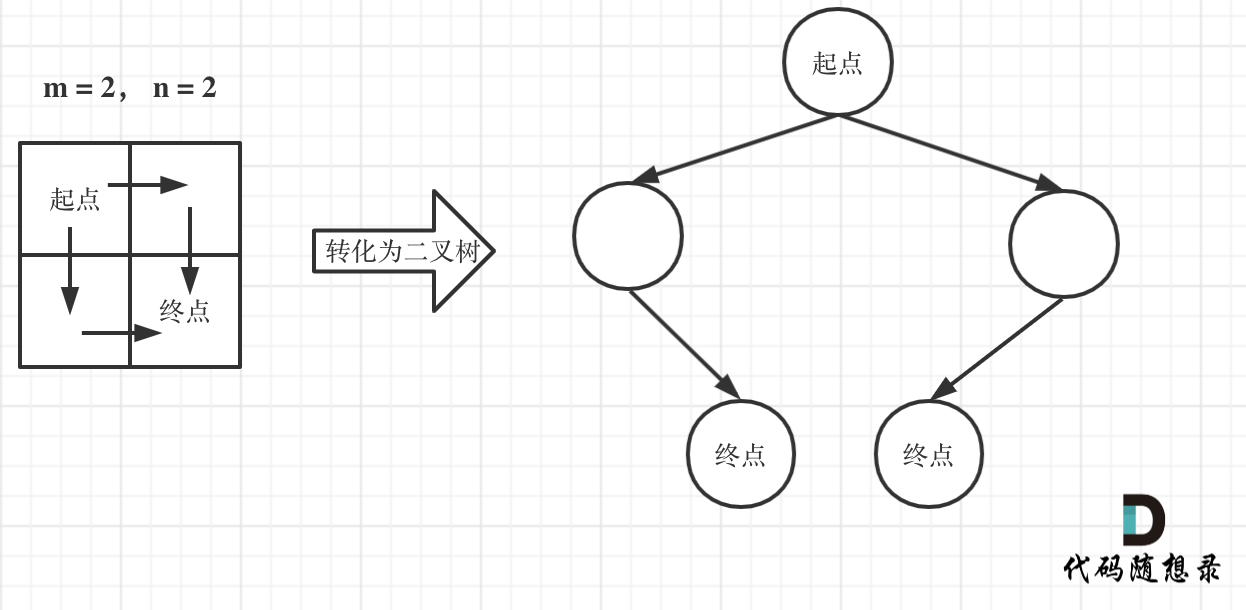
|
||||
|
||||
此时问题就可以转化为求二叉树叶子节点的个数,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -126,7 +133,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
|
|||
|
||||
如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
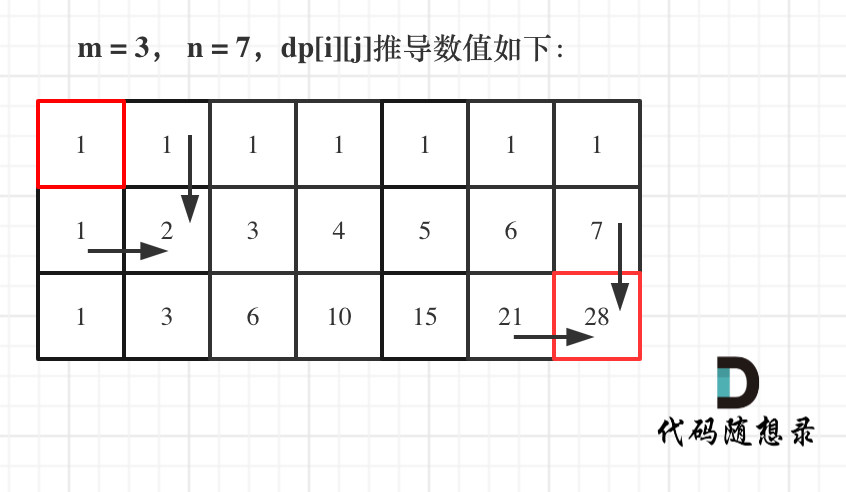
|
||||
|
||||
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -175,7 +182,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在这个图中,可以看出一共m,n的话,无论怎么走,走到终点都需要 m + n - 2 步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
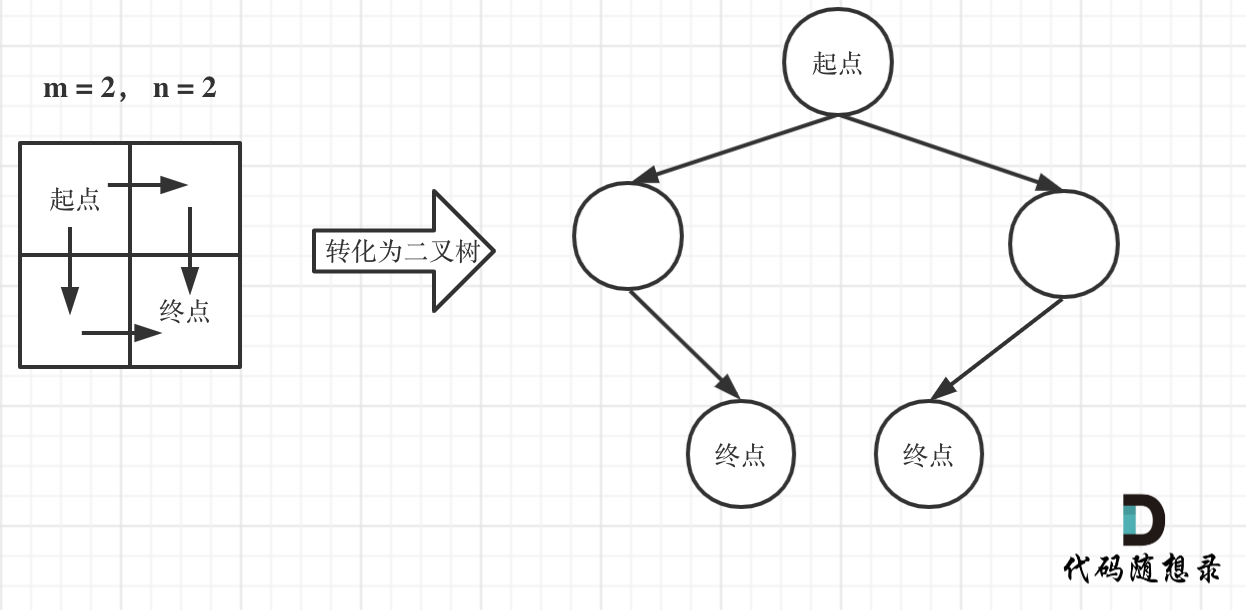
|
||||
|
||||
在这m + n - 2 步中,一定有 m - 1 步是要向下走的,不用管什么时候向下走。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,7 +192,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
那么答案,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
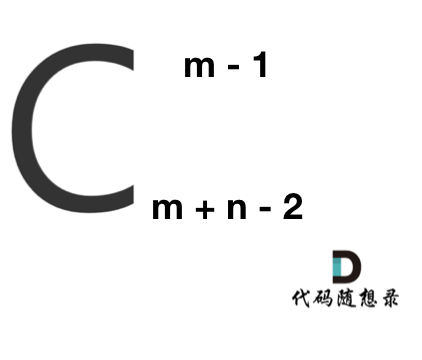
|
||||
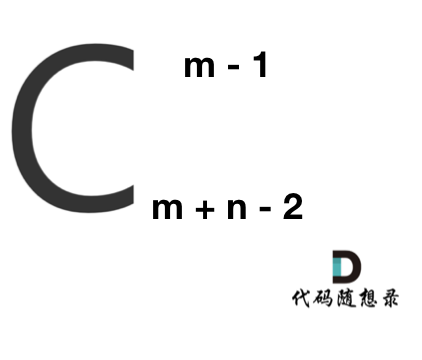
|
||||
|
||||
**求组合的时候,要防止两个int相乘溢出!** 所以不能把算式的分子都算出来,分母都算出来再做除法。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,7 +252,8 @@ public:
|
|||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 1. 确定dp数组下标含义 dp[i][j] 到每一个坐标可能的路径种类
|
||||
|
|
@ -278,7 +286,8 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution: # 动态规划
|
||||
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -289,7 +298,8 @@ class Solution: # 动态规划
|
|||
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
|
||||
dp := make([][]int, m)
|
||||
|
|
@ -309,19 +319,20 @@ func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
|
||||
const dp = Array(m).fill().map(item => Array(n))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||||
dp[0][i] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
|
||||
|
|
@ -330,7 +341,9 @@ var uniquePaths = function(m, n) {
|
|||
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>版本二:直接将dp数值值初始化为1
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {number} m
|
||||
|
|
@ -414,9 +427,9 @@ int **initDP(int m, int n) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//从0,0到i,0只有一种走法,所以dp[i][0]都是1,同理dp[0][j]也是1
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < m; ++i)
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < m; ++i)
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1;
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
|
||||
dp[0][j] = 1;
|
||||
return dp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -440,6 +453,7 @@ int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
滚动数组解法:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
|
||||
int i, j;
|
||||
|
|
@ -455,7 +469,7 @@ int uniquePaths(int m, int n){
|
|||
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dp[n - 1];
|
||||
return dp[n - 1];
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 63. 不同路径 II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths-ii/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,32 +16,33 @@
|
|||
|
||||
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
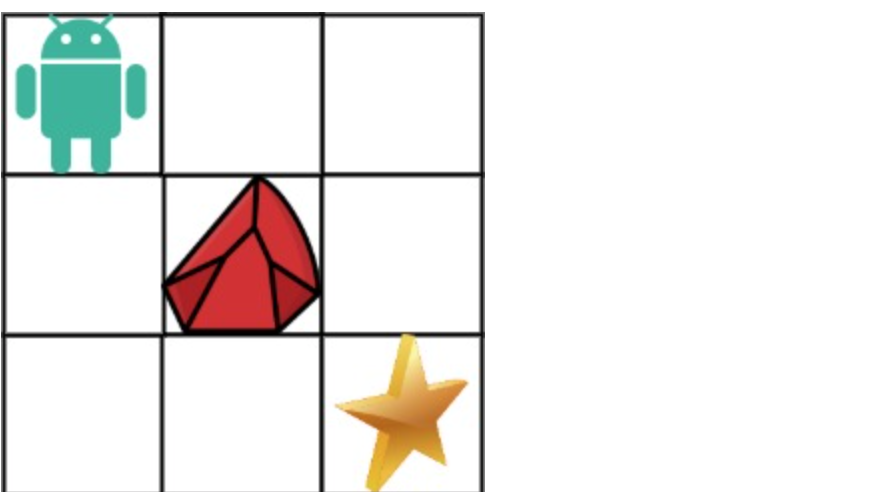
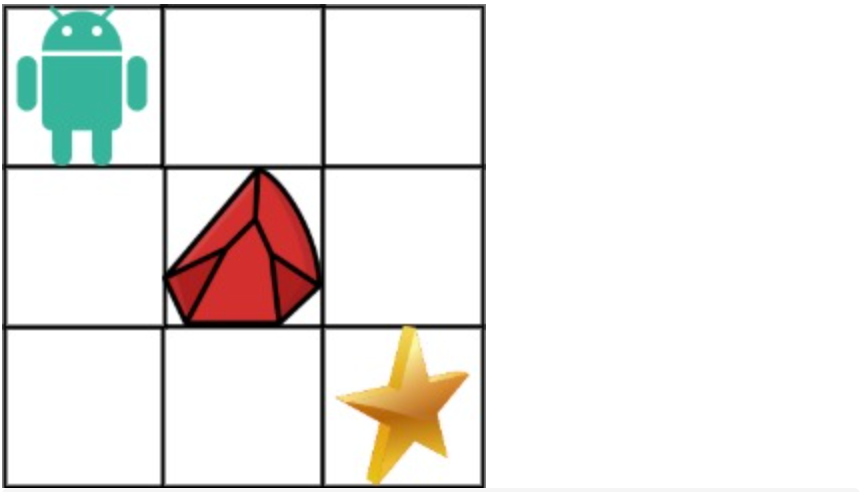
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
|
||||
* 输出:2
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
解释:
|
||||
* 3x3 网格的正中间有一个障碍物。
|
||||
* 从左上角到右下角一共有 2 条不同的路径:
|
||||
1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下
|
||||
2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
|
||||
1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下
|
||||
2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,1],[0,0]]
|
||||
* 输出:1
|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
* m == obstacleGrid.length
|
||||
* n == obstacleGrid[i].length
|
||||
|
||||
* m == obstacleGrid.length
|
||||
* n == obstacleGrid[i].length
|
||||
* 1 <= m, n <= 100
|
||||
* obstacleGrid[i][j] 为 0 或 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -92,7 +95,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[0][j] = 1;
|
|||
|
||||
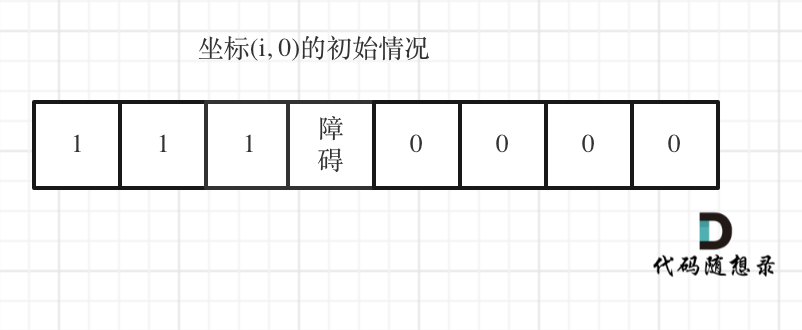
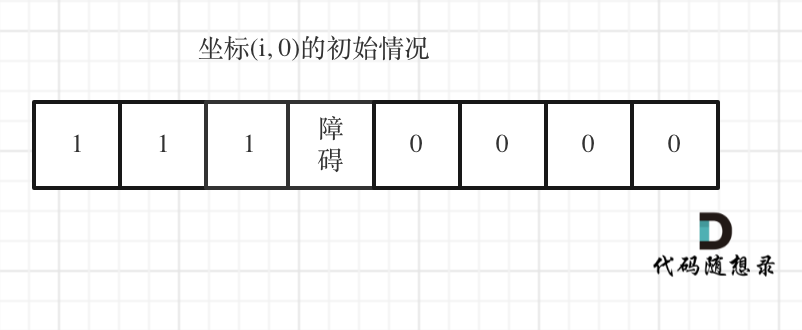
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
下标(0, j)的初始化情况同理。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -126,13 +129,13 @@ for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
拿示例1来举例如题:
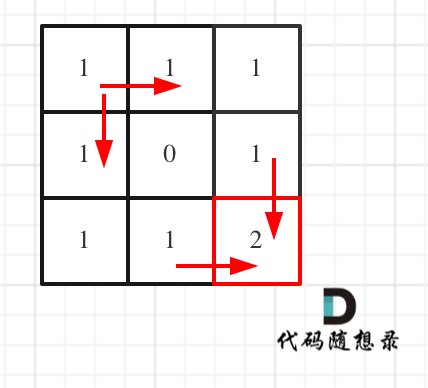
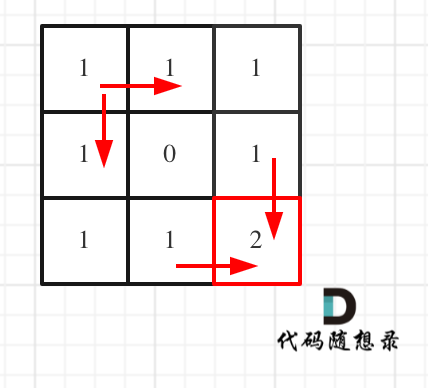
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
对应的dp table 如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果这个图看不同,建议在理解一下递归公式,然后照着文章中说的遍历顺序,自己推导一下!
|
||||
如果这个图看不同,建议在理解一下递归公式,然后照着文章中说的遍历顺序,自己推导一下!
|
||||
|
||||
动规五部分分析完毕,对应C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,6 +166,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
同样我们给出空间优化版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
|
@ -208,7 +212,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -246,11 +250,11 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
|
||||
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
|
||||
int[] dp = new int[n];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n && obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0; j++) {
|
||||
dp[j] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
|
||||
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -316,7 +320,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
if obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1:
|
||||
break
|
||||
curr[j] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(1, m): # 从第二行开始
|
||||
for j in range(n): # 从第一列开始,因为第一列可能有障碍物
|
||||
# 有障碍物处无法通行,状态就设成0
|
||||
|
|
@ -328,7 +332,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
curr[j] = curr[j] + curr[j - 1]
|
||||
# 隐含的状态更新
|
||||
# dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return curr[n - 1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -369,26 +373,27 @@ func uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var uniquePathsWithObstacles = function(obstacleGrid) {
|
||||
const m = obstacleGrid.length
|
||||
const n = obstacleGrid[0].length
|
||||
const dp = Array(m).fill().map(item => Array(n).fill(0))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < m && obstacleGrid[i][0] === 0; ++i) {
|
||||
dp[i][0] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 0; i < n && obstacleGrid[0][i] === 0; ++i) {
|
||||
dp[0][i] = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
|
||||
for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
|
||||
dp[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i][j] === 1 ? 0 : dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -545,9 +550,10 @@ int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int** obstacleGrid, int obstacleGridSize, int* obst
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
空间优化版本:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int** obstacleGrid, int obstacleGridSize, int* obstacleGridColSize){
|
||||
int m = obstacleGridSize;
|
||||
int m = obstacleGridSize;
|
||||
int n = obstacleGridColSize[0];
|
||||
int *dp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
|
||||
int i, j;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -102,7 +102,8 @@ dp[i]: 爬到第i层楼梯,有dp[i]种方法
|
|||
|
||||
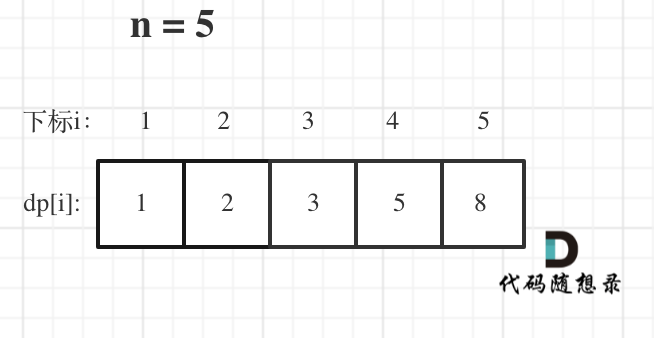
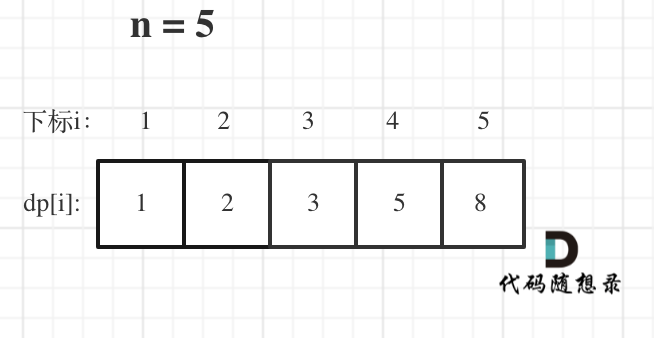
举例当n为5的时候,dp table(dp数组)应该是这样的
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果代码出问题了,就把dp table 打印出来,看看究竟是不是和自己推导的一样。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
|
|||
|
||||
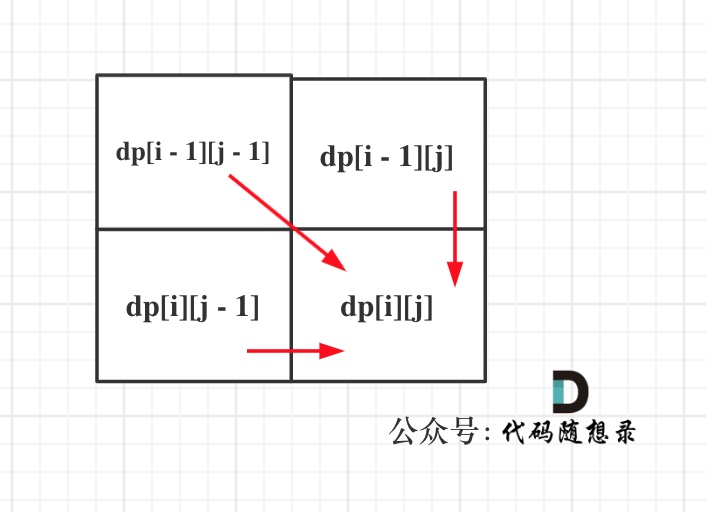
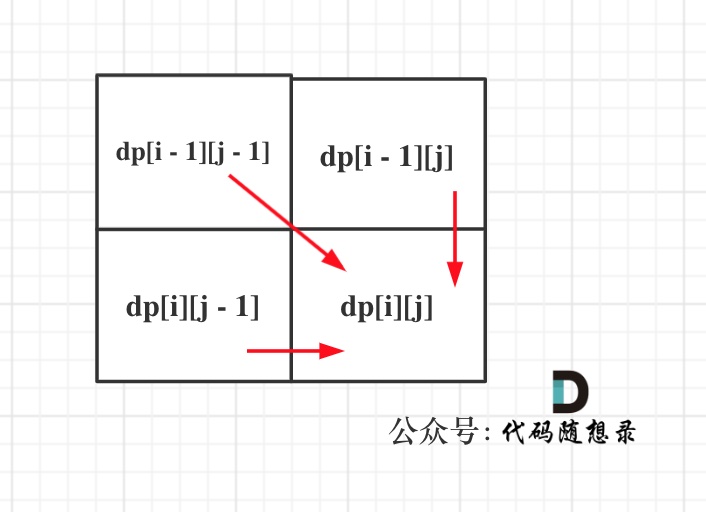
可以看出dp[i][j]是依赖左方,上方和左上方元素的,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以在dp矩阵中一定是从左到右从上到下去遍历。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -193,7 +193,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= word1.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
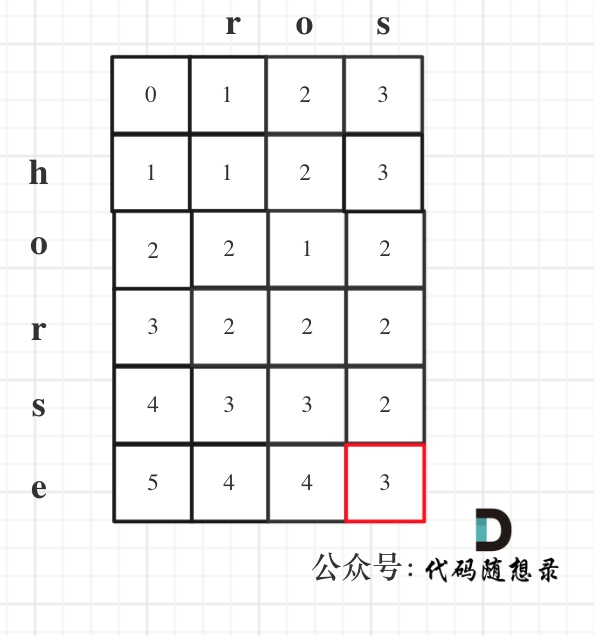
以示例1为例,输入:`word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"`为例,dp矩阵状态图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
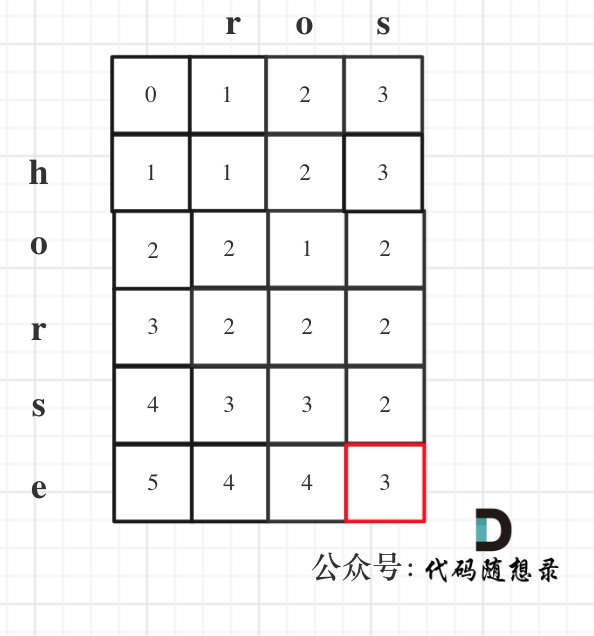
|
||||
|
||||
以上动规五部分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -7,31 +8,32 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 第77题. 组合
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/ )
|
||||
|
||||
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
|
||||
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回 1 ... n 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
输入: n = 4, k = 2
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[2,4],
|
||||
[3,4],
|
||||
[2,3],
|
||||
[1,2],
|
||||
[1,3],
|
||||
[1,4],
|
||||
]
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
输入: n = 4, k = 2
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
[
|
||||
[2,4],
|
||||
[3,4],
|
||||
[2,3],
|
||||
[1,2],
|
||||
[1,3],
|
||||
[1,4],
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[带你学透回溯算法-组合问题(对应力扣题目:77.组合)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv),[组合问题的剪枝操作](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wi4y157er),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本题是回溯法的经典题目。
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,6 +41,7 @@
|
|||
直接的解法当然是使用for循环,例如示例中k为2,很容易想到 用两个for循环,这样就可以输出 和示例中一样的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
int n = 4;
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,7 +69,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
**此时就会发现虽然想暴力搜索,但是用for循环嵌套连暴力都写不出来!**
|
||||
|
||||
咋整?
|
||||
咋整?
|
||||
|
||||
回溯搜索法来了,虽然回溯法也是暴力,但至少能写出来,不像for循环嵌套k层让人绝望。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -86,7 +89,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
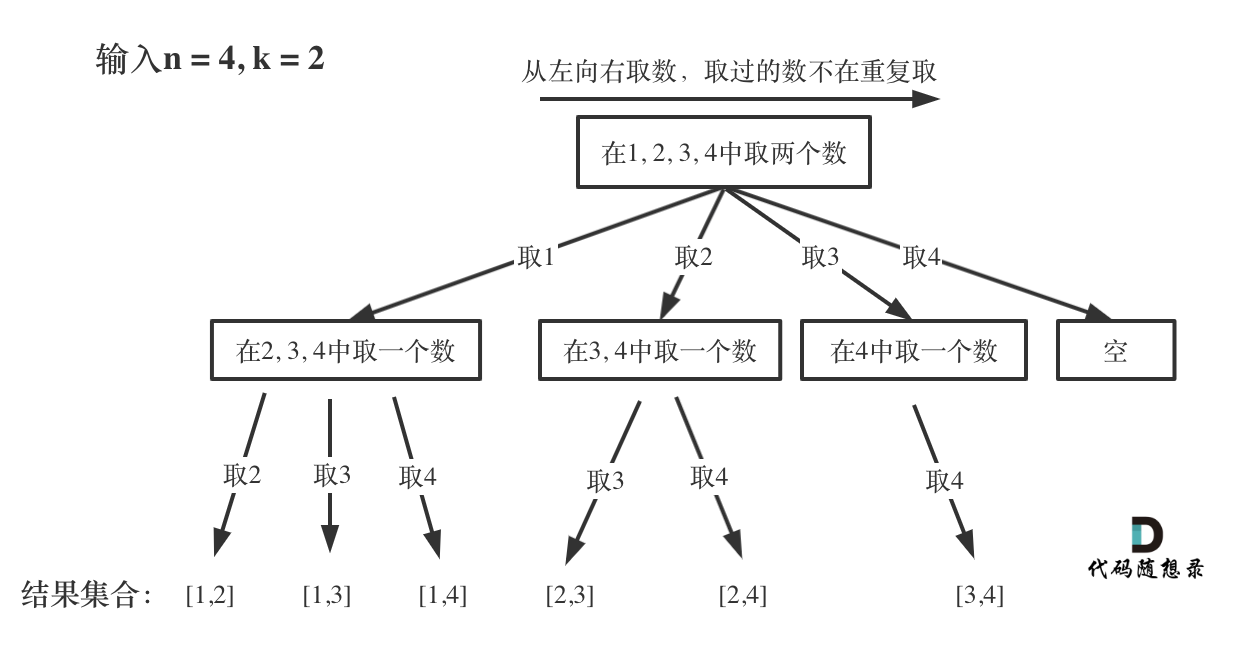
那么我把组合问题抽象为如下树形结构:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出这棵树,一开始集合是 1,2,3,4, 从左向右取数,取过的数,不再重复取。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,7 +97,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
**每次从集合中选取元素,可选择的范围随着选择的进行而收缩,调整可选择的范围**。
|
||||
|
||||
**图中可以发现n相当于树的宽度,k相当于树的深度**。
|
||||
**图中可以发现n相当于树的宽度,k相当于树的深度**。
|
||||
|
||||
那么如何在这个树上遍历,然后收集到我们要的结果集呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,7 +110,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
## 回溯法三部曲
|
||||
|
||||
* 递归函数的返回值以及参数
|
||||
* 递归函数的返回值以及参数
|
||||
|
||||
在这里要定义两个全局变量,一个用来存放符合条件单一结果,一个用来存放符合条件结果的集合。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,25 +127,25 @@ vector<int> path; // 用来存放符合条件结果
|
|||
|
||||
然后还需要一个参数,为int型变量startIndex,这个参数用来记录本层递归的中,集合从哪里开始遍历(集合就是[1,...,n] )。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么要有这个startIndex呢?
|
||||
为什么要有这个startIndex呢?
|
||||
|
||||
**建议在[77.组合视频讲解](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ti4y1L7cv)中,07:36的时候开始听,startIndex 就是防止出现重复的组合**。
|
||||
|
||||
从下图中红线部分可以看出,在集合[1,2,3,4]取1之后,下一层递归,就要在[2,3,4]中取数了,那么下一层递归如何知道从[2,3,4]中取数呢,靠的就是startIndex。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
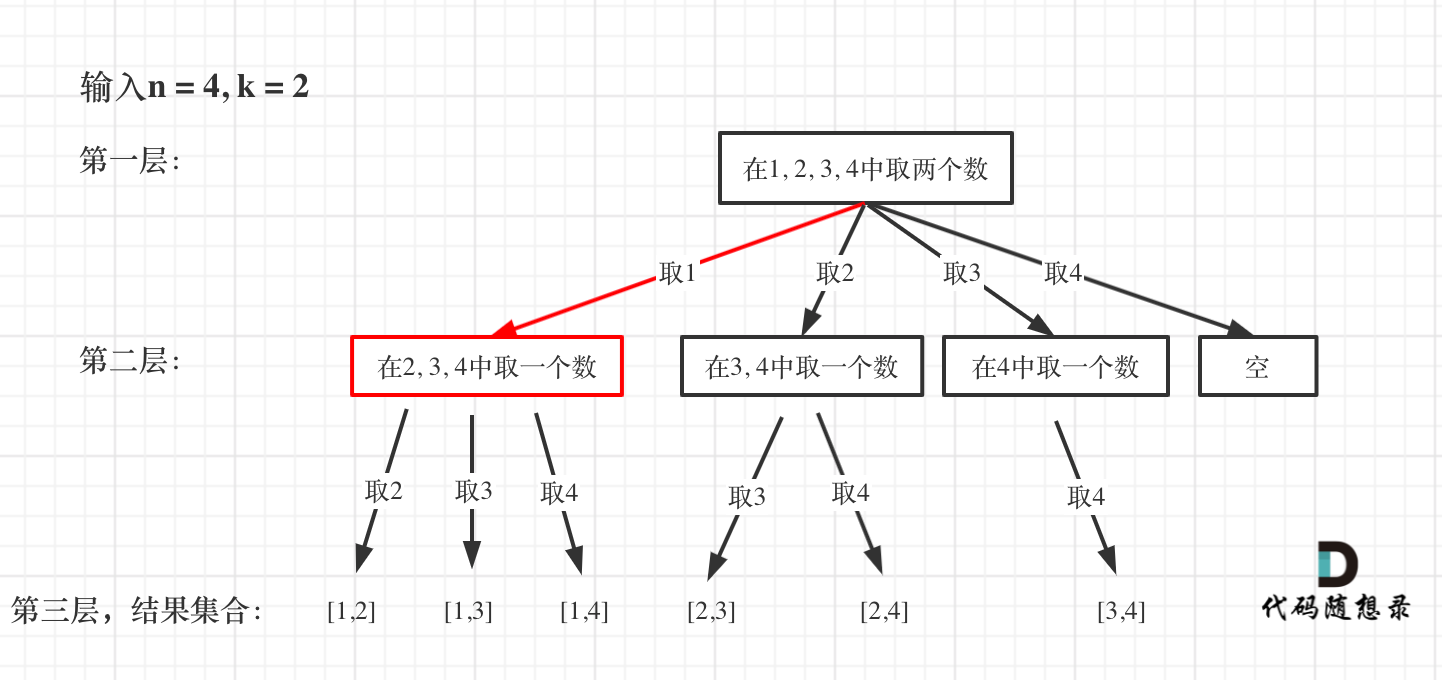
|
||||
|
||||
所以需要startIndex来记录下一层递归,搜索的起始位置。
|
||||
所以需要startIndex来记录下一层递归,搜索的起始位置。
|
||||
|
||||
那么整体代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
vector<vector<int>> result; // 存放符合条件结果的集合
|
||||
vector<int> path; // 用来存放符合条件单一结果
|
||||
void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex)
|
||||
void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 回溯函数终止条件
|
||||
* 回溯函数终止条件
|
||||
|
||||
什么时候到达所谓的叶子节点了呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,7 +153,7 @@ path这个数组的大小如果达到k,说明我们找到了一个子集大小
|
|||
|
||||
如图红色部分:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
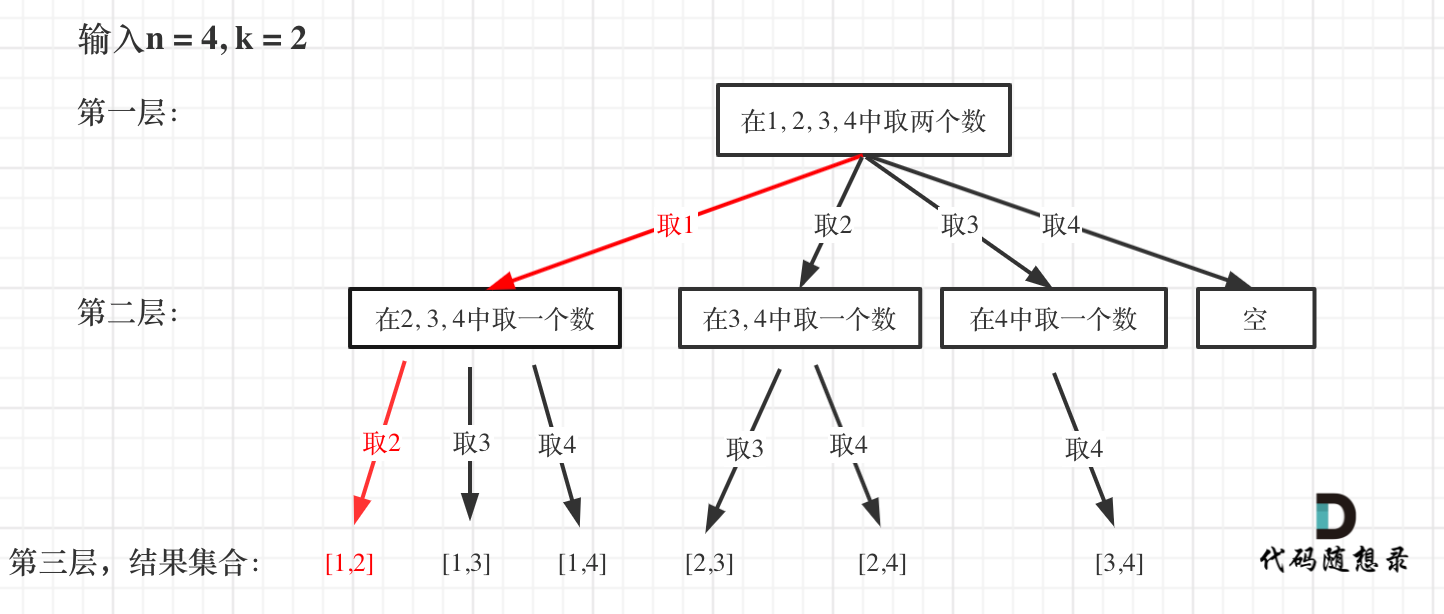
|
||||
|
||||
此时用result二维数组,把path保存起来,并终止本层递归。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,21 +166,21 @@ if (path.size() == k) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 单层搜索的过程
|
||||
* 单层搜索的过程
|
||||
|
||||
回溯法的搜索过程就是一个树型结构的遍历过程,在如下图中,可以看出for循环用来横向遍历,递归的过程是纵向遍历。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
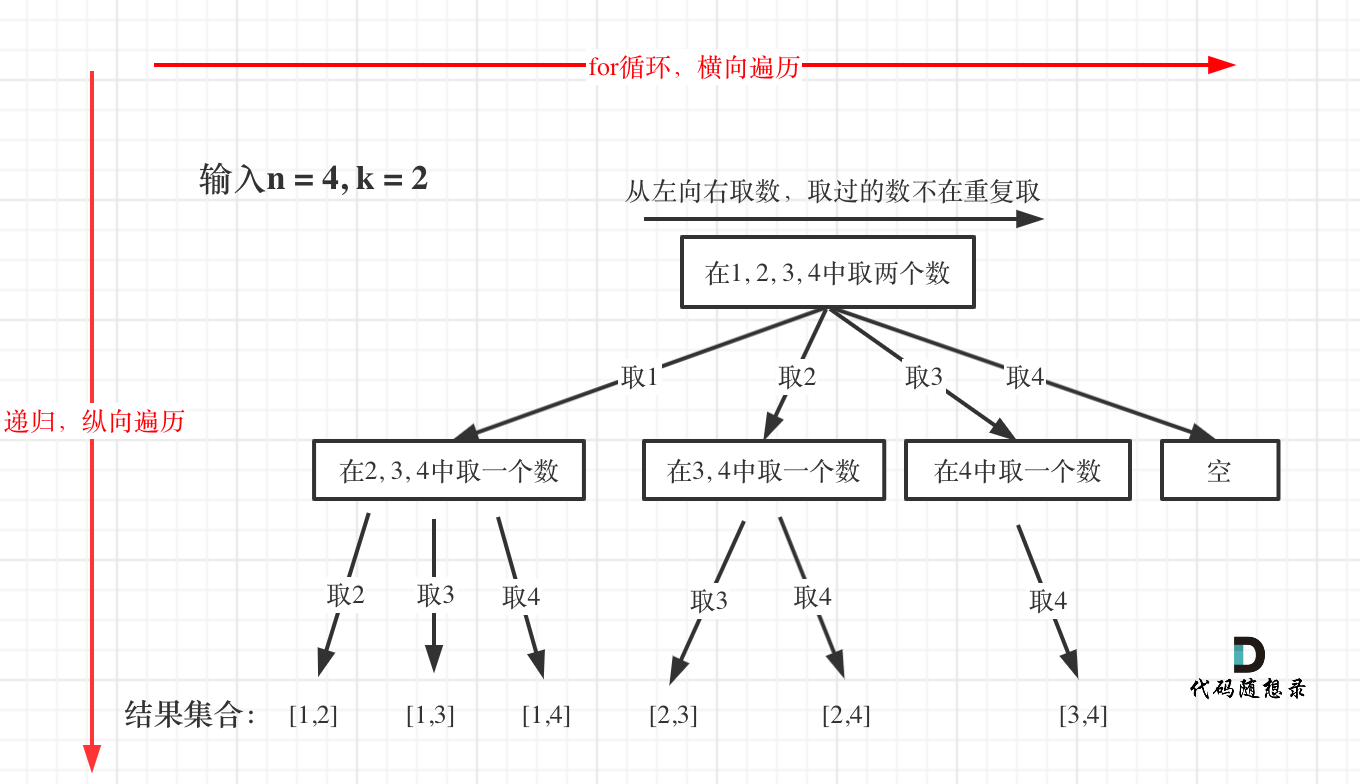
|
||||
|
||||
如此我们才遍历完图中的这棵树。
|
||||
|
||||
for循环每次从startIndex开始遍历,然后用path保存取到的节点i。
|
||||
for循环每次从startIndex开始遍历,然后用path保存取到的节点i。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) { // 控制树的横向遍历
|
||||
path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
|
||||
path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1); // 递归:控制树的纵向遍历,注意下一层搜索要从i+1开始
|
||||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销处理的节点
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -201,7 +204,7 @@ private:
|
|||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
|
||||
path.push_back(i); // 处理节点
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1); // 递归
|
||||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销处理的节点
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -216,9 +219,10 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还记得我们在[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)中给出的回溯法模板么?
|
||||
还记得我们在[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/回溯算法理论基础.html)中给出的回溯法模板么?
|
||||
|
||||
如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
void backtracking(参数) {
|
||||
if (终止条件) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -234,15 +238,15 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**对比一下本题的代码,是不是发现有点像!** 所以有了这个模板,就有解题的大体方向,不至于毫无头绪。
|
||||
**对比一下本题的代码,是不是发现有点像!** 所以有了这个模板,就有解题的大体方向,不至于毫无头绪。
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
组合问题是回溯法解决的经典问题,我们开始的时候给大家列举一个很形象的例子,就是n为100,k为50的话,直接想法就需要50层for循环。
|
||||
|
||||
从而引出了回溯法就是解决这种k层for循环嵌套的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
然后进一步把回溯法的搜索过程抽象为树形结构,可以直观的看出搜索的过程。
|
||||
然后进一步把回溯法的搜索过程抽象为树形结构,可以直观的看出搜索的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
接着用回溯法三部曲,逐步分析了函数参数、终止条件和单层搜索的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -266,7 +270,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
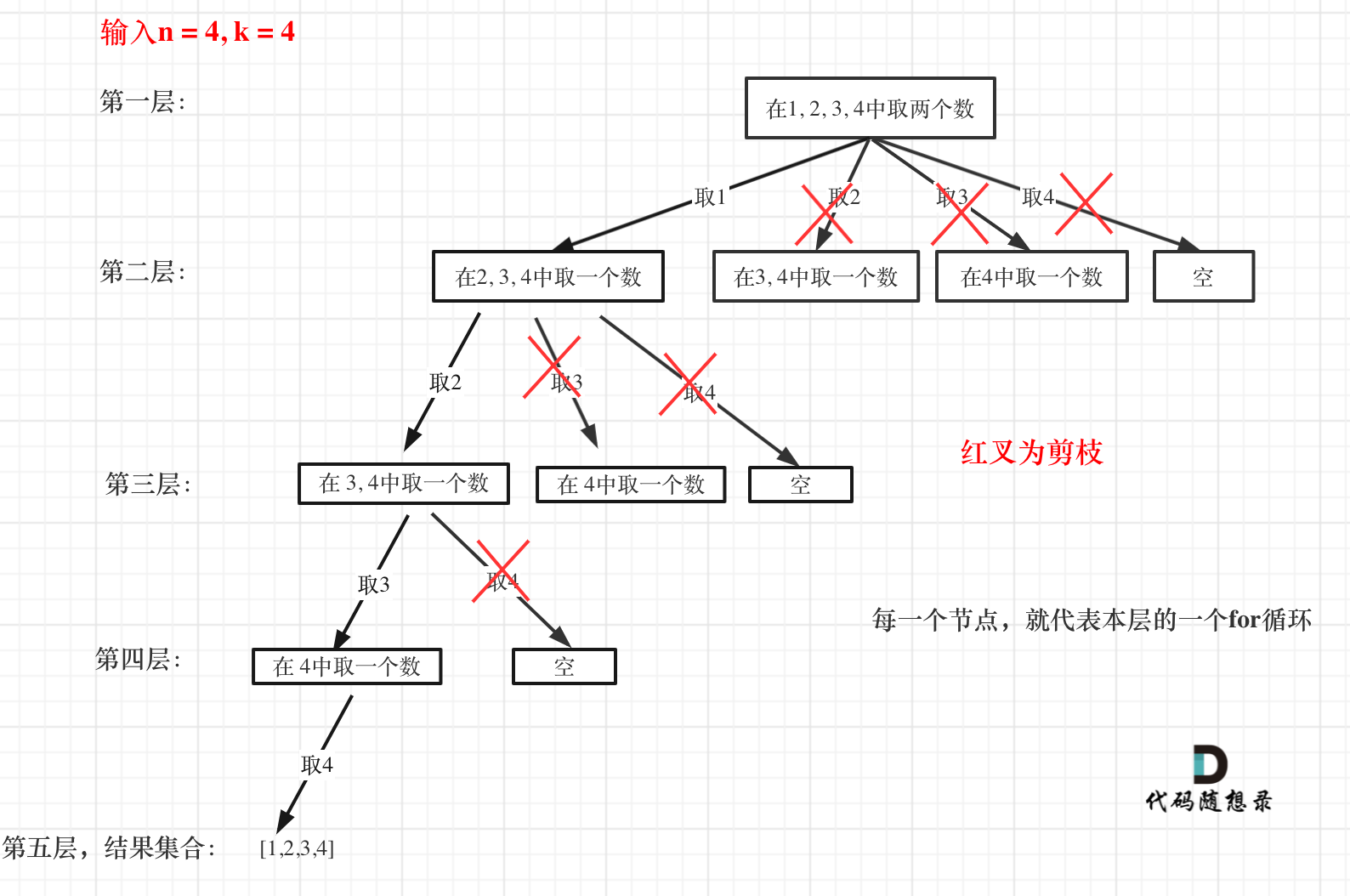
|
||||
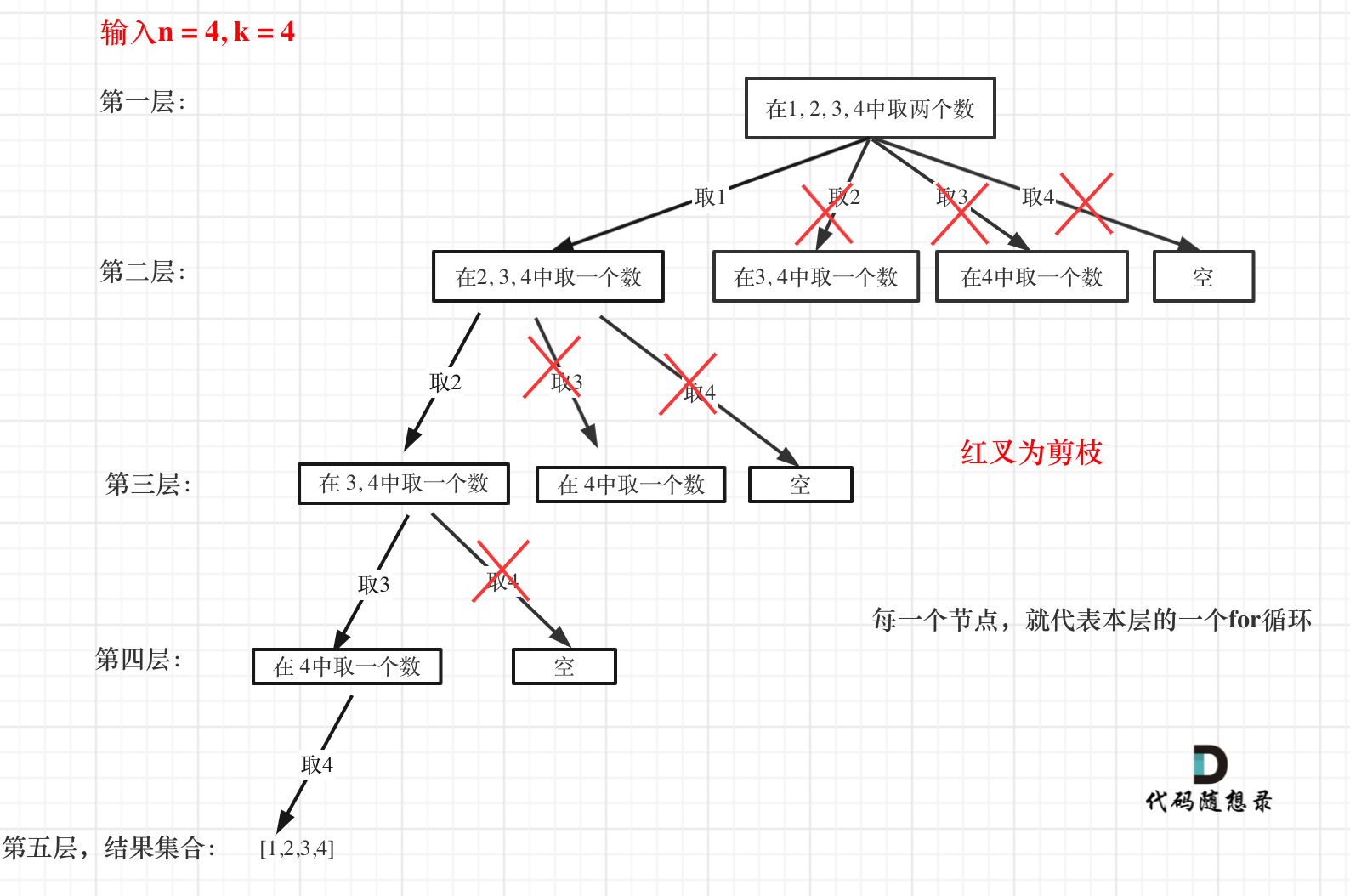
|
||||
|
||||
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -275,6 +279,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
**如果for循环选择的起始位置之后的元素个数 已经不足 我们需要的元素个数了,那么就没有必要搜索了**。
|
||||
|
||||
注意代码中i,就是for循环里选择的起始位置。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -342,6 +347,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
|
|
@ -370,7 +376,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution(object):
|
||||
|
|
@ -417,6 +423,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||||
|
|
@ -434,7 +441,8 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
var (
|
||||
path []int
|
||||
|
|
@ -452,7 +460,7 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
|
|||
tmp := make([]int, k)
|
||||
copy(tmp, path)
|
||||
res = append(res, tmp)
|
||||
return
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := start; i <= n; i++ { // 从start开始,不往回走,避免出现重复组合
|
||||
if n - i + 1 < k - len(path) { // 剪枝
|
||||
|
|
@ -465,9 +473,10 @@ func dfs(n int, k int, start int) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### javascript
|
||||
### javascript
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
let result = []
|
||||
let path = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -536,6 +545,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
fn backtracking(result: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, n: i32, k: i32, start_index: i32) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -561,6 +571,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
|
|
@ -615,6 +626,7 @@ int** combine(int n, int k, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
剪枝:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
int pathTop;
|
||||
|
|
@ -701,13 +713,14 @@ func combine(_ n: Int, _ k: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
|||
### Scala
|
||||
|
||||
暴力:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable // 导包
|
||||
def combine(n: Int, k: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||||
var result = mutable.ListBuffer[List[Int]]() // 存放结果集
|
||||
var path = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]() //存放符合条件的结果
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def backtracking(n: Int, k: Int, startIndex: Int): Unit = {
|
||||
if (path.size == k) {
|
||||
// 如果path的size == k就达到题目要求,添加到结果集,并返回
|
||||
|
|
@ -720,7 +733,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, 1) // 执行回溯
|
||||
result.toList // 最终返回result的List形式,return关键字可以省略
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -743,7 +756,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 剪枝优化
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
|
||||
for (i <- startIndex to (n - (k - path.size) + 1)) {
|
||||
path.append(i) // 先把数字添加进去
|
||||
backtracking(n, k, i + 1) // 进行下一步回溯
|
||||
path = path.take(path.size - 1) // 回溯完再删除掉刚刚添加的数字
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
这么说有点抽象,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
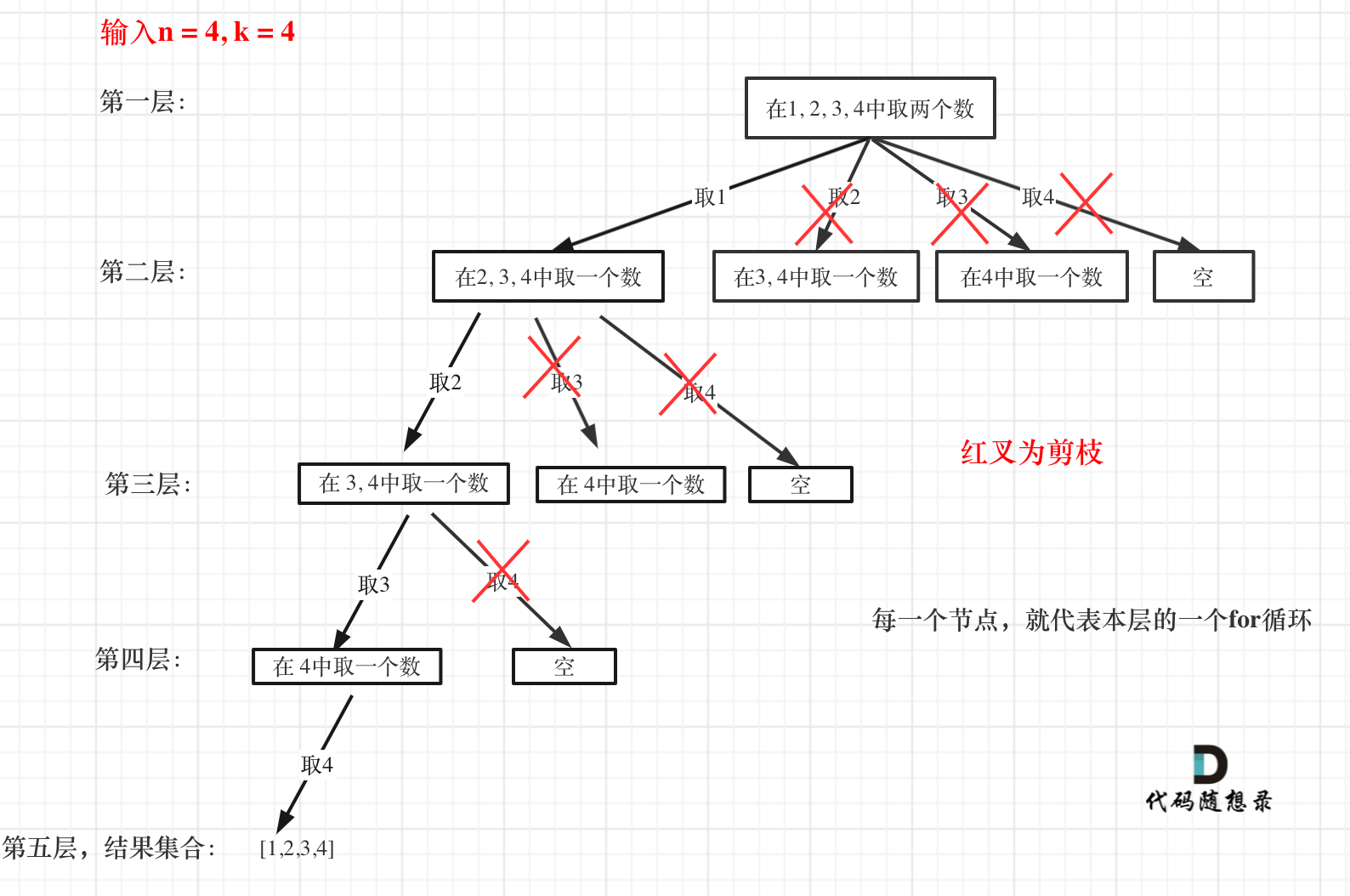
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
图中每一个节点(图中为矩形),就代表本层的一个for循环,那么每一层的for循环从第二个数开始遍历的话,都没有意义,都是无效遍历。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
以示例中nums = [1,2,3]为例把求子集抽象为树型结构,如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从图中红线部分,可以看出**遍历这个树的时候,把所有节点都记录下来,就是要求的子集集合**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ void backtracking(vector<int>& nums, int startIndex) {
|
|||
|
||||
从图中可以看出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
剩余集合为空的时候,就是叶子节点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
用示例中的[1, 2, 2] 来举例,如图所示: (**注意去重需要先对集合排序**)
|
||||
|
||||
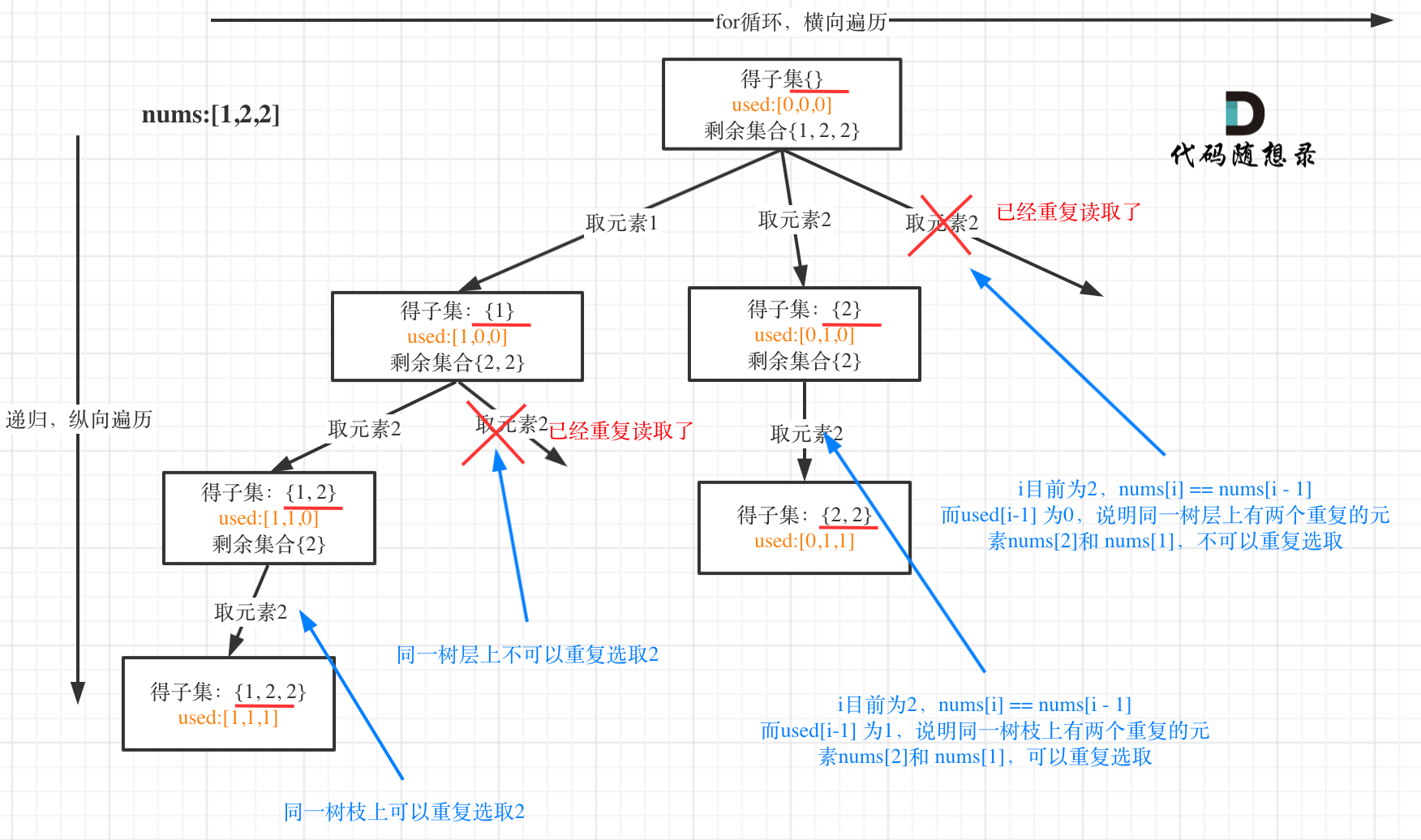
|
||||
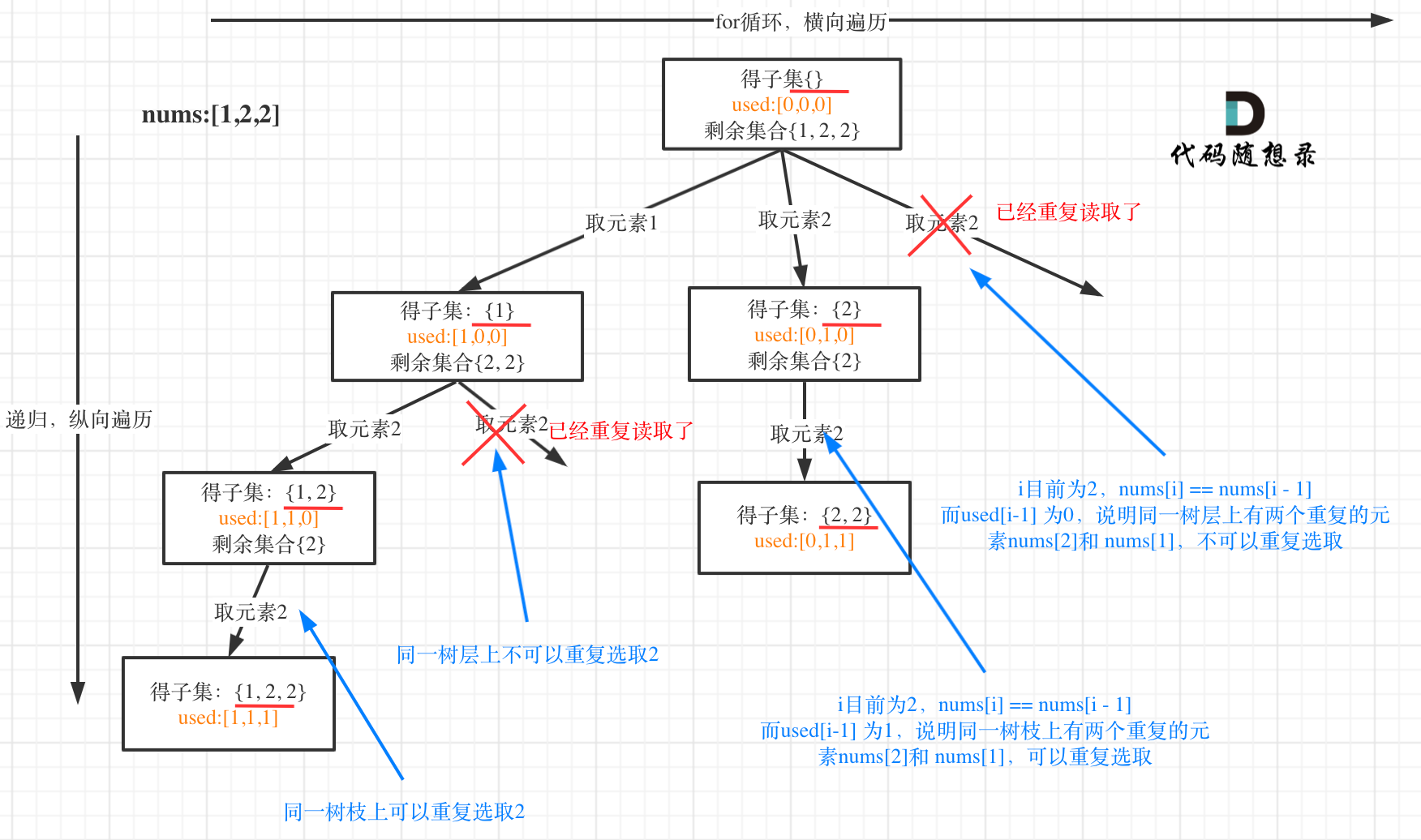
|
||||
|
||||
从图中可以看出,同一树层上重复取2 就要过滤掉,同一树枝上就可以重复取2,因为同一树枝上元素的集合才是唯一子集!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -59,7 +59,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
切割问题可以抽象为树型结构,如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
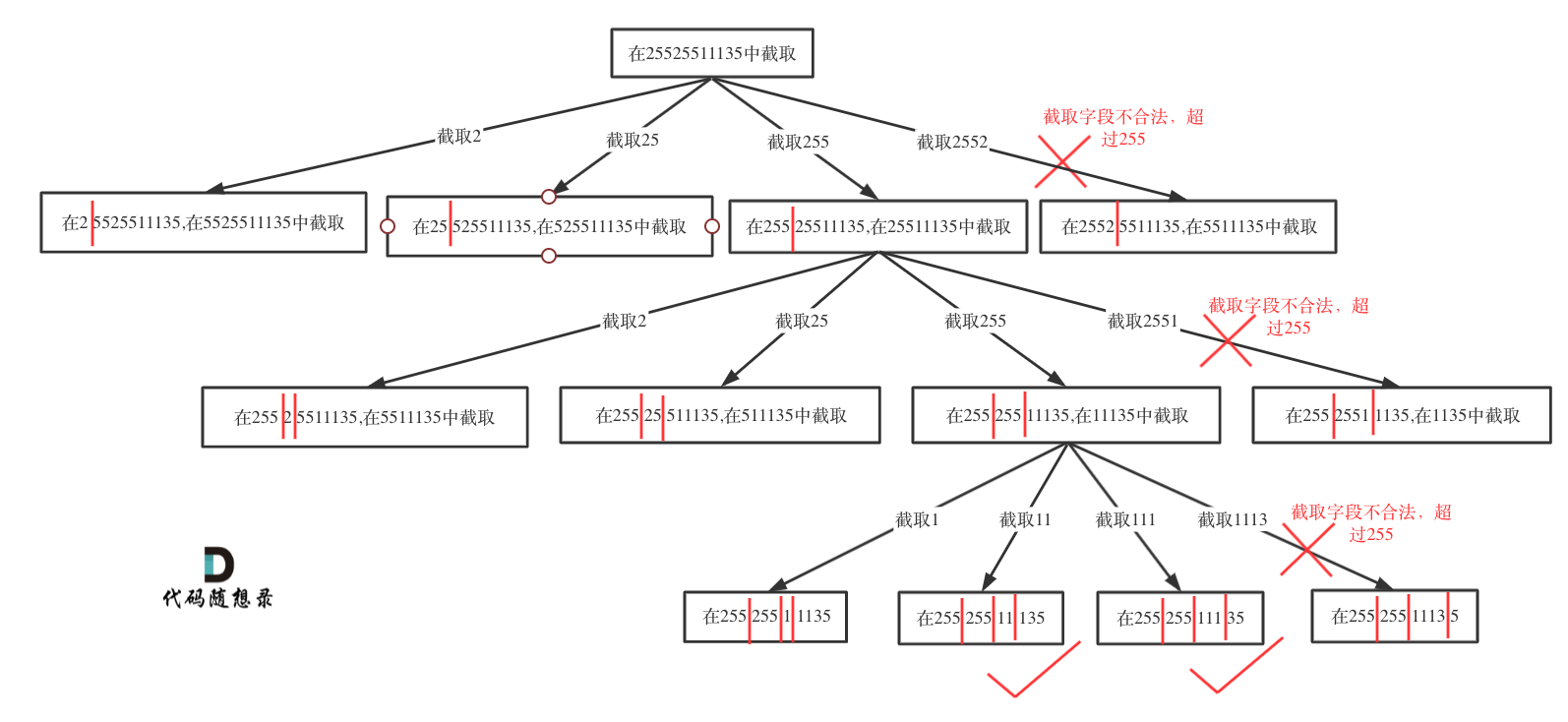
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 回溯三部曲
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,7 +111,8 @@ if (pointNum == 3) { // 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
|
|||
|
||||
如果不合法就结束本层循环,如图中剪掉的分支:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
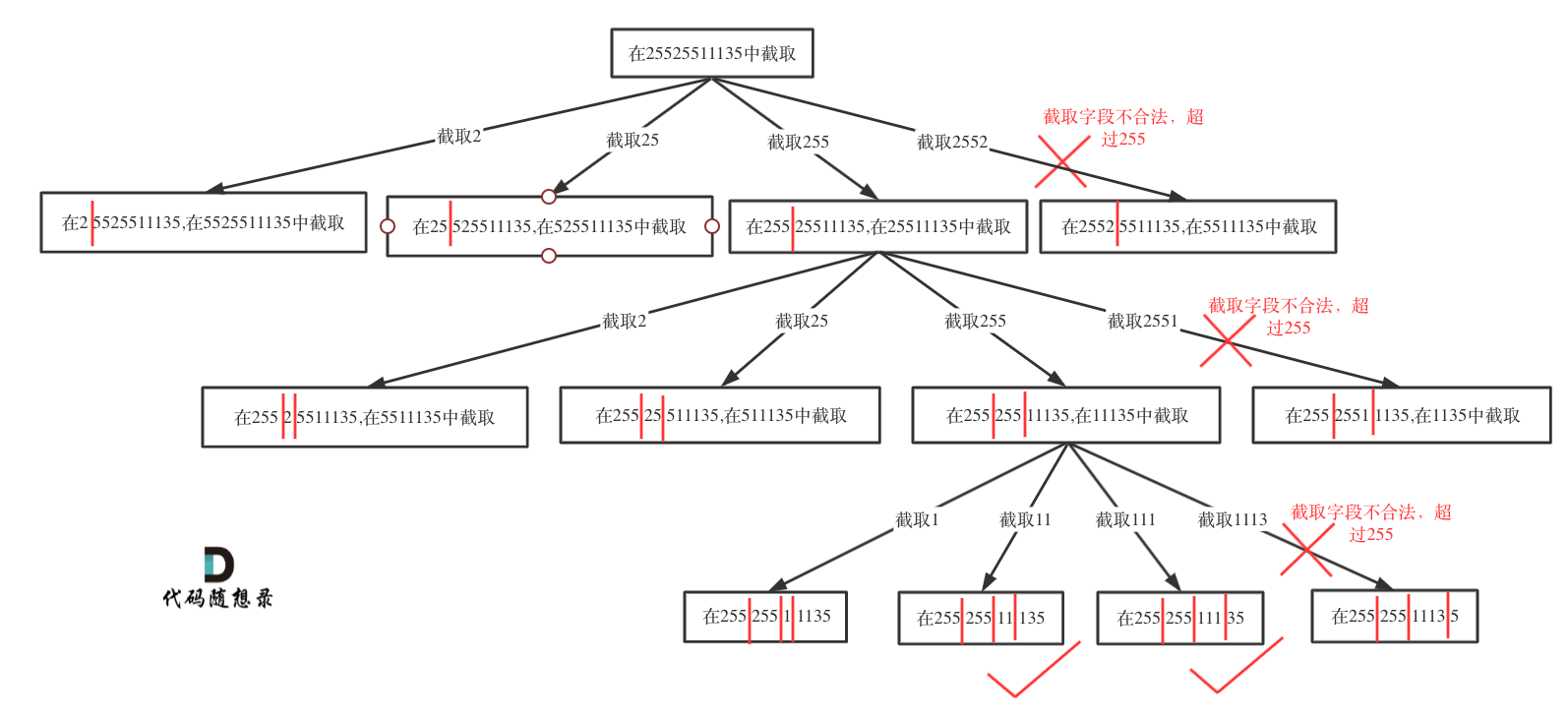
|
||||
|
||||
然后就是递归和回溯的过程:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 96.不同的二叉搜索树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,7 +14,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,11 +29,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
了解了二叉搜索树之后,我们应该先举几个例子,画画图,看看有没有什么规律,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
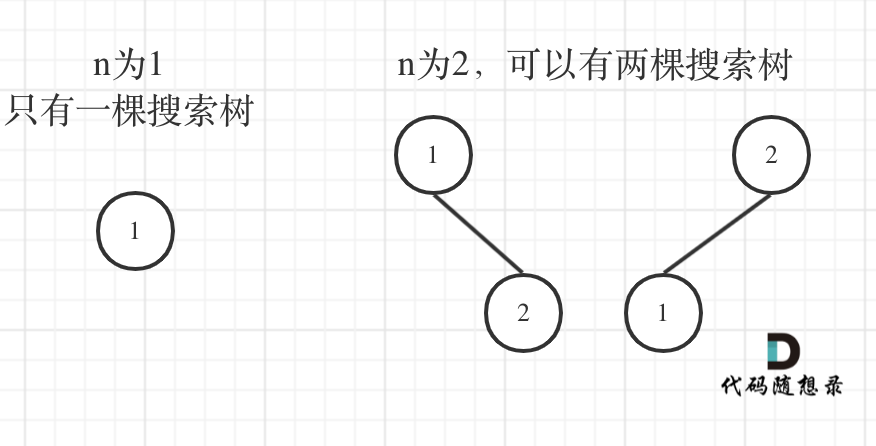
|
||||
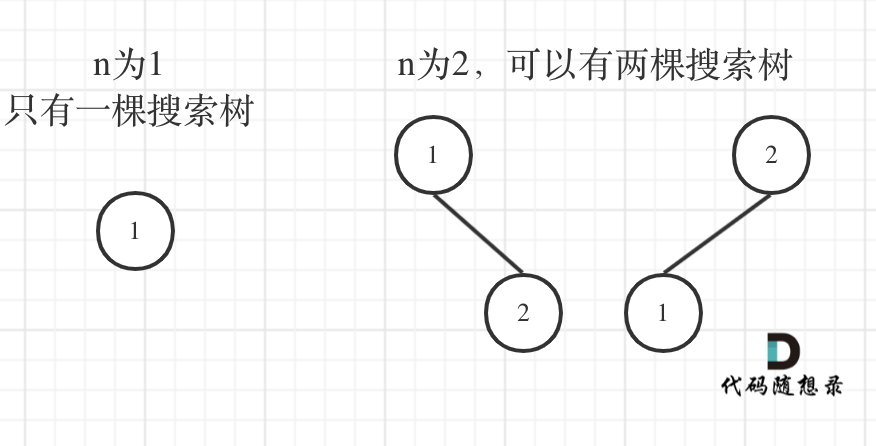
|
||||
|
||||
n为1的时候有一棵树,n为2有两棵树,这个是很直观的。
|
||||
|
||||
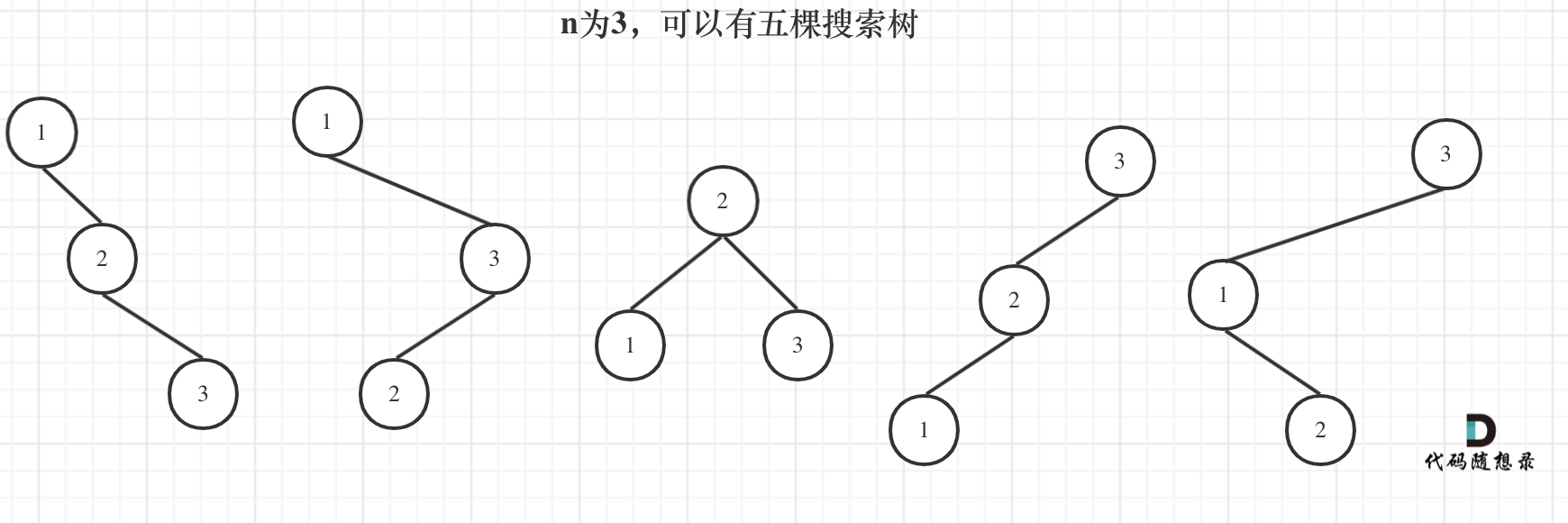
|
||||
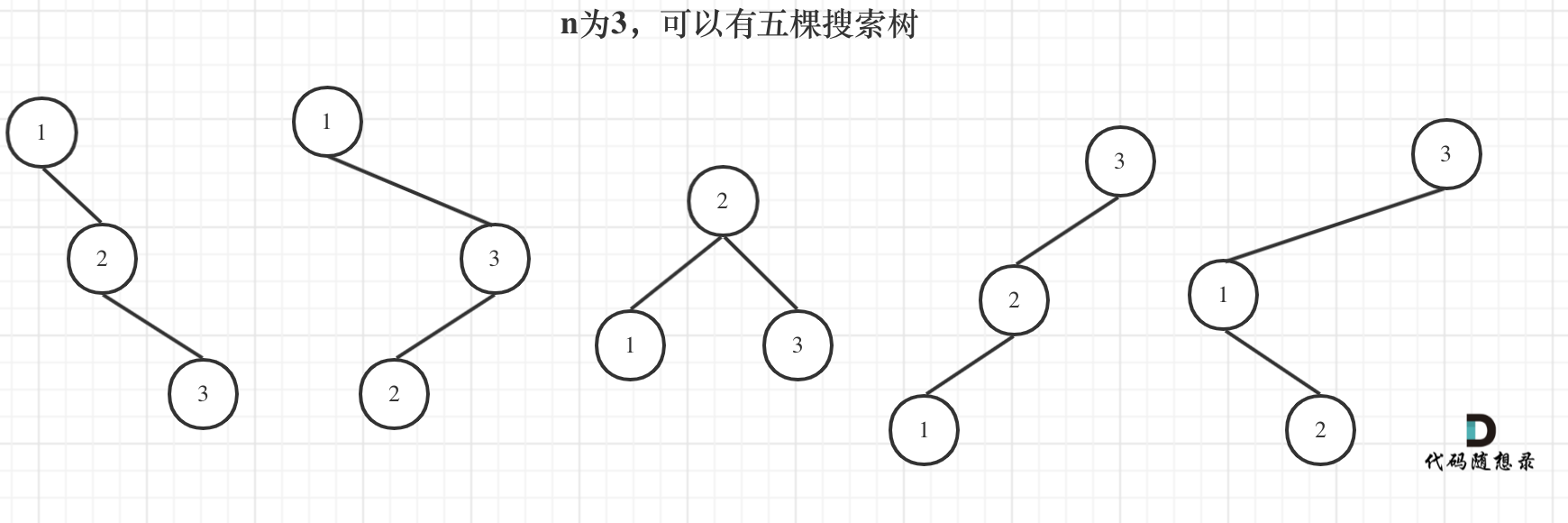
|
||||
|
||||
来看看n为3的时候,有哪几种情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +67,7 @@ dp[3],就是 元素1为头结点搜索树的数量 + 元素2为头结点搜索
|
|||
|
||||
如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
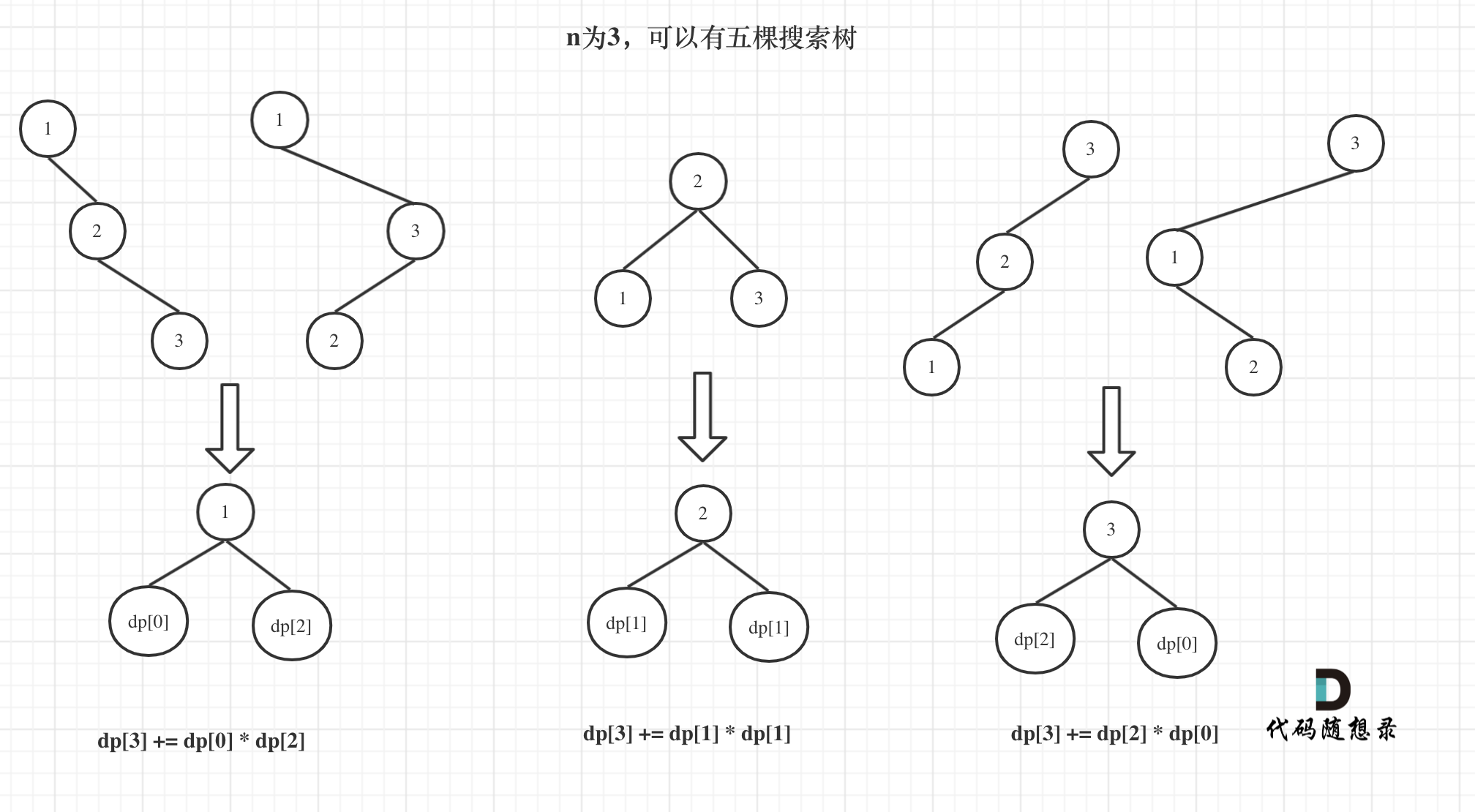
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
此时我们已经找到递推关系了,那么可以用动规五部曲再系统分析一遍。
|
||||
|
|
@ -118,7 +120,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
n为5时候的dp数组状态如图:
|
||||
|
||||
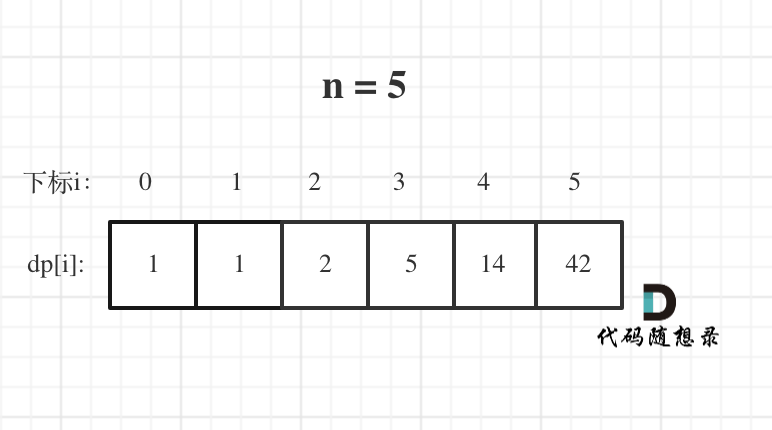
|
||||
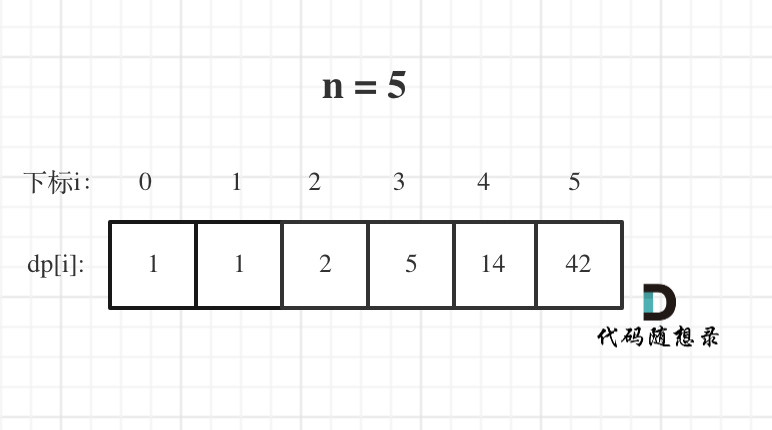
|
||||
|
||||
当然如果自己画图举例的话,基本举例到n为3就可以了,n为4的时候,画图已经比较麻烦了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -168,7 +170,8 @@ public:
|
|||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int numTrees(int n) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,6 +193,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def numTrees(self, n: int) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -202,6 +206,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func numTrees(n int)int{
|
||||
dp := make([]int, n+1)
|
||||
|
|
@ -216,6 +221,7 @@ func numTrees(n int)int{
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
const numTrees =(n) => {
|
||||
let dp = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
|
||||
|
|
@ -241,7 +247,7 @@ function numTrees(n: number): number {
|
|||
dp[0]: -1; 无意义;
|
||||
dp[1]: 1;
|
||||
...
|
||||
dp[i]: 2 * dp[i - 1] +
|
||||
dp[i]: 2 * dp[i - 1] +
|
||||
(dp[1] * dp[i - 2] + dp[2] * dp[i - 3] + ... + dp[i - 2] * dp[1]); 从1加到i-2
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const dp: number[] = [];
|
||||
|
|
@ -282,7 +288,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
int *initDP(int n) {
|
||||
int *dp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 1));
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
|
||||
for(i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
|
||||
dp[i] = 0;
|
||||
return dp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
|
|||
* 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
|
||||
* 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 视频讲解
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ if (root->val > root->left->val && root->val < root->right->val) {
|
|||
|
||||
例如: [10,5,15,null,null,6,20] 这个case:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
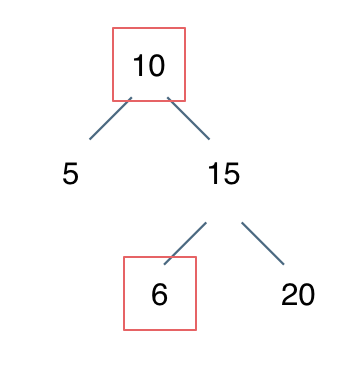
|
||||
|
||||
节点10大于左节点5,小于右节点15,但右子树里出现了一个6 这就不符合了!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
比较的是两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
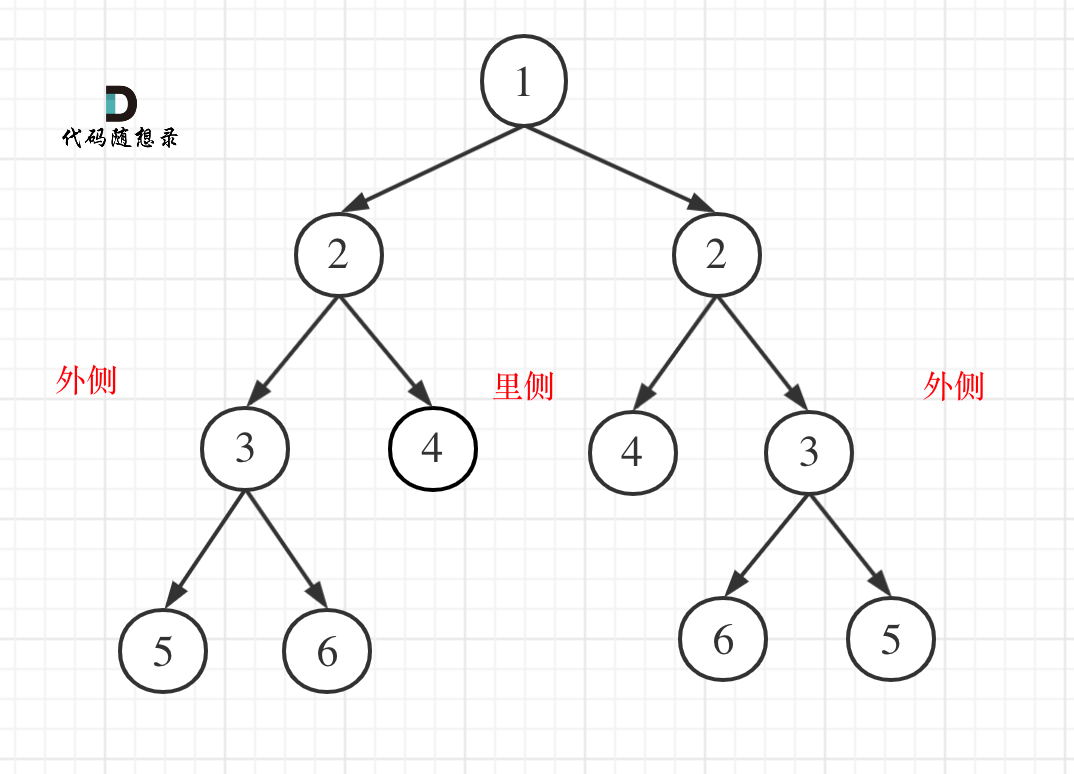
|
||||
|
||||
那么遍历的顺序应该是什么样的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 二叉树层序遍历登场!
|
||||
|
||||
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[讲透二叉树的层序遍历 | 广度优先搜索 | LeetCode:102.二叉树的层序遍历](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1GY4y1u7b2),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +37,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,6 +89,7 @@ public:
|
|||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
# 递归法
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,7 +111,7 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
java:
|
||||
java:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
|
|
@ -168,7 +171,6 @@ python3代码:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
"""二叉树层序遍历迭代解法"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -176,10 +178,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
results = []
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
que = deque([root])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while que:
|
||||
size = len(que)
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,6 +196,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
|
||||
return results
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 递归法
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
|
|
@ -209,7 +212,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return res
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
go:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/**
|
||||
|
|
@ -252,9 +255,9 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
queue := list.New()
|
||||
queue.PushBack(root)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
var tmpArr []int
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for queue.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
length := queue.Len() //保存当前层的长度,然后处理当前层(十分重要,防止添加下层元素影响判断层中元素的个数)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
|
||||
|
|
@ -270,7 +273,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
|||
res = append(res, tmpArr) //放入结果集
|
||||
tmpArr = []int{} //清空层的数据
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -279,7 +282,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
|||
*/
|
||||
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) (res [][]int) {
|
||||
if root == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
curLevel := []*TreeNode{root} // 存放当前层节点
|
||||
|
|
@ -318,7 +321,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
|
|||
while(queue.length !== 0) {
|
||||
// 记录当前层级节点数
|
||||
let length = queue.length;
|
||||
//存放每一层的节点
|
||||
//存放每一层的节点
|
||||
let curLevel = [];
|
||||
for(let i = 0;i < length; i++) {
|
||||
let node = queue.shift();
|
||||
|
|
@ -387,7 +390,9 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
|
|||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -455,7 +460,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -488,6 +493,7 @@ public:
|
|||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
@ -498,10 +504,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
results = []
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
que = deque([root])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while que:
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for _ in range(len(que)):
|
||||
|
|
@ -572,7 +578,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
// 利用链表可以进行 O(1) 头部插入, 这样最后答案不需要再反转
|
||||
LinkedList<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
|
||||
if (root != null) q.offer(root);
|
||||
|
|
@ -584,9 +590,9 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
|
||||
TreeNode node = q.poll();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
temp.add(node.val);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
|
||||
|
||||
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
|
||||
|
|
@ -616,7 +622,7 @@ func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
|||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
queue.PushBack(root)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for queue.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
length := queue.Len()
|
||||
tmp := []int{}
|
||||
|
|
@ -632,12 +638,12 @@ func levelOrderBottom(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
res=append(res, tmp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//反转结果集
|
||||
for i:=0; i<len(res)/2; i++ {
|
||||
res[i], res[len(res)-i-1] = res[len(res)-i-1], res[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -719,6 +725,7 @@ func levelOrderBottom(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] {
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -781,7 +788,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -810,6 +817,7 @@ public:
|
|||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
@ -817,7 +825,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
def rightSideView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# deque来自collections模块,不在力扣平台时,需要手动写入
|
||||
# 'from collections import deque' 导入
|
||||
# deque相比list的好处是,list的pop(0)是O(n)复杂度,deque的popleft()是O(1)复杂度
|
||||
|
|
@ -837,15 +845,15 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
quene.append(node.left)
|
||||
if node.right:
|
||||
quene.append(node.right)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return out_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 执行用时:36 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了89.47%的用户
|
||||
# 内存消耗:14.6 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了96.65%的用户
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// 199.二叉树的右视图
|
||||
|
|
@ -889,10 +897,9 @@ public class N0199 {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
go:
|
||||
|
||||
```GO
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
199. 二叉树的右视图
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
|
@ -932,7 +939,7 @@ var rightSideView = function(root) {
|
|||
//二叉树右视图 只需要把每一层最后一个节点存储到res数组
|
||||
let res = [], queue = [];
|
||||
queue.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
|
||||
// 记录当前层级节点个数
|
||||
let length = queue.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -946,7 +953,7 @@ var rightSideView = function(root) {
|
|||
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -997,6 +1004,7 @@ func rightSideView(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 199.二叉树的右视图
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1060,7 +1068,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个非空二叉树, 返回一个由每层节点平均值组成的数组。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1103,10 +1111,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
results = []
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
que = deque([root])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while que:
|
||||
size = len(que)
|
||||
sum_ = 0
|
||||
|
|
@ -1124,8 +1132,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
|
||||
java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// 637. 二叉树的层平均值
|
||||
public class N0637 {
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1210,7 +1217,7 @@ var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
|
|||
//层级平均值
|
||||
let res = [], queue = [];
|
||||
queue.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
|
||||
//每一层节点个数
|
||||
let length = queue.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1225,7 +1232,7 @@ var averageOfLevels = function(root) {
|
|||
//每一层的平均值存入数组res
|
||||
res.push(sum/length);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1280,7 +1287,9 @@ func averageOfLevels(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Double] {
|
|||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 637.二叉树的层平均值
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1346,7 +1355,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
|
||||
|
||||
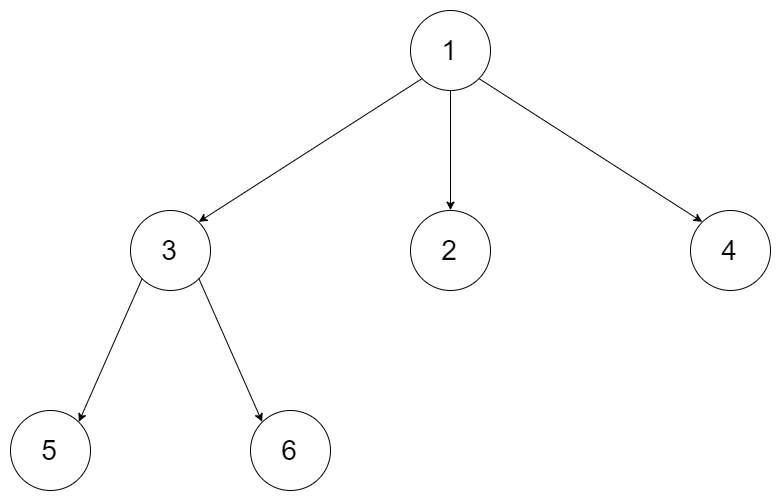
|
||||
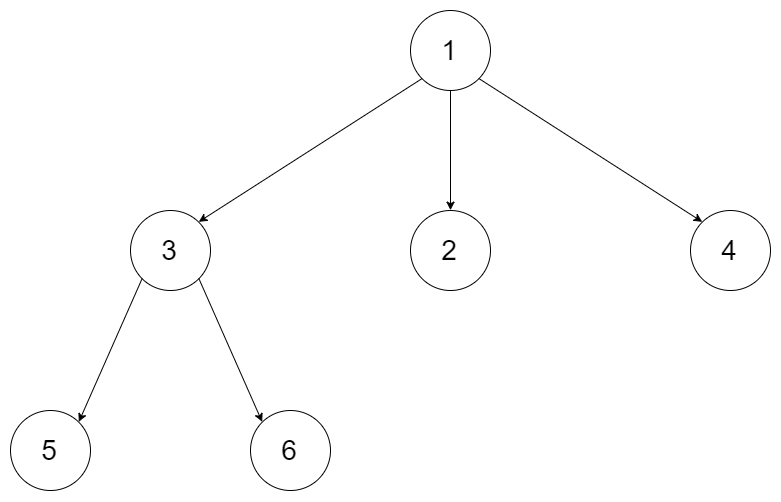
|
||||
|
||||
返回其层序遍历:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1399,10 +1408,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
results = []
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
que = deque([root])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while que:
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for _ in range(len(que)):
|
||||
|
|
@ -1426,16 +1435,16 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
def traversal(root,depth):
|
||||
if len(result)==depth:result.append([])
|
||||
result[depth].append(root.val)
|
||||
if root.children:
|
||||
if root.children:
|
||||
for i in range(len(root.children)):traversal(root.children[i],depth+1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
traversal(root,0)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// 429. N 叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
public class N0429 {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
|
|
@ -1520,7 +1529,7 @@ func levelOrder(root *Node) [][]int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
res = append(res, tmp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1532,7 +1541,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
|
|||
//每一层可能有2个以上,所以不再使用node.left node.right
|
||||
let res = [], queue = [];
|
||||
queue.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while(queue.length && root!==null) {
|
||||
//记录每一层节点个数还是和二叉树一致
|
||||
let length = queue.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1541,7 +1550,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
|
|||
while(length--) {
|
||||
let node = queue.shift();
|
||||
curLevel.push(node.val);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//这里不再是 ndoe.left node.right 而是循坏node.children
|
||||
for(let item of node.children){
|
||||
item && queue.push(item);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1549,7 +1558,7 @@ var levelOrder = function(root) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
res.push(curLevel);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1602,6 +1611,7 @@ func levelOrder(_ root: Node?) -> [[Int]] {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 429.N叉树的层序遍历
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1683,7 +1693,7 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
|
||||
|
||||
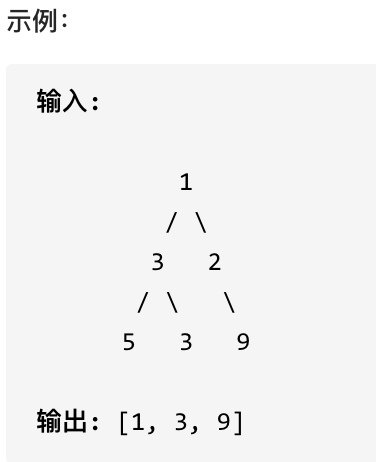
|
||||
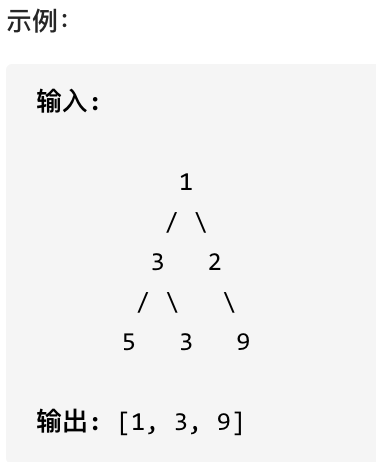
|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -1714,6 +1724,7 @@ public:
|
|||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
@ -1734,6 +1745,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
out_list.append(max(in_list))
|
||||
return out_list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
java代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
|
@ -1754,7 +1766,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
result.add(max);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -1811,8 +1823,8 @@ var largestValues = function(root) {
|
|||
//使用层序遍历
|
||||
let res = [], queue = [];
|
||||
queue.push(root);
|
||||
|
||||
while(root !== null && queue.length) {
|
||||
|
||||
while(root !== null && queue.length) {
|
||||
//设置max初始值就是队列的第一个元素
|
||||
let max = queue[0].val;
|
||||
let length = queue.length;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1825,7 +1837,7 @@ var largestValues = function(root) {
|
|||
//把每一层的最大值放到res数组
|
||||
res.push(max);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1884,6 +1896,7 @@ func largestValues(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [Int] {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 515.在每个树行中找最大值
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1959,9 +1972,9 @@ struct Node {
|
|||
|
||||
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
|
||||
|
||||
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
|
||||
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
|
||||
|
||||
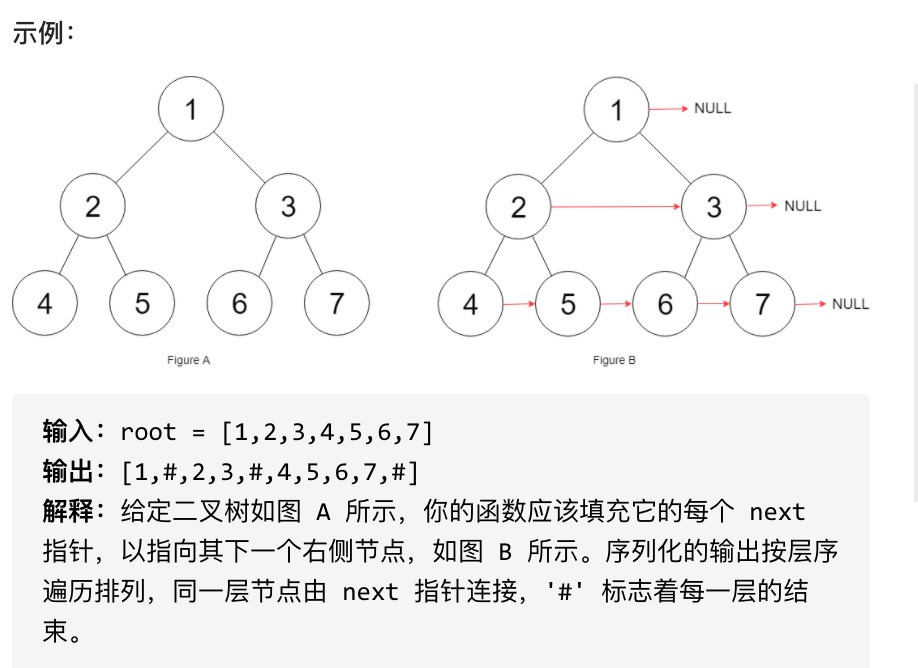
|
||||
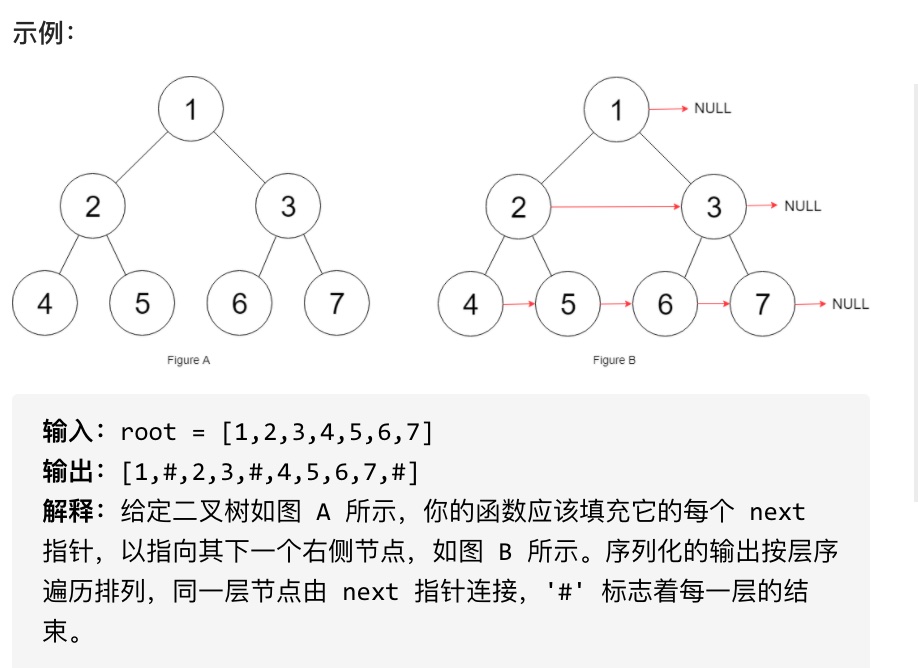
|
||||
|
||||
思路:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2009,24 +2022,24 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
public Node connect(Node root) {
|
||||
Queue<Node> tmpQueue = new LinkedList<Node>();
|
||||
if (root != null) tmpQueue.add(root);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while (tmpQueue.size() != 0){
|
||||
int size = tmpQueue.size();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Node cur = tmpQueue.poll();
|
||||
if (cur.left != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.left);
|
||||
if (cur.right != null) tmpQueue.add(cur.right);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int index = 1; index < size; index++){
|
||||
Node next = tmpQueue.poll();
|
||||
if (next.left != null) tmpQueue.add(next.left);
|
||||
if (next.right != null) tmpQueue.add(next.right);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
cur.next = next;
|
||||
cur = next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -2067,6 +2080,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
first = first.left # 从本层扩展到下一层
|
||||
return root
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
|
||||
```GO
|
||||
|
|
@ -2108,8 +2122,8 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* // Definition for a Node.
|
||||
* function Node(val, left, right, next) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2142,6 +2156,7 @@ var connect = function(root) {
|
|||
};
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
|
|
@ -2200,6 +2215,7 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2228,6 +2244,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -2284,7 +2301,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
int size = queue.size();
|
||||
Node node = null;
|
||||
Node nodePre = null;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||||
if (i == 0) {
|
||||
nodePre = queue.poll(); // 取出本层头一个节点
|
||||
|
|
@ -2307,6 +2324,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
python代码:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
@ -2329,6 +2347,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return root
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
|
||||
```GO
|
||||
|
|
@ -2369,6 +2388,7 @@ func connect(root *Node) *Node {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* // Definition for a Node.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2401,6 +2421,7 @@ var connect = function(root) {
|
|||
return root;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
TypeScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
|
|
@ -2459,6 +2480,7 @@ func connect(_ root: Node?) -> Node? {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2487,6 +2509,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -2501,7 +2524,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回它的最大深度 3 。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2511,7 +2534,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2540,7 +2563,8 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2566,12 +2590,13 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```python 3
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
|
||||
if root == None:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
queue_ = [root]
|
||||
depth = 0
|
||||
while queue_:
|
||||
|
|
@ -2583,7 +2608,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
if cur.left: queue_.append(cur.left)
|
||||
if cur.right: queue_.append(cur.right)
|
||||
depth += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return depth
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -2623,6 +2648,7 @@ func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2700,6 +2726,7 @@ func maxDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 104.二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -2789,7 +2816,8 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int minDepth(TreeNode root){
|
||||
|
|
@ -2838,7 +2866,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
queue_ = [(root,1)]
|
||||
while queue_:
|
||||
cur, depth = queue_.pop(0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if cur.left == None and cur.right == None:
|
||||
return depth
|
||||
#先左子节点,由于左子节点没有孩子,则就是这一层了
|
||||
|
|
@ -2884,12 +2912,13 @@ func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
|
|||
}
|
||||
ans++//记录层数
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return ans+1
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
|
|
@ -2972,6 +3001,7 @@ func minDepth(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
// 111.二叉树的最小深度
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,8 @@
|
|||
示例:
|
||||
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回它的最大深度 3 。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,7 +170,8 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -213,7 +215,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
看完本文,可以一起解决如下两道题目
|
||||
|
||||
* 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,11 +23,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给出
|
||||
|
||||
* 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
|
||||
* 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
|
||||
* 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
|
||||
返回如下的二叉树:
|
||||
返回如下的二叉树:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 视频讲解
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,7 +42,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
流程如图:
|
||||
|
||||
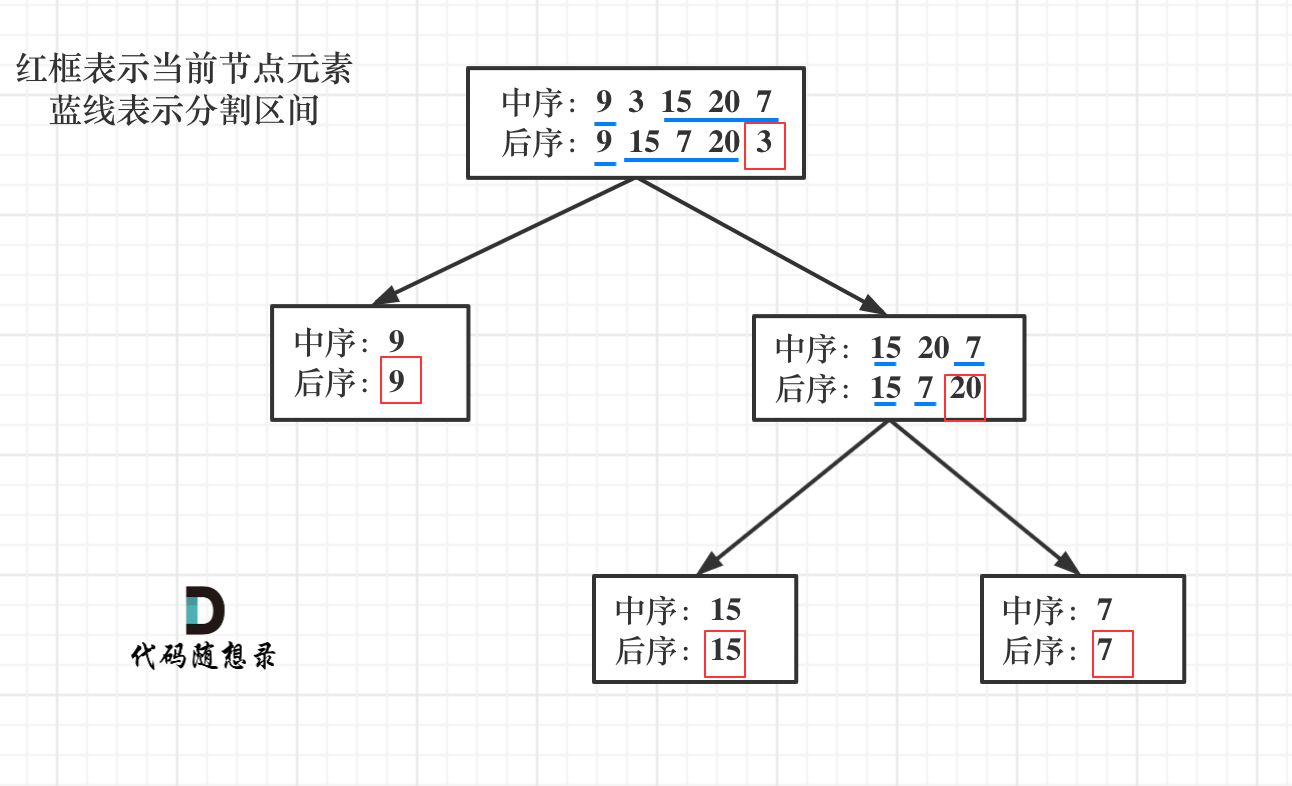
|
||||
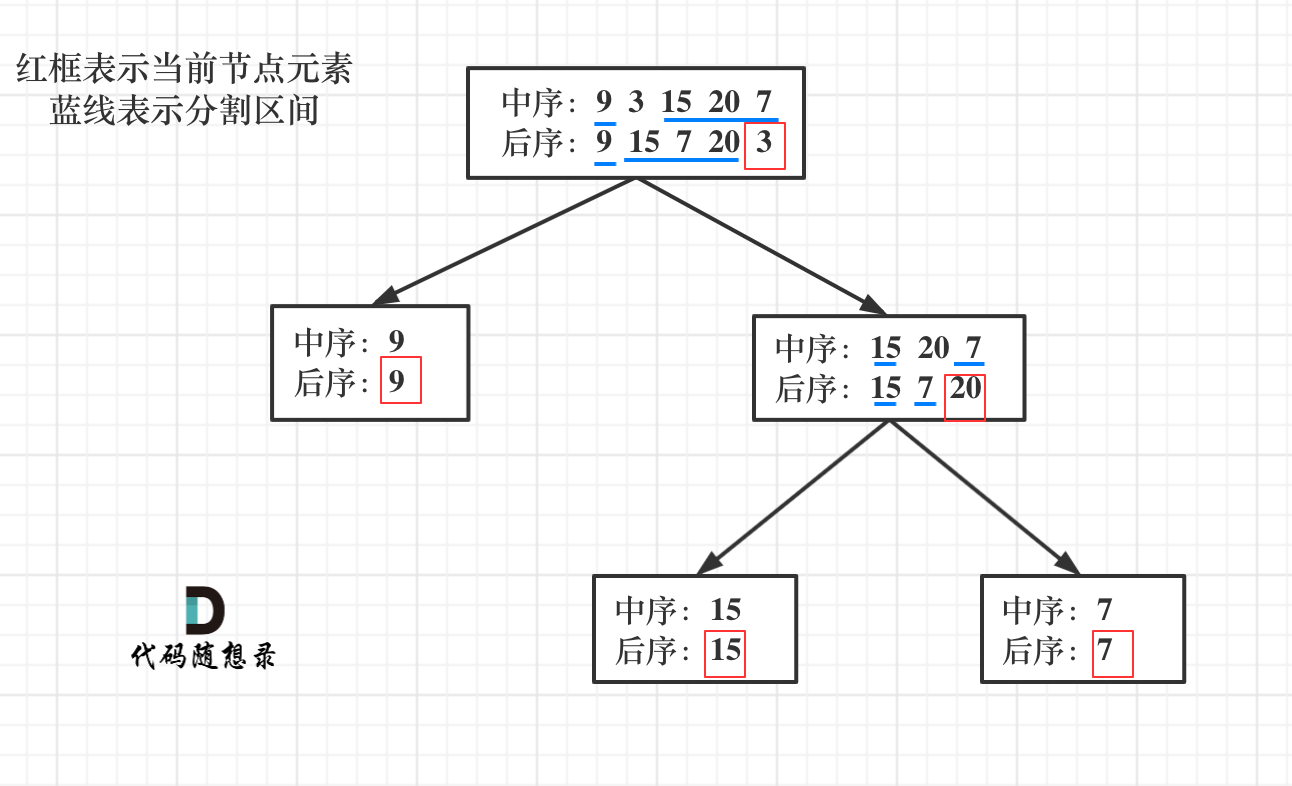
|
||||
|
||||
那么代码应该怎么写呢?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -280,6 +282,7 @@ public:
|
|||
下面给出用下标索引写出的代码版本:(思路是一样的,只不过不用重复定义vector了,每次用下标索引来分割)
|
||||
|
||||
### C++优化版本
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
|
@ -397,7 +400,7 @@ public:
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,11 +414,11 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给出
|
||||
|
||||
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
|
||||
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
|
||||
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
|
||||
返回如下的二叉树:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -558,7 +561,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
举一个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
tree1 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -601,7 +604,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
|
||||
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
|
||||
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
|
||||
|
|
@ -642,7 +645,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]); // 找到前序遍历的第一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
|
||||
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
|
||||
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定前序数列的个数
|
||||
root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
|
||||
root.left = findNode(preorder, preBegin + 1, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1,
|
||||
inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);
|
||||
root.right = findNode(preorder, preBegin + lenOfLeft + 1, preEnd,
|
||||
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
|
||||
|
|
@ -652,18 +655,19 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||||
# 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. 或者说是递归终止条件
|
||||
if not postorder:
|
||||
return
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点
|
||||
root_val = postorder[-1]
|
||||
root = TreeNode(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 第三步: 找切割点.
|
||||
root_index = inorder.index(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -672,7 +676,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
right_inorder = inorder[root_index + 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 第五步: 切割postorder数组. 得到postorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
left_postorder = postorder[:len(left_inorder)]
|
||||
right_postorder = postorder[len(left_inorder): len(postorder) - 1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -682,7 +686,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
root.right = self.buildTree(right_inorder, right_postorder)
|
||||
|
||||
# 第七步: 返回答案
|
||||
return root
|
||||
return root
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
|
||||
|
|
@ -691,22 +695,22 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
class Solution:
|
||||
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
|
||||
# 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. 或者说是递归终止条件
|
||||
if not preorder:
|
||||
if not preorder:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# 第二步: 前序遍历的第一个就是当前的中间节点.
|
||||
# 第二步: 前序遍历的第一个就是当前的中间节点.
|
||||
root_val = preorder[0]
|
||||
root = TreeNode(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
# 第三步: 找切割点.
|
||||
# 第三步: 找切割点.
|
||||
separator_idx = inorder.index(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
# 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
# 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
inorder_left = inorder[:separator_idx]
|
||||
inorder_right = inorder[separator_idx + 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 第五步: 切割preorder数组. 得到preorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟前序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟前序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
preorder_left = preorder[1:1 + len(inorder_left)]
|
||||
preorder_right = preorder[1 + len(inorder_left):]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -723,22 +727,22 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
class Solution:
|
||||
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
|
||||
# 第一步: 特殊情况讨论: 树为空. (递归终止条件)
|
||||
if not postorder:
|
||||
if not postorder:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点.
|
||||
# 第二步: 后序遍历的最后一个就是当前的中间节点.
|
||||
root_val = postorder[-1]
|
||||
root = TreeNode(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
# 第三步: 找切割点.
|
||||
# 第三步: 找切割点.
|
||||
separator_idx = inorder.index(root_val)
|
||||
|
||||
# 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
# 第四步: 切割inorder数组. 得到inorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
inorder_left = inorder[:separator_idx]
|
||||
inorder_right = inorder[separator_idx + 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
# 第五步: 切割postorder数组. 得到postorder数组的左,右半边.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
# ⭐️ 重点1: 中序数组大小一定跟后序数组大小是相同的.
|
||||
postorder_left = postorder[:len(inorder_left)]
|
||||
postorder_right = postorder[len(inorder_left): len(postorder) - 1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -746,7 +750,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
root.left = self.buildTree(inorder_left, postorder_left)
|
||||
root.right = self.buildTree(inorder_right, postorder_right)
|
||||
|
||||
return root
|
||||
return root
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
|
@ -786,7 +790,7 @@ func rebuild(inorder []int, postorder []int, rootIdx int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
|
|||
rootIn := hash[rootV] // 找到根节点在对应的中序数组中的位置
|
||||
root := &TreeNode{Val : rootV} // 构造根节点
|
||||
// 重建左节点和右节点
|
||||
root.Left = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-(r-rootIn)-1, l, rootIn-1)
|
||||
root.Left = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-(r-rootIn)-1, l, rootIn-1)
|
||||
root.Right = rebuild(inorder, postorder, rootIdx-1, rootIn+1, r)
|
||||
return root
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -830,7 +834,7 @@ func build(pre []int, in []int, root int, l, r int) *TreeNode {
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
## JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1031,7 +1035,7 @@ struct TreeNode* buildTree(int* preorder, int preorderSize, int* inorder, int in
|
|||
|
||||
// 4.根据中序遍历数组左右数组的各子大小切割前序遍历数组。也分为左右数组
|
||||
int* leftPreorder = preorder+1;
|
||||
int* rightPreorder = preorder + 1 + leftNum;
|
||||
int* rightPreorder = preorder + 1 + leftNum;
|
||||
|
||||
// 5.递归进入左右数组,将返回的结果作为根结点的左右孩子
|
||||
root->left = buildTree(leftPreorder, leftNum, leftInorder, leftNum);
|
||||
|
|
@ -1056,26 +1060,26 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
inorderBegin: 0,
|
||||
inorderEnd: inorder.count)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
func helper(preorder: [Int], preorderBegin: Int, preorderEnd: Int, inorder: [Int], inorderBegin: Int, inorderEnd: Int) -> TreeNode? {
|
||||
if preorderBegin == preorderEnd {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 前序遍历数组的第一个元素作为分割点
|
||||
let rootValue = preorder[preorderBegin]
|
||||
let root = TreeNode(rootValue)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if preorderEnd - preorderBegin == 1 {
|
||||
return root
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
var index = 0 // 从中序遍历数组中找到根节点的下标
|
||||
if let ind = inorder.firstIndex(of: rootValue) {
|
||||
index = ind
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
root.left = helper(preorder: preorder,
|
||||
preorderBegin: preorderBegin + 1,
|
||||
|
|
@ -1102,28 +1106,28 @@ class Solution_0106 {
|
|||
if postorderEnd - postorderBegin < 1 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 后序遍历数组的最后一个元素作为分割点
|
||||
let rootValue = postorder[postorderEnd - 1]
|
||||
let root = TreeNode(rootValue)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if postorderEnd - postorderBegin == 1 {
|
||||
return root
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 从中序遍历数组中找到根节点的下标
|
||||
var delimiterIndex = 0
|
||||
if let index = inorder.firstIndex(of: rootValue) {
|
||||
delimiterIndex = index
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
root.left = buildTree(inorder: inorder,
|
||||
inorderBegin: inorderBegin,
|
||||
inorderEnd: delimiterIndex,
|
||||
postorder: postorder,
|
||||
postorderBegin: postorderBegin,
|
||||
postorderEnd: postorderBegin + (delimiterIndex - inorderBegin))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
root.right = buildTree(inorder: inorder,
|
||||
inorderBegin: delimiterIndex + 1,
|
||||
inorderEnd: inorderEnd,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 求高度还是求深度,你搞懂了不?
|
||||
|
||||
# 110.平衡二叉树
|
||||
|
|
@ -13,13 +15,13 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
|
||||
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回 true 。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,7 +29,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回 false 。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +47,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
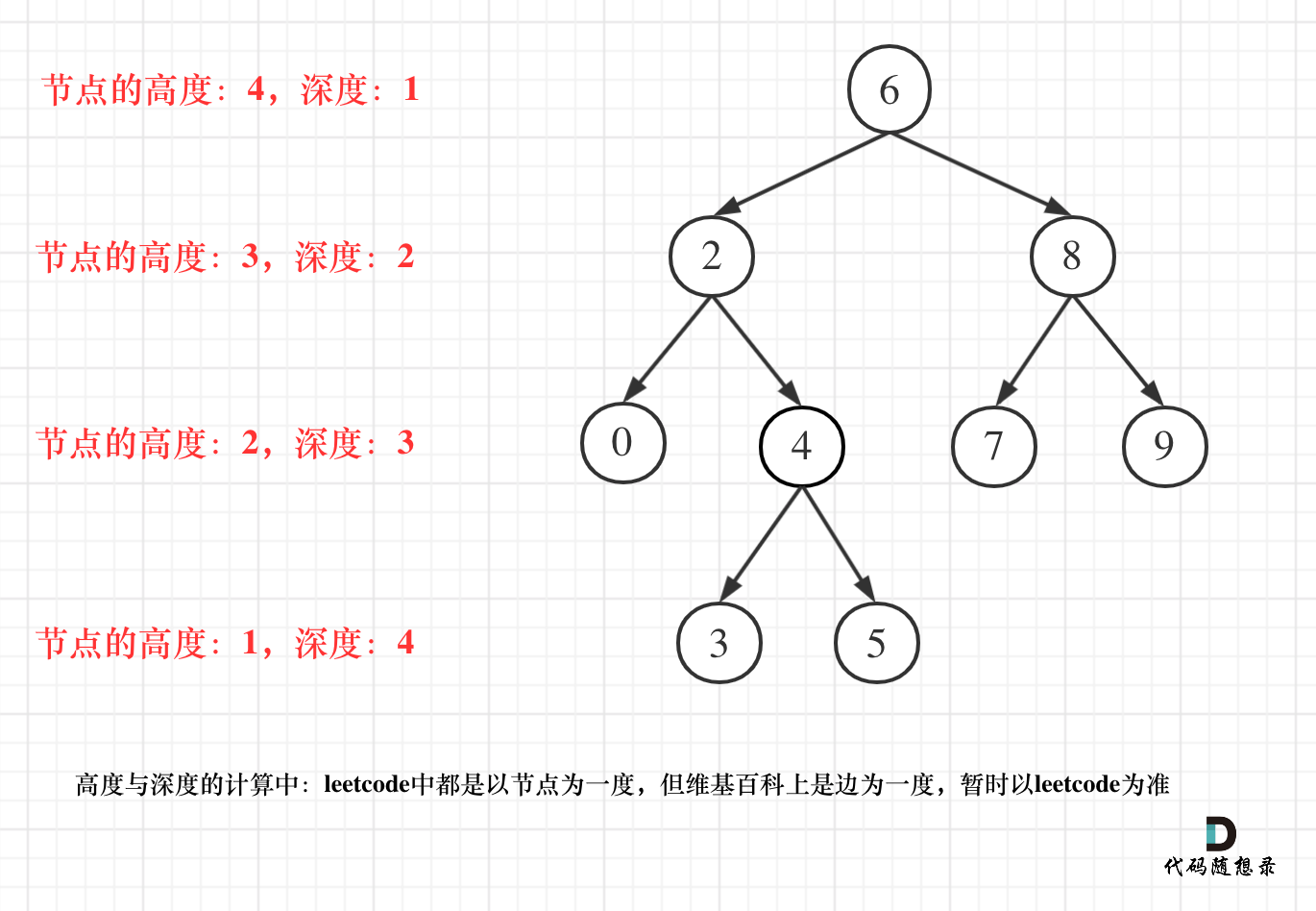
|
||||
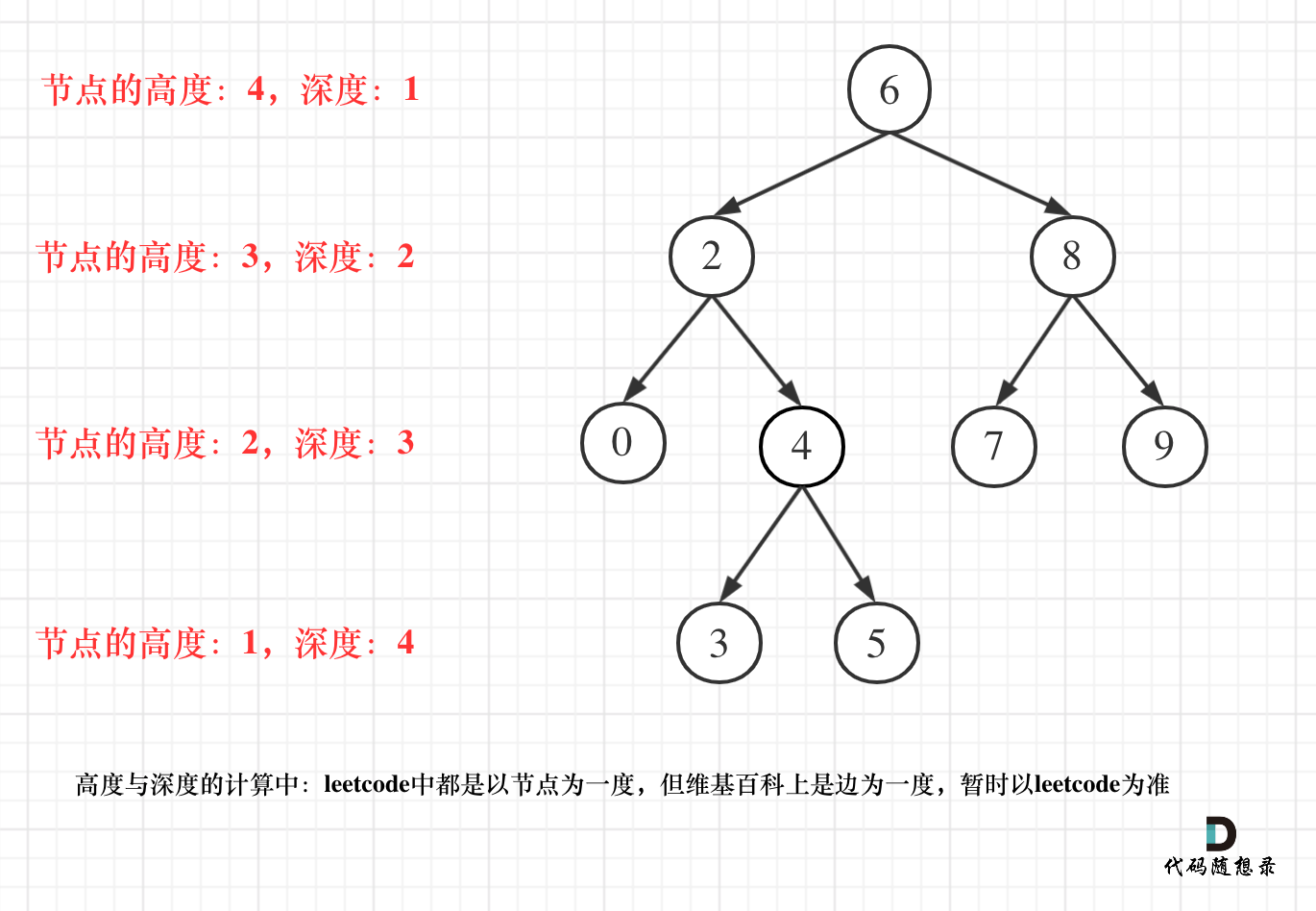
|
||||
|
||||
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,我们暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟要在这上面刷题)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -125,7 +127,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
1. 明确递归函数的参数和返回值
|
||||
|
||||
参数:当前传入节点。
|
||||
参数:当前传入节点。
|
||||
返回值:以当前传入节点为根节点的树的高度。
|
||||
|
||||
那么如何标记左右子树是否差值大于1呢?
|
||||
|
|
@ -496,9 +498,10 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
# class TreeNode:
|
||||
|
|
@ -512,7 +515,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_height(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
|
||||
# Base Case
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
|
|
@ -531,6 +534,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
|
||||
|
|
@ -557,9 +561,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
|
||||
h := getHeight(root)
|
||||
h := getHeight(root)
|
||||
if h == -1 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -588,7 +593,9 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JavaScript
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var isBalanced = function(root) {
|
||||
//还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1
|
||||
|
|
@ -614,6 +621,7 @@ var isBalanced = function(root) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
// 获取当前节点的高度
|
||||
var getHeight = function (curNode) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -644,7 +652,7 @@ var isBalanced = function (root) {
|
|||
let queue = [root];
|
||||
while (queue.length) {
|
||||
let node = queue[queue.length - 1]; // 取出栈顶
|
||||
queue.pop();
|
||||
queue.pop();
|
||||
if (Math.abs(getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right)) > 1) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -676,6 +684,7 @@ function isBalanced(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
|||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
//如果结点不存在,返回0
|
||||
|
|
@ -706,6 +715,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
//计算结点深度
|
||||
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -717,7 +727,7 @@ int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
|
|||
stack[stackTop++] = node;
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
int depth = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//当栈中有元素时,进行迭代遍历
|
||||
while(stackTop) {
|
||||
//取出栈顶元素
|
||||
|
|
@ -741,7 +751,7 @@ int getDepth(struct TreeNode* node) {
|
|||
tempNode = stack[--stackTop];
|
||||
depth--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -750,11 +760,11 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
|
|||
//开辟栈空间
|
||||
struct TreeNode** stack = (struct TreeNode**)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode*) * 10000);
|
||||
int stackTop = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//若根节点不存在,返回True
|
||||
if(!root)
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//将根节点入栈
|
||||
stack[stackTop++] = root;
|
||||
//当栈中有元素时,进行遍历
|
||||
|
|
@ -764,7 +774,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
|
|||
//计算左右子树的深度
|
||||
int diff = getDepth(node->right) - getDepth(node->left);
|
||||
//若深度的绝对值大于1,返回False
|
||||
if(diff > 1 || diff < -1)
|
||||
if(diff > 1 || diff < -1)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
//如果栈顶结点有左右结点,将左右结点入栈
|
||||
if(node->left)
|
||||
|
|
@ -780,6 +790,7 @@ bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
|
|||
### Swift:
|
||||
|
||||
>递归
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
func isBalanced(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Bool {
|
||||
// -1 已经不是平衡二叉树
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回它的最小深度 2.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,7 +46,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
本题还有一个误区,在处理节点的过程中,最大深度很容易理解,最小深度就不那么好理解,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
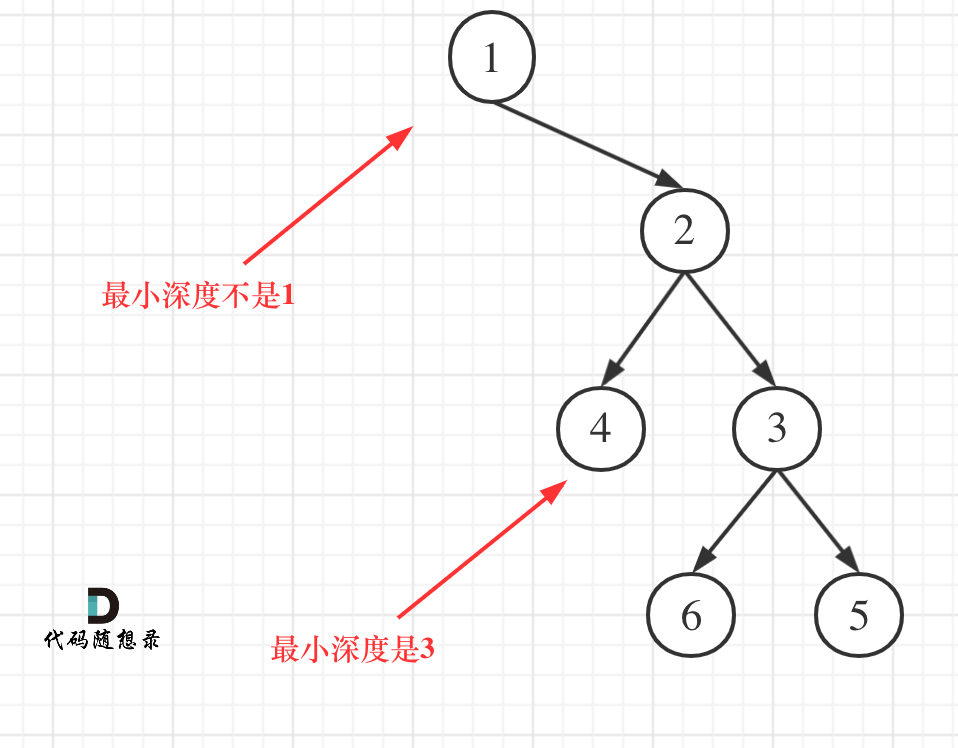
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这就重新审题了,题目中说的是:**最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。**,注意是**叶子节点**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,7 +88,7 @@ return result;
|
|||
|
||||
这个代码就犯了此图中的误区:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果这么求的话,没有左孩子的分支会算为最短深度。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,18 +1,20 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 112. 路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
|
||||
|
||||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
|
||||
|
||||
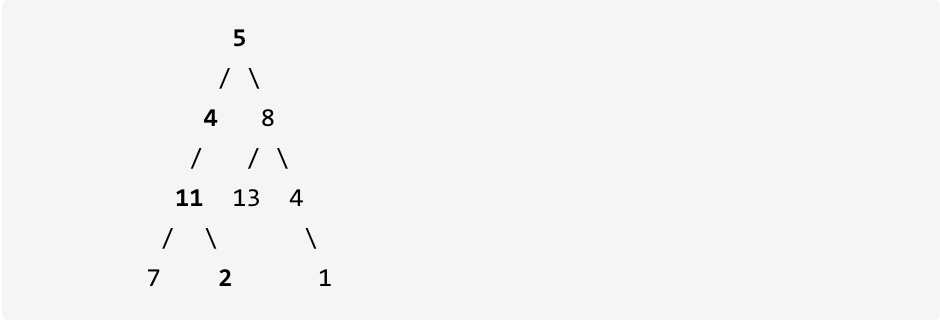
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +55,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
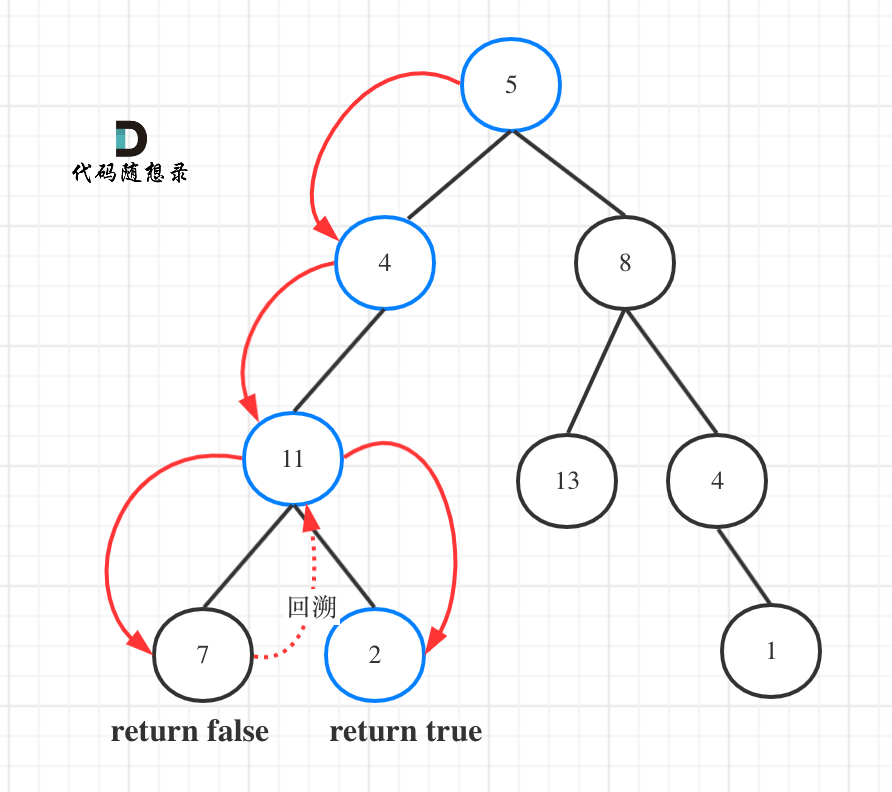
|
||||
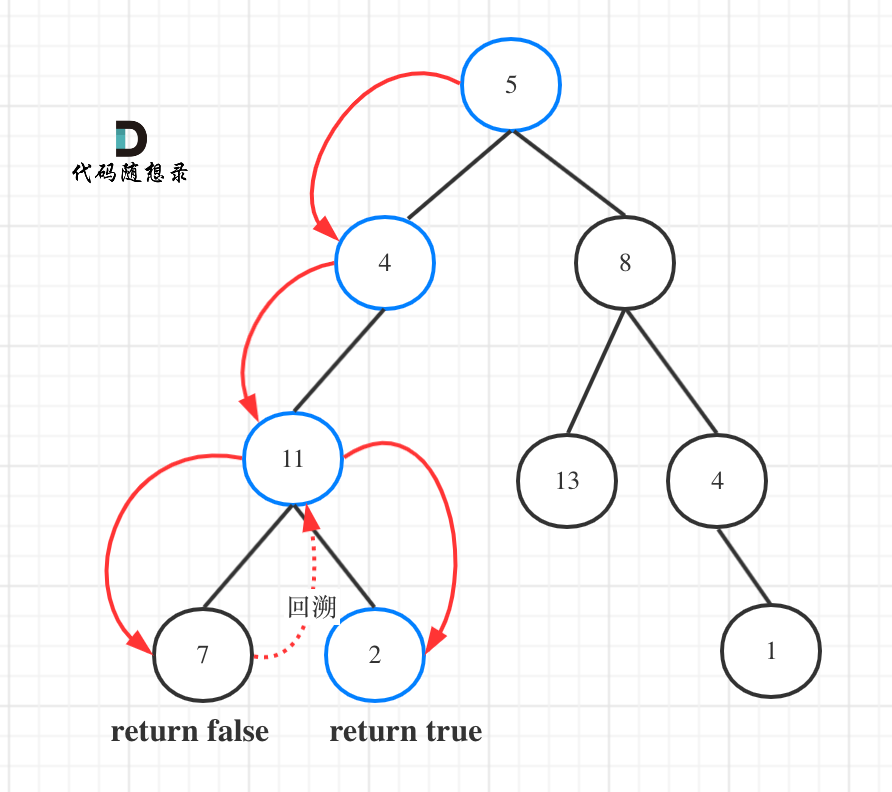
|
||||
|
||||
图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -222,13 +224,13 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
|
||||
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -237,7 +239,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
为了尽可能的把细节体现出来,我写出如下代码(**这份代码并不简洁,但是逻辑非常清晰**)
|
||||
|
|
@ -303,6 +305,7 @@ public:
|
|||
## java
|
||||
|
||||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class solution {
|
||||
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -333,9 +336,9 @@ class solution {
|
|||
// lc112 简洁方法
|
||||
class solution {
|
||||
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 叶子节点判断是否符合
|
||||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetsum;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -344,7 +347,9 @@ class solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class solution {
|
||||
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -363,7 +368,7 @@ class solution {
|
|||
// 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
|
||||
if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetsum) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||||
if(node.right != null){
|
||||
stack1.push(node.right);
|
||||
|
|
@ -377,7 +382,7 @@ class solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -447,6 +452,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class solution:
|
||||
def haspathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> bool:
|
||||
|
|
@ -472,55 +478,57 @@ class solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代 - 层序遍历**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class solution:
|
||||
def haspathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> bool:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
|
||||
stack = [] # [(当前节点,路径数值), ...]
|
||||
stack.append((root, root.val))
|
||||
|
||||
while stack:
|
||||
while stack:
|
||||
cur_node, path_sum = stack.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
if not cur_node.left and not cur_node.right and path_sum == targetsum:
|
||||
if not cur_node.left and not cur_node.right and path_sum == targetsum:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
|
||||
if cur_node.right:
|
||||
stack.append((cur_node.right, path_sum + cur_node.right.val))
|
||||
if cur_node.right:
|
||||
stack.append((cur_node.right, path_sum + cur_node.right.val))
|
||||
|
||||
if cur_node.left:
|
||||
if cur_node.left:
|
||||
stack.append((cur_node.left, path_sum + cur_node.left.val))
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class solution:
|
||||
def pathsum(self, root: treenode, targetsum: int) -> list[list[int]]:
|
||||
|
||||
def traversal(cur_node, remain):
|
||||
def traversal(cur_node, remain):
|
||||
if not cur_node.left and not cur_node.right:
|
||||
if remain == 0:
|
||||
if remain == 0:
|
||||
result.append(path[:])
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if cur_node.left:
|
||||
if cur_node.left:
|
||||
path.append(cur_node.left.val)
|
||||
traversal(cur_node.left, remain-cur_node.left.val)
|
||||
path.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
if cur_node.right:
|
||||
if cur_node.right:
|
||||
path.append(cur_node.right.val)
|
||||
traversal(cur_node.right, remain-cur_node.right.val)
|
||||
path.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
result, path = [], []
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
if not root:
|
||||
return []
|
||||
path.append(root.val)
|
||||
traversal(root, targetsum - root.val)
|
||||
|
|
@ -528,6 +536,7 @@ class solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代法,用第二个队列保存目前的总和与路径**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||||
|
|
@ -569,7 +578,7 @@ func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
|
|||
if root == nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
targetSum -= root.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
|
||||
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
|
||||
return true
|
||||
|
|
@ -602,10 +611,10 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
|
|||
|
||||
targetSum -= node.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
|
||||
*currPath = append(*currPath, node.Val) // 把当前节点放到路径记录里
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
|
||||
// 不能直接将currPath放到result里面, 因为currPath是共享的, 每次遍历子树时都会被修改
|
||||
pathCopy := make([]int, len(*currPath))
|
||||
pathCopy := make([]int, len(*currPath))
|
||||
for i, element := range *currPath {
|
||||
pathCopy[i] = element
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -623,6 +632,7 @@ func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
|
|||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @param {treenode} root
|
||||
|
|
@ -639,7 +649,7 @@ let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
|||
|
||||
// 左(空节点不遍历).遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
|
||||
if (node.left && traversal(node.left, cnt - node.left.val)) return true;
|
||||
// 右(空节点不遍历)
|
||||
// 右(空节点不遍历)
|
||||
if (node.right && traversal(node.right, cnt - node.right.val)) return true;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
|
@ -652,7 +662,9 @@ let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
|||
// return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代**
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||||
if(root === null) return false;
|
||||
|
|
@ -681,9 +693,10 @@ let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
### 0113.路径总和-ii
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
let pathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
||||
// 递归法
|
||||
|
|
@ -715,7 +728,9 @@ let pathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
|||
return res;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**递归 精简版**
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var pathsum = function(root, targetsum) {
|
||||
//递归方法
|
||||
|
|
@ -739,7 +754,9 @@ var pathsum = function(root, targetsum) {
|
|||
return resPath;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代**
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
let pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||||
if(root === null) return [];
|
||||
|
|
@ -905,7 +922,7 @@ func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
|
|||
guard let root = root else {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -913,52 +930,54 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, _ count: Int) -> Bool {
|
|||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil && count == 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
|
||||
if traversal(leftNode, count - leftNode.val) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
|
||||
if traversal(rightNode, count - rightNode.val) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代**
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
|
||||
guard let root = root else {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
var stack = Array<(TreeNode, Int)>()
|
||||
stack.append((root, root.val))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while !stack.isEmpty {
|
||||
let node = stack.removeLast()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if node.0.left == nil && node.0.right == nil && targetSum == node.1 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let rightNode = node.0.right {
|
||||
stack.append((rightNode, node.1 + rightNode.val))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let leftNode = node.0.left {
|
||||
stack.append((leftNode, node.1 + leftNode.val))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -989,12 +1008,12 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
|
|||
result.append(path)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil{
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
|
||||
path.append(leftNode.val)
|
||||
count -= leftNode.val
|
||||
|
|
@ -1002,7 +1021,7 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
|
|||
count += leftNode.val// 回溯
|
||||
path.removeLast()// 回溯
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
|
||||
path.append(rightNode.val)
|
||||
count -= rightNode.val
|
||||
|
|
@ -1015,8 +1034,10 @@ func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
> 0112.路径总和
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
> 递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
||||
// 递归结束条件:若当前节点不存在,返回false
|
||||
|
|
@ -1025,13 +1046,14 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
|||
// 若当前节点为叶子节点,且targetSum-root的值为0。(当前路径上的节点值的和满足条件)返回true
|
||||
if(!root->right && !root->left && targetSum == root->val)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 查看左子树和右子树的所有节点是否满足条件
|
||||
return hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
迭代法:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
// 存储一个节点以及当前的和
|
||||
struct Pair {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1056,7 +1078,7 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
|||
// 若栈顶元素为叶子节点,且和为targetSum时,返回true
|
||||
if(!topPair.node->left && !topPair.node->right && topPair.sum == targetSum)
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 若当前栈顶节点有左右孩子,计算和并入栈
|
||||
if(topPair.node->left) {
|
||||
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->left, topPair.sum + topPair.node->left->val};
|
||||
|
|
@ -1070,7 +1092,9 @@ bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
|||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
int** ret;
|
||||
int* path;
|
||||
|
|
@ -1139,6 +1163,7 @@ int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** retur
|
|||
### 0112.路径总和
|
||||
|
||||
**递归:**
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
|
||||
|
|
@ -1163,6 +1188,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代:**
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||||
|
|
@ -1187,6 +1213,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
### 0113.路径总和 II
|
||||
|
||||
**递归:**
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -127,7 +127,8 @@ dp[0][1]表示第0天不持有股票,不持有股票那么现金就是0,所
|
|||
|
||||
以示例1,输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]为例,dp数组状态如下:
|
||||
|
||||
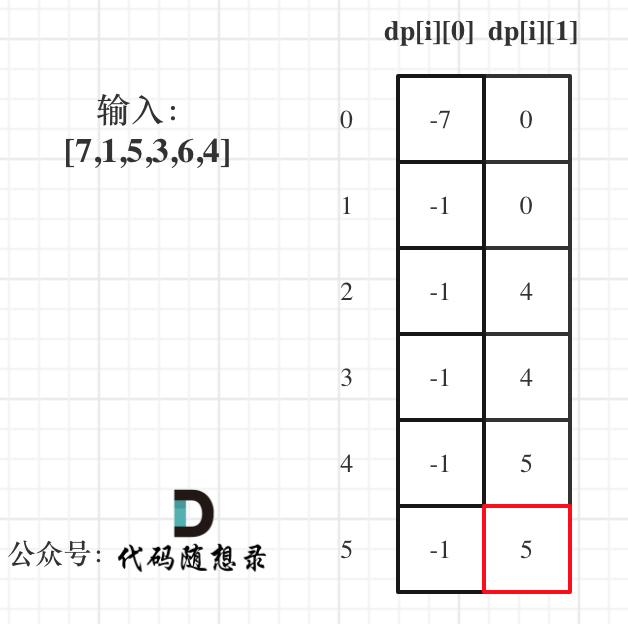
|
||||
|
||||
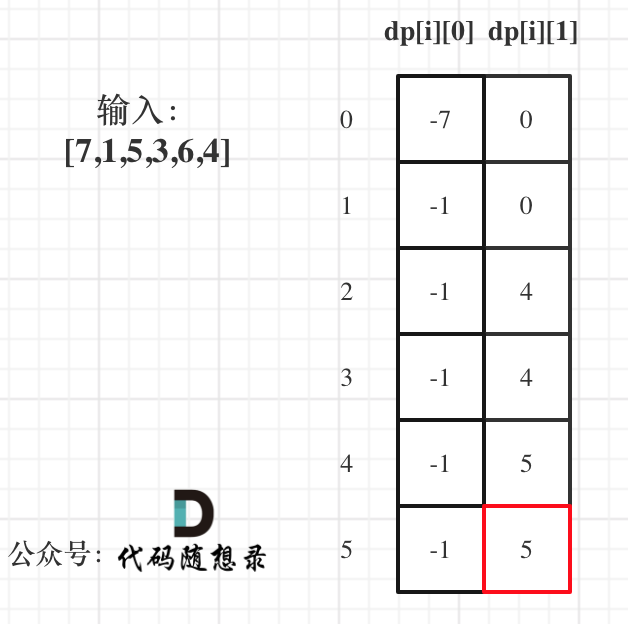
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dp[5][1]就是最终结果。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -62,7 +62,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
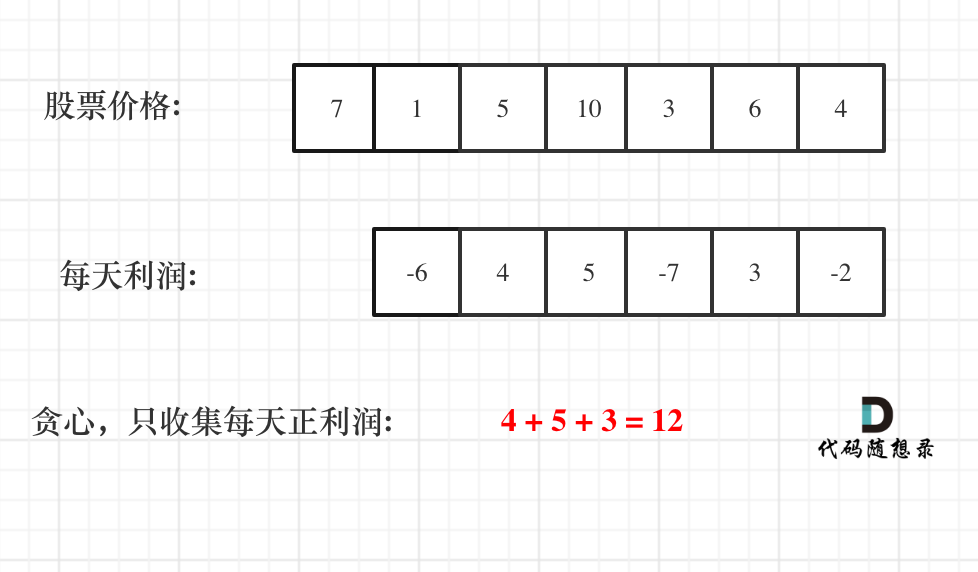
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学陷入:第一天怎么就没有利润呢,第一天到底算不算的困惑中。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -116,7 +116,8 @@ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]);
|
|||
|
||||
以输入[1,2,3,4,5]为例
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
大家可以看到红色框为最后两次卖出的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
|||
|
||||
以输入:"aabc" 为例:
|
||||
|
||||
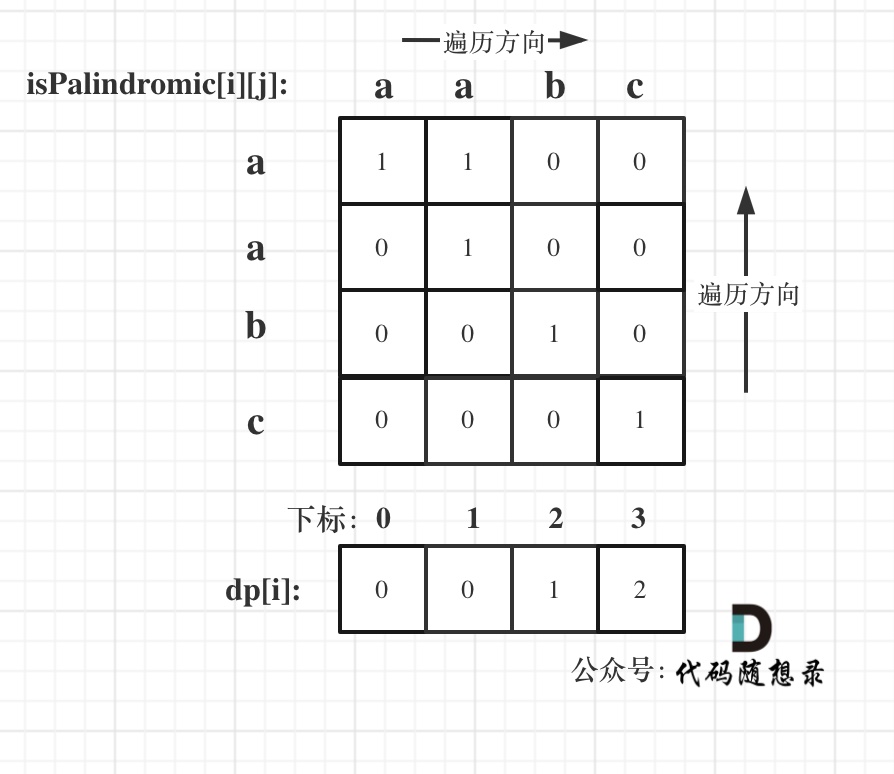
|
||||
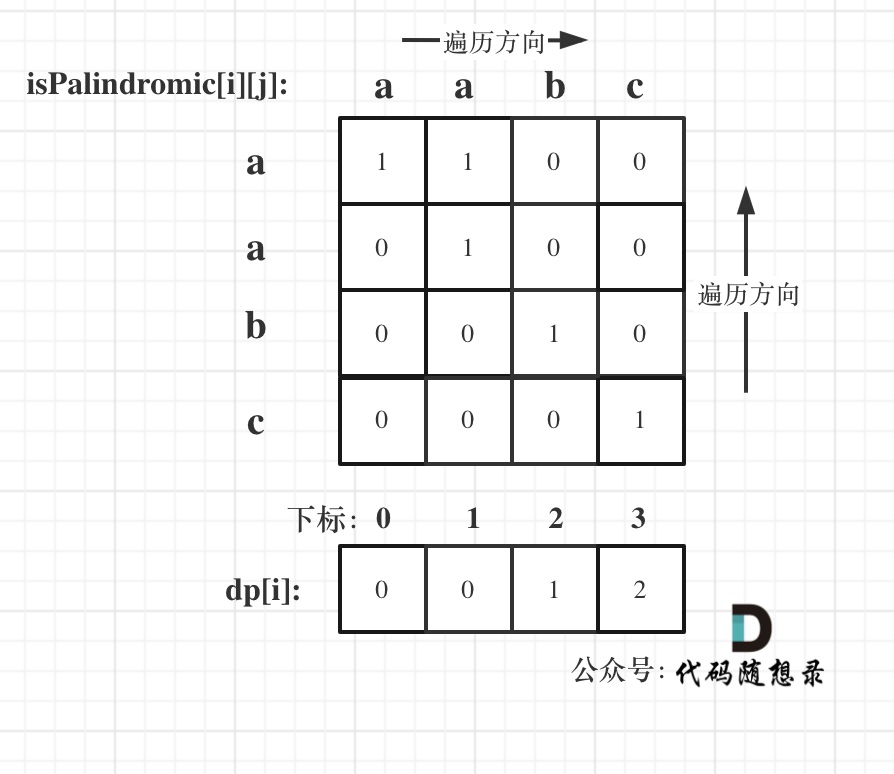
|
||||
|
||||
以上分析完毕,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -53,7 +53,8 @@ for (int i = 1; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
再确定左孩子大于右孩子的情况(从后向前遍历)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,7 +79,8 @@ for (int i = 1; i < ratings.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
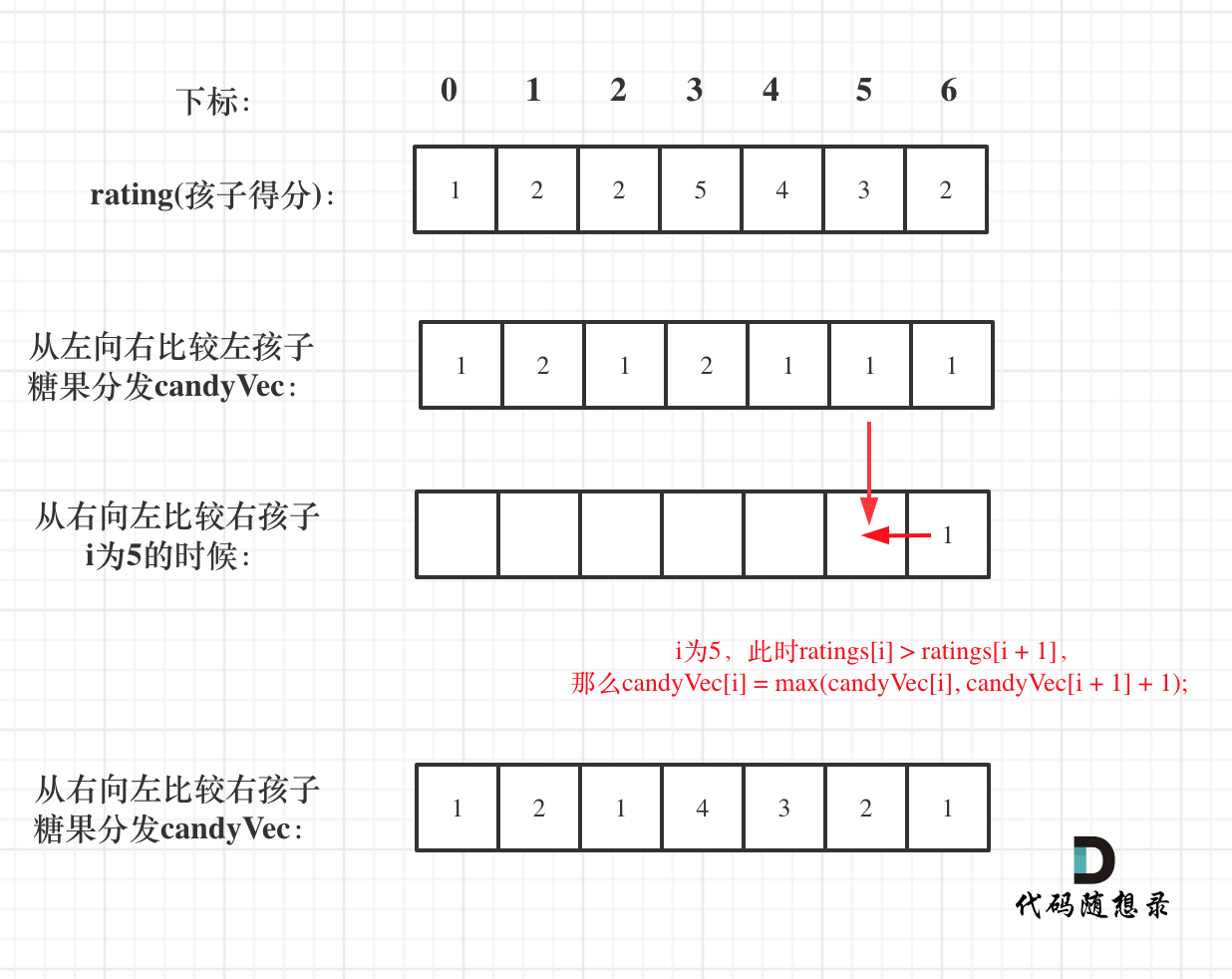
|
||||
|
||||
所以该过程代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -181,7 +181,8 @@ dp[0]表示如果字符串为空的话,说明出现在字典里。
|
|||
|
||||
以输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"]为例,dp状态如图:
|
||||
|
||||
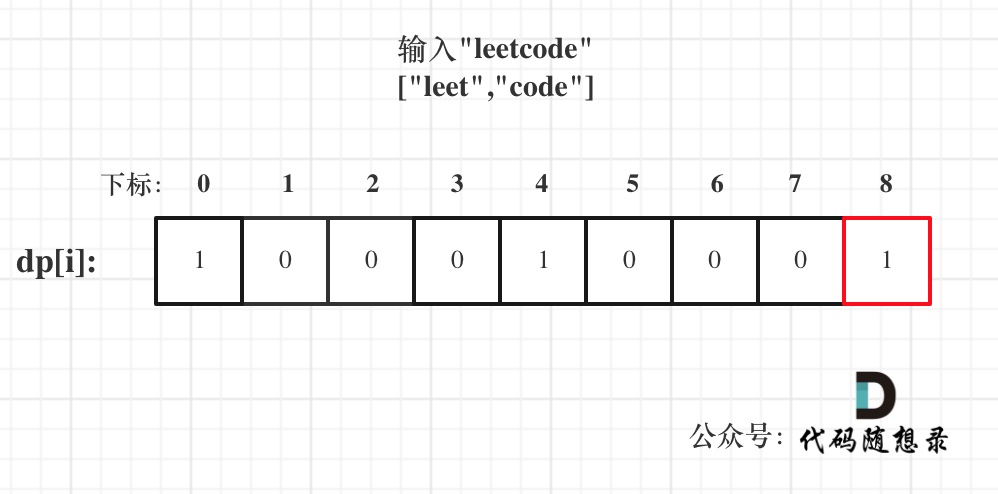
|
||||
|
||||
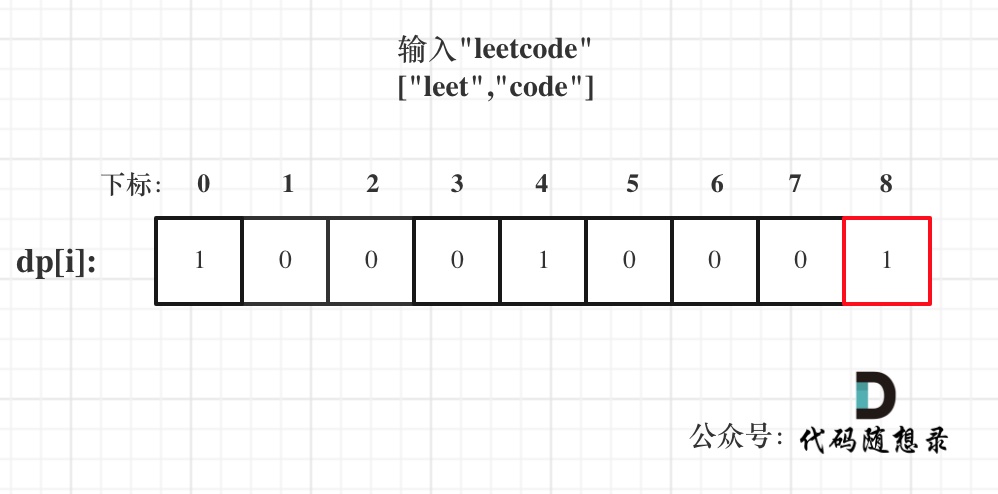
|
||||
|
||||
dp[s.size()]就是最终结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -6,6 +7,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 找到有没有环已经很不容易了,还要让我找到环的入口?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -14,13 +16,13 @@
|
|||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
|
||||
|
||||
题意:
|
||||
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
|
||||
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
|
||||
|
||||
为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
|
||||
|
||||
**说明**:不允许修改给定的链表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
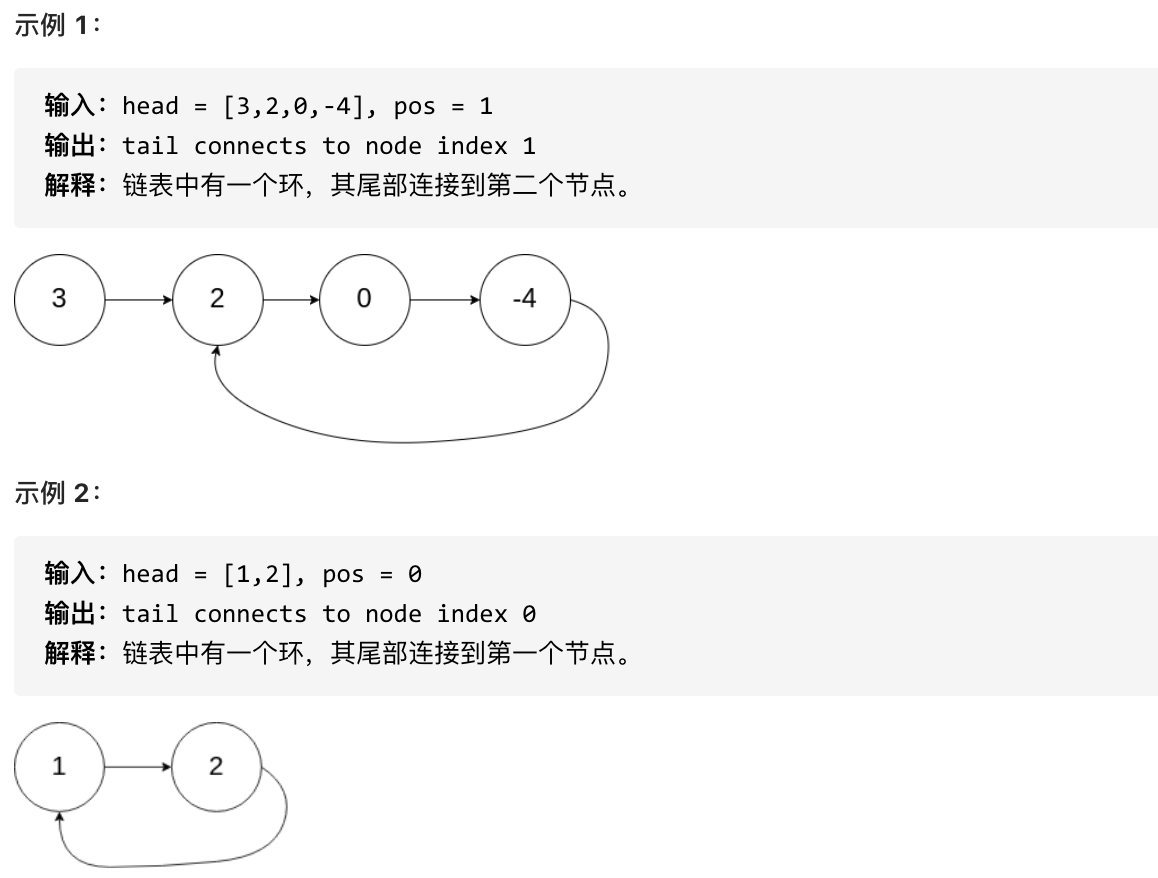
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +50,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
会发现最终都是这种情况, 如下图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
fast和slow各自再走一步, fast和slow就相遇了
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,20 +151,20 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
即文章[链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](https://programmercarl.com/0142.环形链表II.html)中如下的地方:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
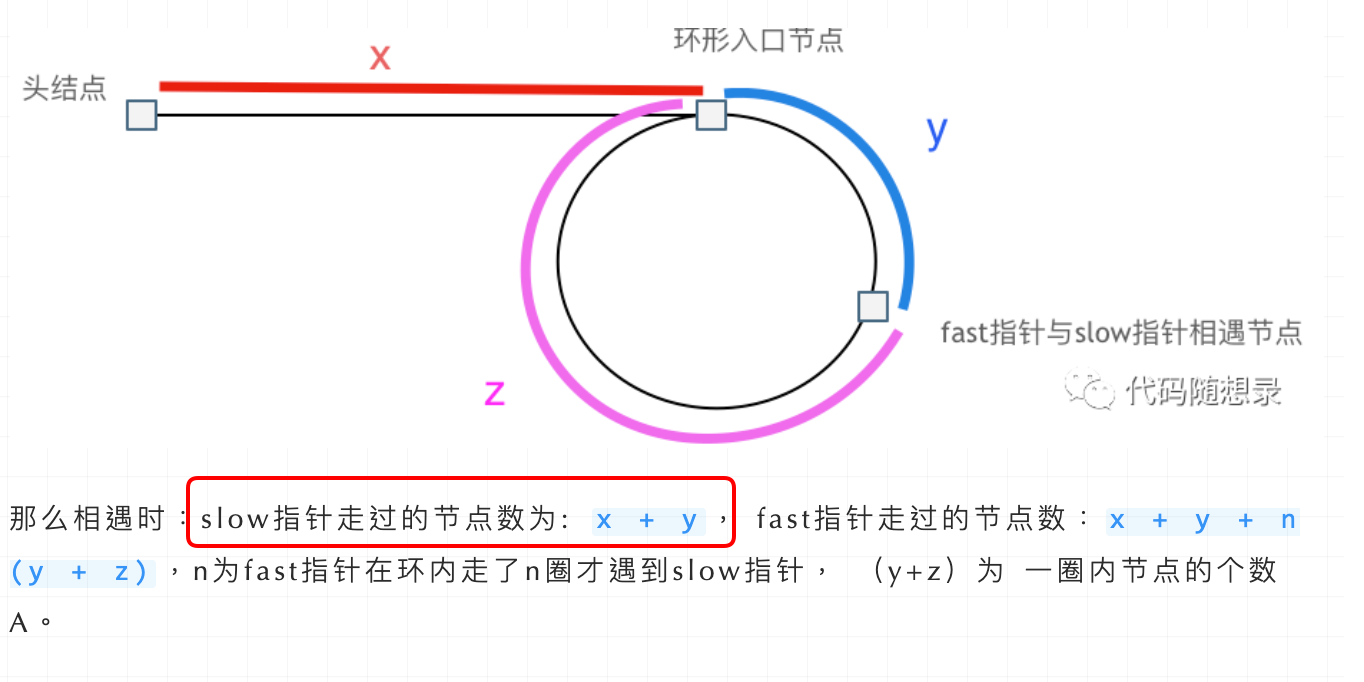
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先slow进环的时候,fast一定是先进环来了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果slow进环入口,fast也在环入口,那么把这个环展开成直线,就是如下图的样子:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
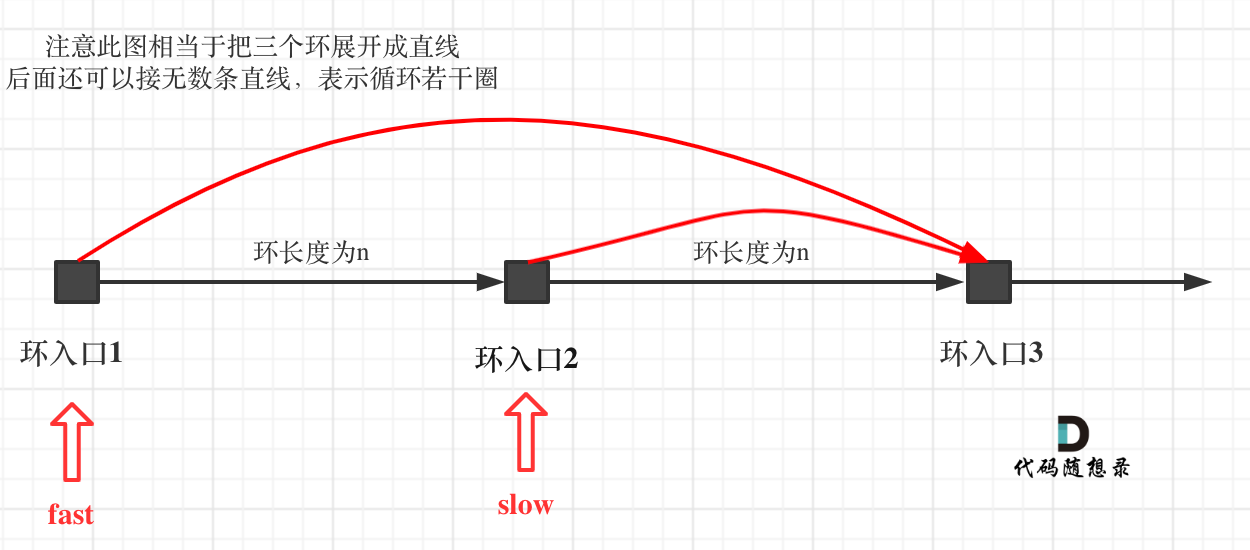
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出如果slow 和 fast同时在环入口开始走,一定会在环入口3相遇,slow走了一圈,fast走了两圈。
|
||||
|
||||
重点来了,slow进环的时候,fast一定是在环的任意一个位置,如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
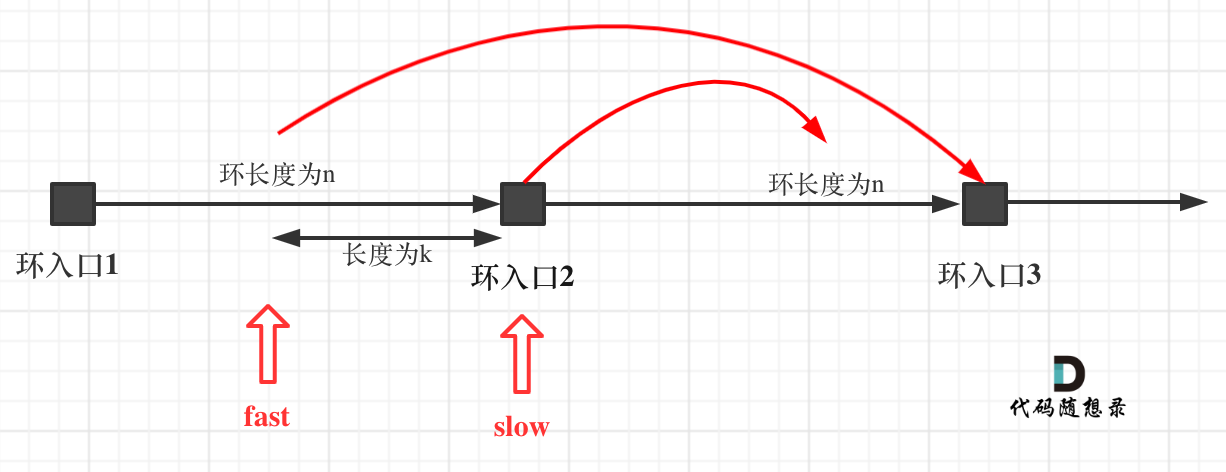
|
||||
|
||||
那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -187,6 +189,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -235,6 +238,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
|
||||
slow, fast := head, head
|
||||
|
|
@ -267,7 +271,7 @@ var detectCycle = function(head) {
|
|||
let slow =head.next, fast = head.next.next;
|
||||
while(fast && fast.next && fast!== slow) {
|
||||
slow = slow.next;
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next;
|
||||
fast = fast.next.next;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!fast || !fast.next ) return null;
|
||||
slow = head;
|
||||
|
|
@ -374,6 +378,7 @@ ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def detectCycle(head: ListNode): ListNode = {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ for (int j = 1; j < 2 * k; j += 2) {
|
|||
|
||||
以输入[1,2,3,4,5],k=2为例。
|
||||
|
||||
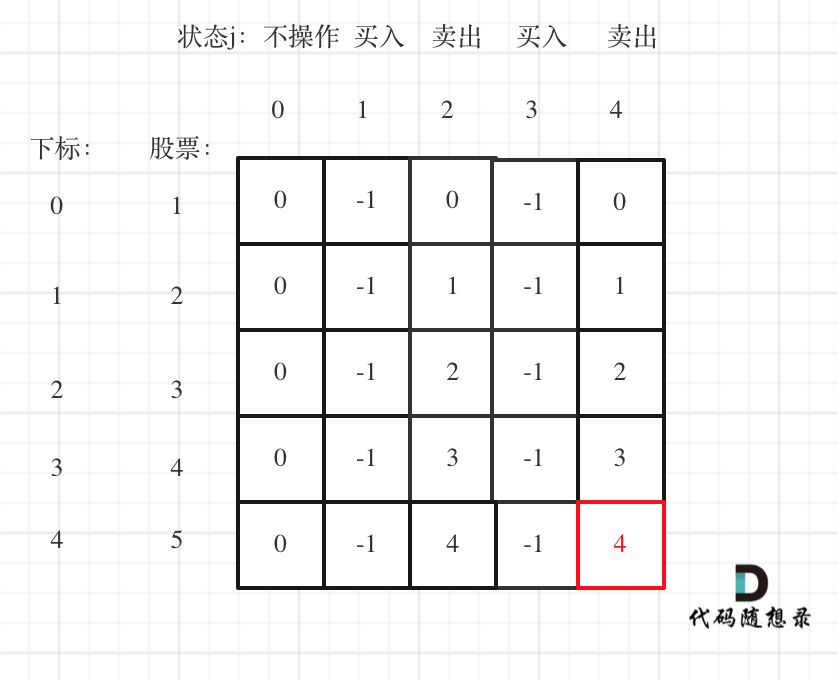
|
||||
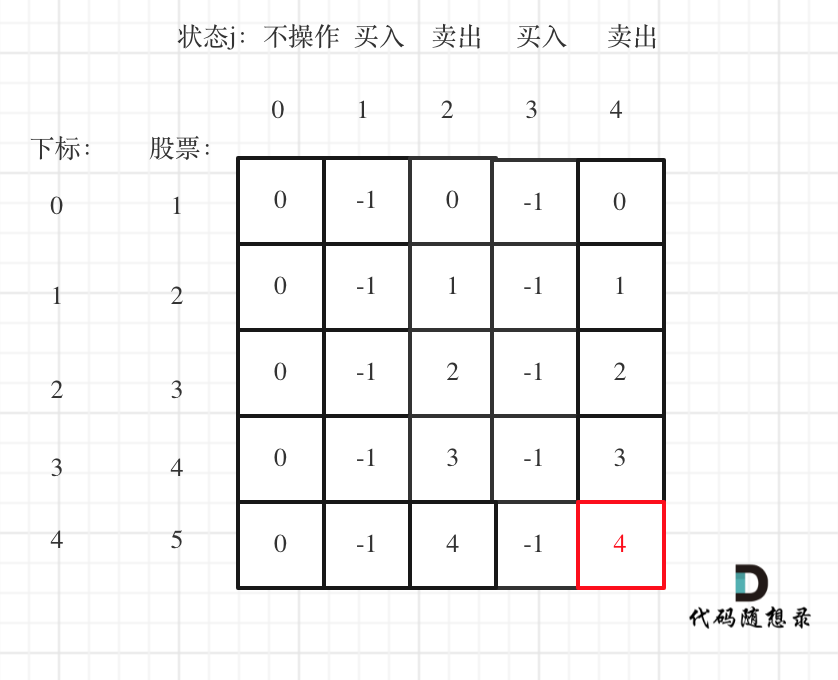
|
||||
|
||||
最后一次卖出,一定是利润最大的,dp[prices.size() - 1][2 * k]即红色部分就是最后求解。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ for (int i = 2; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
以示例二,输入[2,7,9,3,1]为例。
|
||||
|
||||
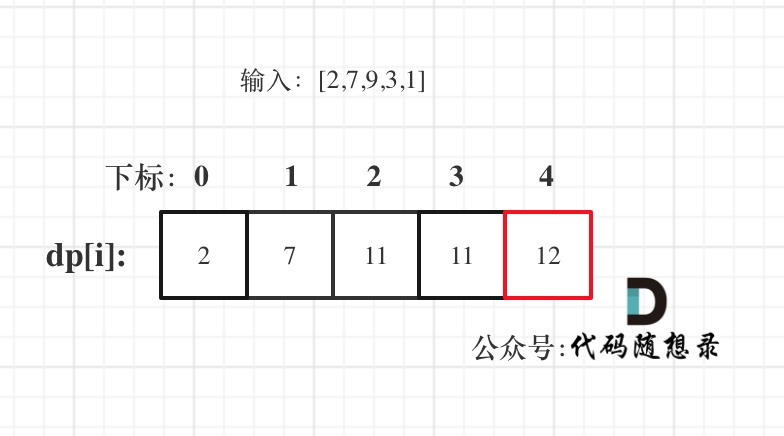
|
||||
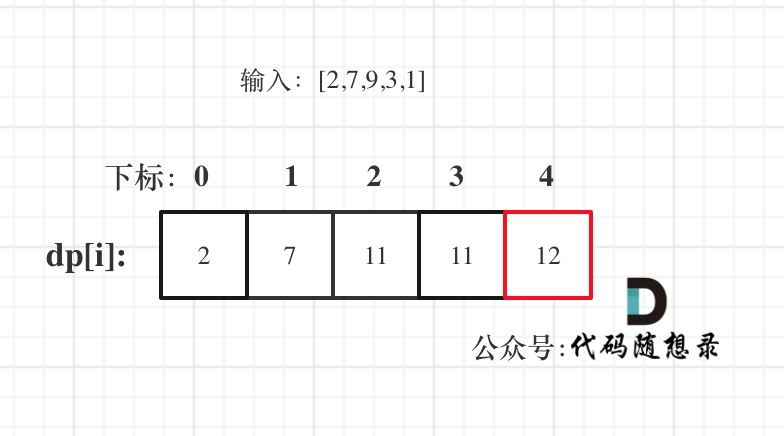
|
||||
|
||||
红框dp[nums.size() - 1]为结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 链表操作中,可以使用原链表来直接进行删除操作,也可以设置一个虚拟头结点再进行删除操作,接下来看一看哪种方式更方便。
|
||||
|
||||
# 203.移除链表元素
|
||||
|
|
@ -13,17 +15,17 @@
|
|||
|
||||
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
|
||||
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
|
||||
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
输入:head = [], val = 1
|
||||
输出:[]
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
输入:head = [], val = 1
|
||||
输出:[]
|
||||
|
||||
示例 3:
|
||||
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
|
||||
输出:[]
|
||||
示例 3:
|
||||
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
|
||||
输出:[]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,11 +34,11 @@
|
|||
|
||||
这里以链表 1 4 2 4 来举例,移除元素4。
|
||||
|
||||
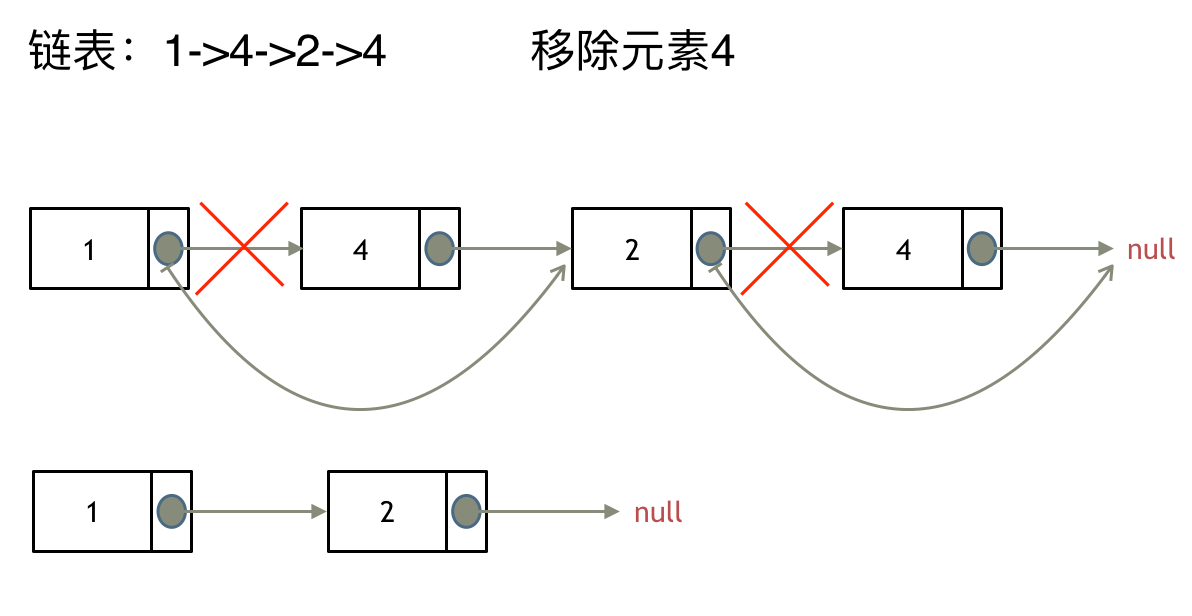
|
||||
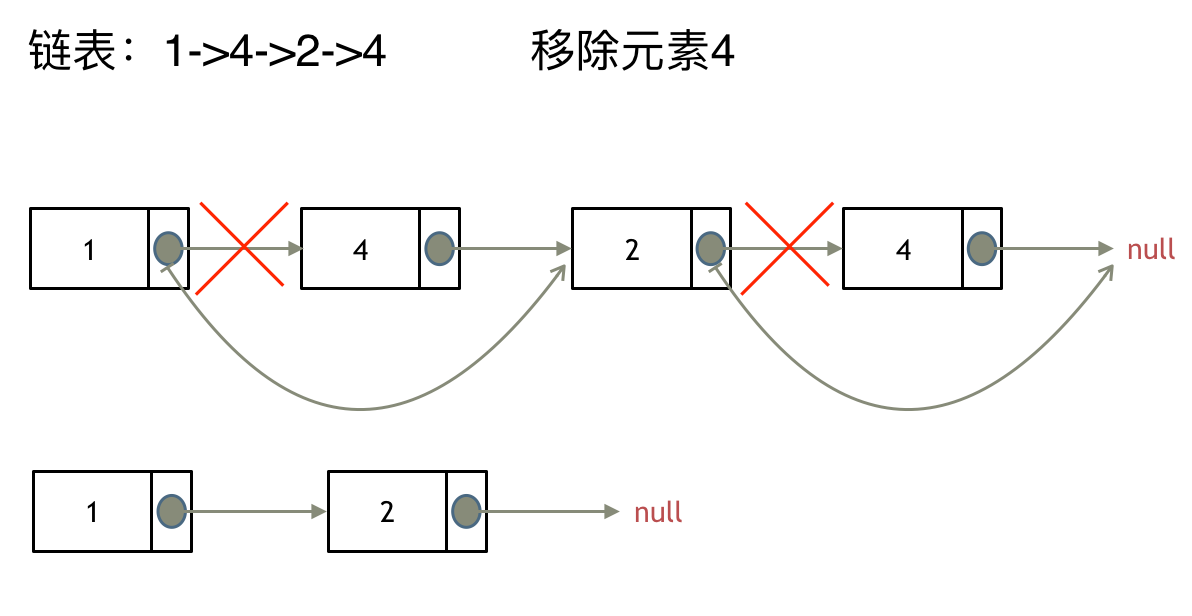
|
||||
|
||||
如果使用C,C++编程语言的话,不要忘了还要从内存中删除这两个移除的节点, 清理节点内存之后如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**当然如果使用java ,python的话就不用手动管理内存了。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,23 +49,23 @@
|
|||
那么因为单链表的特殊性,只能指向下一个节点,刚刚删除的是链表的中第二个,和第四个节点,那么如果删除的是头结点又该怎么办呢?
|
||||
|
||||
这里就涉及如下链表操作的两种方式:
|
||||
|
||||
* **直接使用原来的链表来进行删除操作。**
|
||||
* **设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
来看第一种操作:直接使用原来的链表来进行移除。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
移除头结点和移除其他节点的操作是不一样的,因为链表的其他节点都是通过前一个节点来移除当前节点,而头结点没有前一个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
所以头结点如何移除呢,其实只要将头结点向后移动一位就可以,这样就从链表中移除了一个头结点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
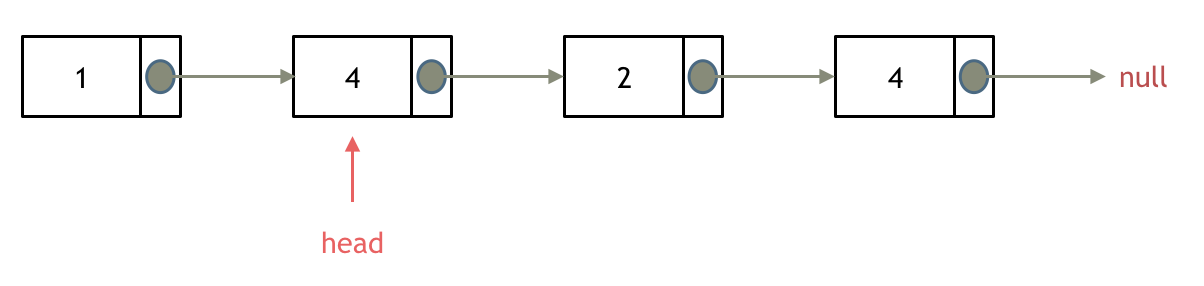
|
||||
|
||||
依然别忘将原头结点从内存中删掉。
|
||||

|
||||
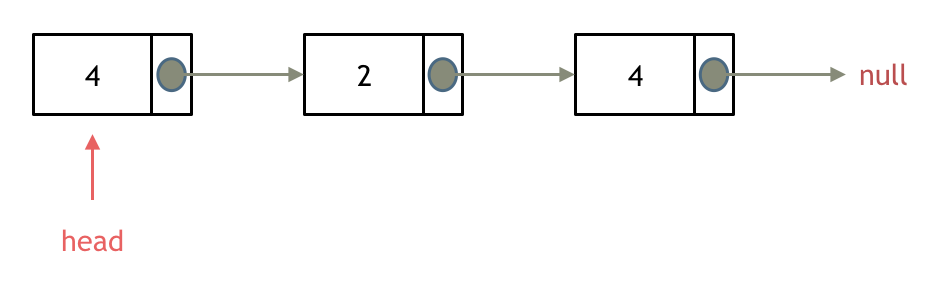
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这样移除了一个头结点,是不是发现,在单链表中移除头结点 和 移除其他节点的操作方式是不一样,其实在写代码的时候也会发现,需要单独写一段逻辑来处理移除头结点的情况。
|
||||
|
|
@ -74,7 +76,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
来看看如何设置一个虚拟头。依然还是在这个链表中,移除元素1。
|
||||
|
||||
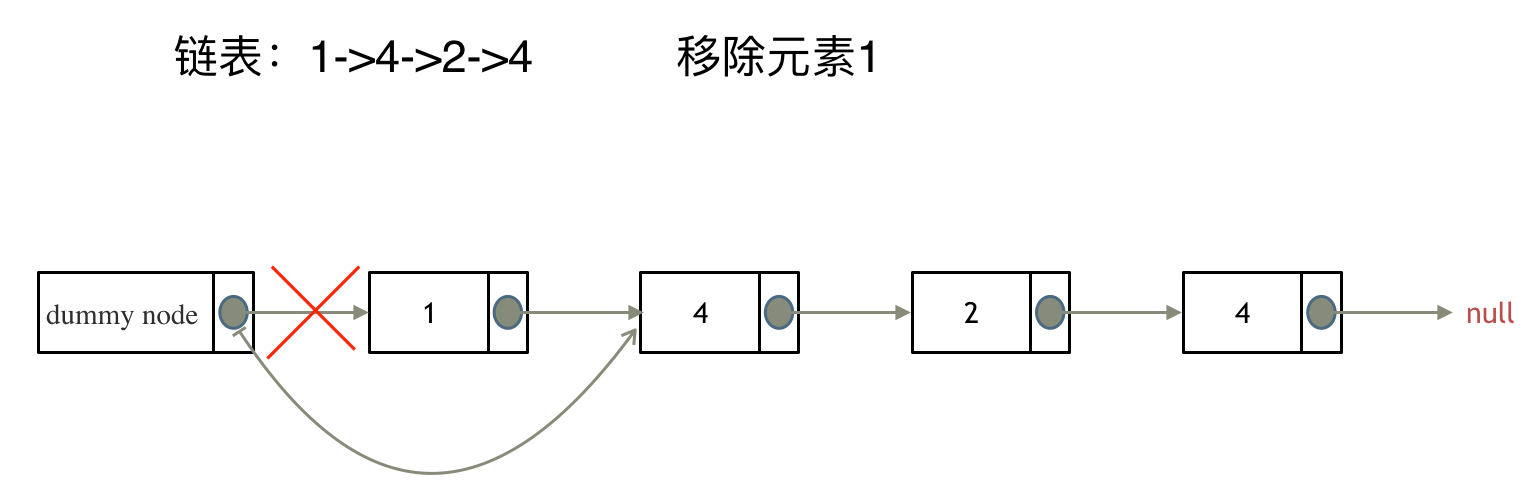
|
||||
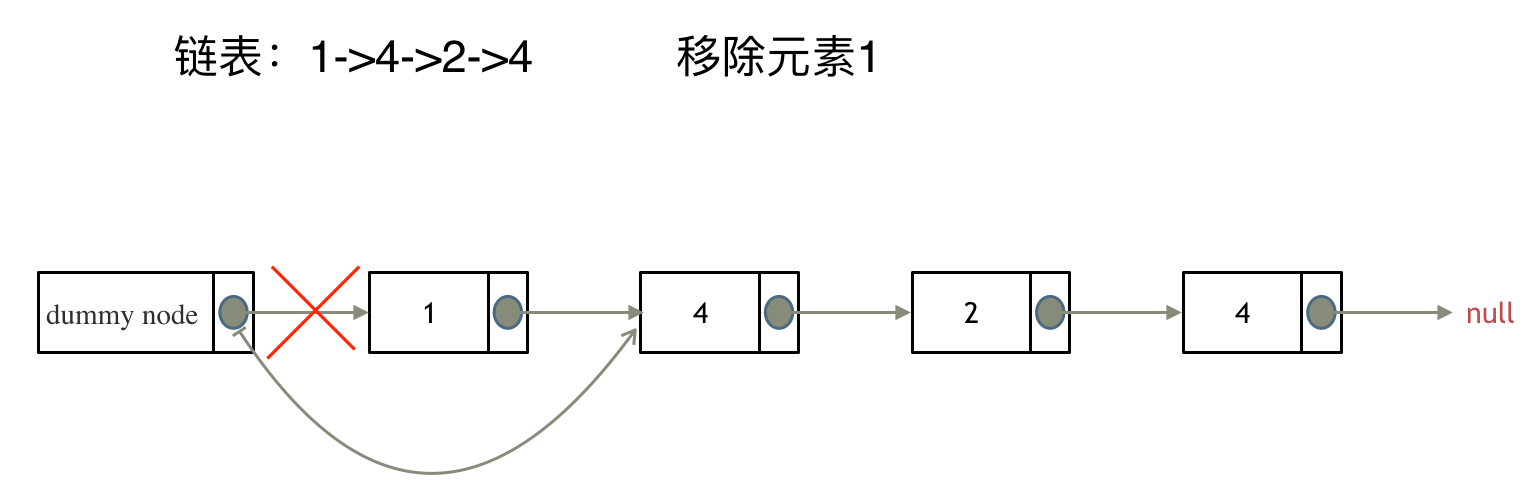
|
||||
|
||||
这里来给链表添加一个虚拟头结点为新的头结点,此时要移除这个旧头结点元素1。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,8 +148,10 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
C:
|
||||
用原来的链表操作:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
|
||||
struct ListNode* temp;
|
||||
|
|
@ -168,7 +172,7 @@ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
|
|||
// 将cur->next设置为cur->next->next并删除cur->next
|
||||
cur->next = temp->next;
|
||||
free(temp);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 若cur->next不等于val,则将cur后移一位
|
||||
else
|
||||
cur = cur->next;
|
||||
|
|
@ -178,7 +182,9 @@ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
|
|||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
设置一个虚拟头结点:
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,6 +218,7 @@ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 添加虚节点方式
|
||||
|
|
@ -292,6 +299,7 @@ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
# class ListNode:
|
||||
|
|
@ -335,7 +343,7 @@ func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
javaScript:
|
||||
javaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
/**
|
||||
|
|
@ -442,6 +450,7 @@ func removeElements(_ head: ListNode?, _ val: Int) -> ListNode? {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
PHP:
|
||||
|
||||
```php
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
|
|
@ -469,6 +478,7 @@ func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
RUST:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
|
||||
|
|
@ -476,7 +486,7 @@ RUST:
|
|||
// pub val: i32,
|
||||
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// impl ListNode {
|
||||
// #[inline]
|
||||
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
|
||||
|
|
@ -504,7 +514,9 @@ impl Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Scala:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||||
|
|
@ -535,7 +547,9 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Kotlin:
|
||||
|
||||
```kotlin
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Example:
|
||||
|
|
@ -569,6 +583,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
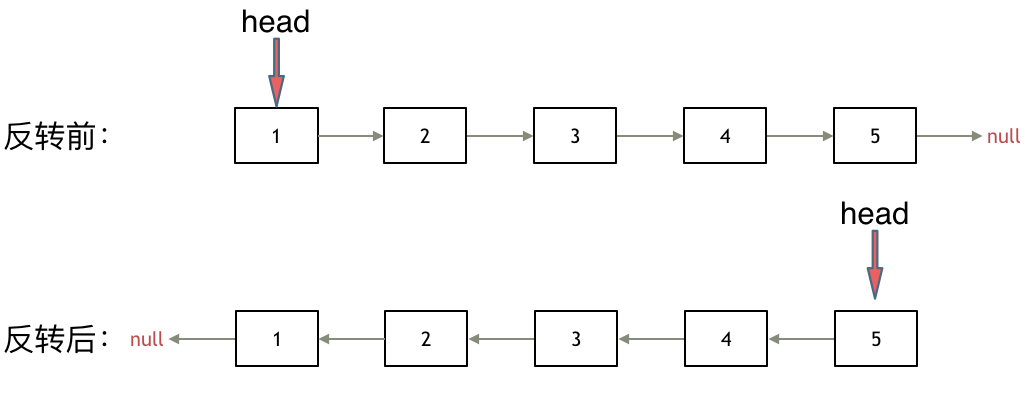
|
||||
|
||||
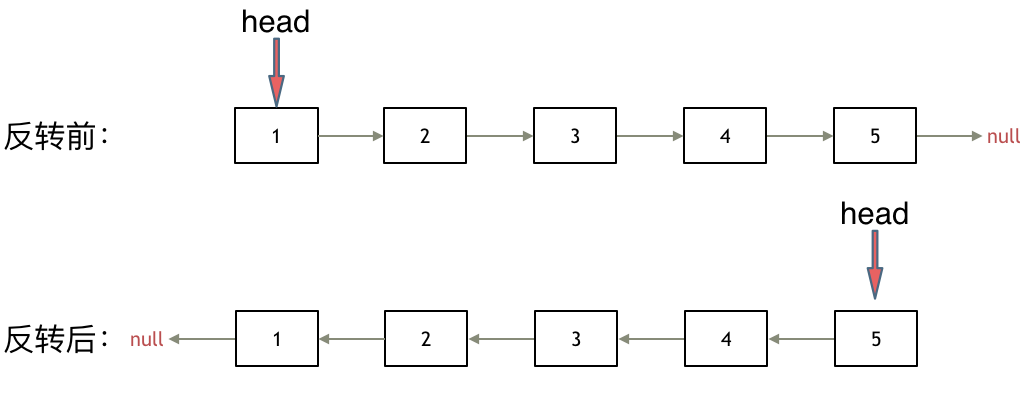
|
||||
|
||||
之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
解题的关键在于 窗口的起始位置如何移动,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以发现**滑动窗口的精妙之处在于根据当前子序列和大小的情况,不断调节子序列的起始位置。从而将O(n^2)暴力解法降为O(n)。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -39,15 +39,15 @@
|
|||
|
||||
* 情况一:考虑不包含首尾元素
|
||||
|
||||
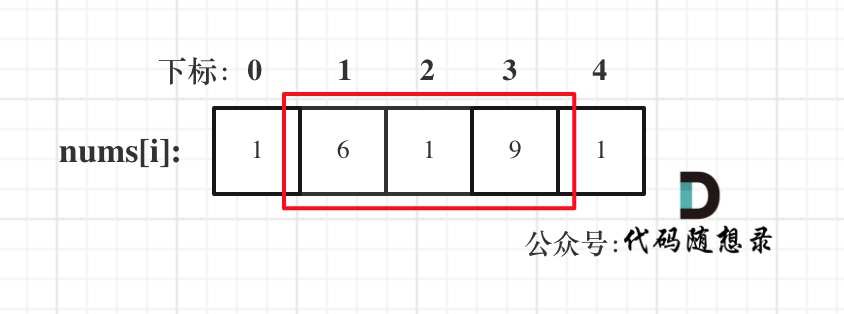
|
||||
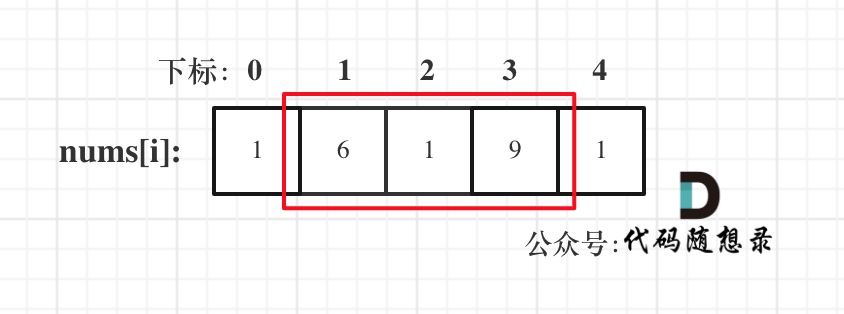
|
||||
|
||||
* 情况二:考虑包含首元素,不包含尾元素
|
||||
|
||||
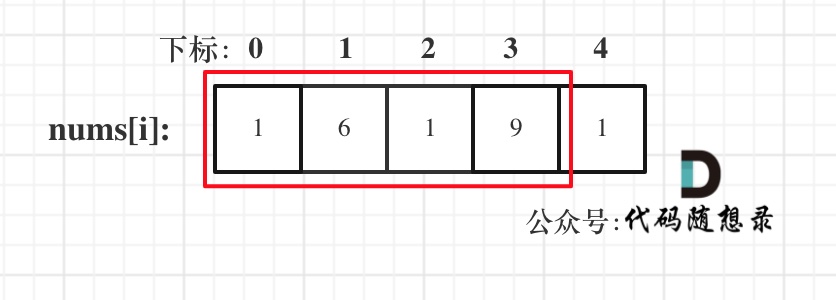
|
||||
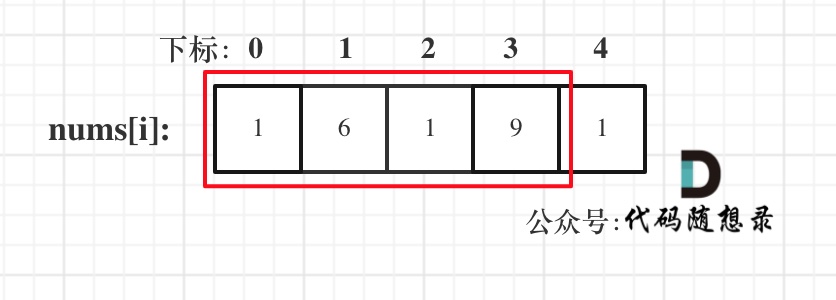
|
||||
|
||||
* 情况三:考虑包含尾元素,不包含首元素
|
||||
|
||||
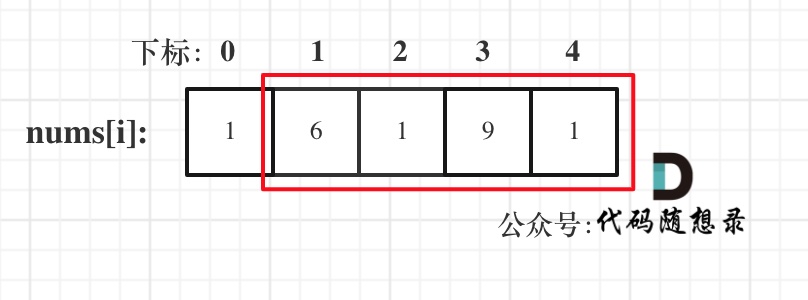
|
||||
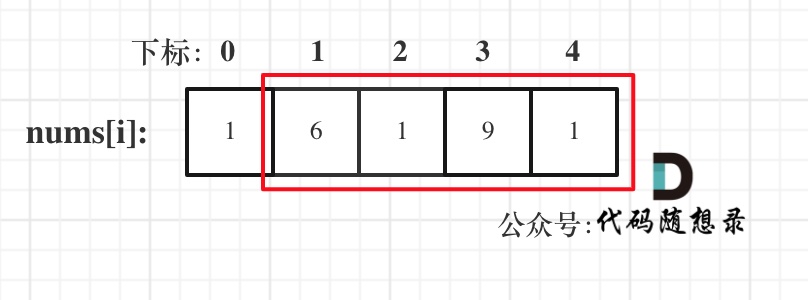
|
||||
|
||||
**注意我这里用的是"考虑"**,例如情况三,虽然是考虑包含尾元素,但不一定要选尾部元素! 对于情况三,取nums[1] 和 nums[3]就是最大的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -7,17 +8,19 @@
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 别看本篇选的是组合总和III,而不是组合总和,本题和上一篇77.组合相比难度刚刚好!
|
||||
|
||||
# 216.组合总和III
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/)
|
||||
|
||||
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
|
||||
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
|
||||
|
||||
说明:
|
||||
|
||||
* 所有数字都是正整数。
|
||||
* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
|
||||
* 解集不能包含重复的组合。
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
输入: k = 3, n = 7
|
||||
|
|
@ -46,7 +49,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
选取过程如图:
|
||||
|
||||
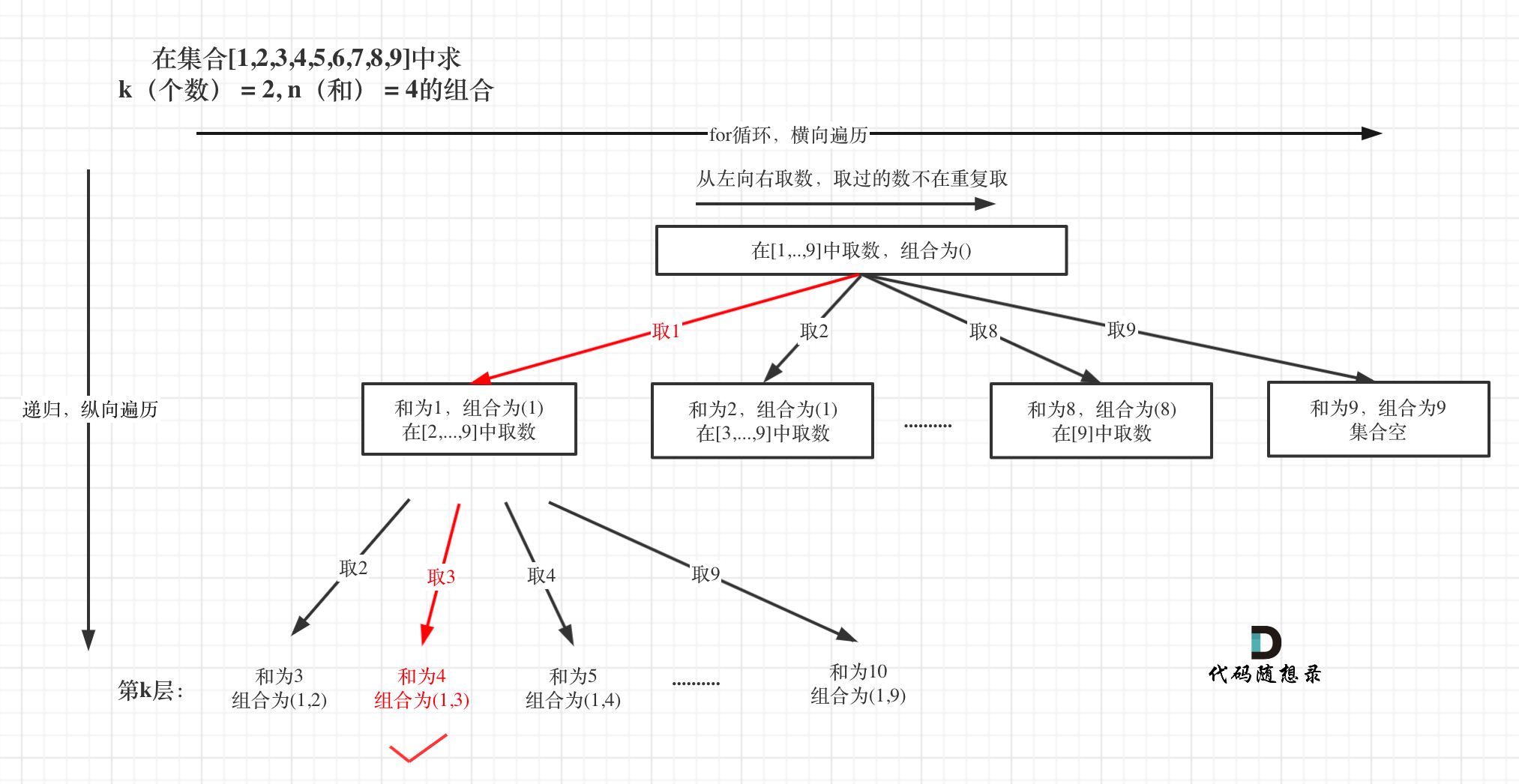
|
||||
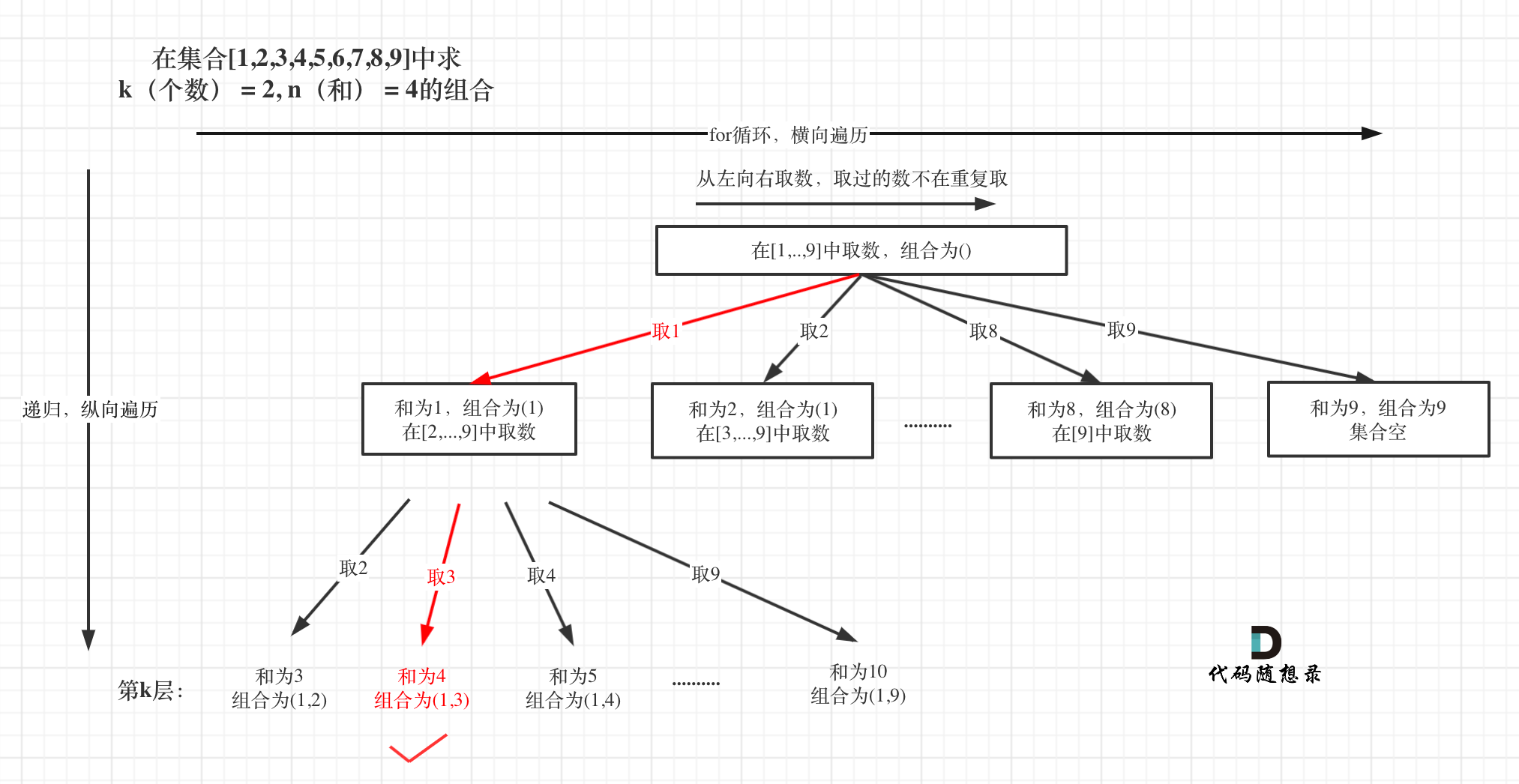
|
||||
|
||||
图中,可以看出,只有最后取到集合(1,3)和为4 符合条件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,6 +83,7 @@ vector<vector<int>> result;
|
|||
vector<int> path;
|
||||
void backtracking(int targetSum, int k, int sum, int startIndex)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其实这里sum这个参数也可以省略,每次targetSum减去选取的元素数值,然后判断如果targetSum为0了,说明收集到符合条件的结果了,我这里为了直观便于理解,还是加一个sum参数。
|
||||
|
||||
还要强调一下,回溯法中递归函数参数很难一次性确定下来,一般先写逻辑,需要啥参数了,填什么参数。
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,7 +112,7 @@ if (path.size() == k) {
|
|||
本题和[77. 组合](https://programmercarl.com/0077.组合.html)区别之一就是集合固定的就是9个数[1,...,9],所以for循环固定i<=9
|
||||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||

|
||||
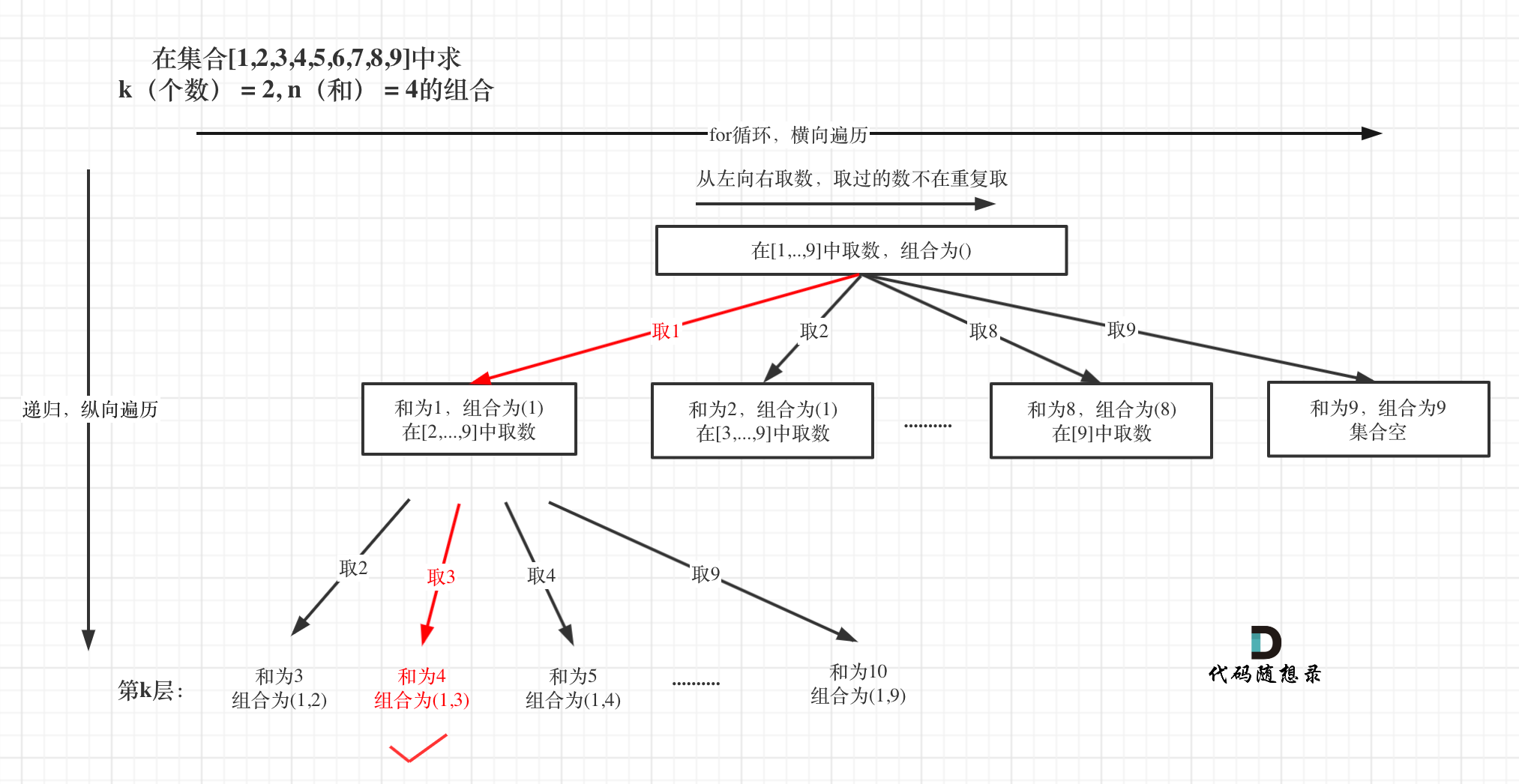
|
||||
|
||||
处理过程就是 path收集每次选取的元素,相当于树型结构里的边,sum来统计path里元素的总和。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -166,7 +170,7 @@ public:
|
|||
这道题目,剪枝操作其实是很容易想到了,想必大家看上面的树形图的时候已经想到了。
|
||||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
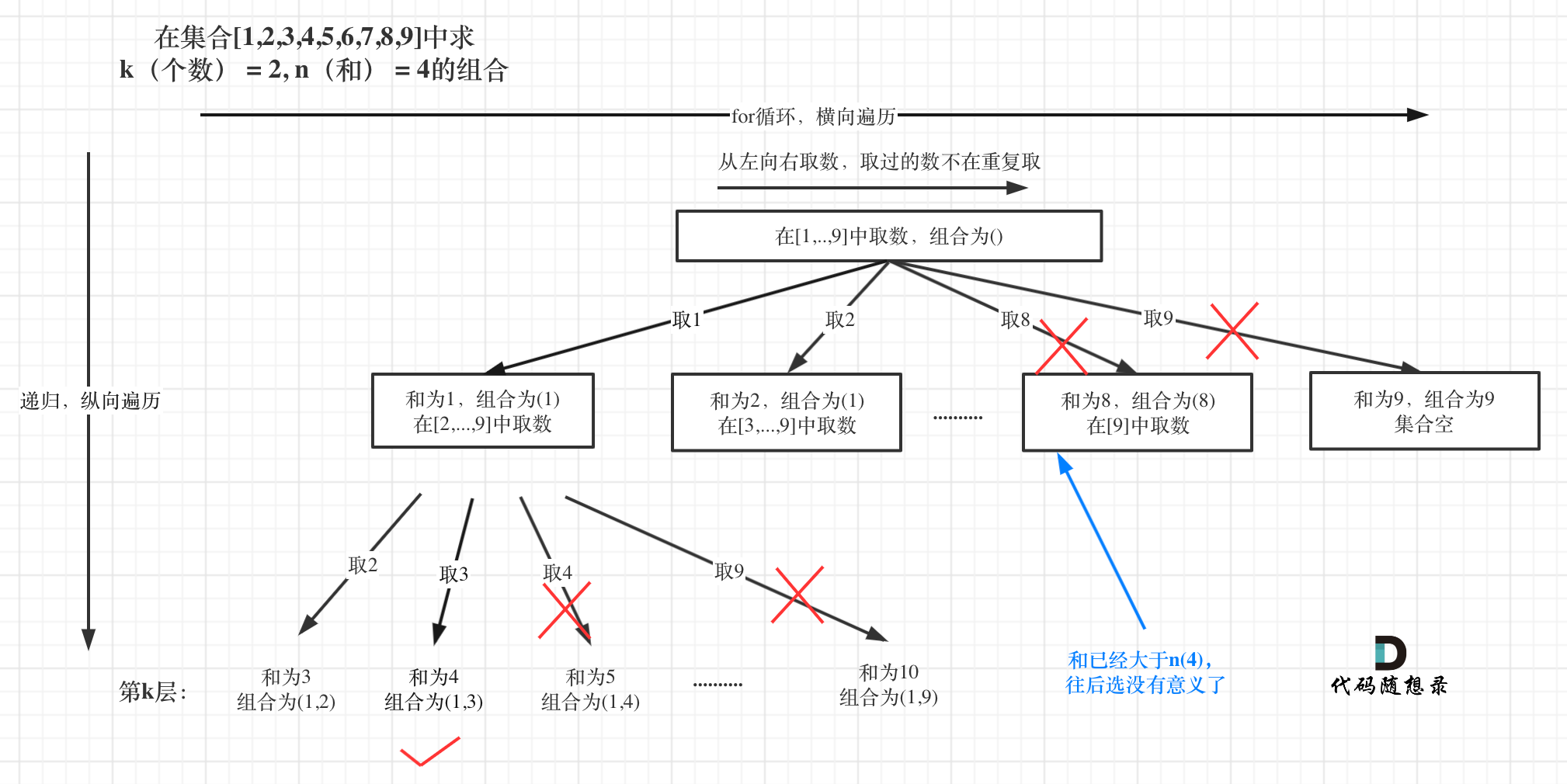
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
已选元素总和如果已经大于n(图中数值为4)了,那么往后遍历就没有意义了,直接剪掉。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -181,7 +185,6 @@ if (sum > targetSum) { // 剪枝操作
|
|||
当然这个剪枝也可以放在 调用递归之前,即放在这里,只不过要记得 要回溯操作给做了。
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++) { // 剪枝
|
||||
sum += i; // 处理
|
||||
path.push_back(i); // 处理
|
||||
|
|
@ -250,6 +253,7 @@ public:
|
|||
## Java
|
||||
|
||||
模板方法
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
|
|
@ -317,6 +321,7 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
其他方法
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
|
||||
|
|
@ -429,12 +434,12 @@ var combinationSum3 = function(k, n) {
|
|||
const dfs = (path,index) => {
|
||||
// 剪枝操作
|
||||
if (sum > n){
|
||||
return
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (path.length == k) {
|
||||
if(sum == n){
|
||||
res.push([...path]);
|
||||
return
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (let i = index; i <= 9 - (k-path.length) + 1;i++) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
我来举一个典型的例子如题:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src='https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200920221638903.png' width=600> </img></div>
|
||||
<img src='https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20200920221638903-20230310123444151.png' width=600> </img>
|
||||
|
||||
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -161,10 +161,10 @@ public:
|
|||
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
|
||||
|
||||
完全二叉树(一)如图:
|
||||
|
||||
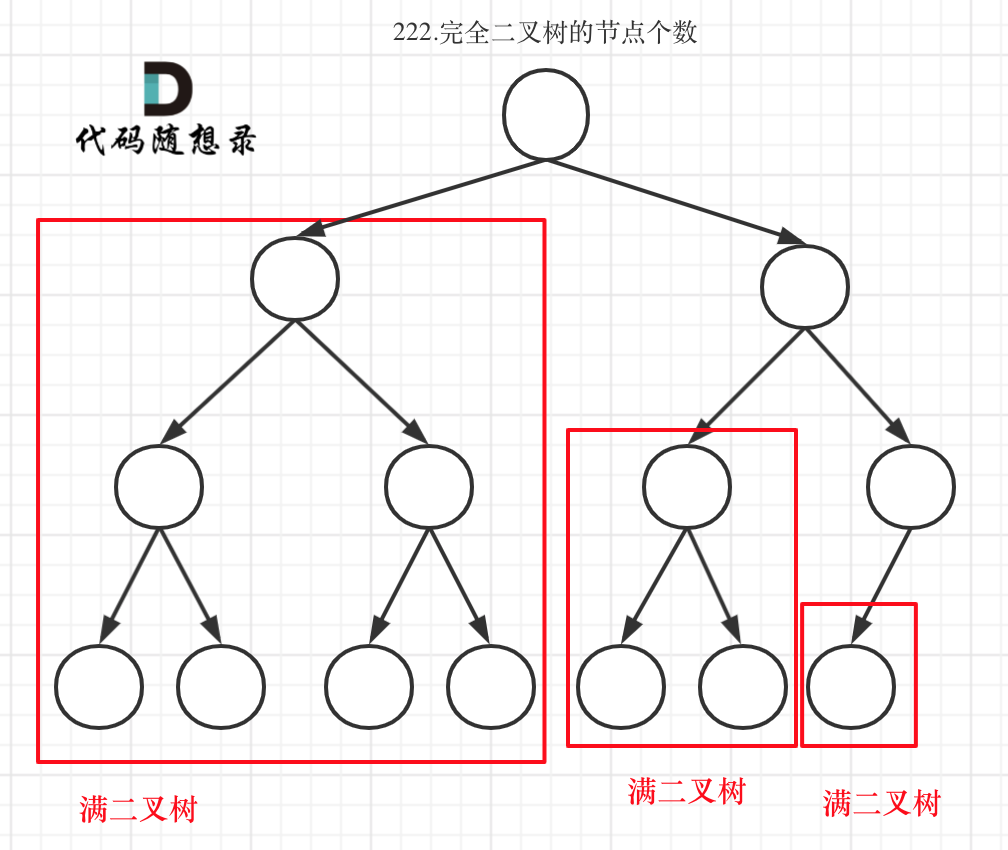
|
||||
|
||||
完全二叉树(二)如图:
|
||||

|
||||
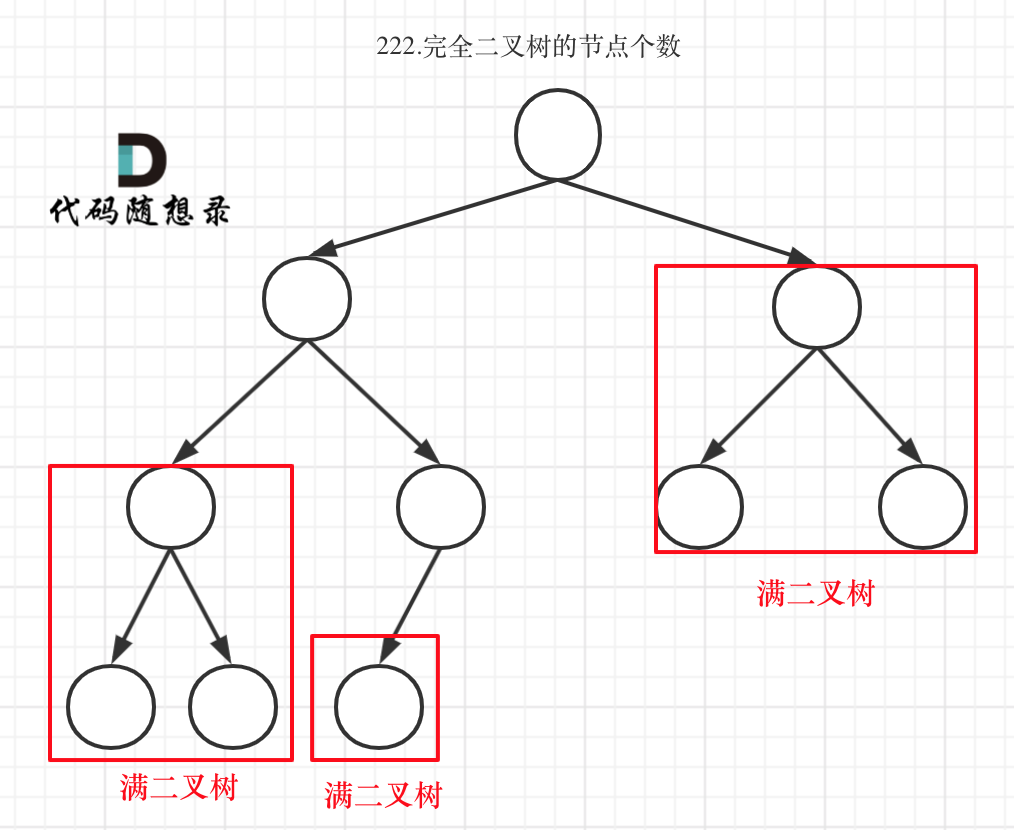
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
翻转一棵二叉树。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目背后有一个让程序员心酸的故事,听说 Homebrew的作者Max Howell,就是因为没在白板上写出翻转二叉树,最后被Google拒绝了。(真假不做判断,权当一个乐子哈)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +34,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如果要从整个树来看,翻转还真的挺复杂,整个树以中间分割线进行翻转,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以发现想要翻转它,其实就把每一个节点的左右孩子交换一下就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
|
||||
|
|
@ -130,7 +131,7 @@ left与right的逻辑处理; // 中
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
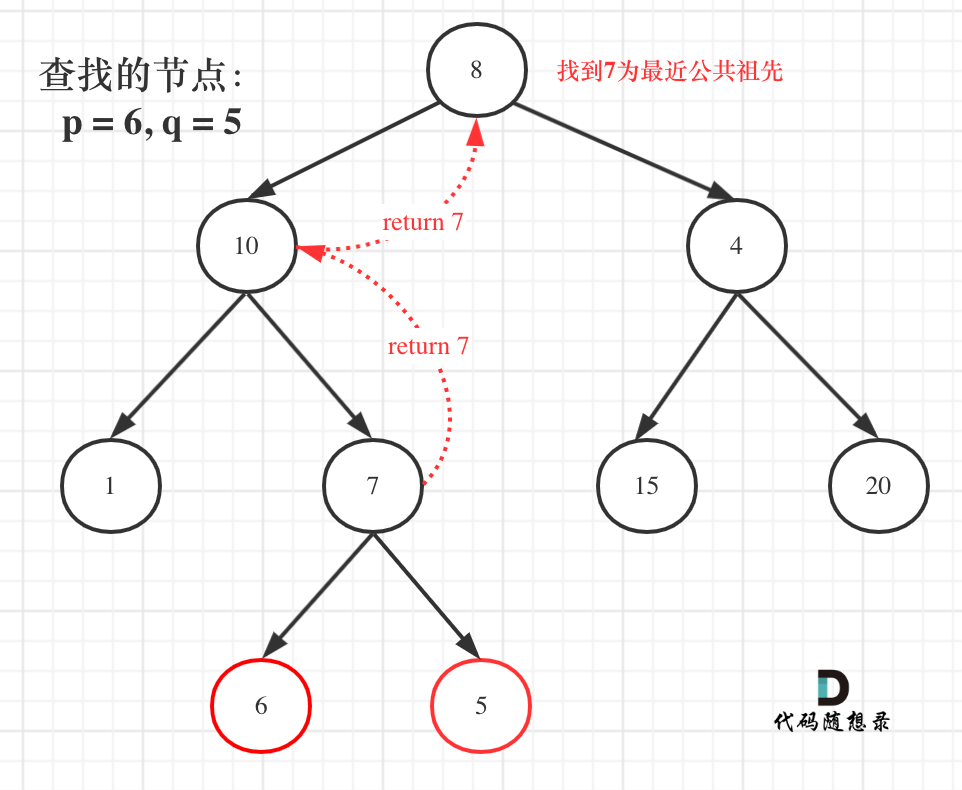
|
||||
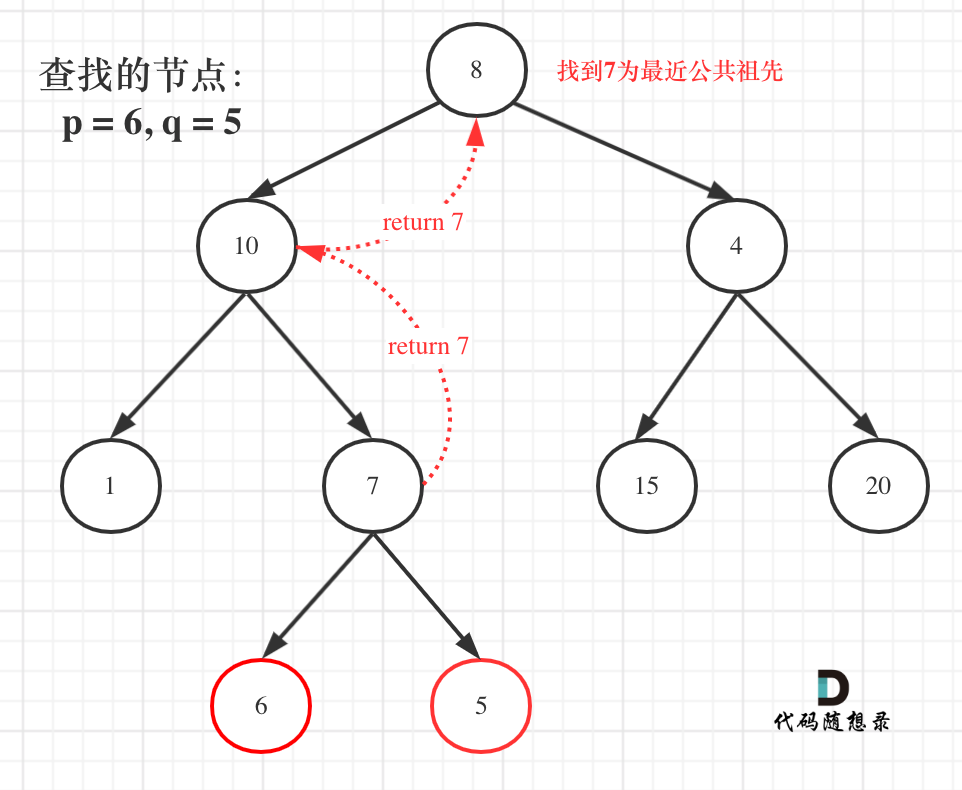
|
||||
|
||||
就像图中一样直接返回7,多美滋滋。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,7 +164,7 @@ TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
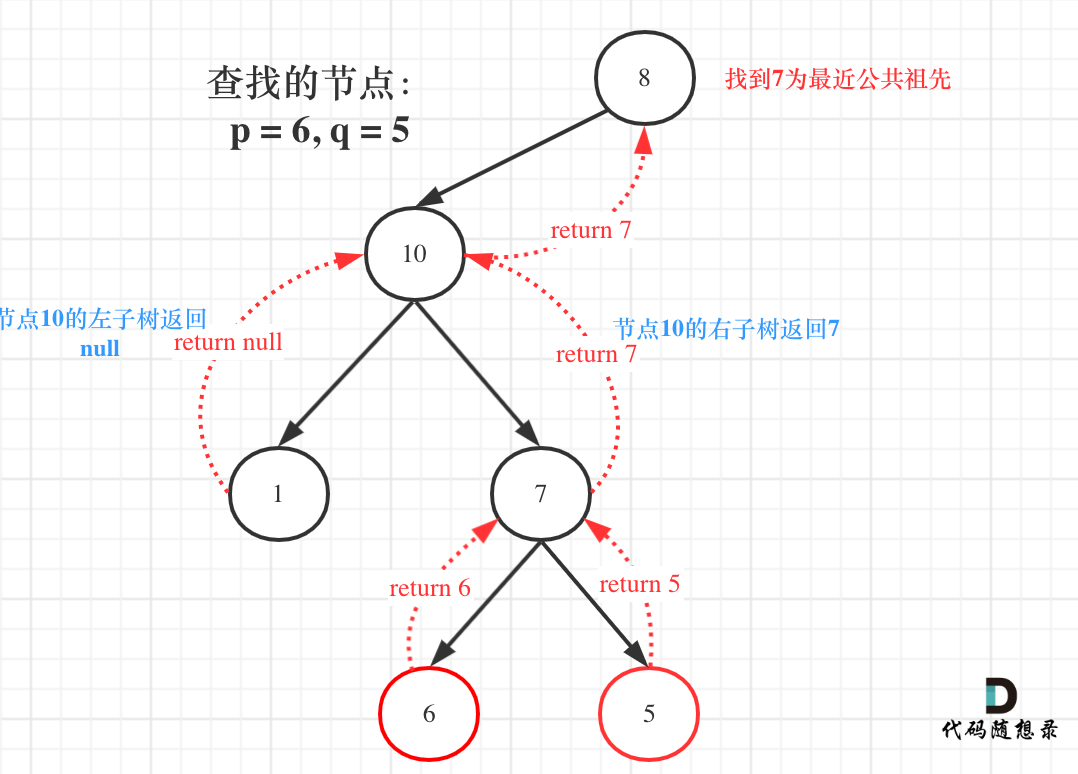
|
||||
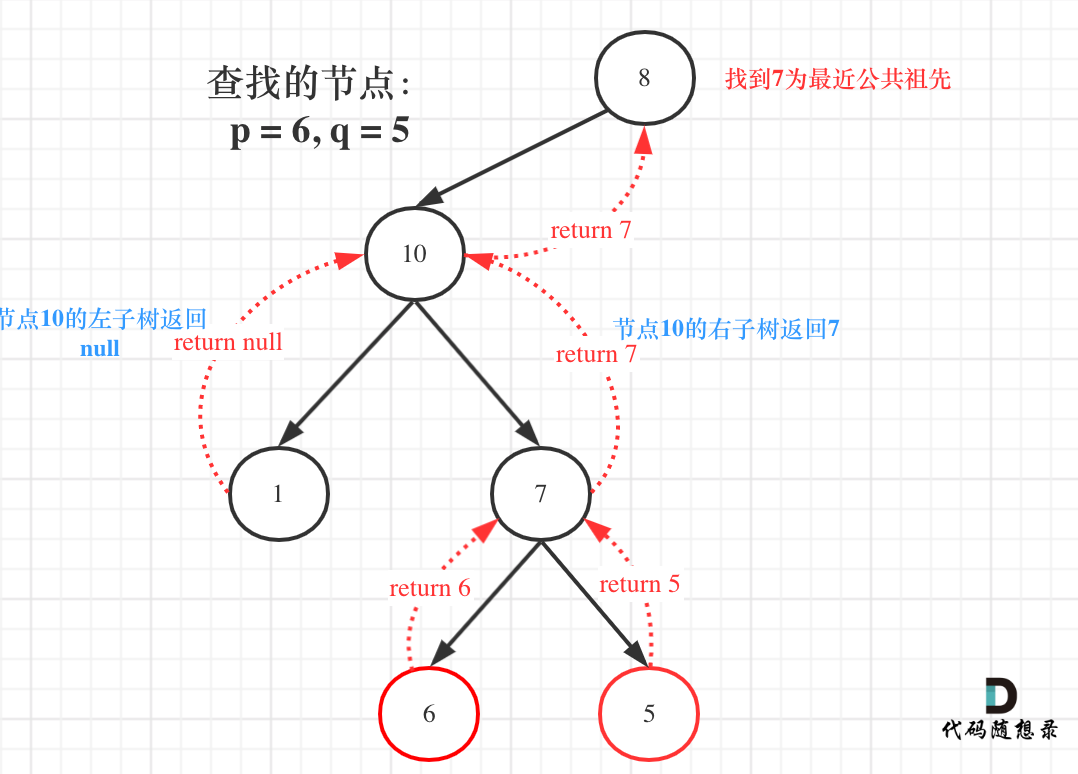
|
||||
|
||||
图中节点10的左子树返回null,右子树返回目标值7,那么此时节点10的处理逻辑就是把右子树的返回值(最近公共祖先7)返回上去!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -184,7 +185,7 @@ else { // (left == NULL && right == NULL)
|
|||
|
||||
那么寻找最小公共祖先,完整流程图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
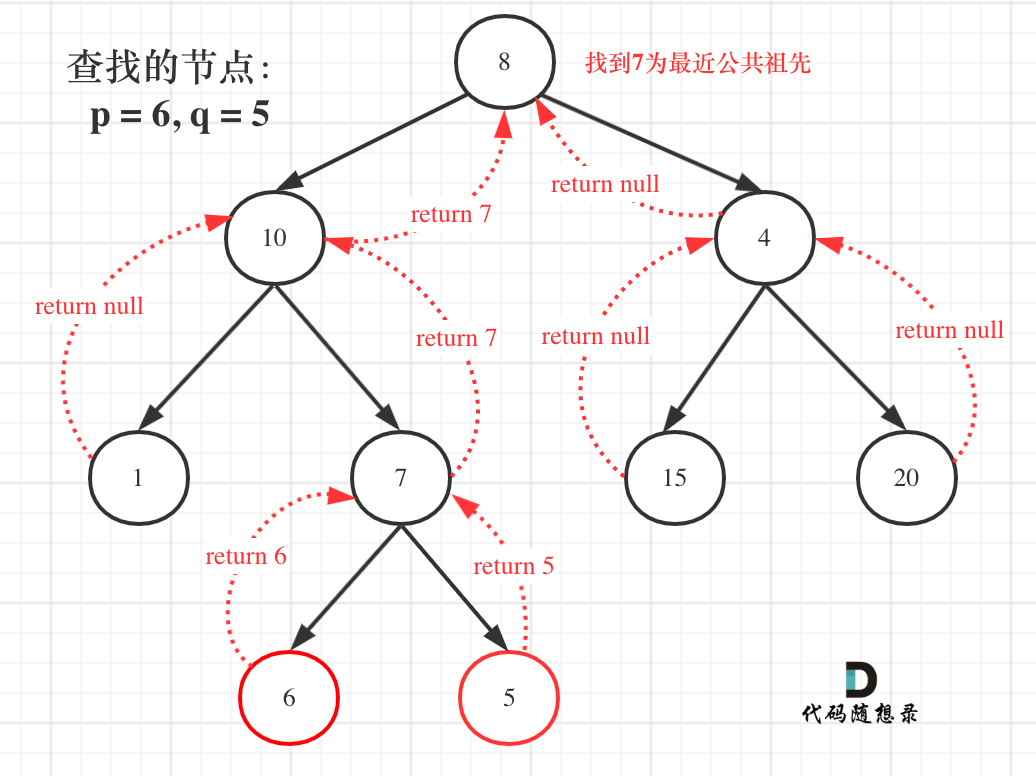
|
||||
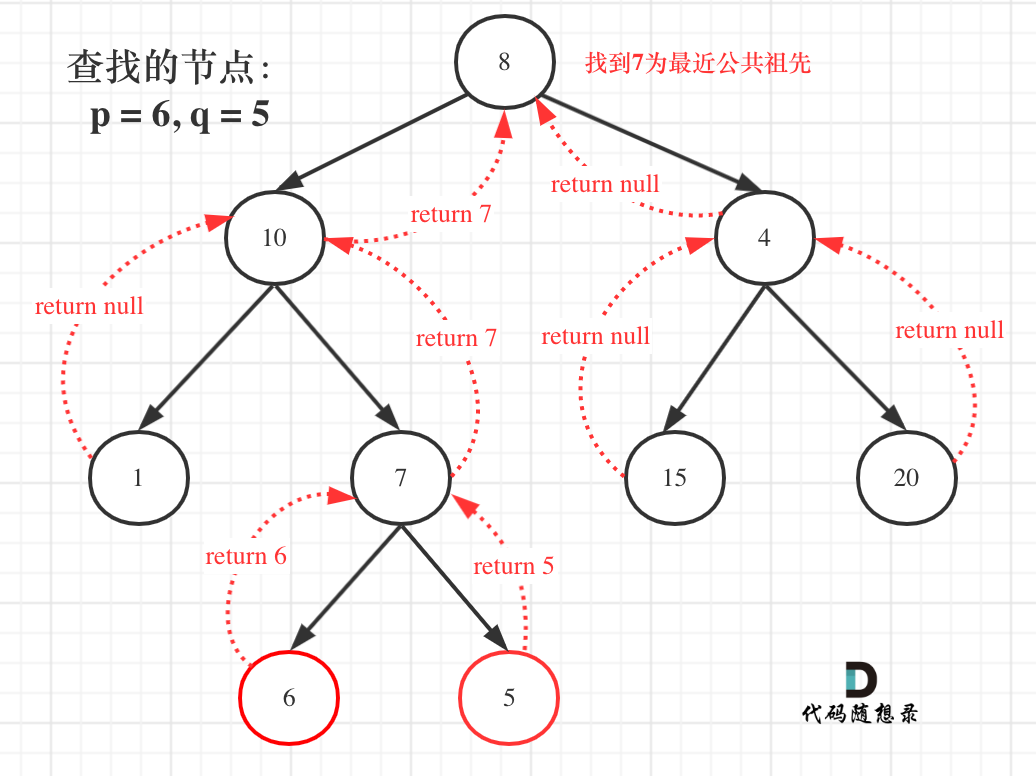
|
||||
|
||||
**从图中,大家可以看到,我们是如何回溯遍历整棵二叉树,将结果返回给头结点的!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
|||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
前序遍历以及回溯的过程如图:
|
||||
|
||||
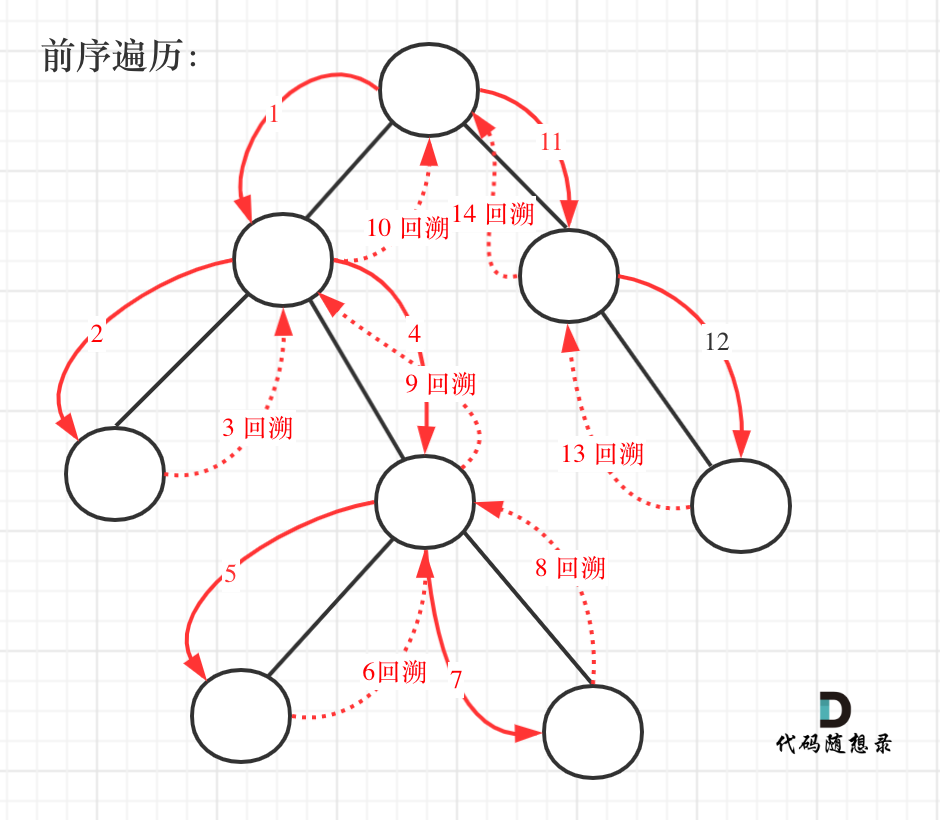
|
||||
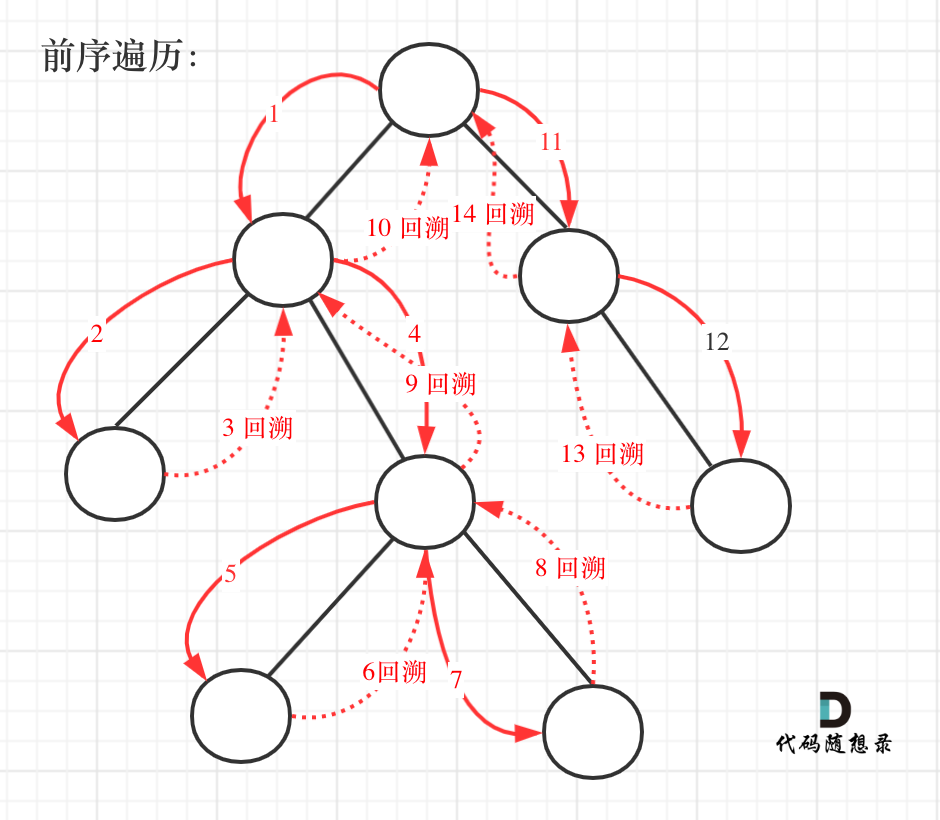
|
||||
|
||||
我们先使用递归的方式,来做前序遍历。**要知道递归和回溯就是一家的,本题也需要回溯。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -94,7 +94,8 @@ for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { // 遍历背包
|
|||
|
||||
已输入n为5例,dp状态图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
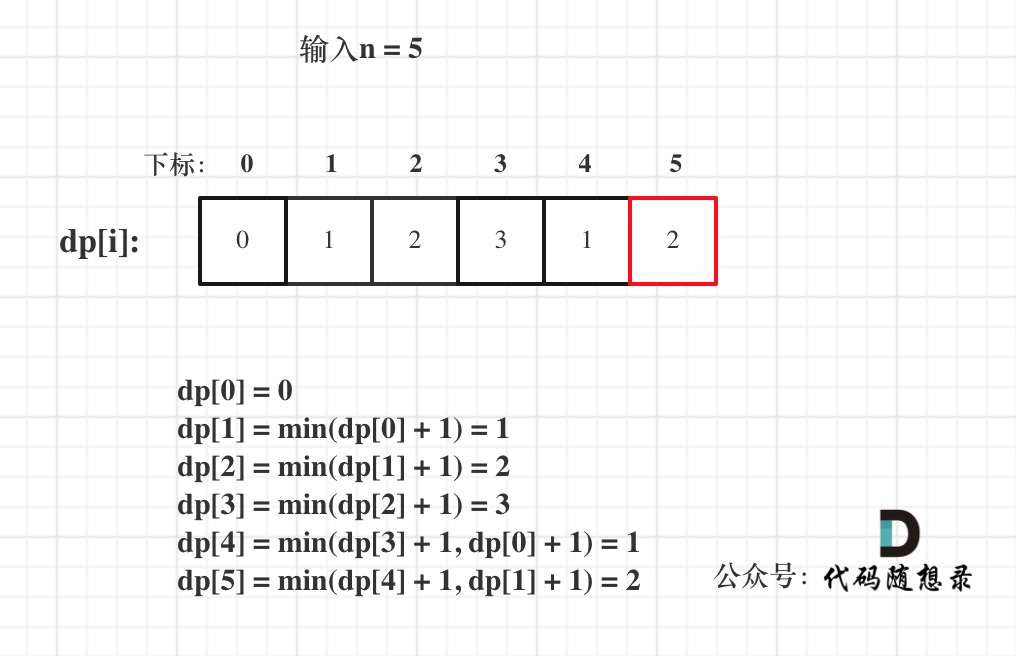
|
||||
|
||||
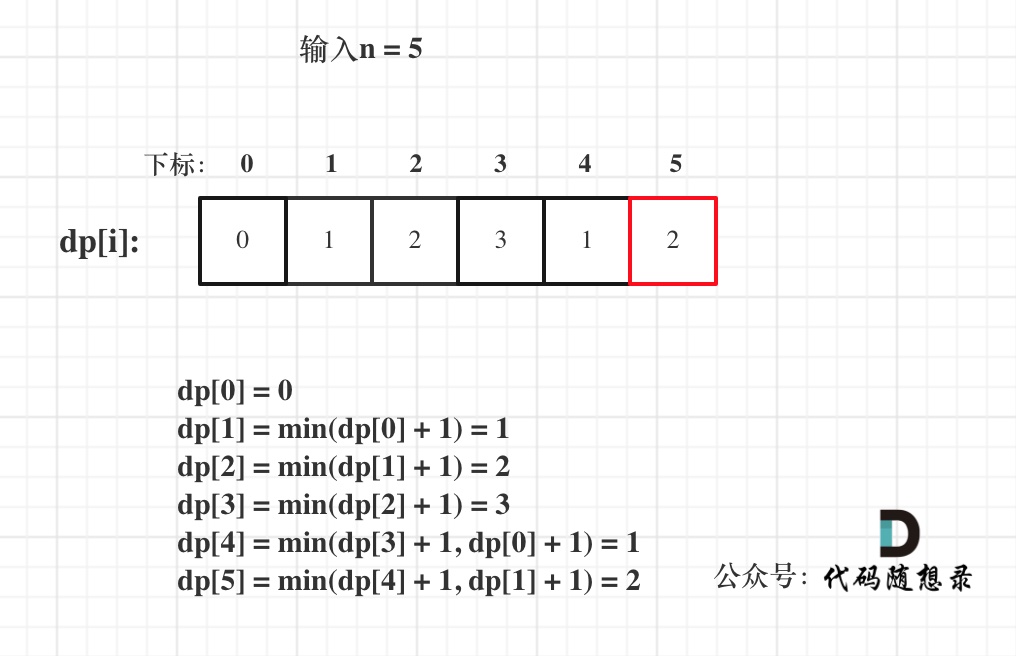
|
||||
|
||||
dp[0] = 0
|
||||
dp[1] = min(dp[0] + 1) = 1
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
输入:[0,1,0,3,2],dp数组的变化如下:
|
||||
|
||||
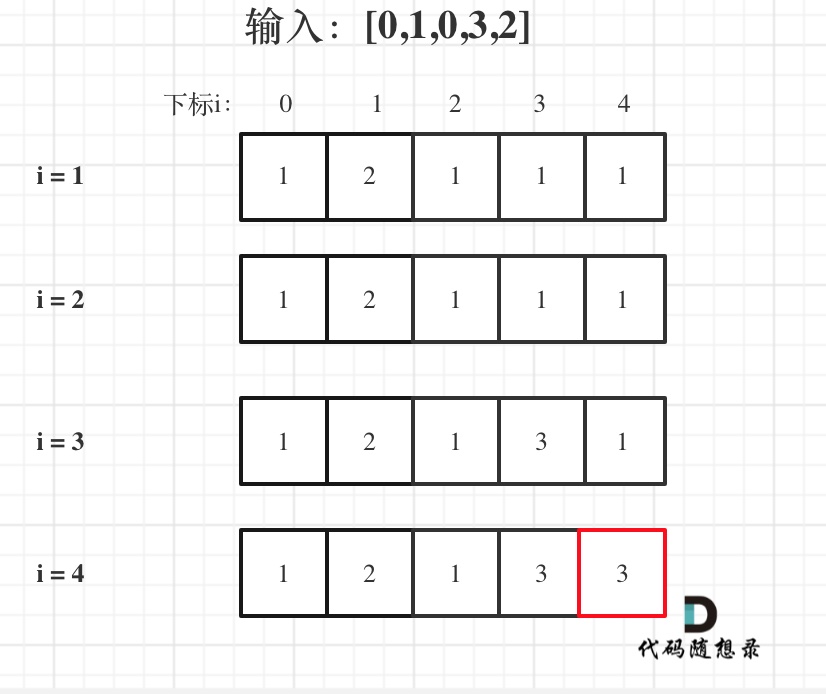
|
||||
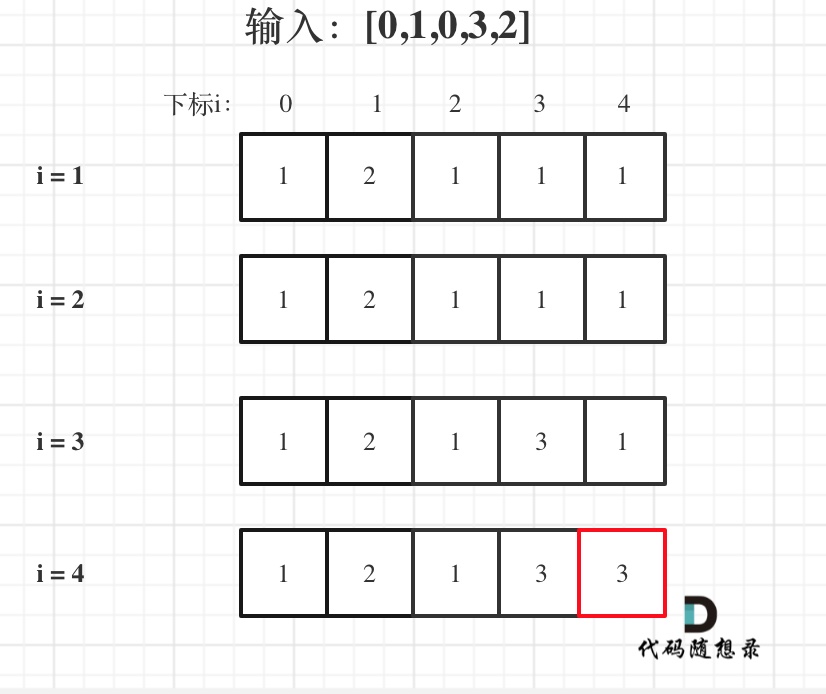
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果代码写出来,但一直AC不了,那么就把dp数组打印出来,看看对不对!
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ dp[i][j],第i天状态为j,所剩的最多现金为dp[i][j]。
|
|||
* 状态三:今天卖出股票
|
||||
* 状态四:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
j的状态为:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -133,7 +133,8 @@ dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2];
|
|||
|
||||
以 [1,2,3,0,2] 为例,dp数组如下:
|
||||
|
||||
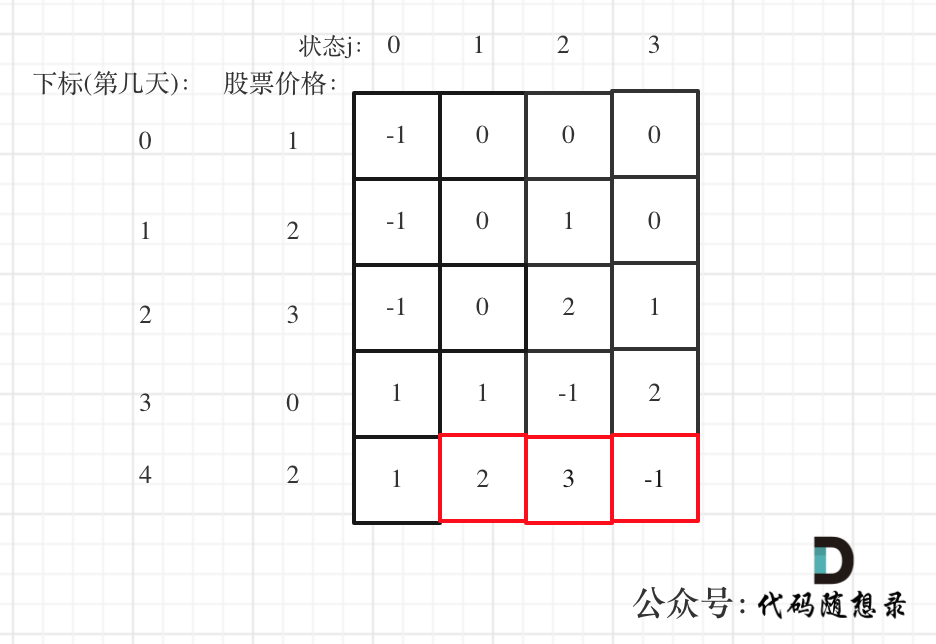
|
||||
|
||||
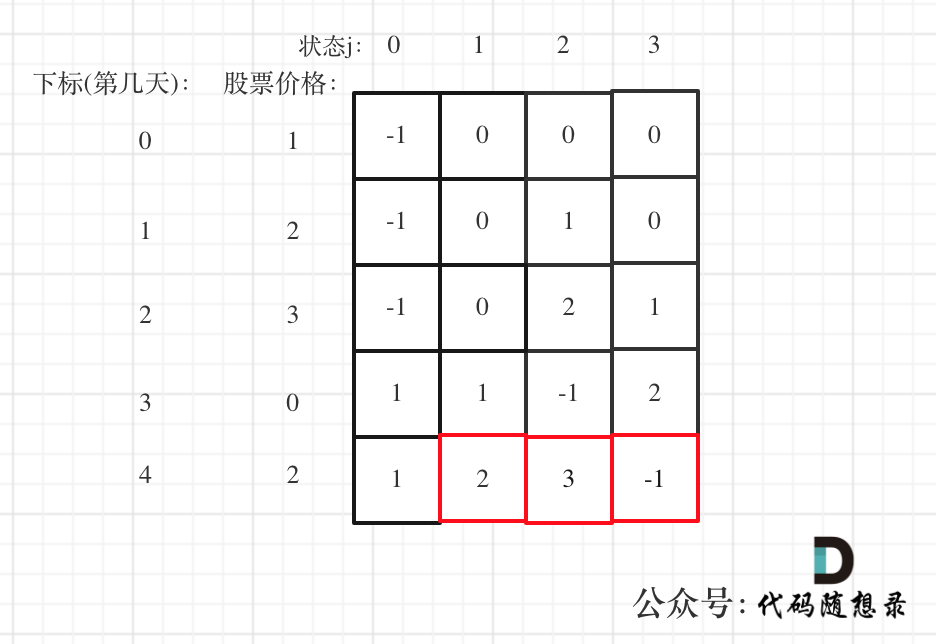
|
||||
|
||||
最后结果是取 状态二,状态三,和状态四的最大值,不少同学会把状态四忘了,状态四是冷冻期,最后一天如果是冷冻期也可能是最大值。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ dp[0] = 0;
|
|||
|
||||
以输入:coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 5为例
|
||||
|
||||
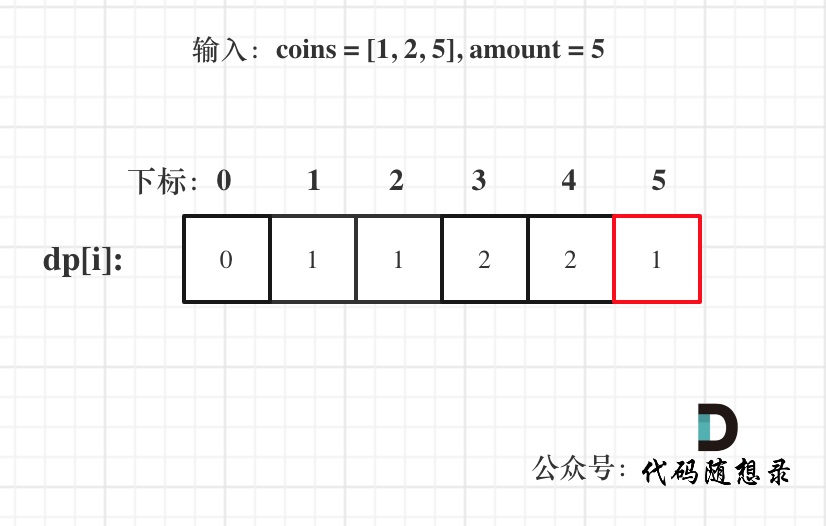
|
||||
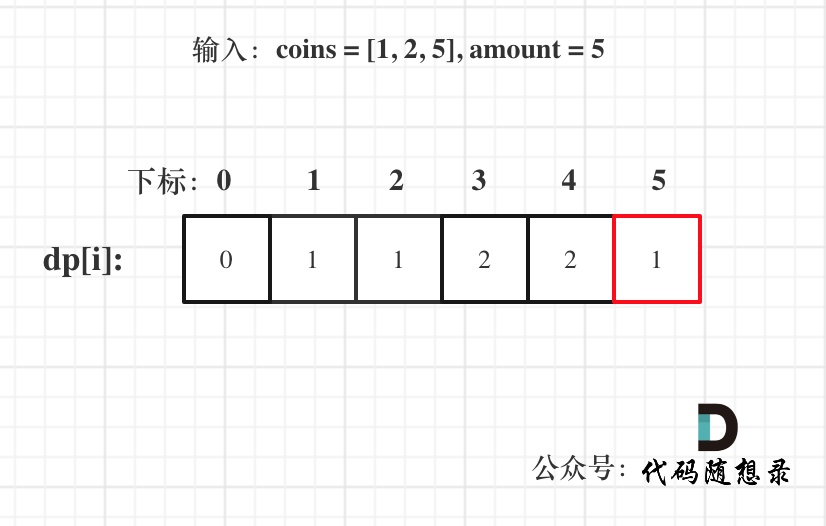
|
||||
|
||||
dp[amount]为最终结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
对于死循环,我来举一个有重复机场的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
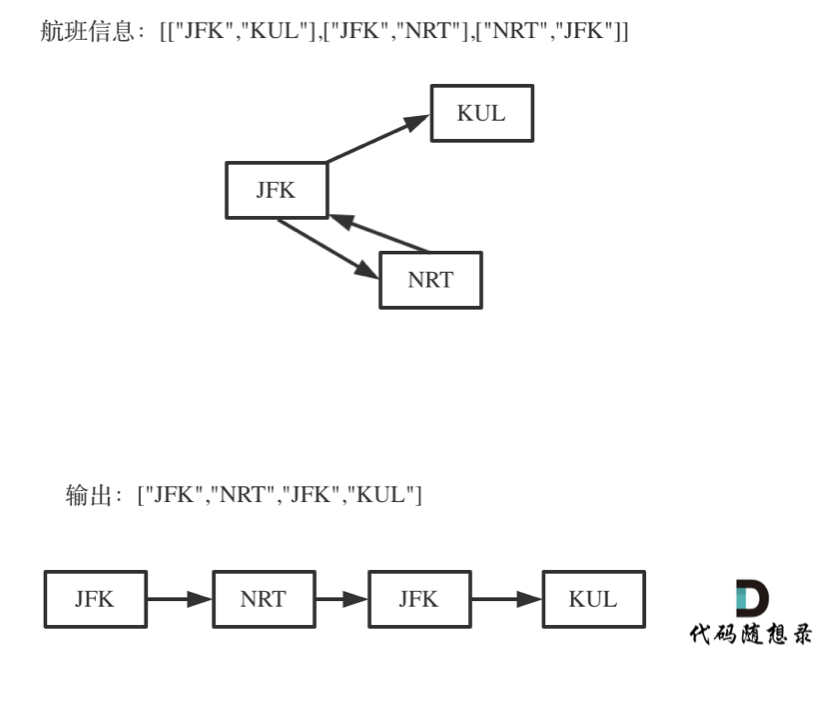
|
||||
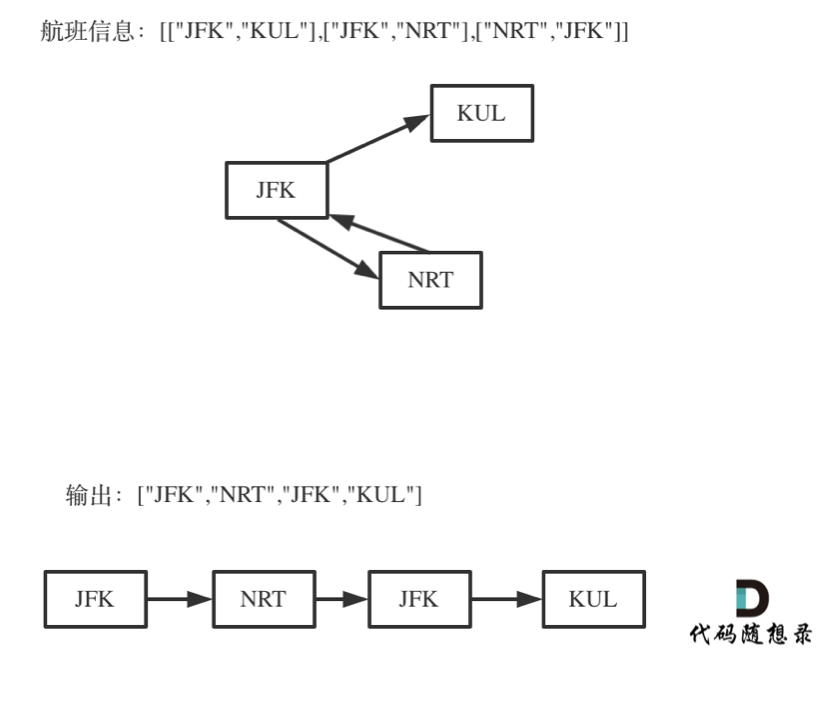
|
||||
|
||||
为什么要举这个例子呢,就是告诉大家,出发机场和到达机场也会重复的,**如果在解题的过程中没有对集合元素处理好,就会死循环。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ void backtracking(参数) {
|
|||
|
||||
本题以输入:[["JFK", "KUL"], ["JFK", "NRT"], ["NRT", "JFK"]为例,抽象为树形结构如下:
|
||||
|
||||
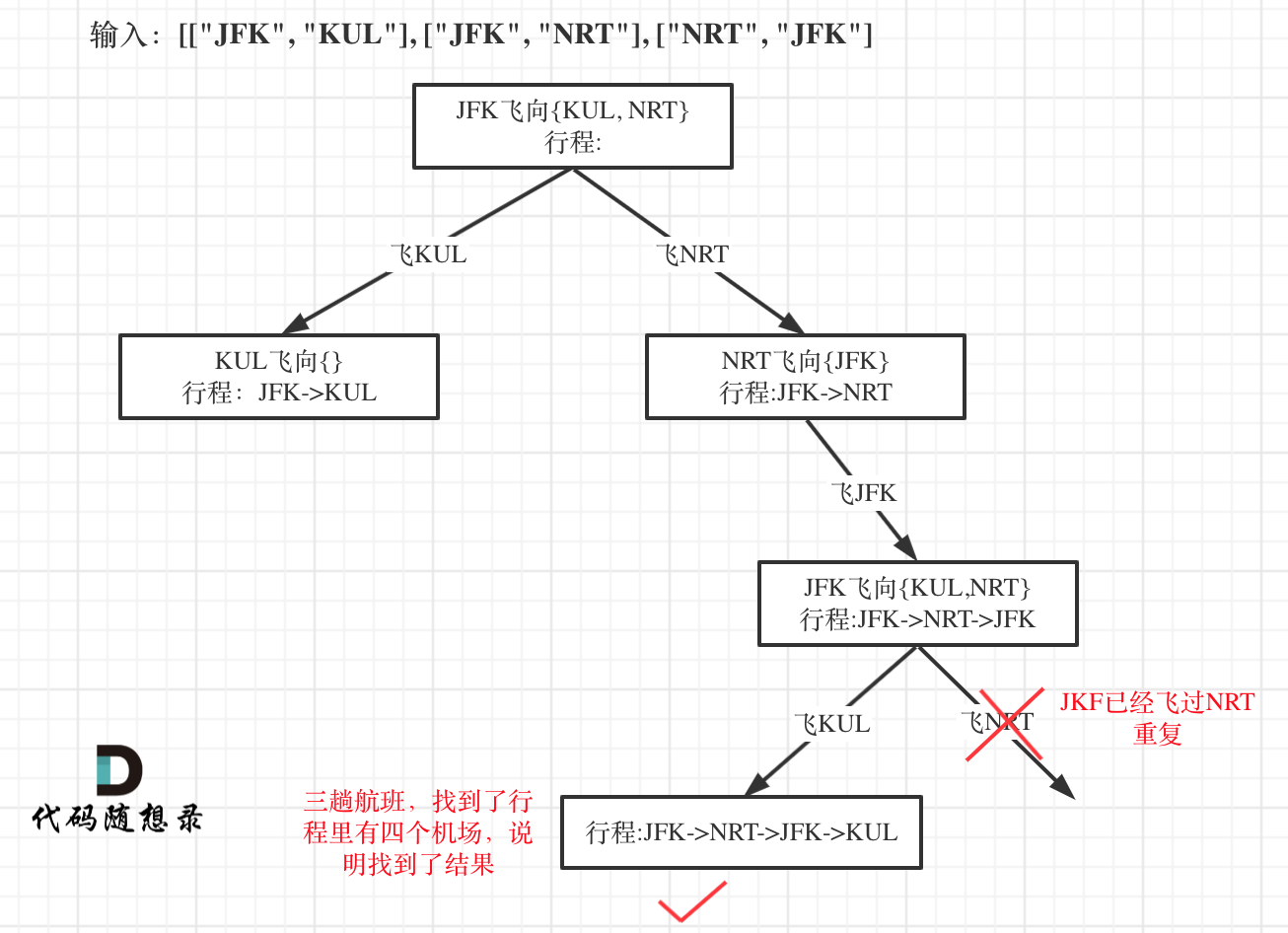
|
||||
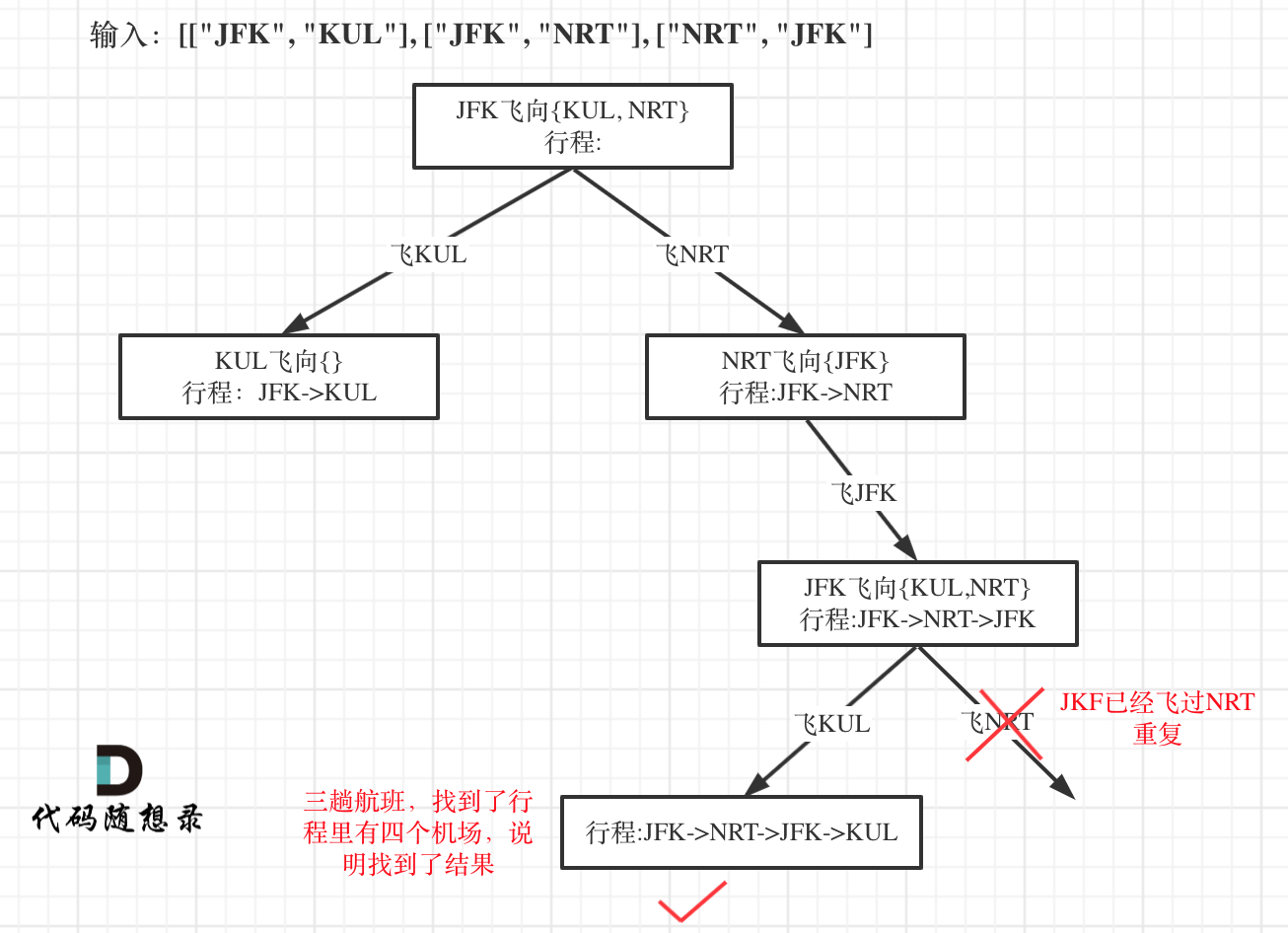
|
||||
|
||||
开始回溯三部曲讲解:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ bool backtracking(int ticketNum, vector<string>& result) {
|
|||
|
||||
因为我们只需要找到一个行程,就是在树形结构中唯一的一条通向叶子节点的路线,如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
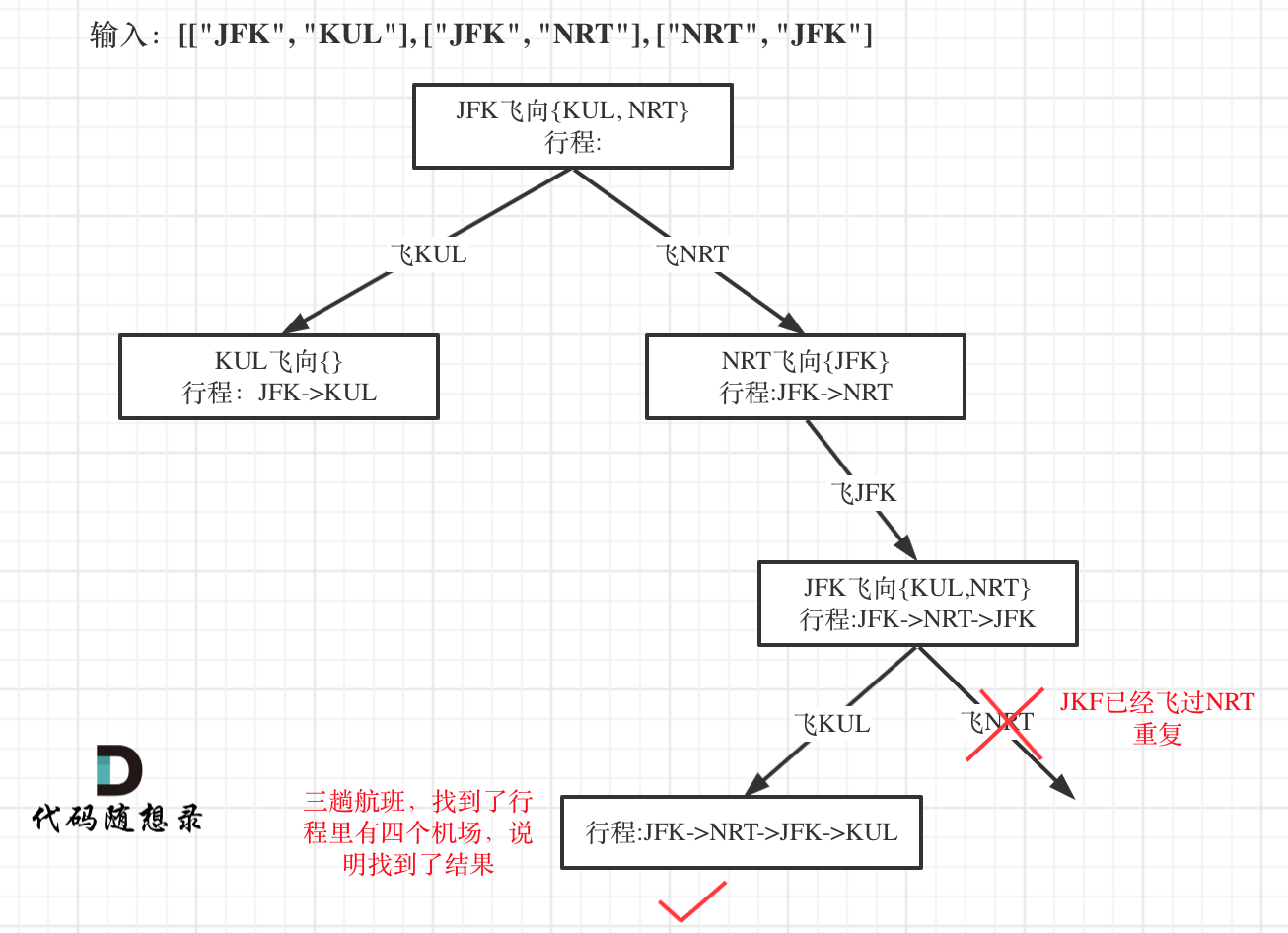
|
||||
|
||||
所以找到了这个叶子节点了直接返回,这个递归函数的返回值问题我们在讲解二叉树的系列的时候,在这篇[二叉树:递归函数究竟什么时候需要返回值,什么时候不要返回值?](https://programmercarl.com/0112.路径总和.html)详细介绍过。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
计算在不触动警报的情况下,小偷一晚能够盗取的最高金额。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ for (int i = 3; i <= n ; i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
举例当n为10 的时候,dp数组里的数值,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
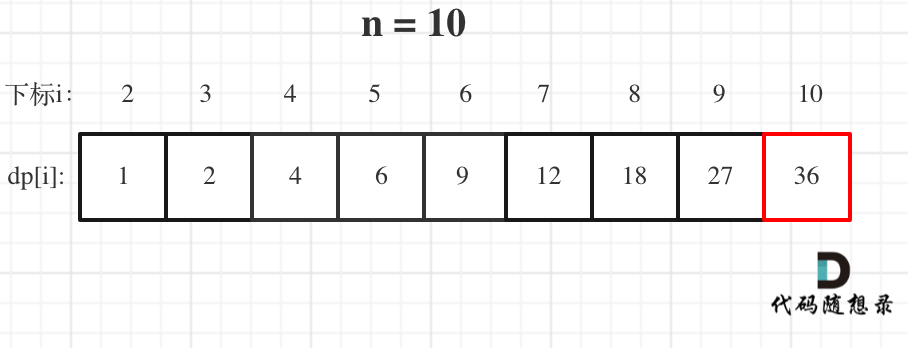
|
||||
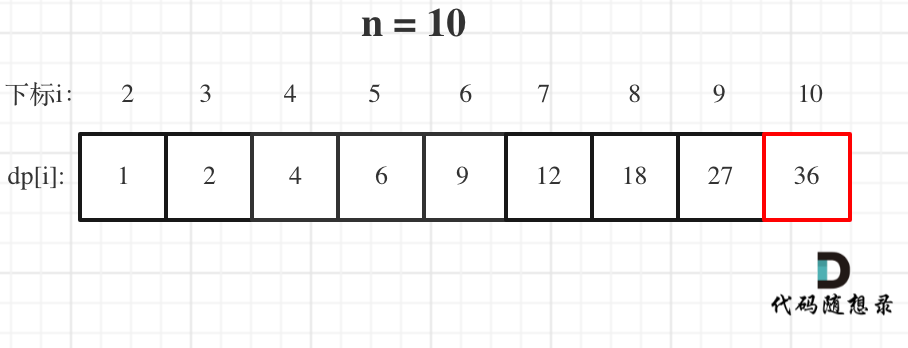
|
||||
|
||||
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
题意:给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**说明:**
|
||||
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
用示例二来举例,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
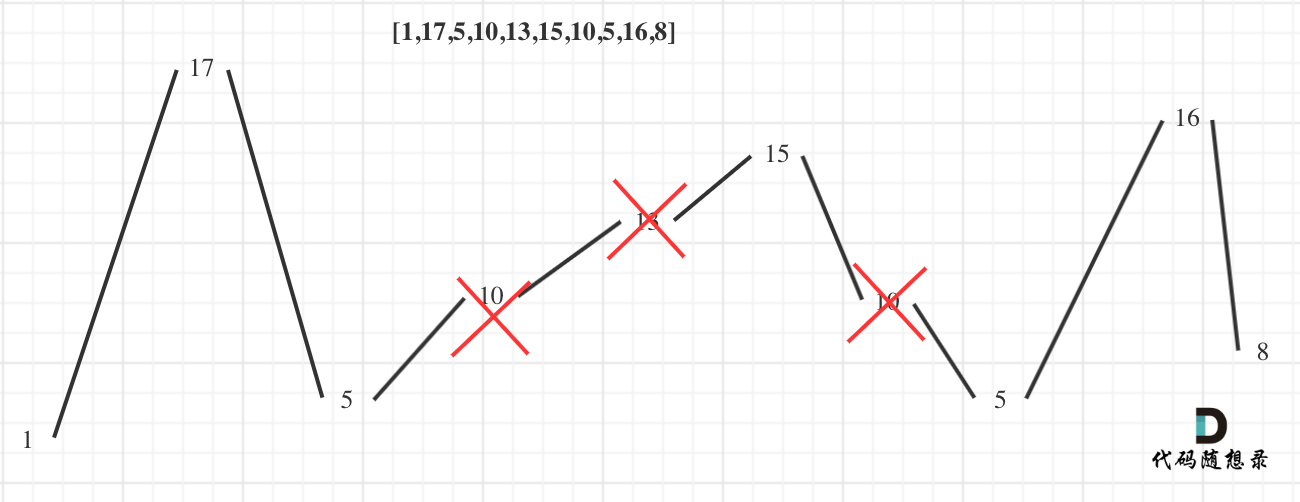
|
||||
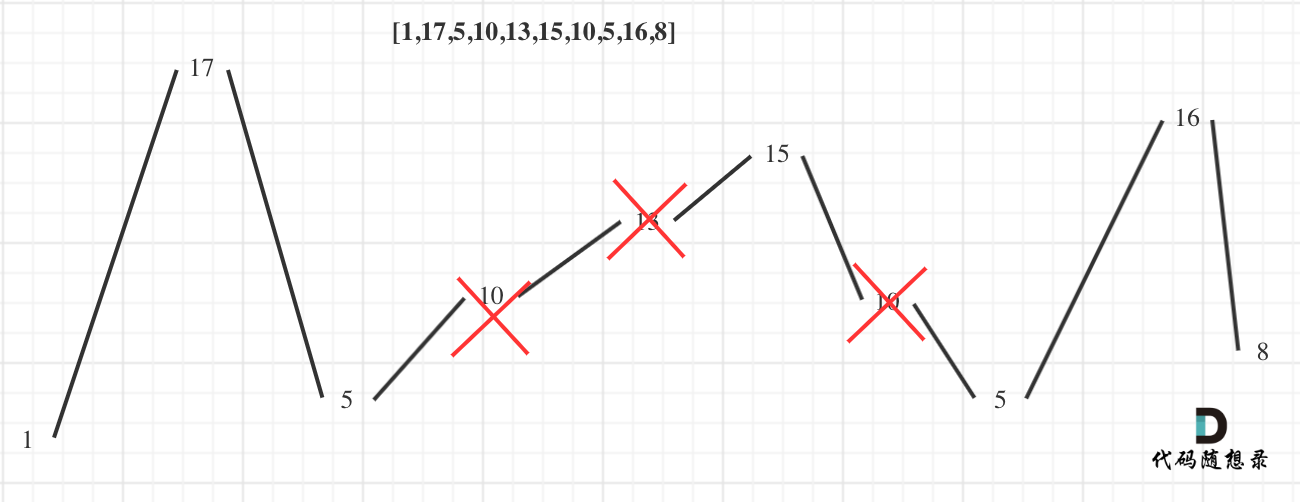
|
||||
|
||||
**局部最优:删除单调坡度上的节点(不包括单调坡度两端的节点),那么这个坡度就可以有两个局部峰值**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -103,7 +103,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
那么为了规则统一,针对序列[2,5],可以假设为[2,2,5],这样它就有坡度了即preDiff = 0,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
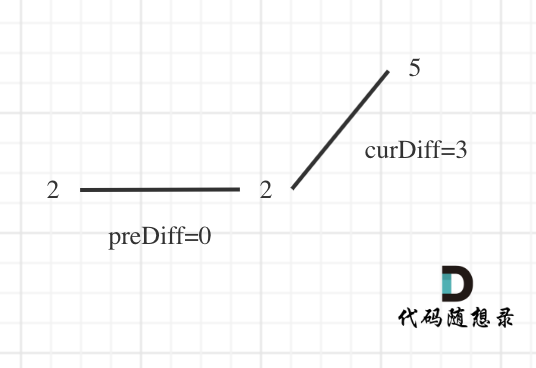
|
||||
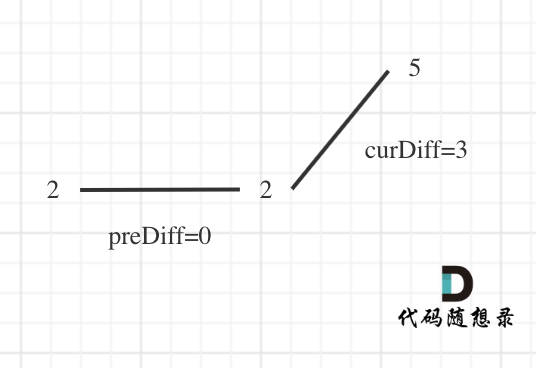
|
||||
|
||||
针对以上情形,result初始为1(默认最右面有一个峰值),此时curDiff > 0 && preDiff <= 0,那么result++(计算了左面的峰值),最后得到的result就是2(峰值个数为2即摆动序列长度为2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ dp[i](考虑nums[j])可以由 dp[i - nums[j]](不考虑nums[j]) 推导
|
|||
|
||||
我们再来用示例中的例子推导一下:
|
||||
|
||||
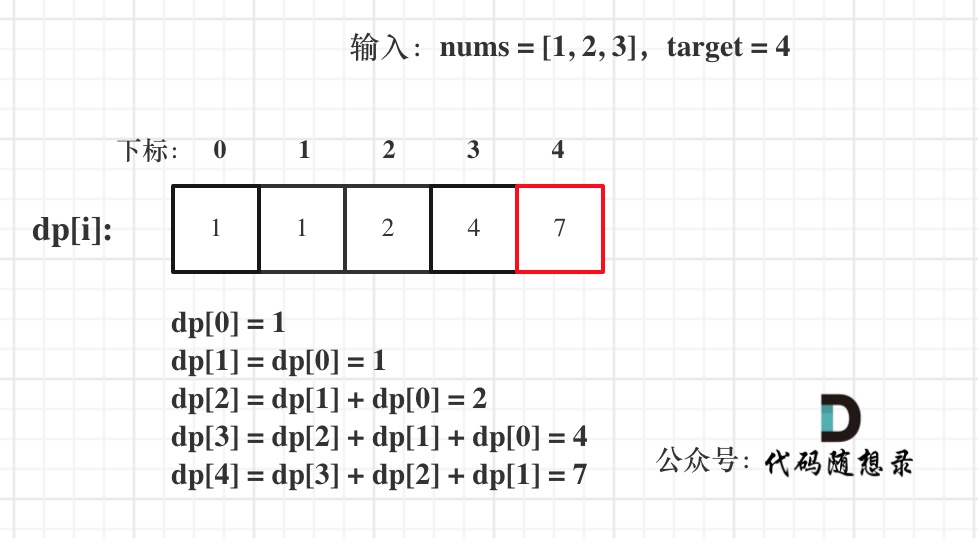
|
||||
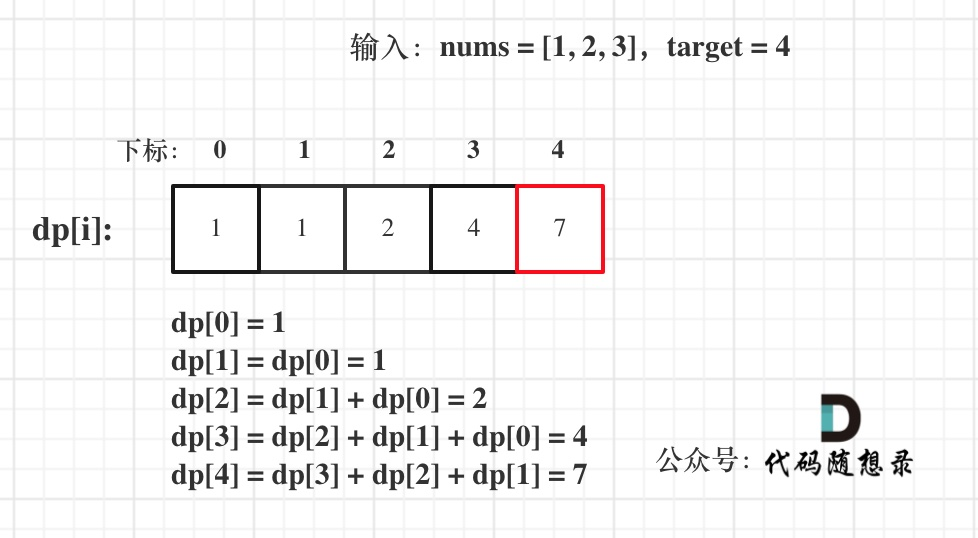
|
||||
|
||||
如果代码运行处的结果不是想要的结果,就把dp[i]都打出来,看看和我们推导的一不一样。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -77,7 +77,8 @@ if (s[i - 1] != t[j - 1]),此时相当于t要删除元素,t如果把当前
|
|||
|
||||
因为这样的定义在dp二维矩阵中可以留出初始化的区间,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
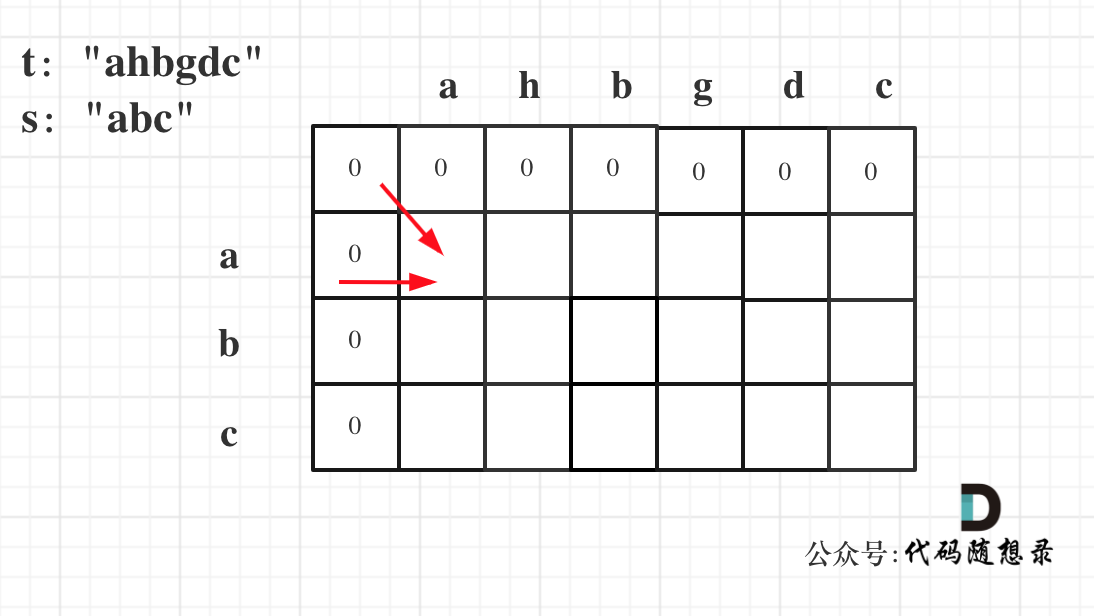
|
||||
|
||||
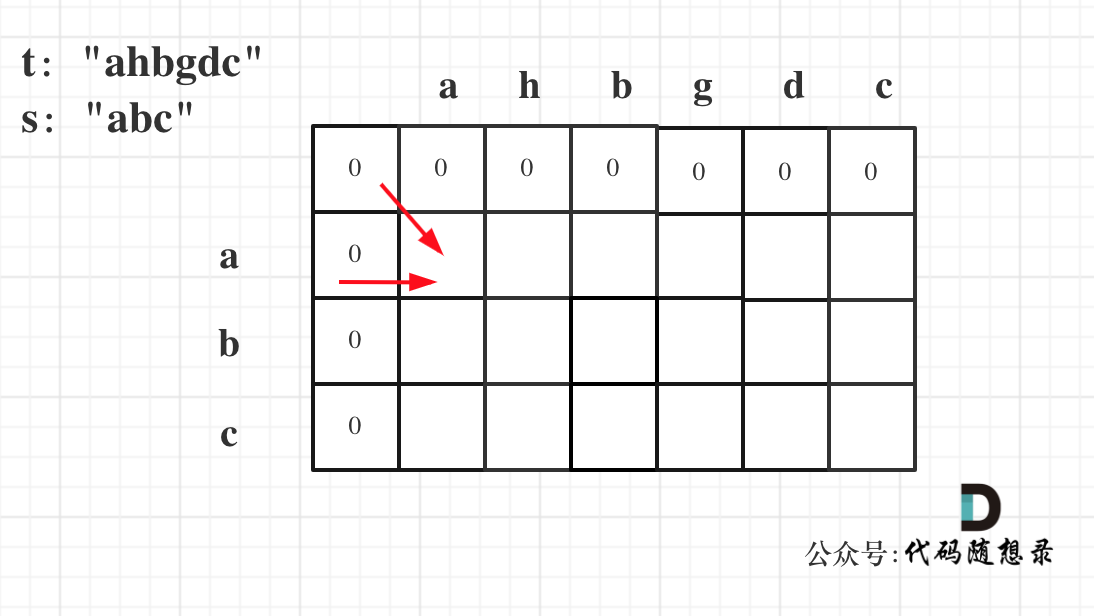
|
||||
|
||||
如果要是定义的dp[i][j]是以下标i为结尾的字符串s和以下标j为结尾的字符串t,初始化就比较麻烦了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,13 +95,15 @@ vector<vector<int>> dp(s.size() + 1, vector<int>(t.size() + 1, 0));
|
|||
|
||||
如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
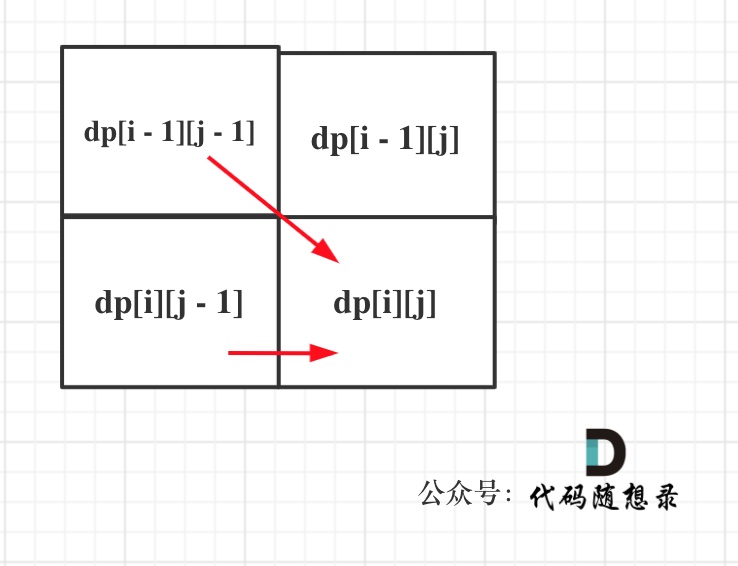
|
||||
|
||||
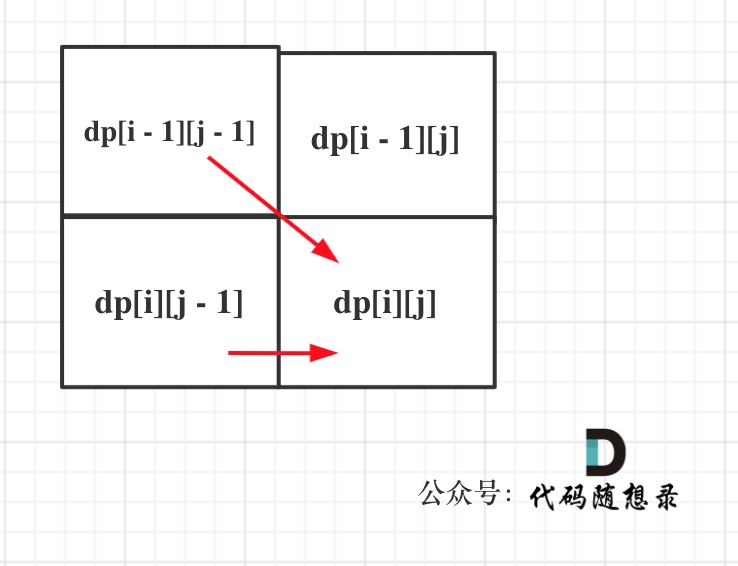
|
||||
|
||||
5. 举例推导dp数组
|
||||
|
||||
以示例一为例,输入:s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc",dp状态转移图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
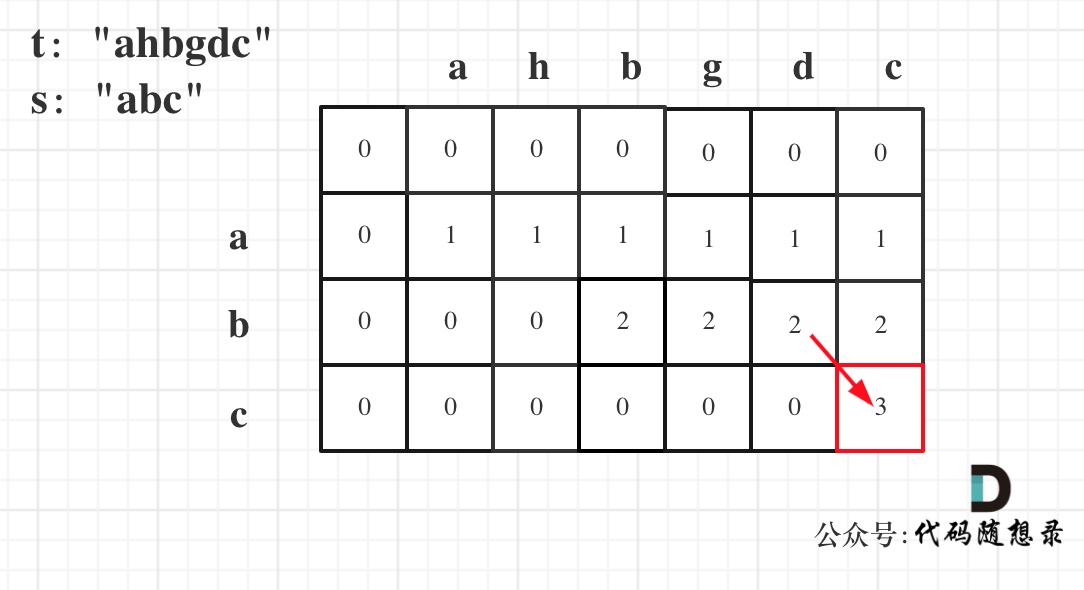
|
||||
|
||||
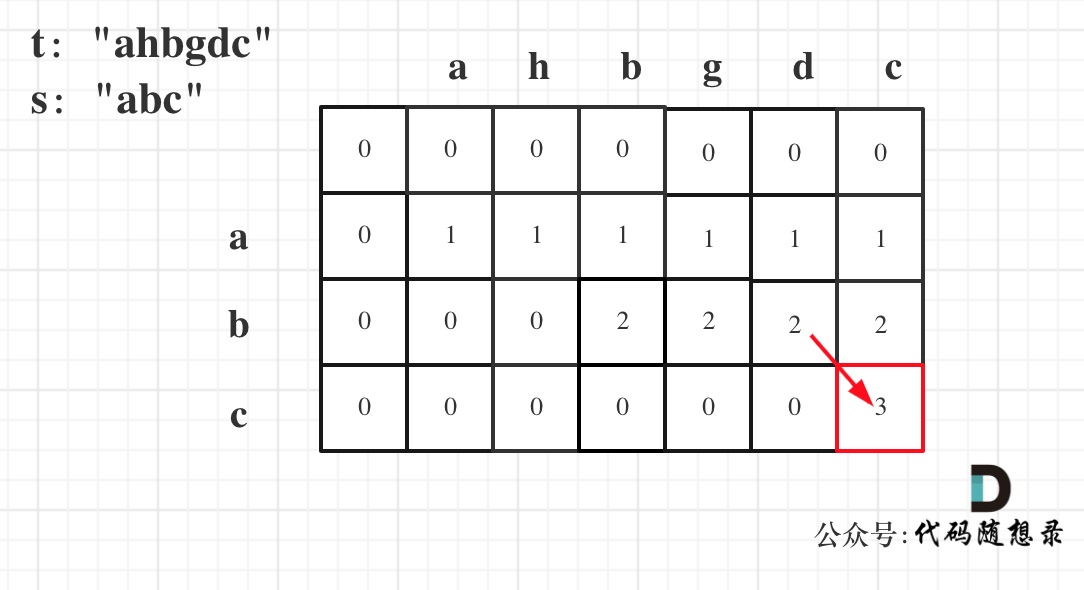
|
||||
|
||||
dp[i][j]表示以下标i-1为结尾的字符串s和以下标j-1为结尾的字符串t 相同子序列的长度,所以如果dp[s.size()][t.size()] 与 字符串s的长度相同说明:s与t的最长相同子序列就是s,那么s 就是 t 的子序列。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 视频讲解
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,8 +28,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
大家思考一下如下图中二叉树,左叶子之和究竟是多少?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**其实是0,因为这棵树根本没有左叶子!**
|
||||
|
||||
但看这个图的左叶子之和是多少?
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
以图中{5,2} 为例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
按照身高排序之后,优先按身高高的people的k来插入,后序插入节点也不会影响前面已经插入的节点,最终按照k的规则完成了队列。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -148,7 +148,8 @@ dp[j]的数值一定是小于等于j的。
|
|||
|
||||
用例1,输入[1,5,11,5] 为例,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
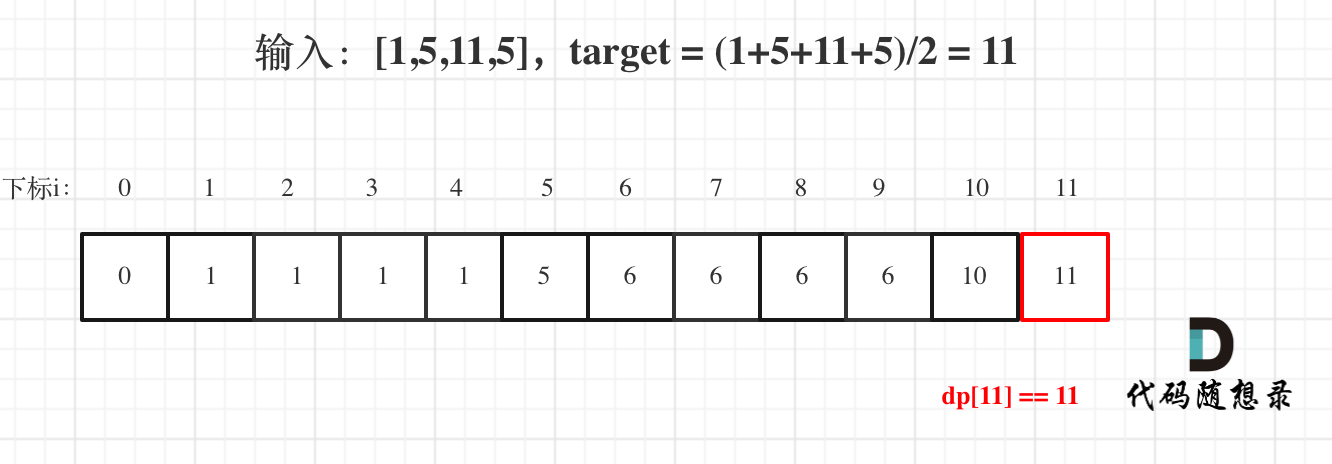
|
||||
|
||||
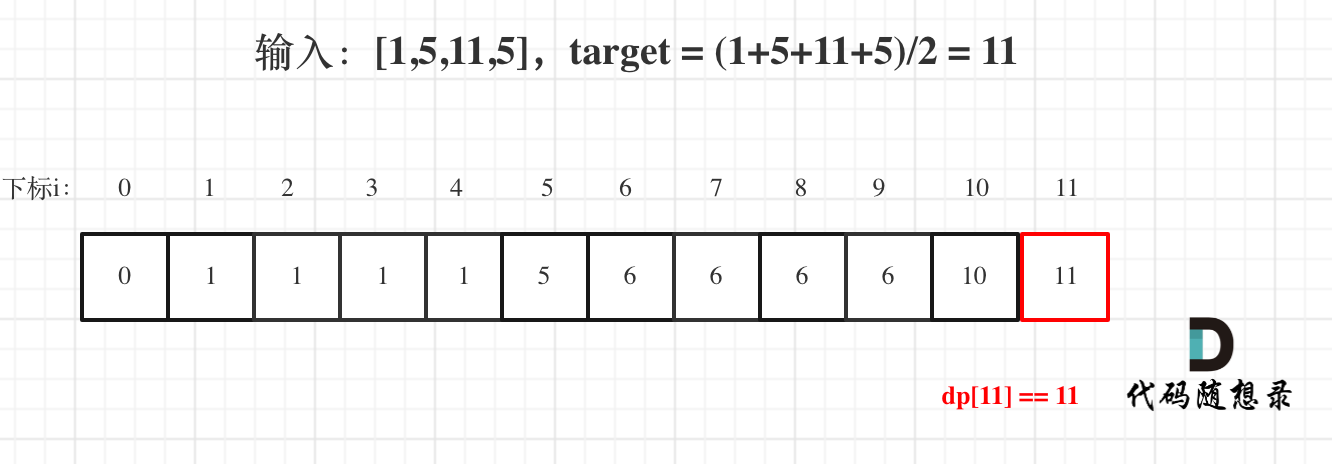
|
||||
|
||||
最后dp[11] == 11,说明可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
以题目示例: [[10,16],[2,8],[1,6],[7,12]]为例,如图:(方便起见,已经排序)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
可以看出首先第一组重叠气球,一定是需要一个箭,气球3,的左边界大于了 第一组重叠气球的最小右边界,所以再需要一支箭来射气球3了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
其实本题并不是多重背包,再来看一下这个图,捋清几种背包的关系
|
||||
|
||||
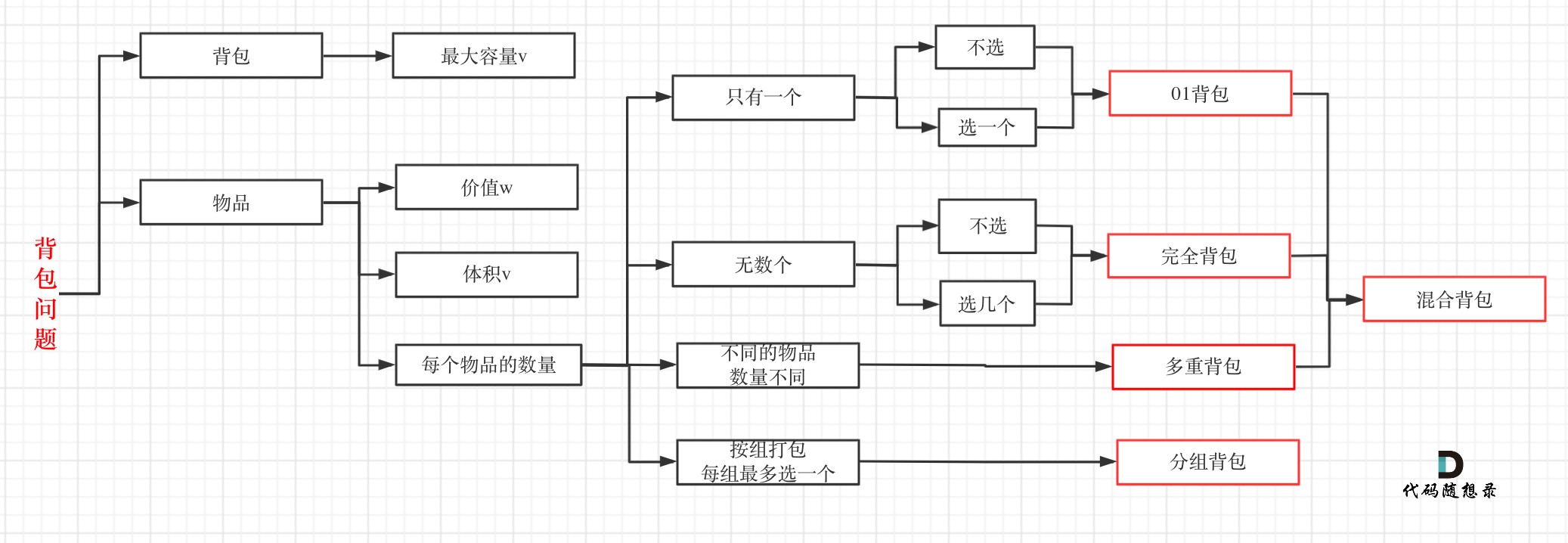
|
||||
|
||||
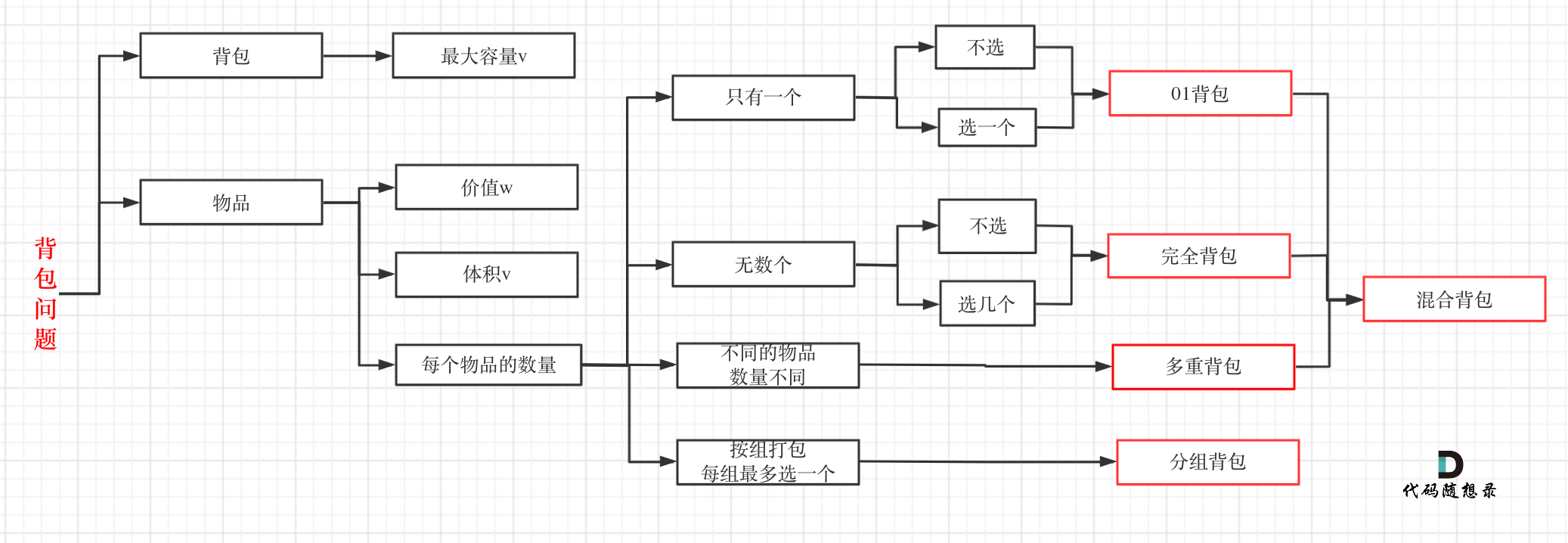
|
||||
|
||||
多重背包是每个物品,数量不同的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -128,7 +129,7 @@ for (string str : strs) { // 遍历物品
|
|||
最后dp数组的状态如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
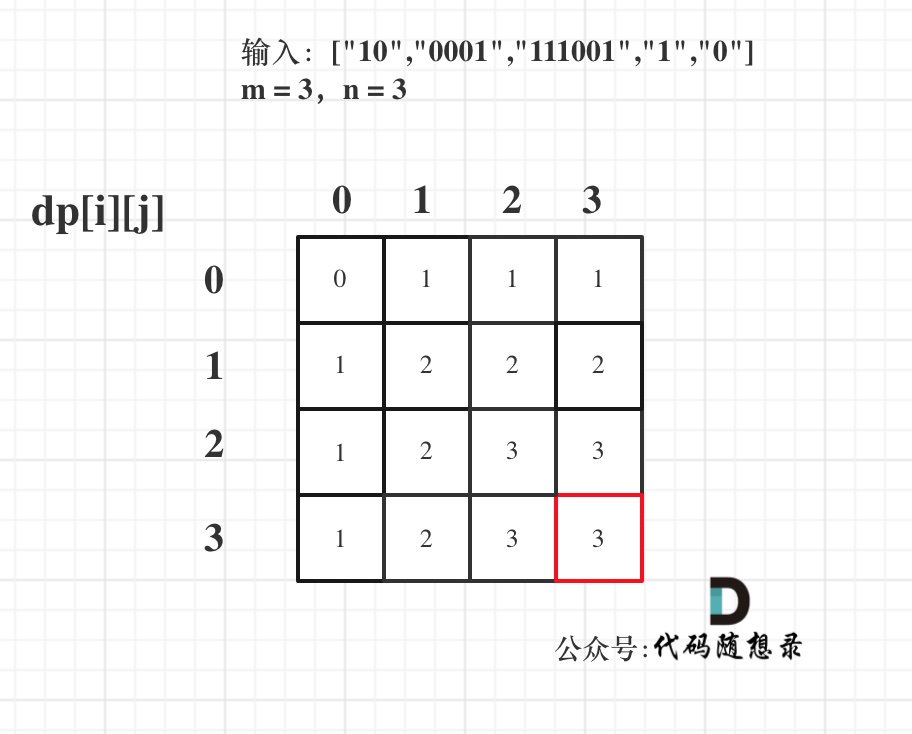
|
||||
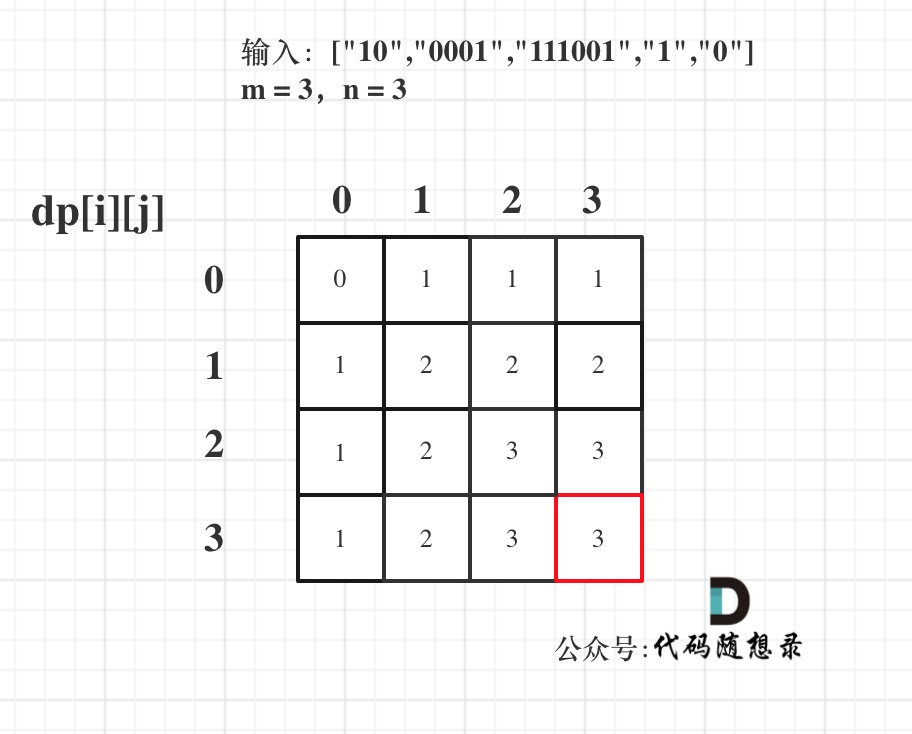
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
以上动规五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -46,7 +46,10 @@
|
|||
|
||||
为了有鲜明的对比,我用[4, 7, 6, 7]这个数组来举例,抽象为树形结构如图:
|
||||
|
||||
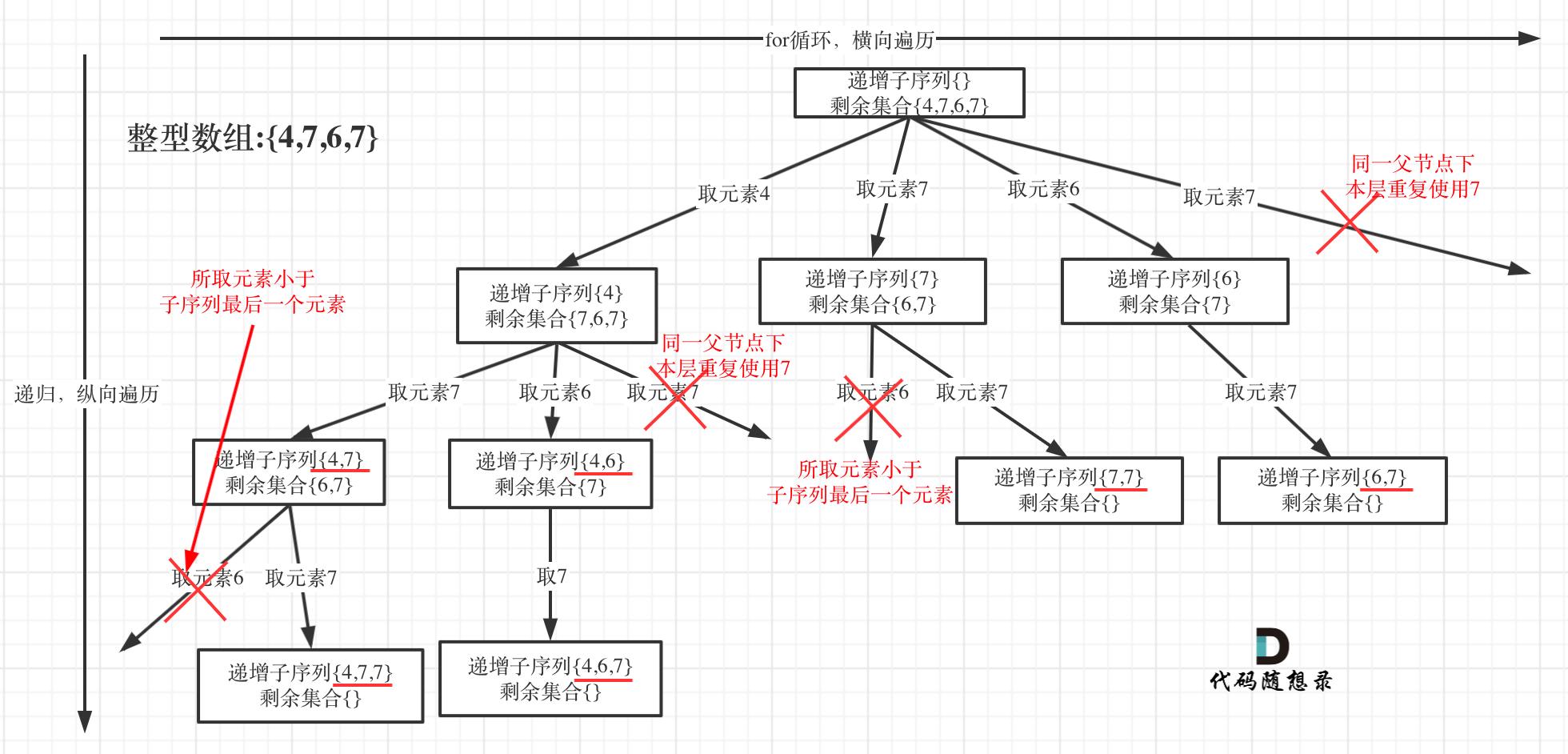
|
||||
|
||||
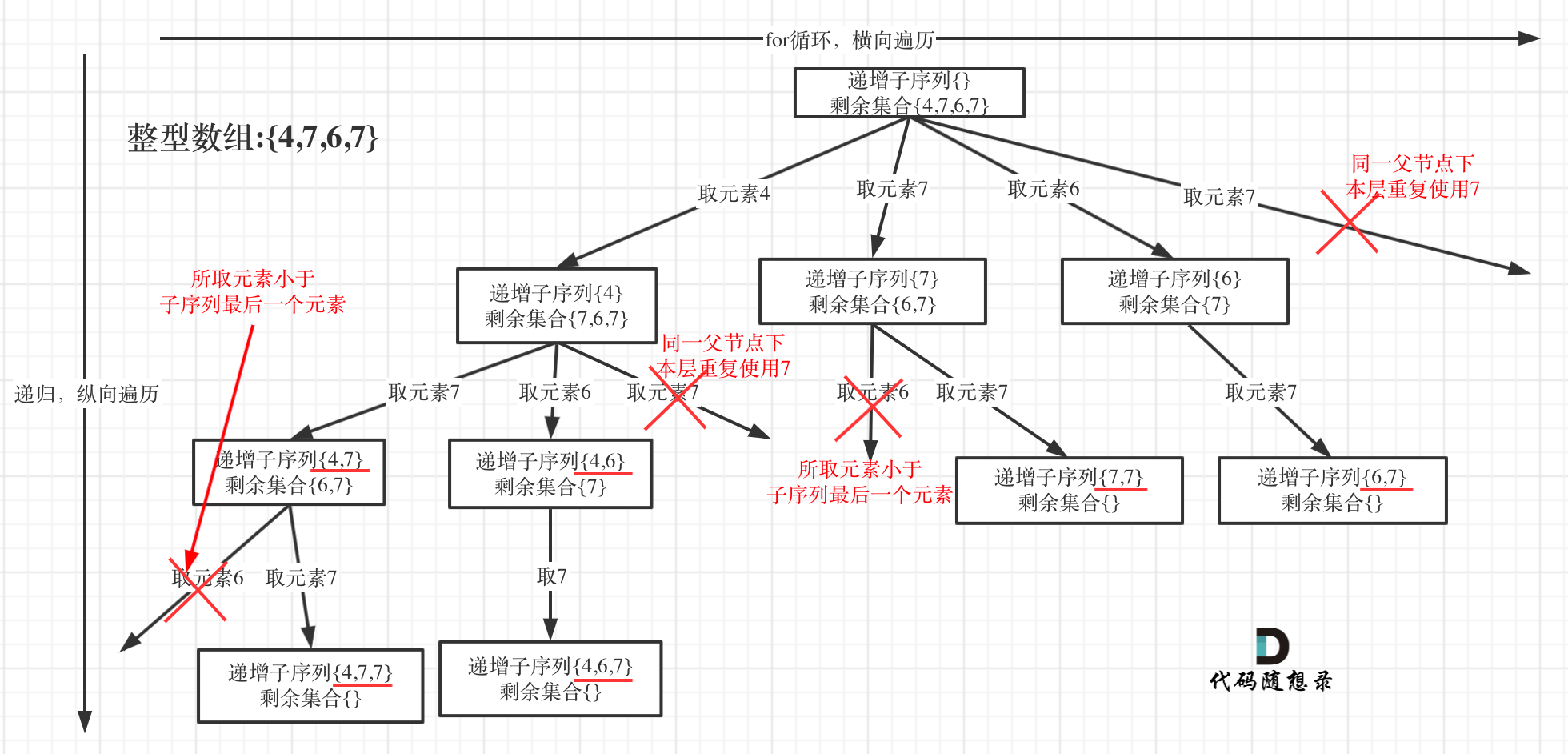
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 回溯三部曲
|
||||
|
|
@ -78,7 +81,7 @@ if (path.size() > 1) {
|
|||
|
||||
* 单层搜索逻辑
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
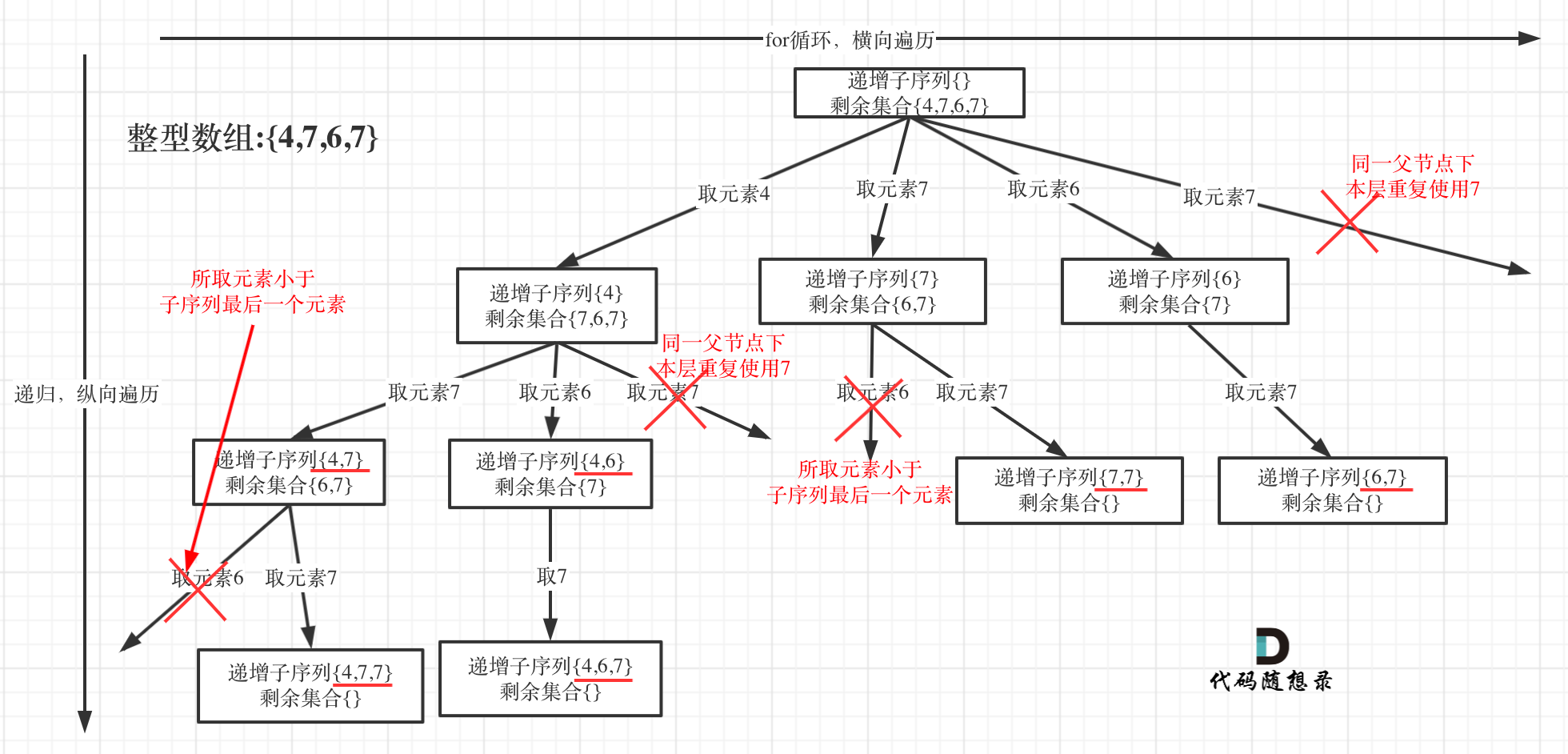
|
||||
在图中可以看出,**同一父节点下的同层上使用过的元素就不能再使用了**
|
||||
|
||||
那么单层搜索代码如下:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ bagSize = (S + sum) / 2 = (3 + 5) / 2 = 4
|
|||
|
||||
dp数组状态变化如下:
|
||||
|
||||
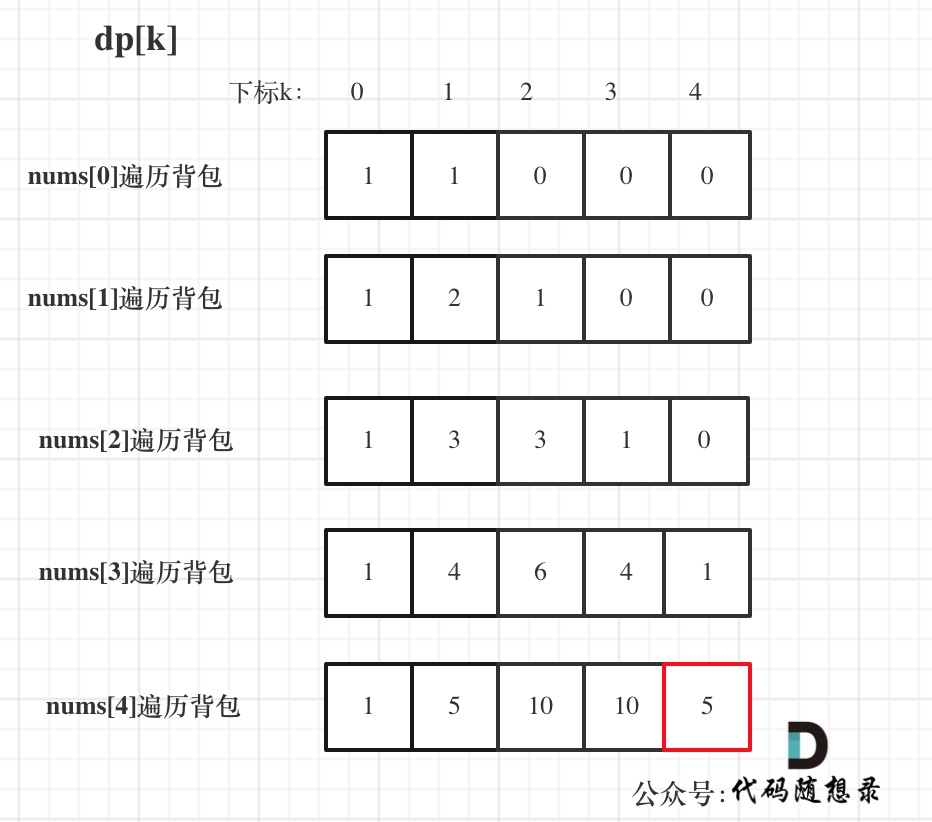
|
||||
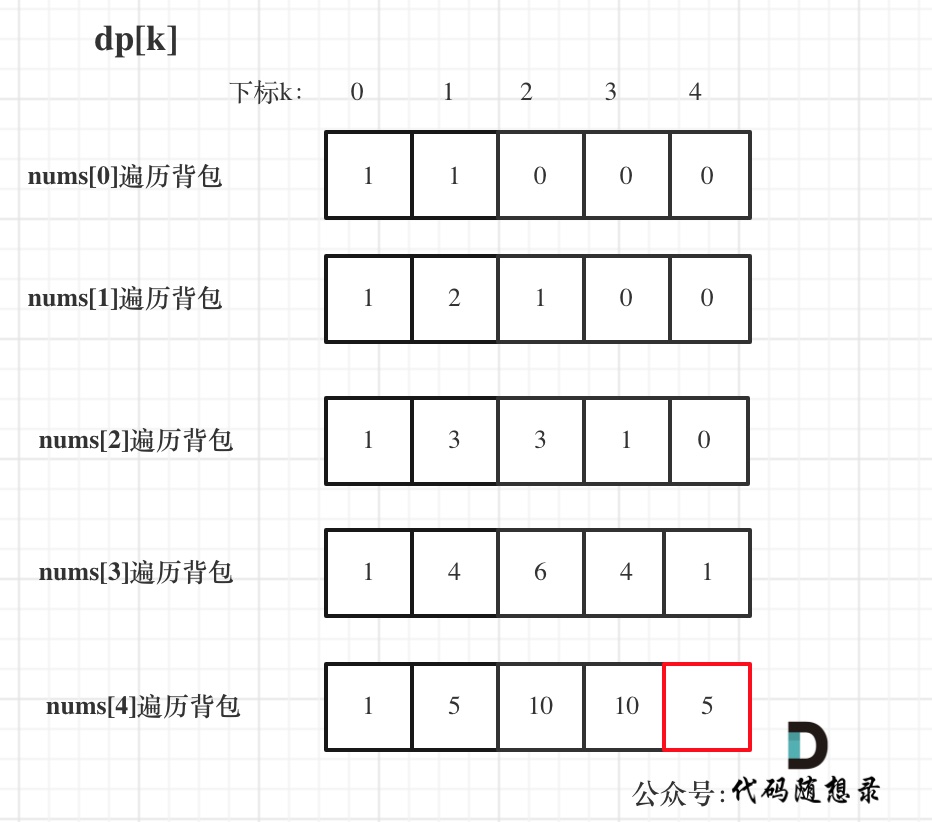
|
||||
|
||||
C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
返回[2].
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
中序遍历代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,13 +11,14 @@
|
|||
|
||||
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 视频讲解
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,10 +1,12 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
# 516.最长回文子序列
|
||||
|
||||
# 516.最长回文子序列
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +54,7 @@
|
|||
如果s[i]与s[j]相同,那么dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1] + 2;
|
||||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
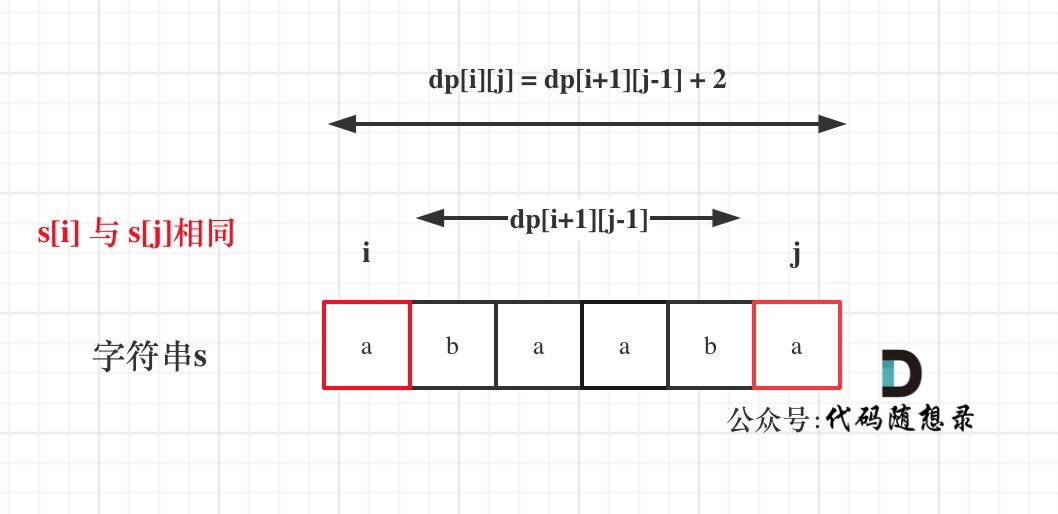
|
||||
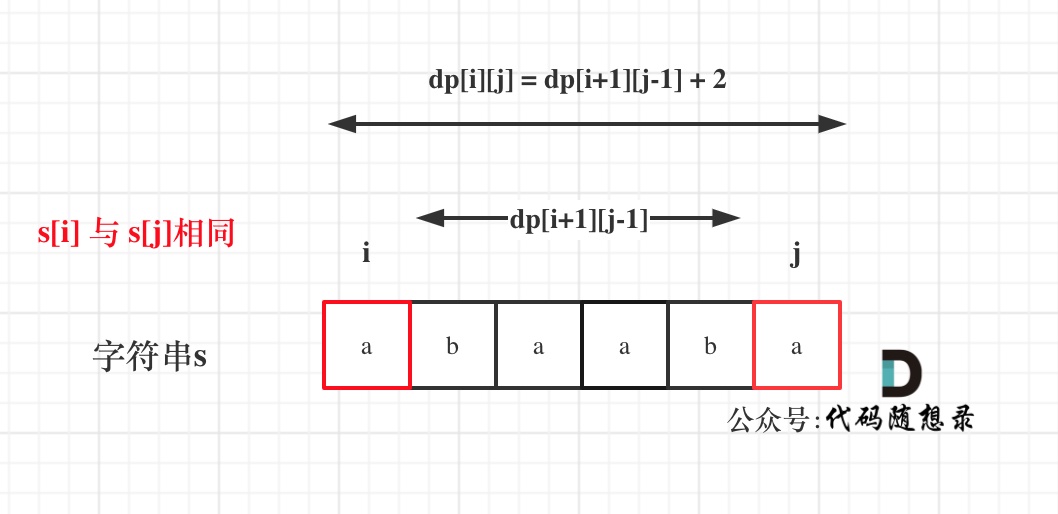
|
||||
|
||||
(如果这里看不懂,回忆一下dp[i][j]的定义)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,7 +66,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
那么dp[i][j]一定是取最大的,即:dp[i][j] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
|
||||
|
||||
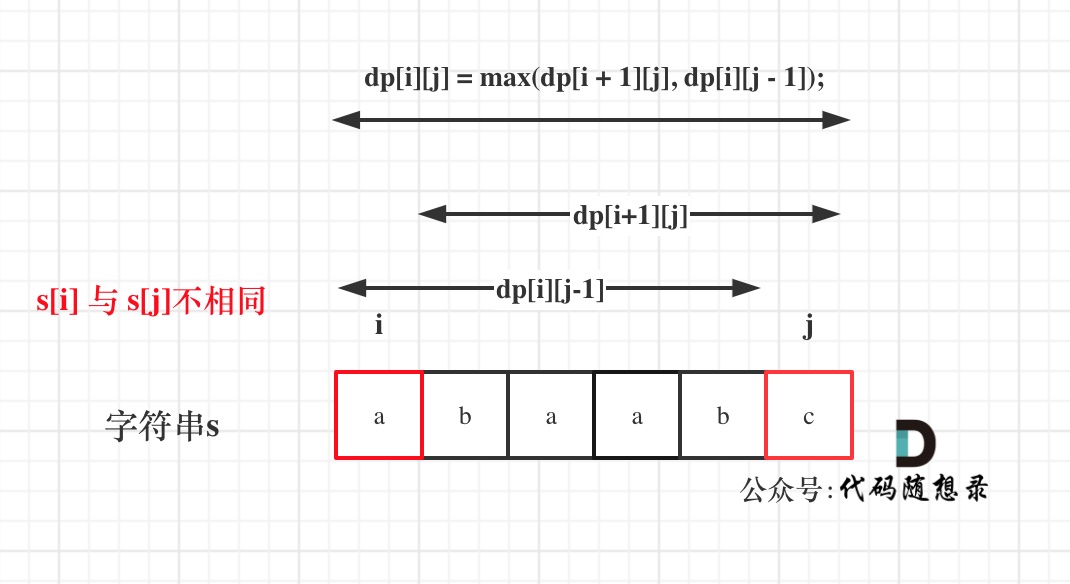
|
||||
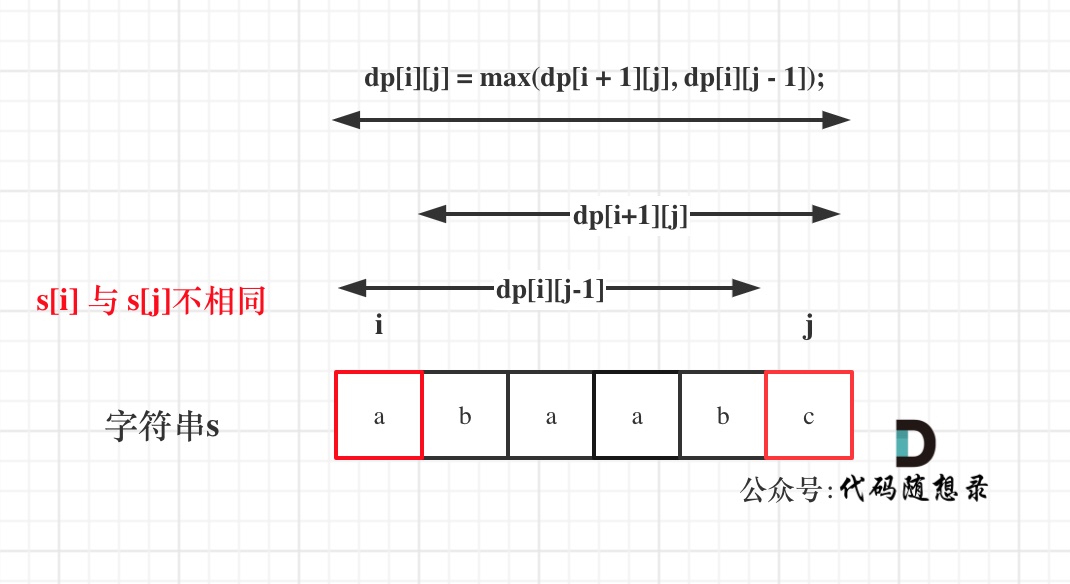
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -91,7 +93,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) dp[i][i] = 1;
|
|||
|
||||
4. 确定遍历顺序
|
||||
|
||||
从递归公式中,可以看出,dp[i][j] 依赖于 dp[i + 1][j - 1] ,dp[i + 1][j] 和 dp[i][j - 1],如图:
|
||||
从递归公式中,可以看出,dp[i][j] 依赖于 dp[i + 1][j - 1] ,dp[i + 1][j] 和 dp[i][j - 1],如图:
|
||||
|
||||
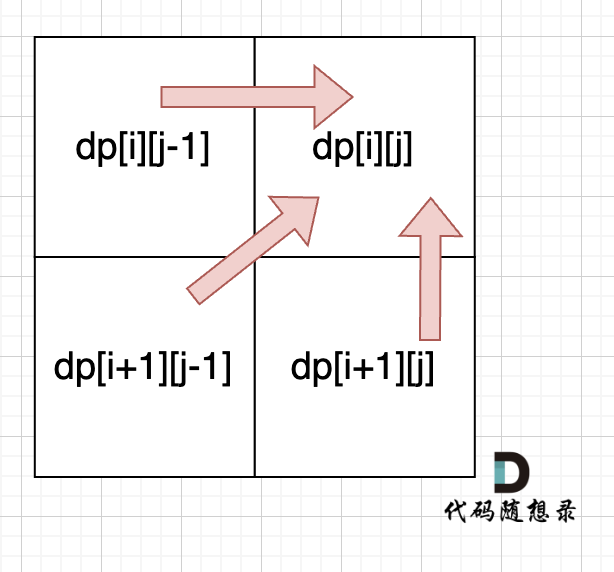
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -117,7 +119,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
|||
|
||||
输入s:"cbbd" 为例,dp数组状态如图:
|
||||
|
||||
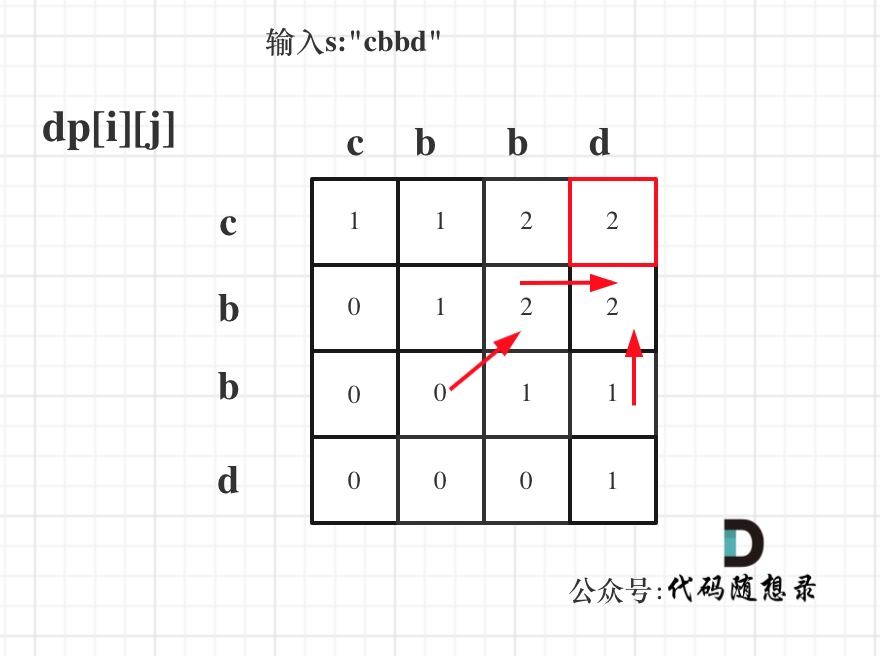
|
||||
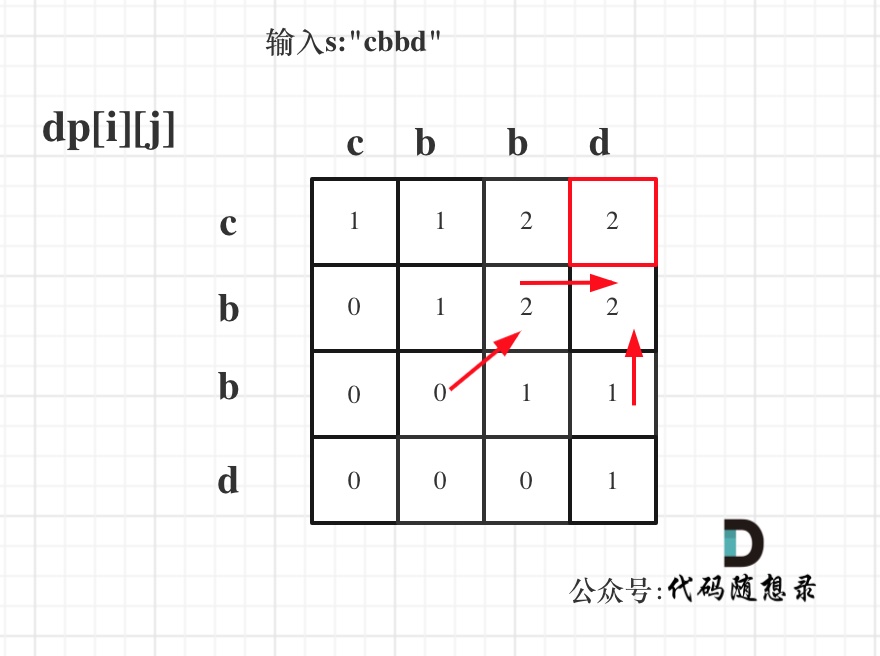
|
||||
|
||||
红色框即:dp[0][s.size() - 1]; 为最终结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -147,6 +149,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class Solution {
|
||||
public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,6 +172,7 @@ public class Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def longestPalindromeSubseq(self, s: str) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,6 +189,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
```Go
|
||||
func longestPalindromeSubseq(s string) int {
|
||||
size := len(s)
|
||||
|
|
@ -213,11 +218,12 @@ func longestPalindromeSubseq(s string) int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Javascript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
const longestPalindromeSubseq = (s) => {
|
||||
const strLen = s.length;
|
||||
let dp = Array.from(Array(strLen), () => Array(strLen).fill(0));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for(let i = 0; i < strLen; i++) {
|
||||
dp[i][i] = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -241,7 +247,7 @@ TypeScript:
|
|||
```typescript
|
||||
function longestPalindromeSubseq(s: string): number {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
dp[i][j]:[i,j]区间内,最长回文子序列的长度
|
||||
dp[i][j]:[i,j]区间内,最长回文子序列的长度
|
||||
*/
|
||||
const length: number = s.length;
|
||||
const dp: number[][] = new Array(length).fill(0)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -158,7 +158,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= amount; j++) { // 遍历背包容量
|
|||
|
||||
输入: amount = 5, coins = [1, 2, 5] ,dp状态图如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
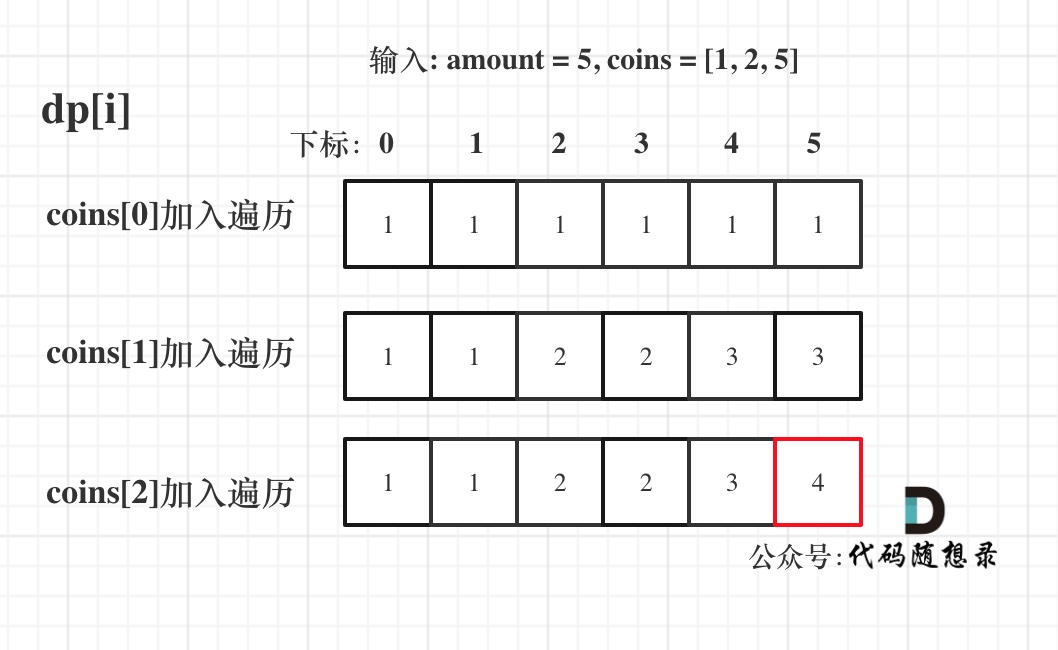
|
||||
|
||||
最后红色框dp[amount]为最终结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
提示:树中至少有 2 个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
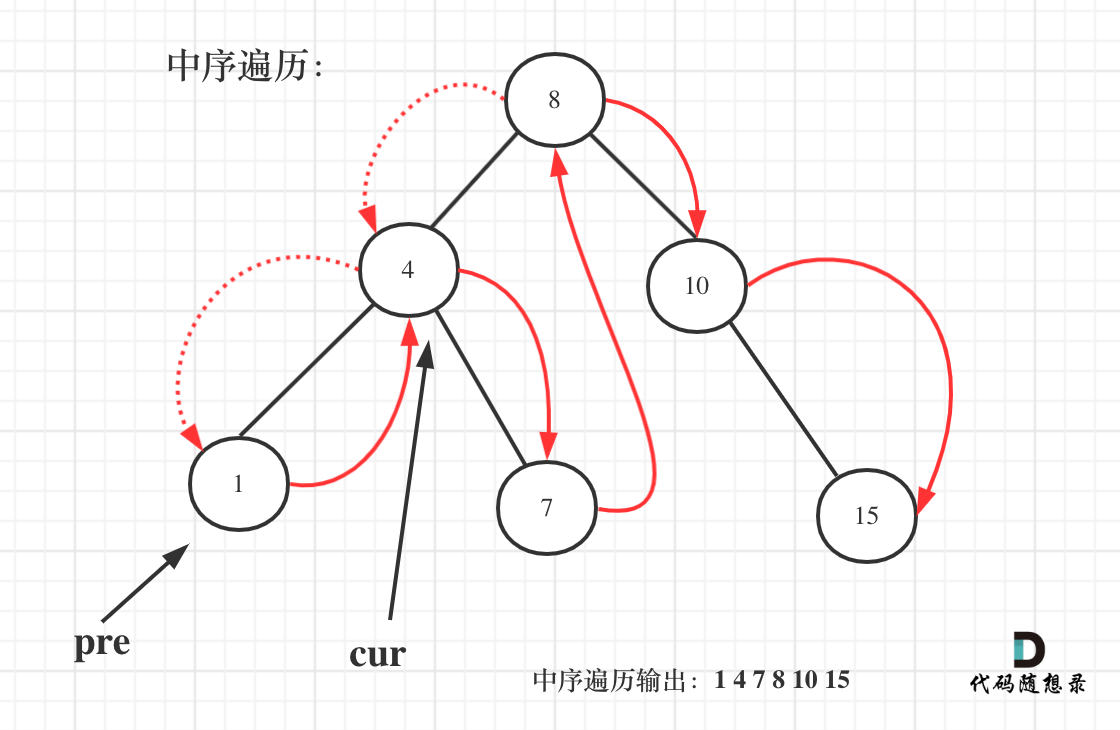
|
||||
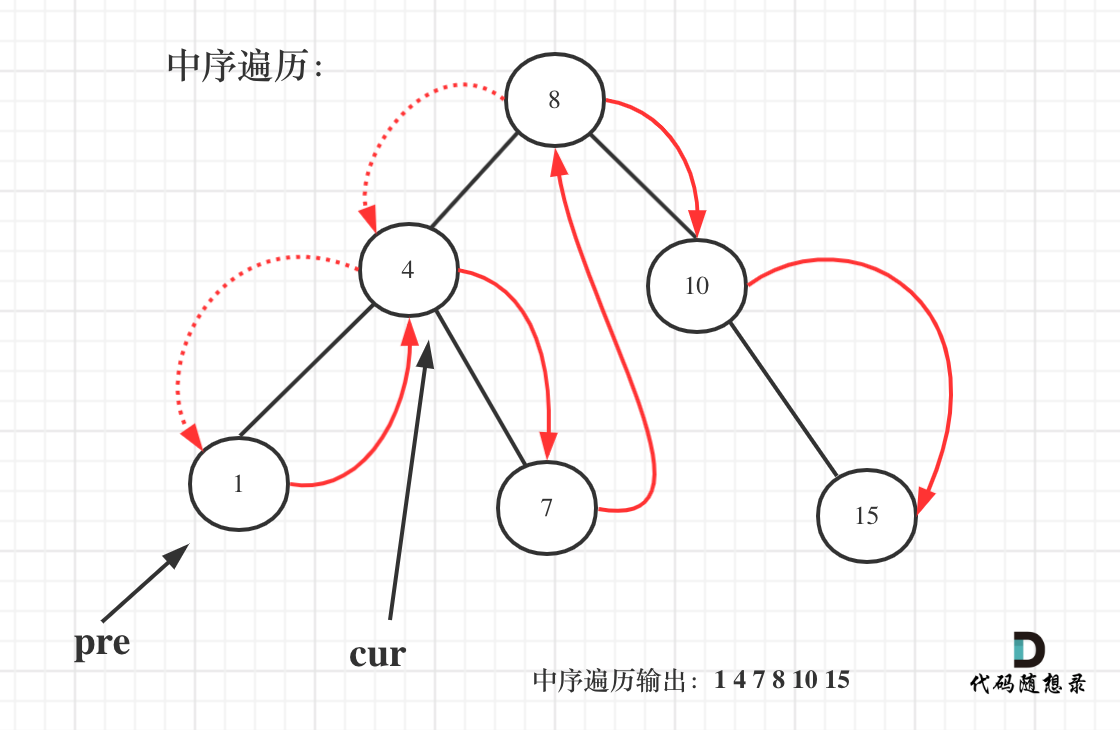
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学不知道在递归中如何记录前一个节点的指针,其实实现起来是很简单的,大家只要看过一次,写过一次,就掌握了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
|
||||
* 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,7 +68,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
遍历顺序如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
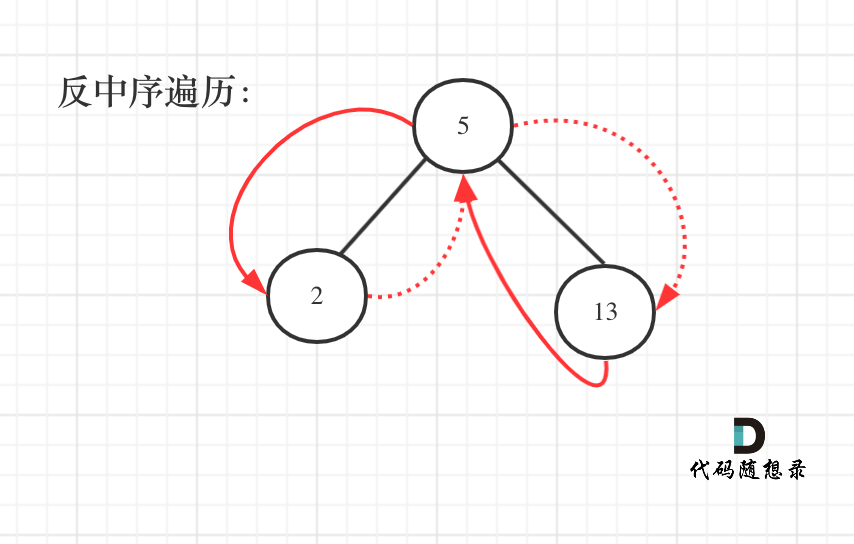
|
||||
|
||||
本题依然需要一个pre指针记录当前遍历节点cur的前一个节点,这样才方便做累加。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ for (int j = 0; j <= word2.size(); j++) dp[0][j] = j;
|
|||
|
||||
以word1:"sea",word2:"eat"为例,推导dp数组状态图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
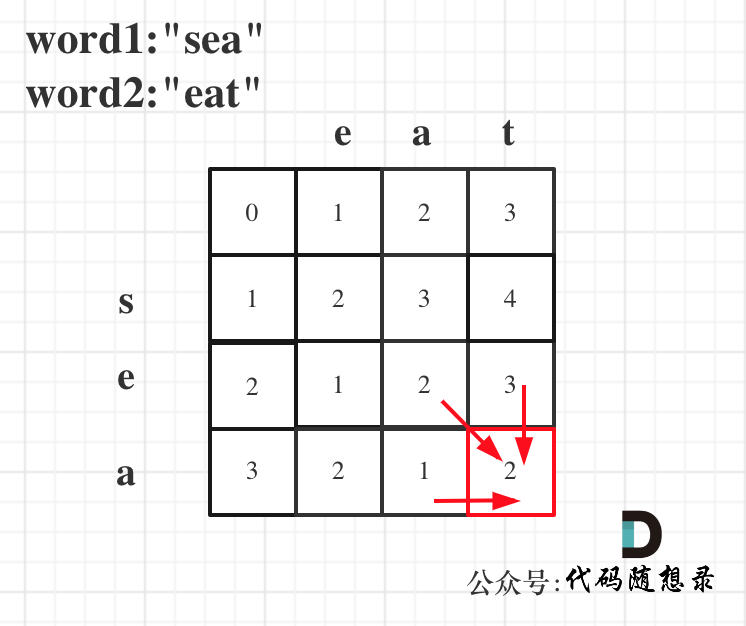
|
||||
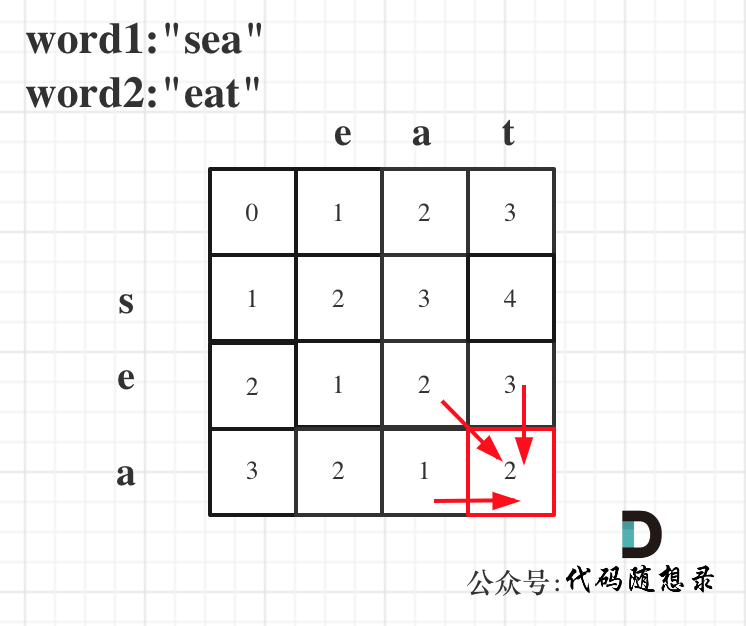
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
以上分析完毕,代码如下:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ dp[i][j]可以初始化为true么? 当然不行,怎能刚开始就全都匹
|
|||
|
||||
dp[i + 1][j - 1] 在 dp[i][j]的左下角,如图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
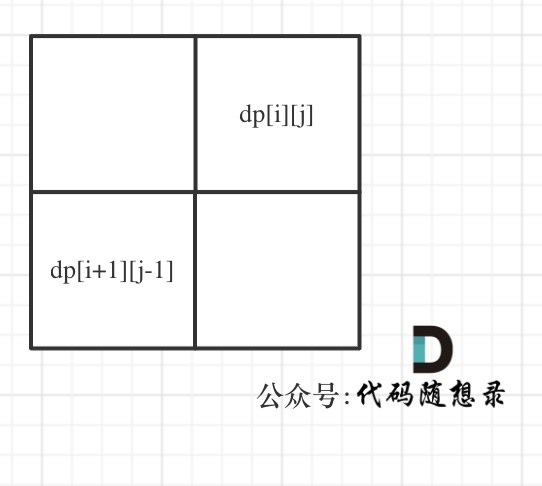
|
||||
|
||||
如果这矩阵是从上到下,从左到右遍历,那么会用到没有计算过的dp[i + 1][j - 1],也就是根据不确定是不是回文的区间[i+1,j-1],来判断了[i,j]是不是回文,那结果一定是不对的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 注意遍历顺序
|
|||
|
||||
举例,输入:"aaa",dp[i][j]状态如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
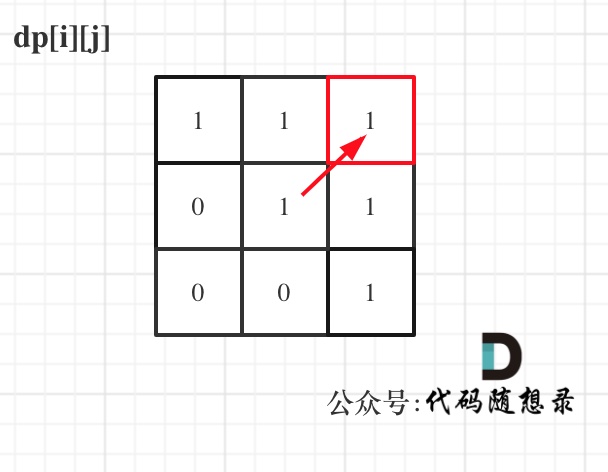
|
||||
|
||||
图中有6个true,所以就是有6个回文子串。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果不对递归有深刻的理解,本题有点难
|
||||
> 单纯移除一个节点那还不够,要修剪!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,13 +14,13 @@
|
|||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree/)
|
||||
|
||||
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
|
||||
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
# 算法公开课
|
||||
|
||||
**《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:[你修剪的方式不对,我来给你纠正一下!| LeetCode:669. 修剪二叉搜索树](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17P41177ud?share_source=copy_web),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +52,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
我们在重新关注一下第二个示例,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
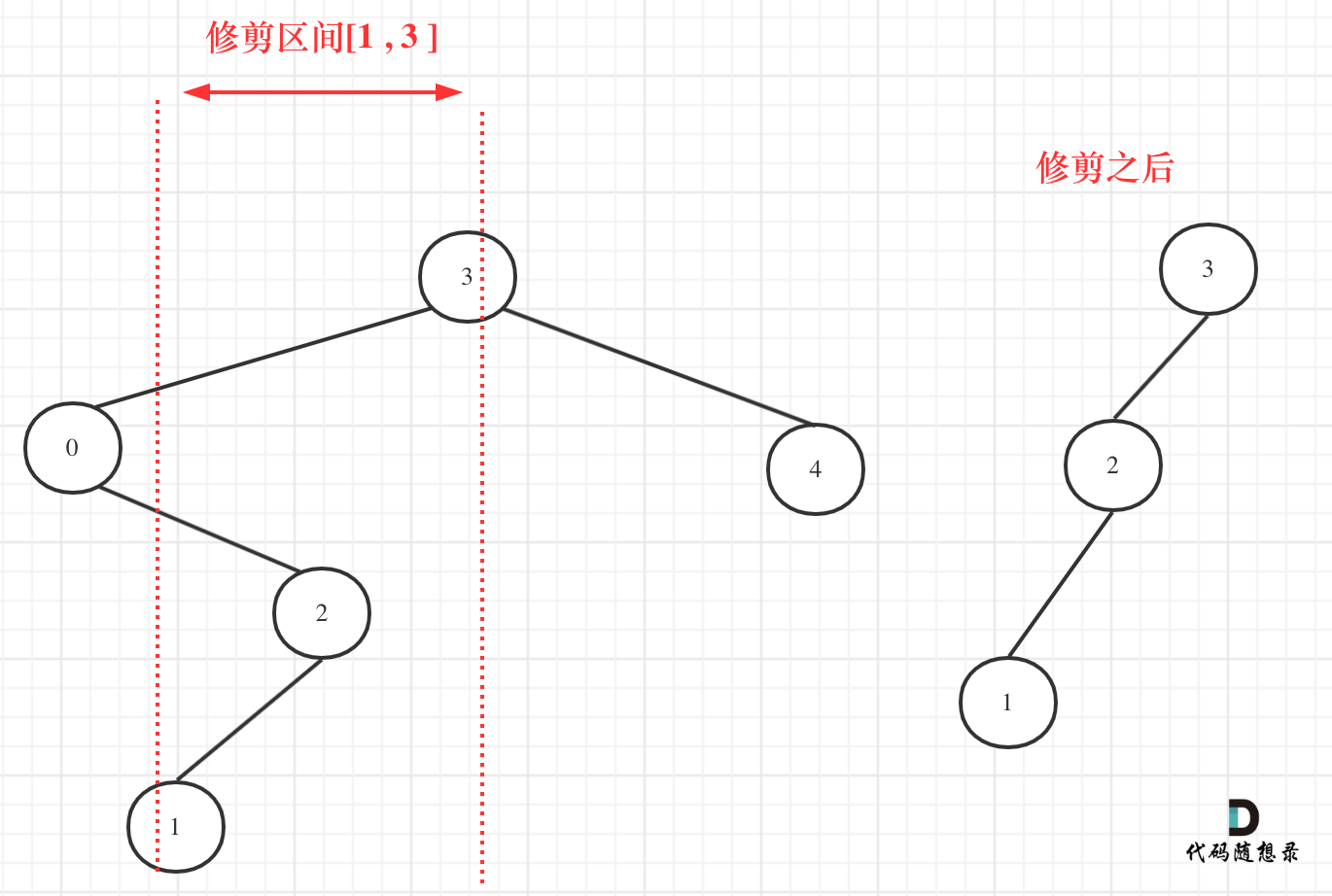
|
||||
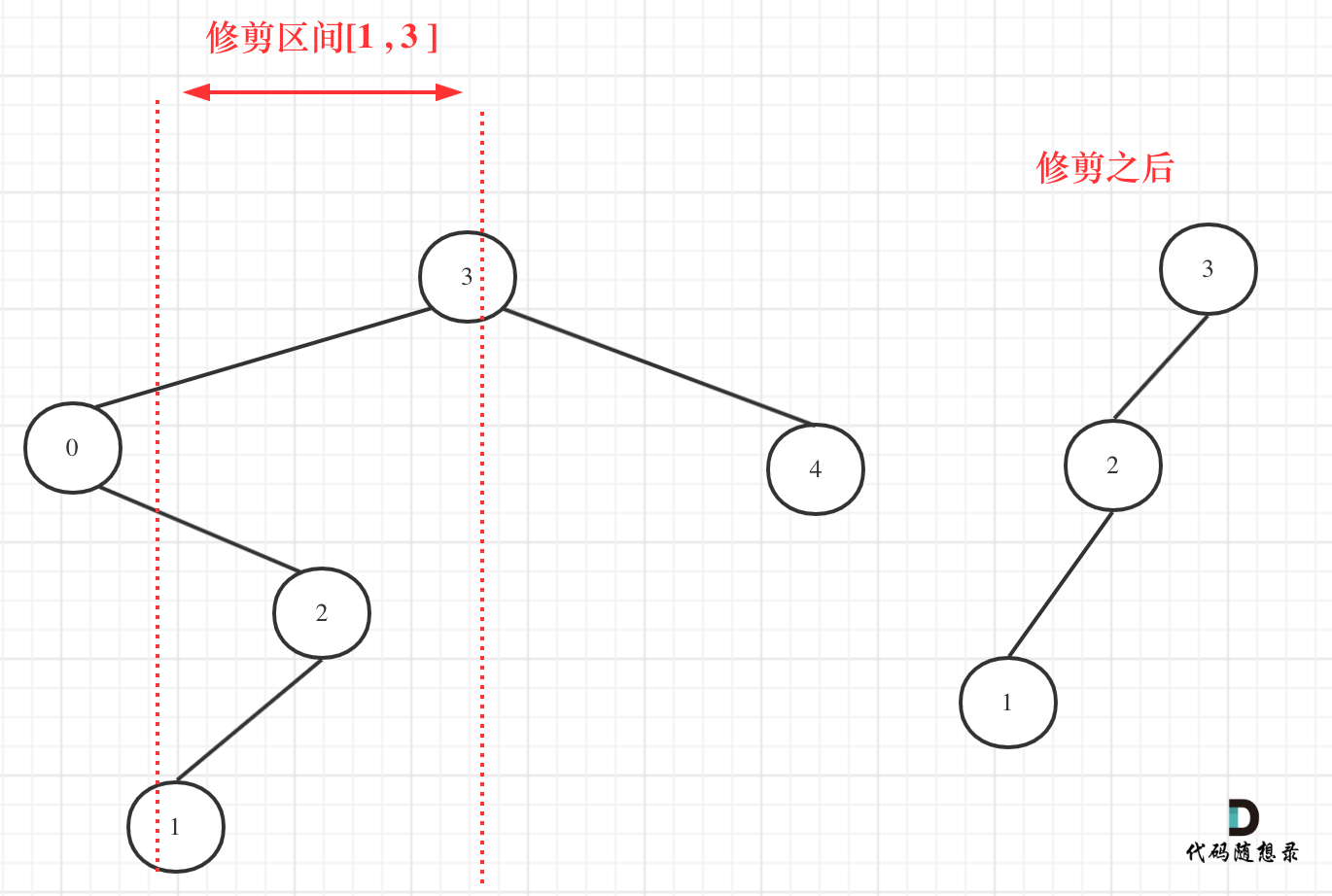
|
||||
|
||||
**所以以上的代码是不可行的!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -60,7 +62,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在上图中我们发现节点0并不符合区间要求,那么将节点0的右孩子 节点2 直接赋给 节点3的左孩子就可以了(就是把节点0从二叉树中移除),如图:
|
||||
|
||||
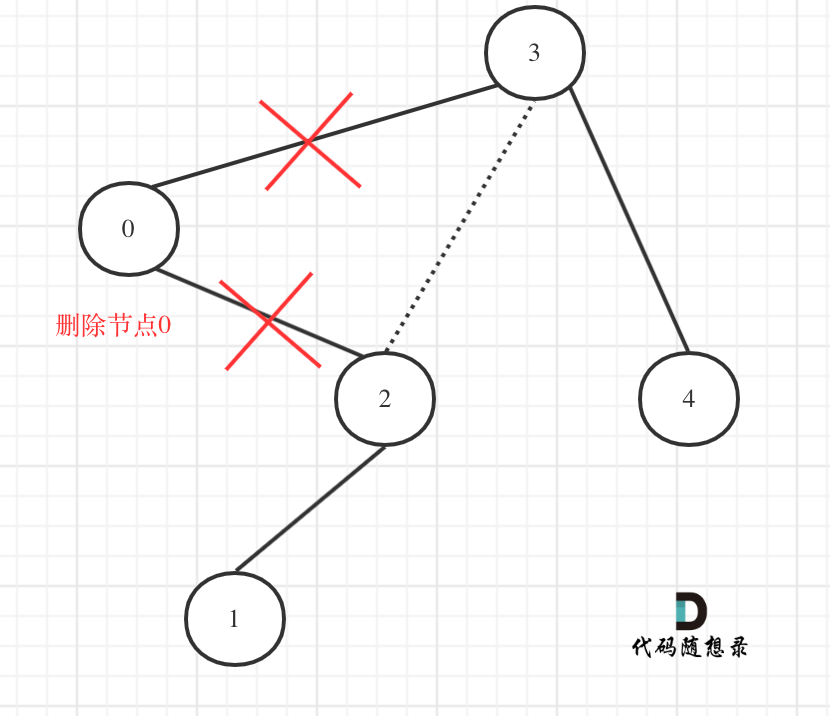
|
||||
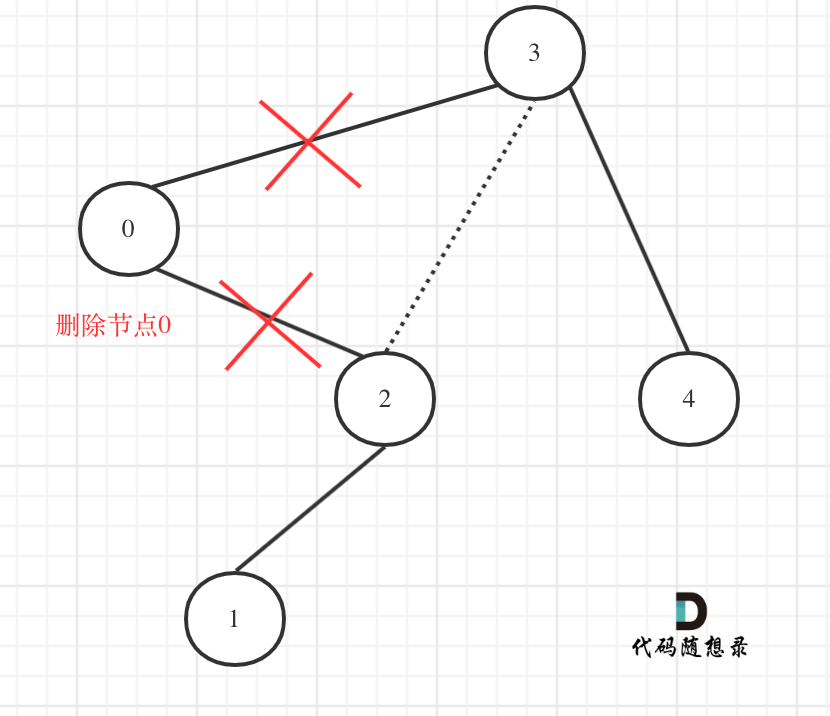
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
理解了最关键部分了我们再递归三部曲:
|
||||
|
|
@ -127,9 +129,10 @@ return root;
|
|||
|
||||
在回顾一下上面的代码,针对下图中二叉树的情况:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
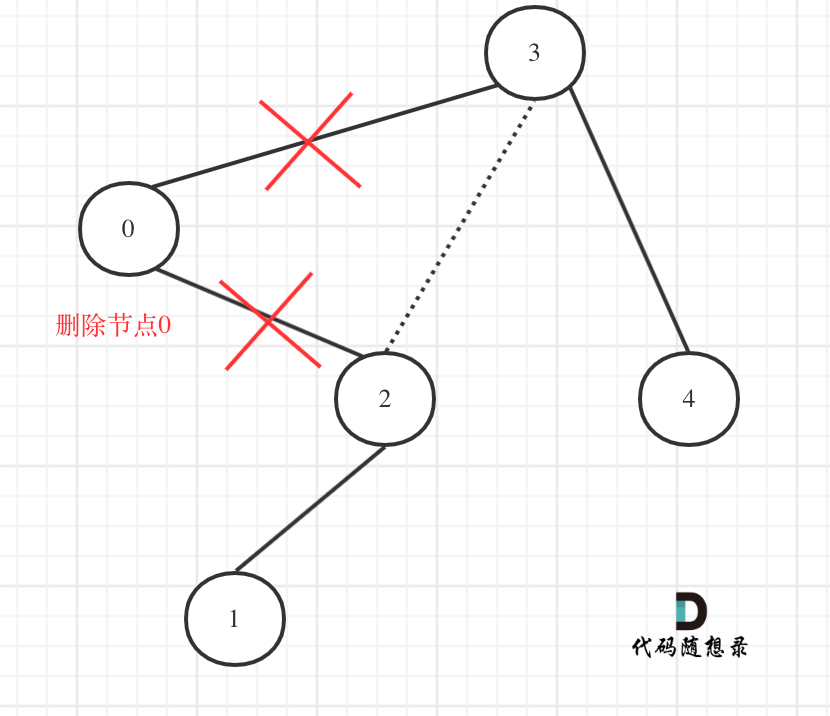
|
||||
|
||||
如下代码相当于把节点0的右孩子(节点2)返回给上一层,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
if (root->val < low) {
|
||||
TreeNode* right = trimBST(root->right, low, high); // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点
|
||||
|
|
@ -243,7 +246,7 @@ public:
|
|||
# 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Java
|
||||
## Java
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
|
|
@ -266,8 +269,10 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
**递归**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
# class TreeNode:
|
||||
|
|
@ -287,7 +292,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
if root.val < low:
|
||||
# 若当前root节点小于左界:只考虑其右子树,用于替代更新后的其本身,抛弃其左子树整体
|
||||
return self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if high < root.val:
|
||||
# 若当前root节点大于右界:只考虑其左子树,用于替代更新后的其本身,抛弃其右子树整体
|
||||
return self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
|
||||
|
|
@ -300,6 +305,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**迭代**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
|
||||
|
|
@ -325,10 +331,9 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
return root
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
## Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) *TreeNode {
|
||||
if root == nil {
|
||||
|
|
@ -384,6 +389,7 @@ func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) *TreeNode {
|
|||
## JavaScript版本
|
||||
|
||||
迭代:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
|
||||
if(root === null) {
|
||||
|
|
@ -416,8 +422,9 @@ var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
递归:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var trimBST = function (root,low,high) {
|
||||
var trimBST = function (root,low,high) {
|
||||
if(root === null) {
|
||||
return null;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -486,6 +493,7 @@ function trimBST(root: TreeNode | null, low: number, high: number): TreeNode | n
|
|||
## Scala
|
||||
|
||||
递归法:
|
||||
|
||||
```scala
|
||||
object Solution {
|
||||
def trimBST(root: TreeNode, low: Int, high: Int): TreeNode = {
|
||||
|
|
@ -502,6 +510,7 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
## rust
|
||||
|
||||
// 递归
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
pub fn trim_bst(
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
输入:[1,3,5,4,7]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**如果代码写出来了,怎么改都通过不了,那么把dp和count打印出来看看对不对!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,8 @@ for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
已输入nums = [1,3,5,4,7]为例,dp数组状态如下:
|
||||
|
||||
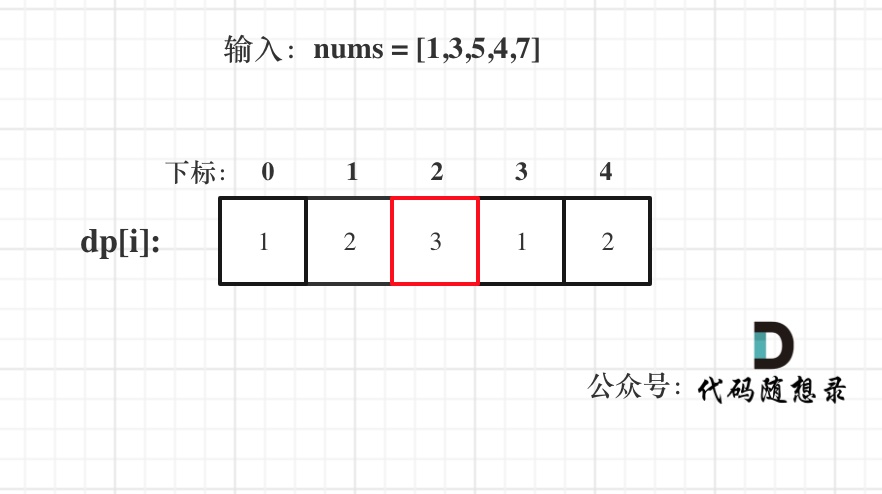
|
||||
|
||||
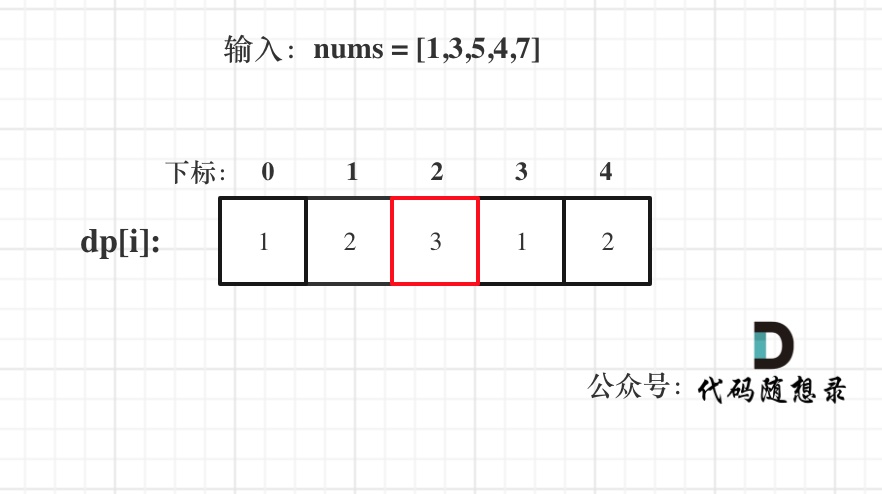
|
||||
|
||||
**注意这里要取dp[i]里的最大值,所以dp[2]才是结果!**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在上述示例中,如果要找的值是 5,但因为没有节点值为 5,我们应该返回 NULL。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -125,7 +126,7 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
中间节点如果大于3就向左走,如果小于3就向右走,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以迭代法代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回任意有效的结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
提示:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
例如在数组:1,2,3,4,7,9,10中查找元素2,如图所示:
|
||||
|
||||
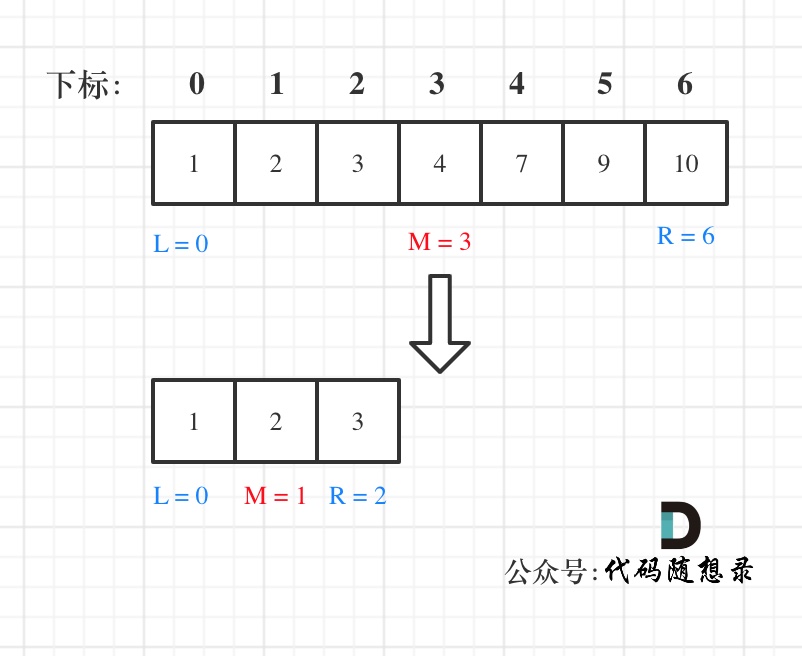
|
||||
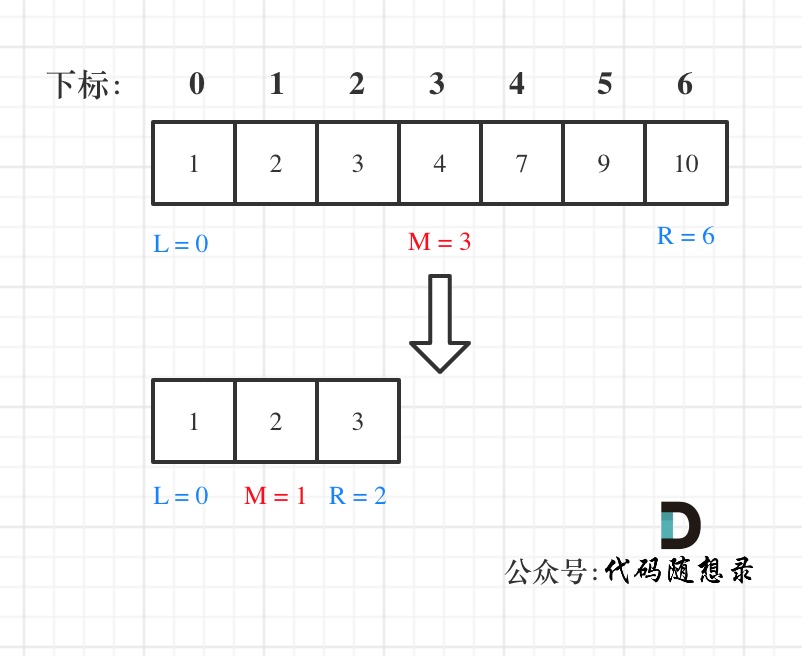
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:(详细注释)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +98,8 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在数组:1,2,3,4,7,9,10中查找元素2,如图所示:(**注意和方法一的区别**)
|
||||
|
||||
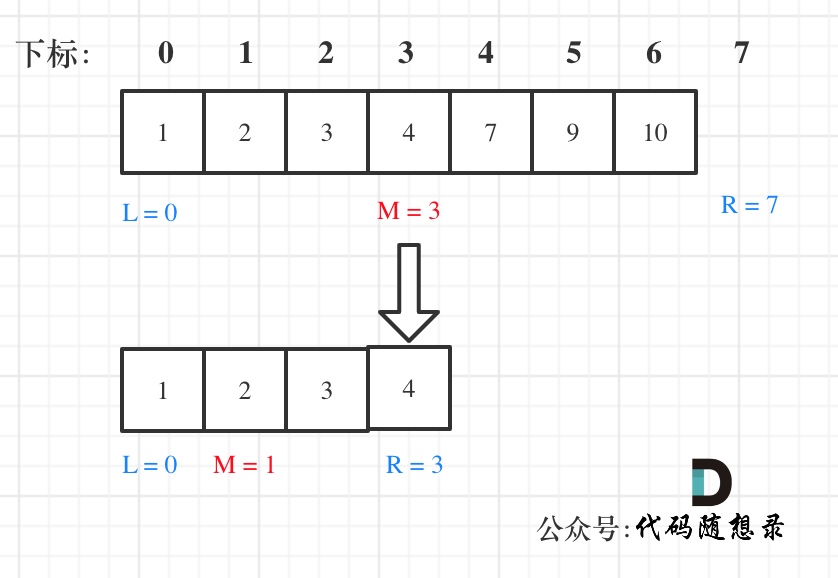
|
||||
|
||||
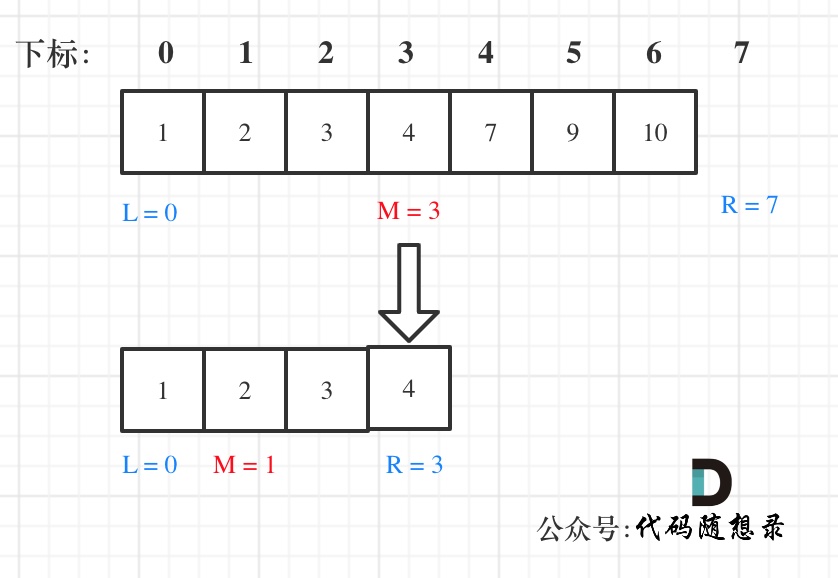
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:(详细注释)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
|||
* deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,10 +33,10 @@
|
|||
如果对链表的虚拟头结点不清楚,可以看这篇文章:[链表:听说用虚拟头节点会方便很多?](https://programmercarl.com/0203.移除链表元素.html)
|
||||
|
||||
删除链表节点:
|
||||
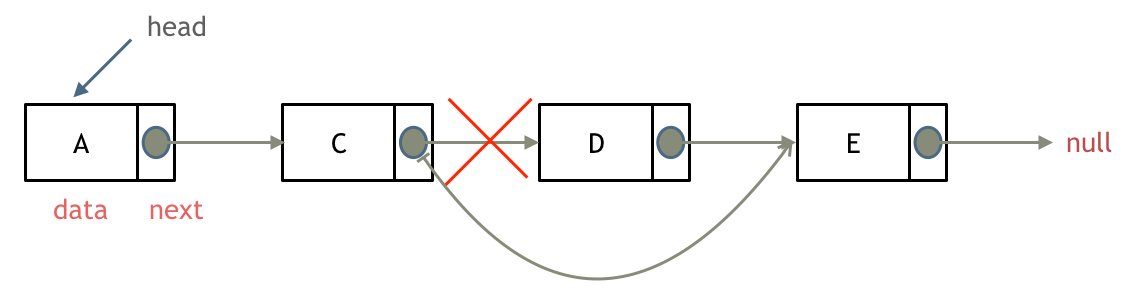
|
||||
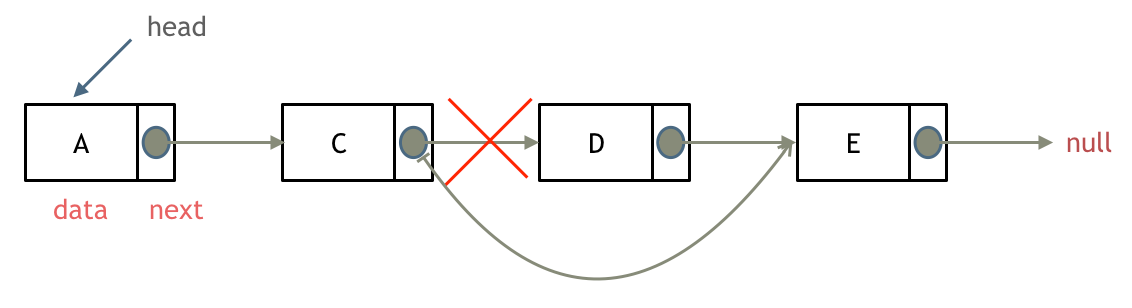
|
||||
|
||||
添加链表节点:
|
||||
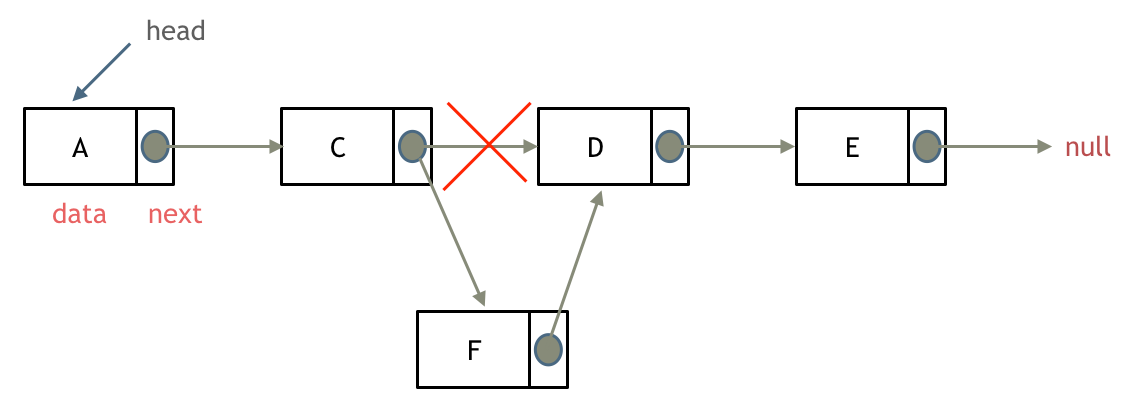
|
||||
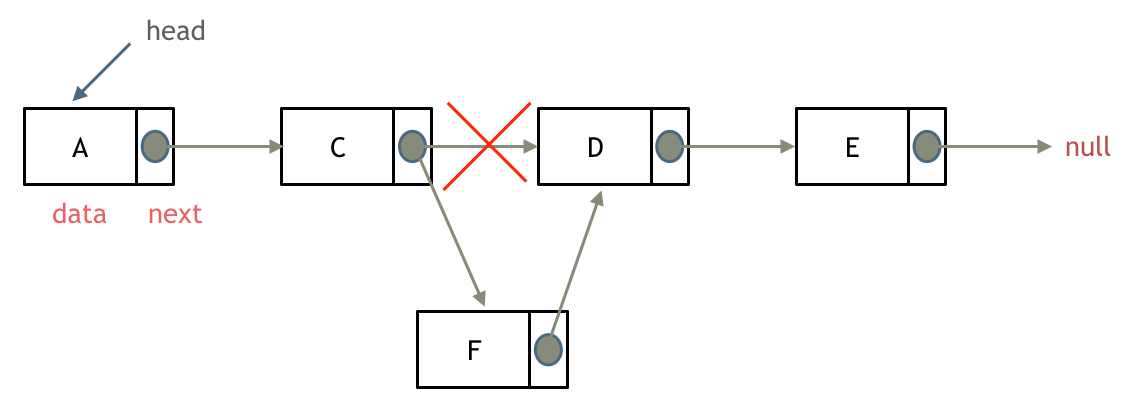
|
||||
|
||||
这道题目设计链表的五个接口:
|
||||
* 获取链表第index个节点的数值
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -93,7 +93,8 @@ for (int i = 1; i <= nums1.size(); i++) {
|
|||
|
||||
拿示例1中,A: [1,2,3,2,1],B: [3,2,1,4,7]为例,画一个dp数组的状态变化,如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
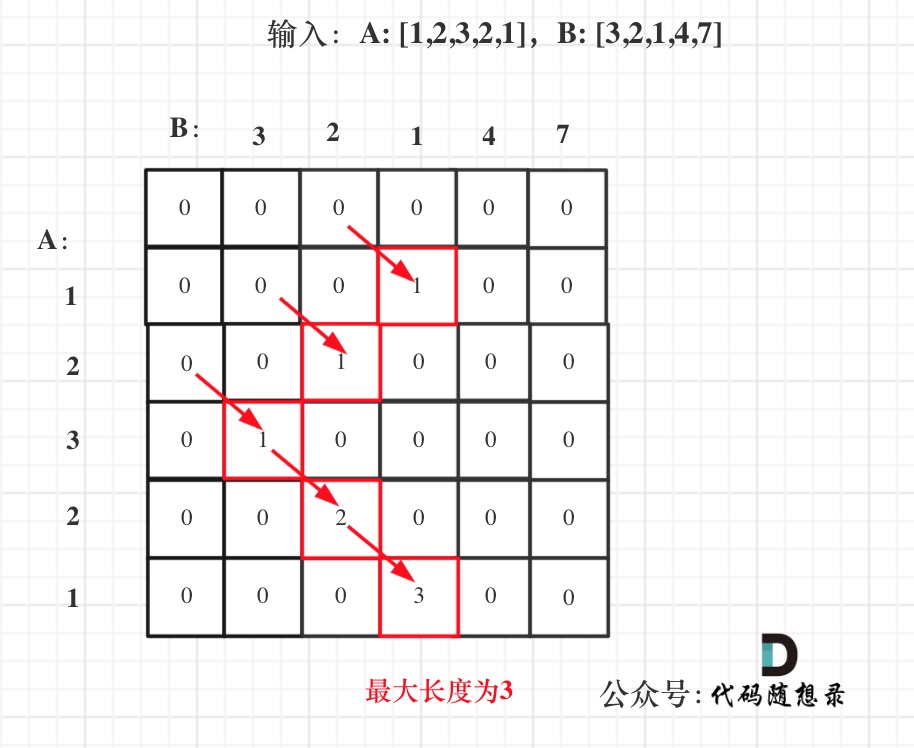
|
||||
|
||||
以上五部曲分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,7 +125,8 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
在如下图中:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
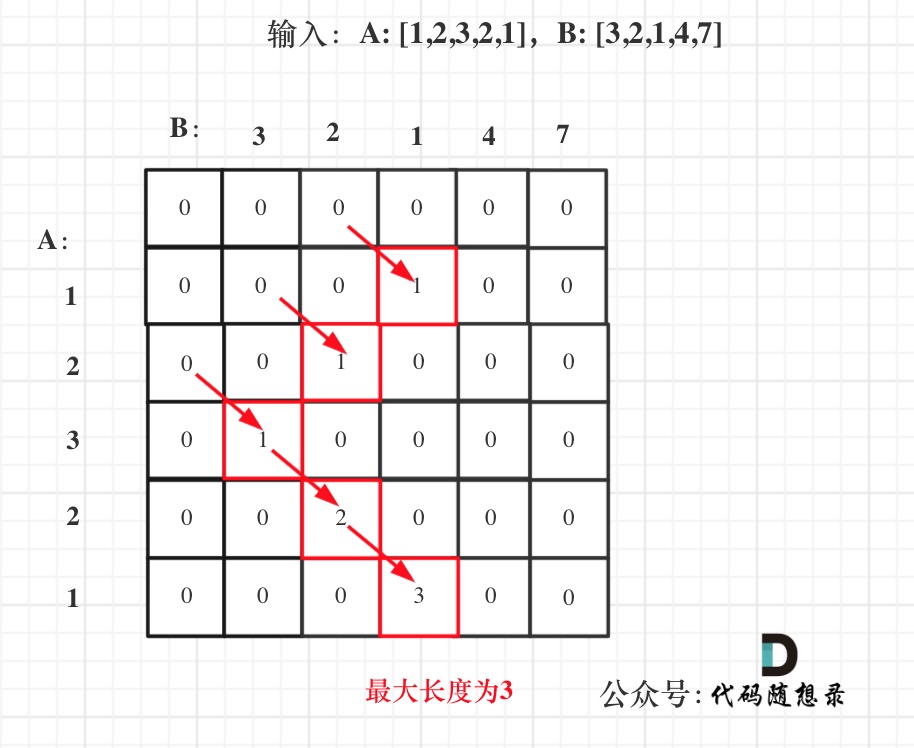
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以看出dp[i][j]都是由dp[i - 1][j - 1]推出。那么压缩为一维数组,也就是dp[j]都是由dp[j - 1]推出。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,15 +6,16 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 739. 每日温度
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/)
|
||||
|
||||
请根据每日 气温 列表,重新生成一个列表。对应位置的输出为:要想观测到更高的气温,至少需要等待的天数。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
|
||||
请根据每日 气温 列表,重新生成一个列表。对应位置的输出为:要想观测到更高的气温,至少需要等待的天数。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,给定一个列表 temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73],你的输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。
|
||||
例如,给定一个列表 temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73],你的输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。
|
||||
|
||||
提示:气温 列表长度的范围是 [1, 30000]。每个气温的值的均为华氏度,都是在 [30, 100] 范围内的整数。
|
||||
提示:气温 列表长度的范围是 [1, 30000]。每个气温的值的均为华氏度,都是在 [30, 100] 范围内的整数。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,7 +34,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
**单调栈的本质是空间换时间**,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素高的元素,优点是整个数组只需要遍历一次。
|
||||
|
||||
**更直白来说,就是用一个栈来记录我们遍历过的元素**,因为我们遍历数组的时候,我们不知道之前都遍历了哪些元素,以至于遍历一个元素找不到是不是之前遍历过一个更小的,所以我们需要用一个容器(这里用单调栈)来记录我们遍历过的元素。
|
||||
**更直白来说,就是用一个栈来记录我们遍历过的元素**,因为我们遍历数组的时候,我们不知道之前都遍历了哪些元素,以至于遍历一个元素找不到是不是之前遍历过一个更小的,所以我们需要用一个容器(这里用单调栈)来记录我们遍历过的元素。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在使用单调栈的时候首先要明确如下几点:
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,79 +61,79 @@
|
|||
|
||||
**把这三种情况分析清楚了,也就理解透彻了**。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们用temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 71, 72, 76, 73]为例来逐步分析,输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。
|
||||
接下来我们用temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 71, 72, 76, 73]为例来逐步分析,输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
首先先将第一个遍历元素加入单调栈
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
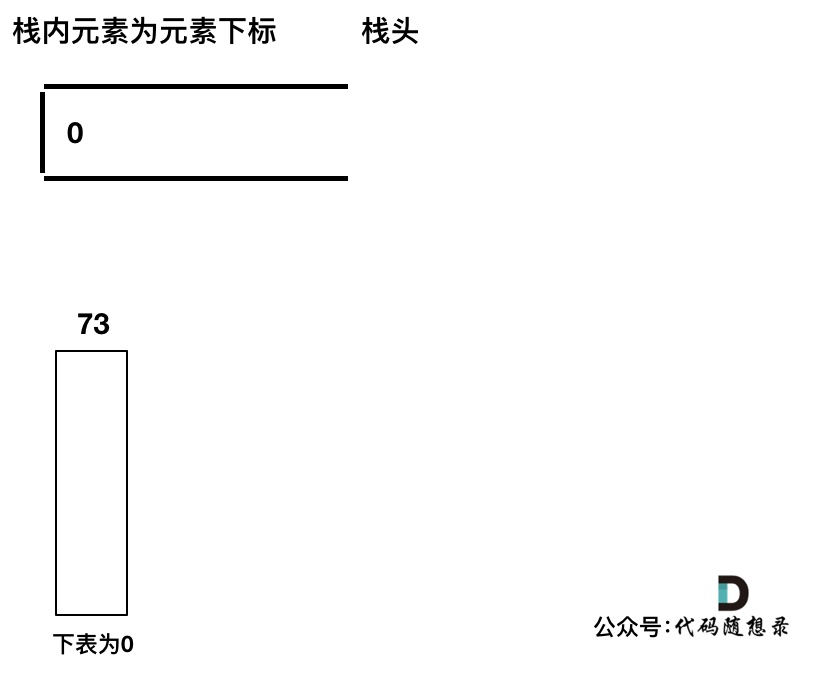
|
||||
|
||||
---------
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[1] = 74,因为T[1] > T[0](当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况)。
|
||||
|
||||
我们要保持一个递增单调栈(从栈头到栈底),所以将T[0]弹出,T[1]加入,此时result数组可以记录了,result[0] = 1,即T[0]右面第一个比T[0]大的元素是T[1]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
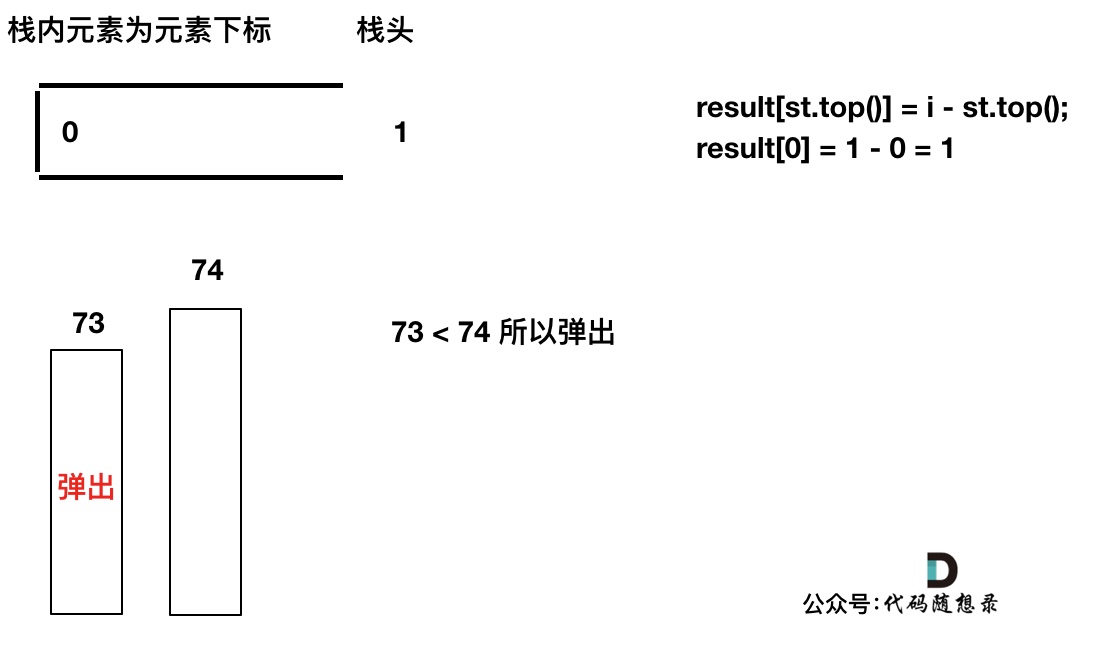
|
||||
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[2],同理,T[1]弹出
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
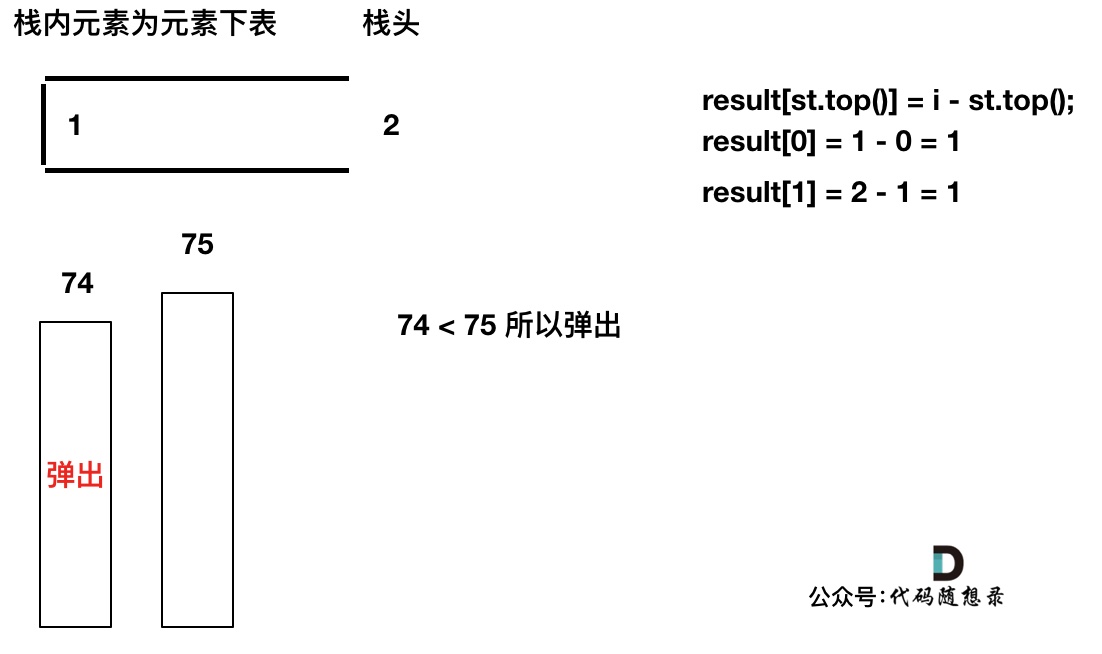
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[3],T[3] < T[2] (当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),加T[3]加入单调栈。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
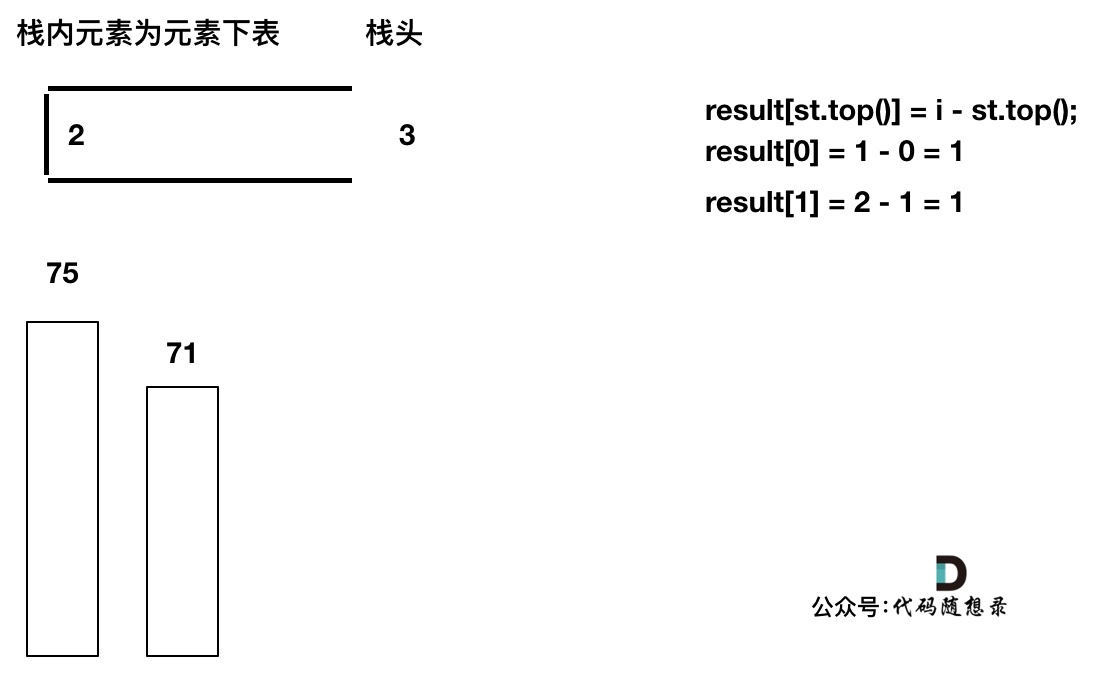
|
||||
|
||||
---------
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[4],T[4] == T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),此时依然要加入栈,不用计算距离,因为我们要求的是右面第一个大于本元素的位置,而不是大于等于!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
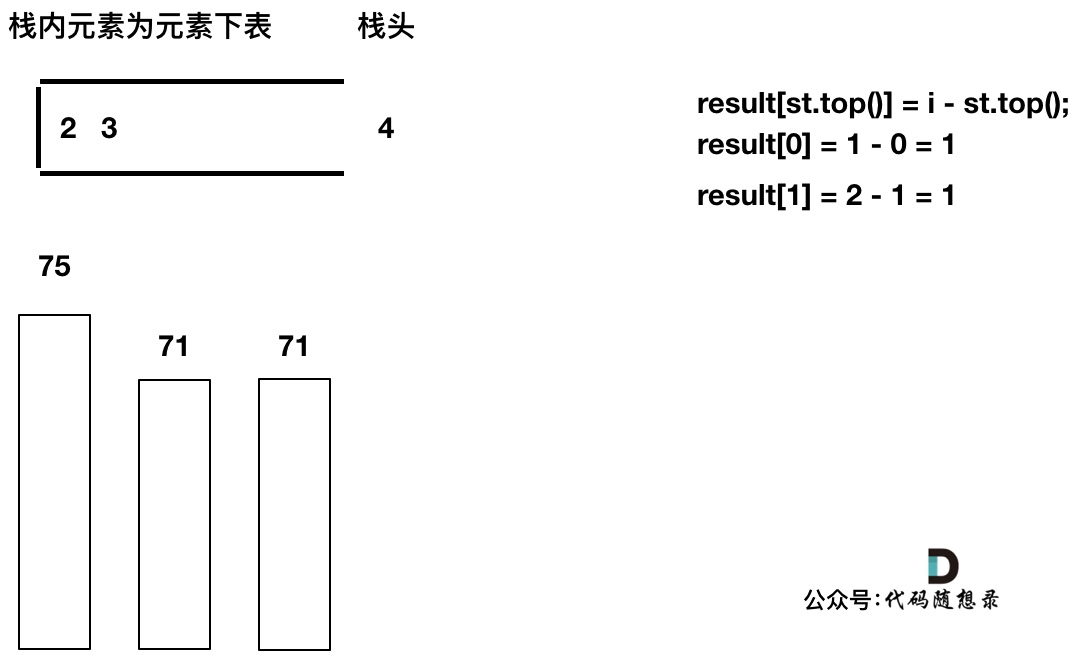
|
||||
|
||||
---------
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[5],T[5] > T[4] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[4]弹出,同时计算距离,更新result
|
||||

|
||||
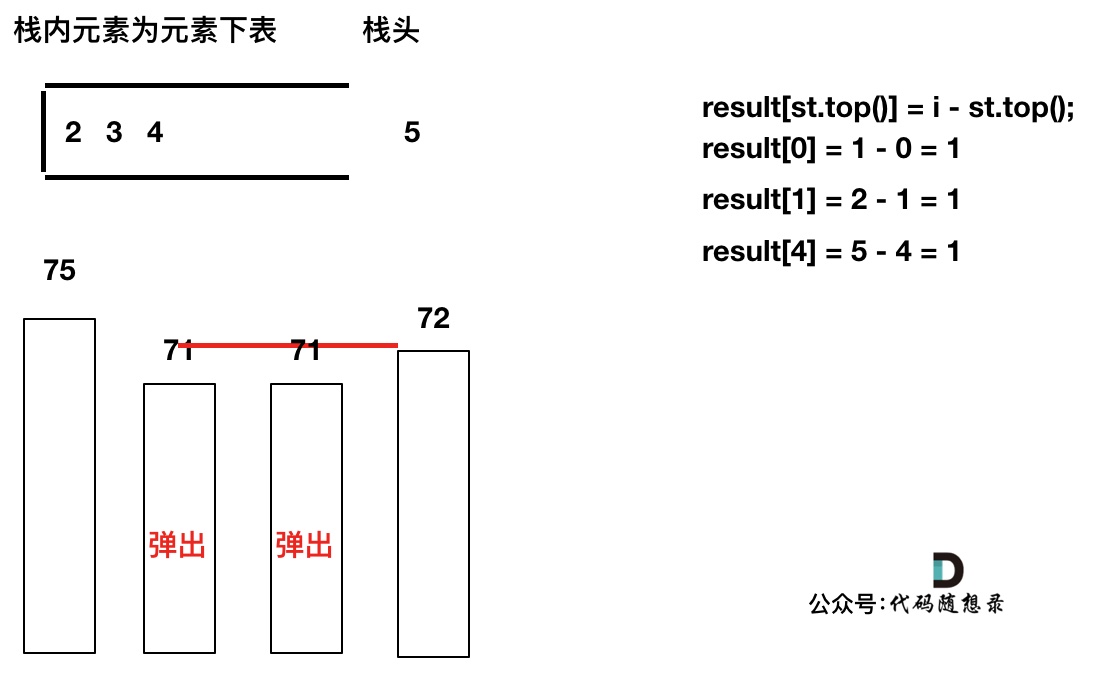
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
T[4]弹出之后, T[5] > T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[3]继续弹出,同时计算距离,更新result
|
||||

|
||||
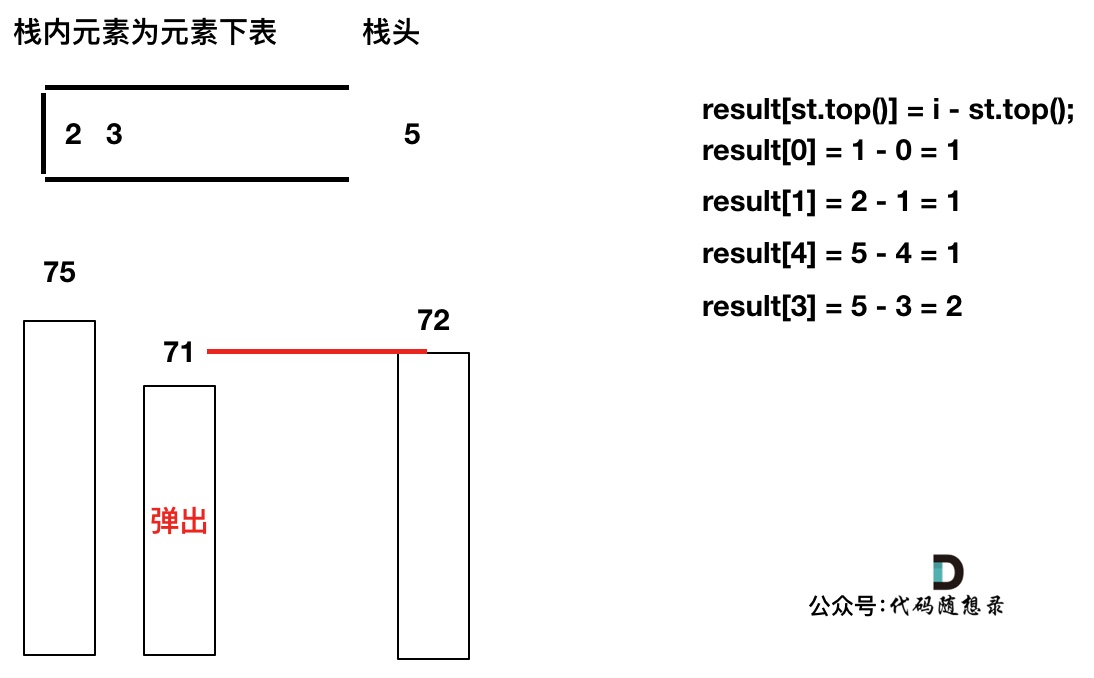
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
直到发现T[5]小于T[st.top()],终止弹出,将T[5]加入单调栈
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
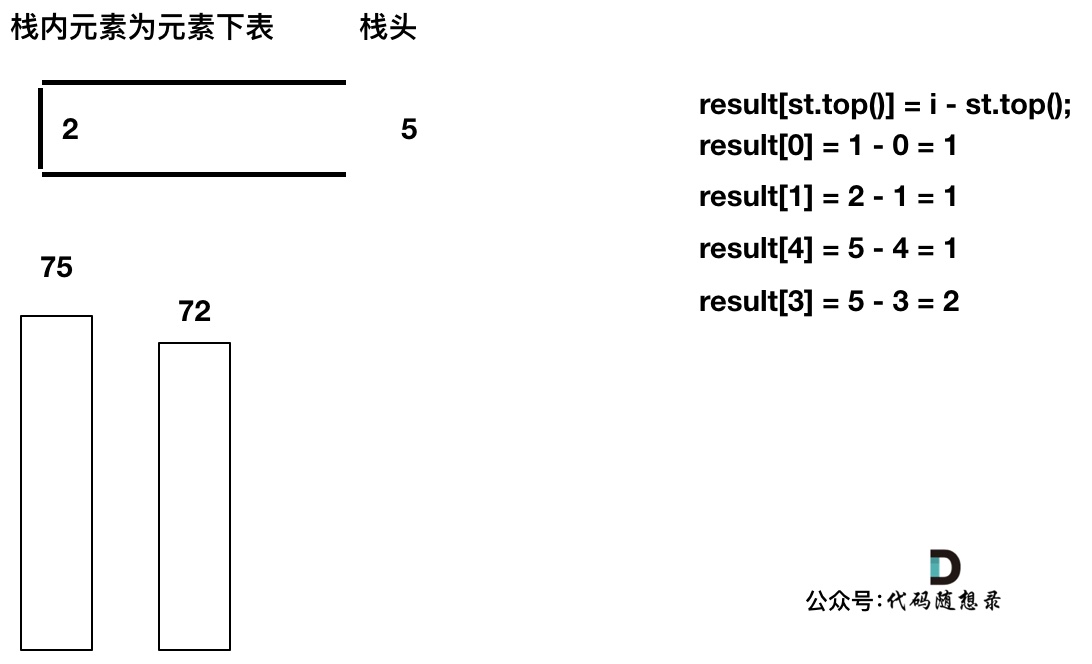
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[6],同理,需要将栈里的T[5],T[2]弹出
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
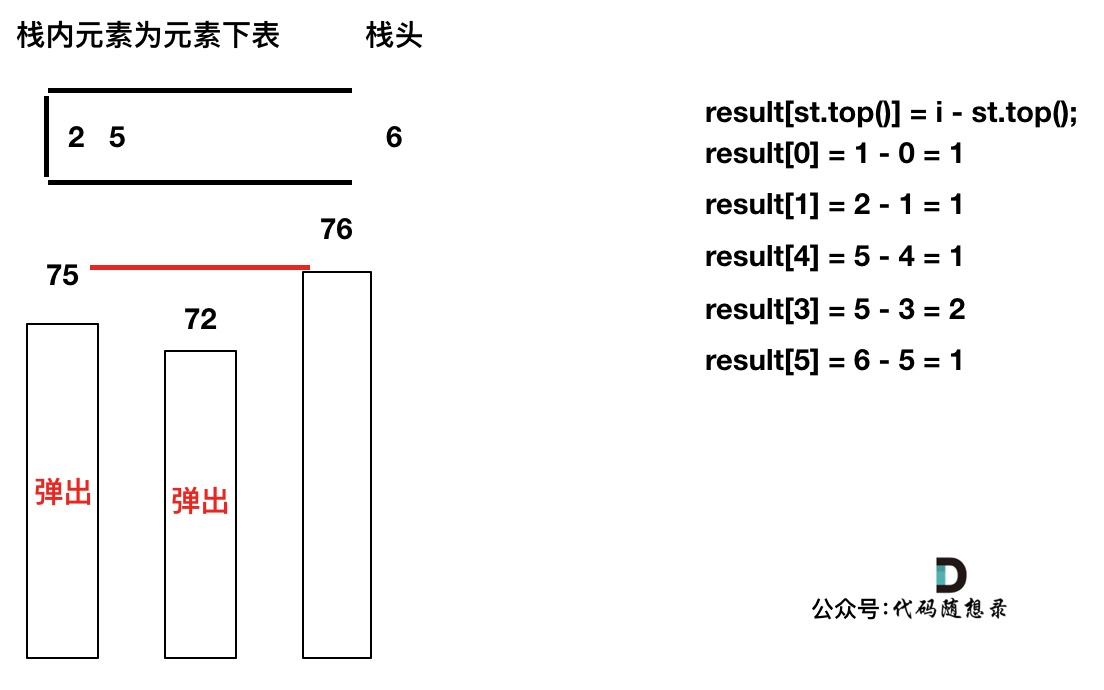
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
同理,继续弹出
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
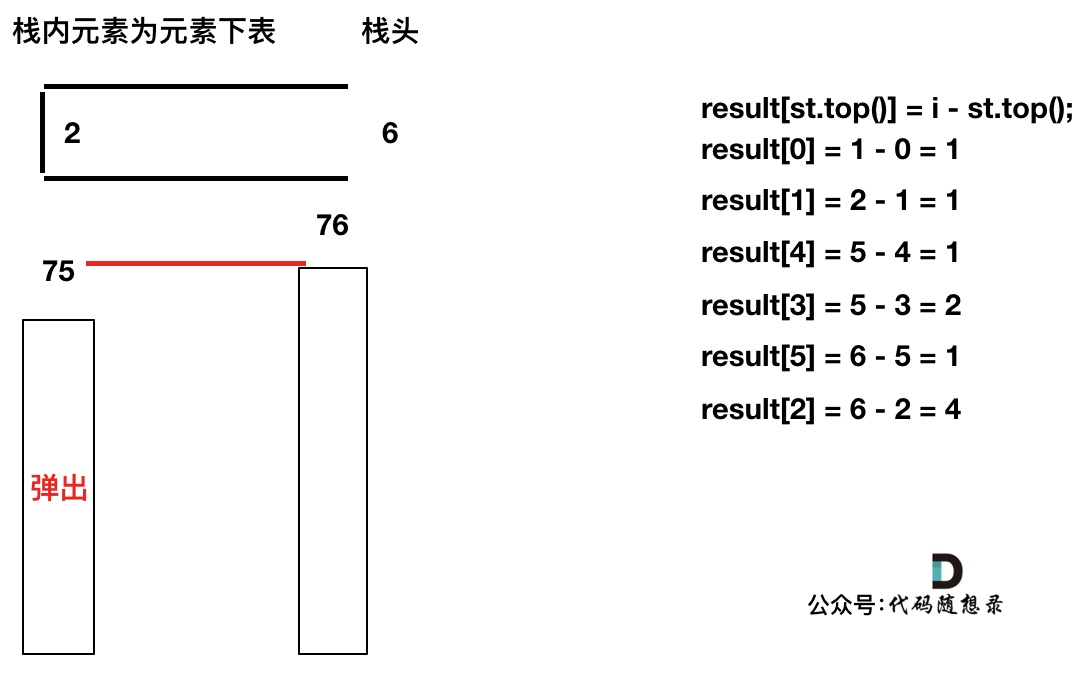
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
此时栈里只剩下了T[6]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
------------
|
||||
|
||||
加入T[7], T[7] < T[6] 直接入栈,这就是最后的情况,result数组也更新完了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
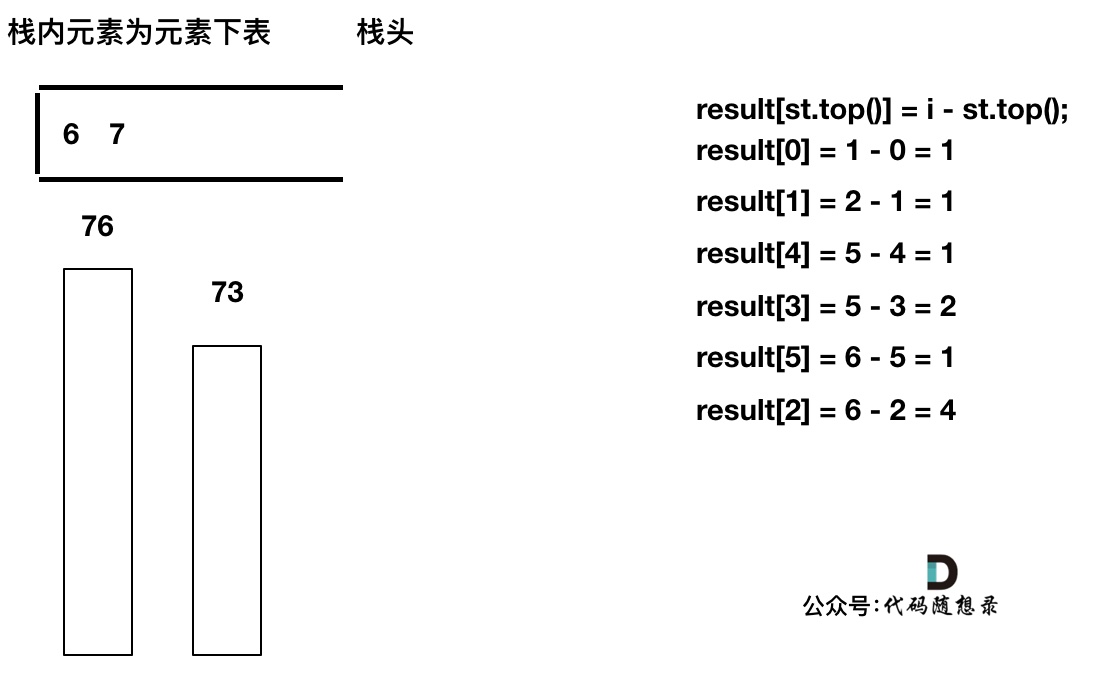
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
此时有同学可能就疑惑了,那result[6] , result[7]怎么没更新啊,元素也一直在栈里。
|
||||
|
|
@ -144,7 +146,7 @@ T[4]弹出之后, T[5] > T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[
|
|||
* 情况二:当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
|
||||
* 情况三:当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上过程,大家可以自己再模拟一遍,就会发现:只有单调栈递增(从栈口到栈底顺序),就是求右边第一个比自己大的,单调栈递减的话,就是求右边第一个比自己小的。
|
||||
通过以上过程,大家可以自己再模拟一遍,就会发现:只有单调栈递增(从栈口到栈底顺序),就是求右边第一个比自己大的,单调栈递减的话,就是求右边第一个比自己小的。
|
||||
|
||||
C++代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -198,6 +200,7 @@ public:
|
|||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -210,26 +213,26 @@ public:
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
Java:
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
// 版本 1
|
||||
// 版本 1
|
||||
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int lens=temperatures.length;
|
||||
int []res=new int[lens];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
如果当前遍历的元素 大于栈顶元素,表示 栈顶元素的 右边的最大的元素就是 当前遍历的元素,
|
||||
所以弹出 栈顶元素,并记录
|
||||
如果栈不空的话,还要考虑新的栈顶与当前元素的大小关系
|
||||
所以弹出 栈顶元素,并记录
|
||||
如果栈不空的话,还要考虑新的栈顶与当前元素的大小关系
|
||||
否则的话,可以直接入栈。
|
||||
注意,单调栈里 加入的元素是 下标。
|
||||
*/
|
||||
Deque<Integer> stack=new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
stack.push(0);
|
||||
for(int i=1;i<lens;i++){
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if(temperatures[i]<=temperatures[stack.peek()]){
|
||||
stack.push(i);
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
|
|
@ -243,16 +246,16 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//--------这 是一条分界线
|
||||
// 版本 2
|
||||
// 版本 2
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
|
||||
int lens=temperatures.length;
|
||||
int []res=new int[lens];
|
||||
Deque<Integer> stack=new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
for(int i=0;i<lens;i++){
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[stack.peek()]){
|
||||
res[stack.peek()]=i-stack.peek();
|
||||
stack.pop();
|
||||
|
|
@ -263,10 +266,12 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def dailyTemperatures(self, temperatures: List[int]) -> List[int]:
|
||||
|
|
@ -282,9 +287,10 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
answer[stack[-1]]=i-stack[-1]
|
||||
stack.pop()
|
||||
stack.append(i)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Go:
|
||||
|
||||
> 暴力法
|
||||
|
|
@ -341,6 +347,7 @@ func dailyTemperatures(temperatures []int) []int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 单调栈法(精简版本)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 单调递减栈
|
||||
func dailyTemperatures(num []int) []int {
|
||||
|
|
@ -362,6 +369,7 @@ func dailyTemperatures(num []int) []int {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JavaScript:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
// 版本一
|
||||
var dailyTemperatures = function(temperatures) {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
明白原理之后,代码并不复杂,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +6,7 @@
|
|||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 968.监控二叉树
|
||||
|
||||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-cameras/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,7 +19,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:[0,0,null,0,0]
|
||||
* 输出:1
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,7 +27,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
示例 2:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* 输入:[0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
|
||||
* 输出:2
|
||||
|
|
@ -139,7 +141,7 @@ if (cur == NULL) return 2;
|
|||
|
||||
如图:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
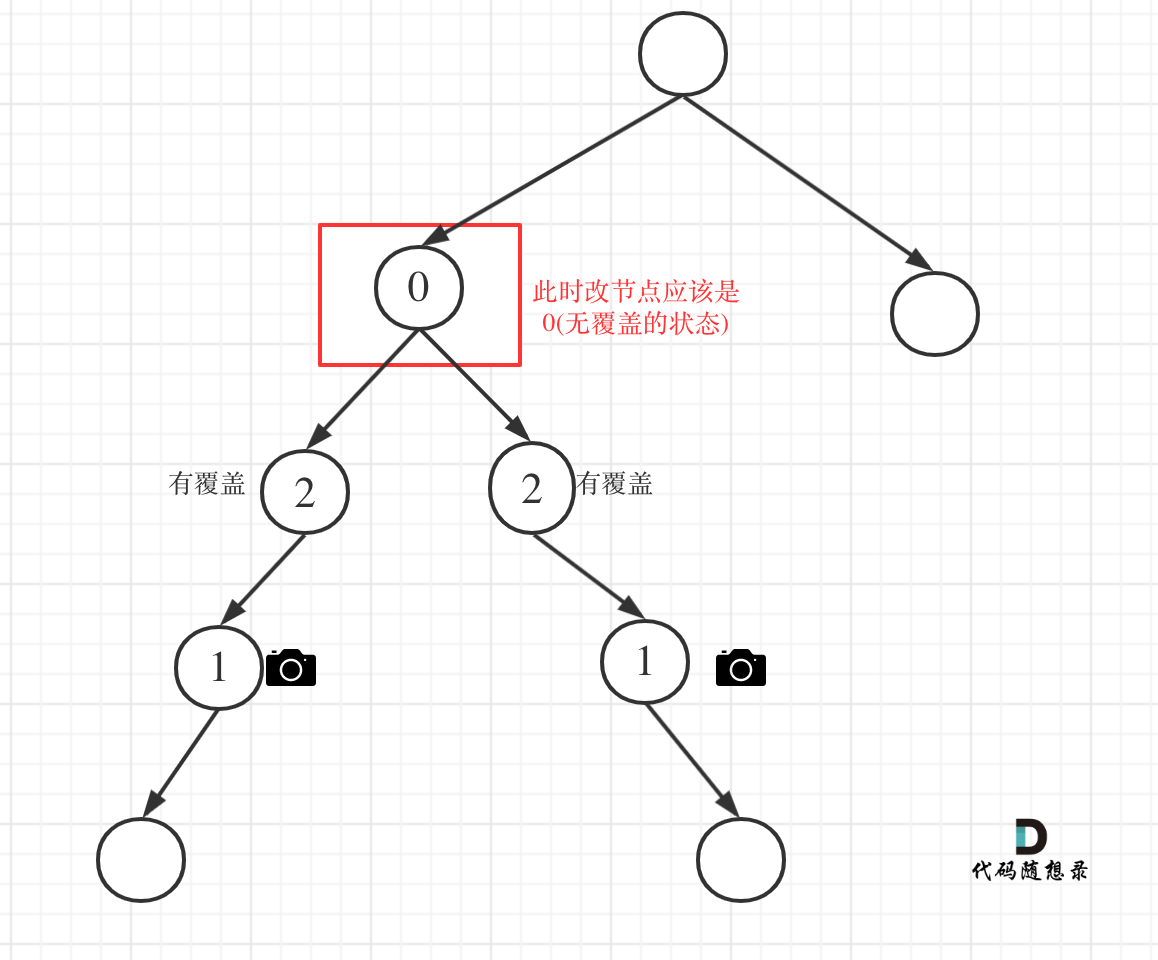
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -163,6 +165,7 @@ if (left == 2 && right == 2) return 0;
|
|||
此时摄像头的数量要加一,并且return 1,代表中间节点放摄像头。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
|
||||
result++;
|
||||
|
|
@ -186,7 +189,7 @@ if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
|
|||
|
||||
**从这个代码中,可以看出,如果left == 1, right == 0 怎么办?其实这种条件在情况2中已经判断过了**,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
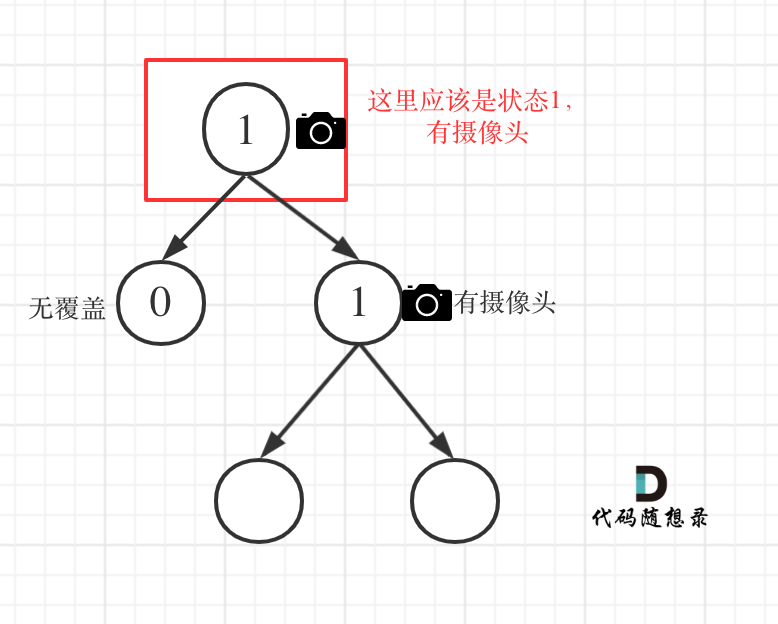
|
||||
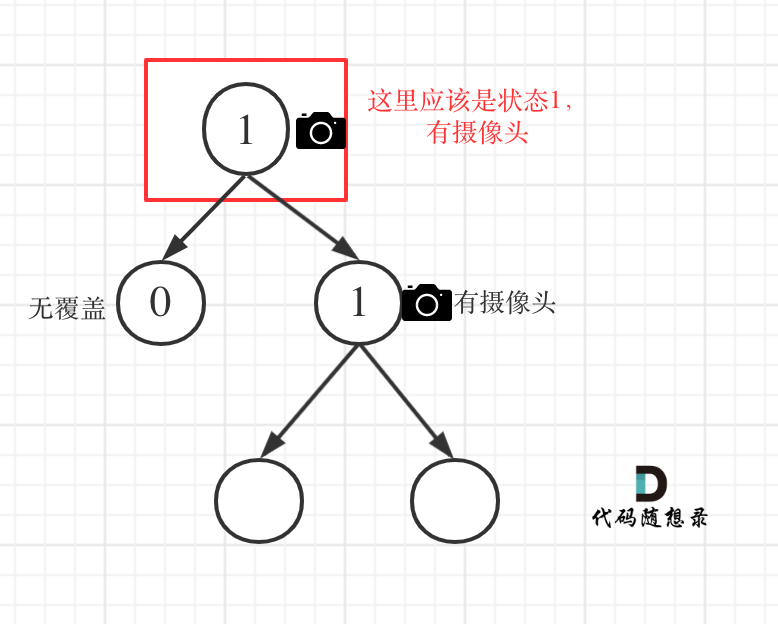
|
||||
|
||||
这种情况也是大多数同学容易迷惑的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -194,7 +197,7 @@ if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
|
|||
|
||||
以上都处理完了,递归结束之后,可能头结点 还有一个无覆盖的情况,如图:
|
||||
|
||||
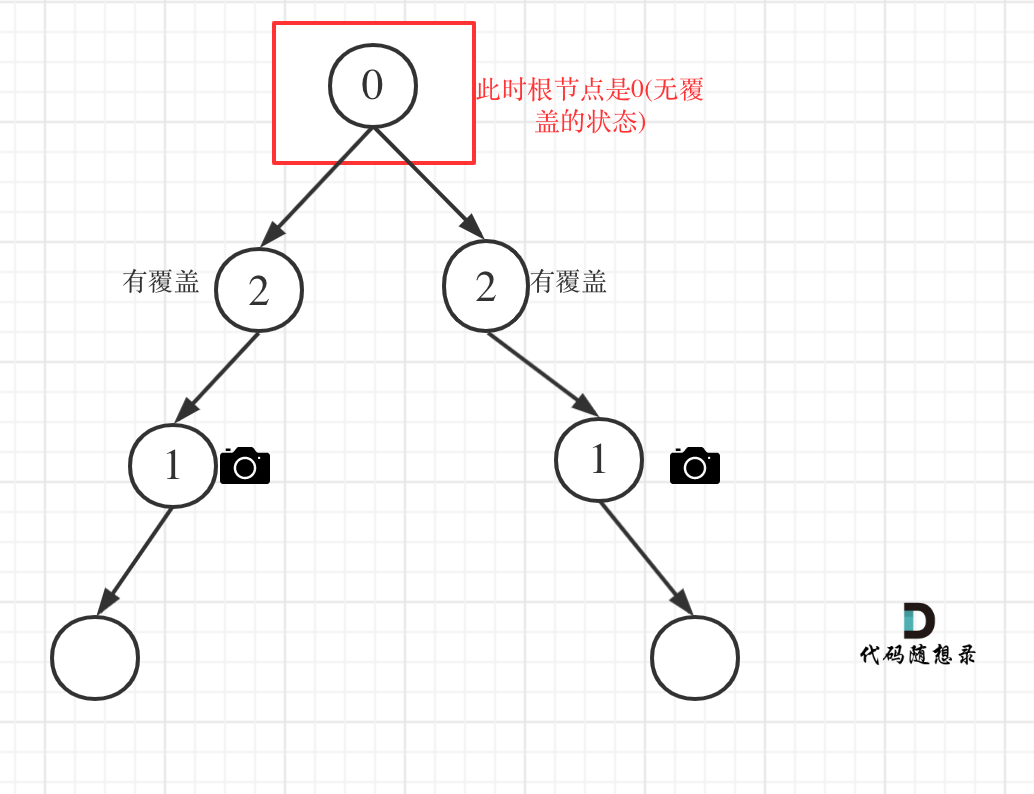
|
||||
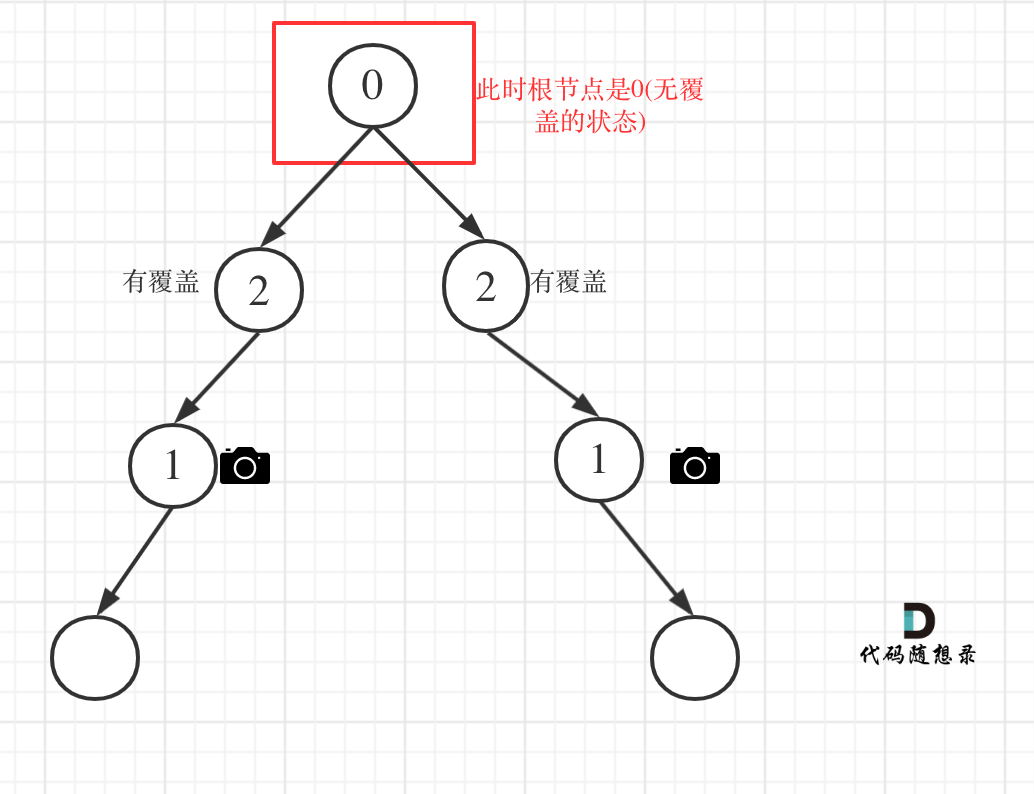
|
||||
|
||||
所以递归结束之后,还要判断根节点,如果没有覆盖,result++,代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -311,7 +314,8 @@ public:
|
|||
## 其他语言版本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
### Java
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
int res=0;
|
||||
|
|
@ -324,32 +328,32 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
/**
|
||||
节点的状态值:
|
||||
0 表示无覆盖
|
||||
0 表示无覆盖
|
||||
1 表示 有摄像头
|
||||
2 表示有覆盖
|
||||
2 表示有覆盖
|
||||
后序遍历,根据左右节点的情况,来判读 自己的状态
|
||||
*/
|
||||
public int minCame(TreeNode root){
|
||||
if(root==null){
|
||||
// 空节点默认为 有覆盖状态,避免在叶子节点上放摄像头
|
||||
// 空节点默认为 有覆盖状态,避免在叶子节点上放摄像头
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
int left=minCame(root.left);
|
||||
int right=minCame(root.right);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 如果左右节点都覆盖了的话, 那么本节点的状态就应该是无覆盖,没有摄像头
|
||||
if(left==2&&right==2){
|
||||
//(2,2)
|
||||
//(2,2)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}else if(left==0||right==0){
|
||||
// 左右节点都是无覆盖状态,那 根节点此时应该放一个摄像头
|
||||
// (0,0) (0,1) (0,2) (1,0) (2,0)
|
||||
// (0,0) (0,1) (0,2) (1,0) (2,0)
|
||||
// 状态值为 1 摄像头数 ++;
|
||||
res++;
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
// 左右节点的 状态为 (1,1) (1,2) (2,1) 也就是左右节点至少存在 1个摄像头,
|
||||
// 那么本节点就是处于被覆盖状态
|
||||
// 那么本节点就是处于被覆盖状态
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -357,7 +361,8 @@ class Solution {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class Solution:
|
||||
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
|
||||
|
|
@ -367,19 +372,19 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
# 0: 该节点未覆盖
|
||||
# 1: 该节点有摄像头
|
||||
# 2: 该节点有覆盖
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
result = 0
|
||||
# 从下往上遍历:后序(左右中)
|
||||
def traversal(curr: TreeNode) -> int:
|
||||
nonlocal result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if not curr: return 2
|
||||
left = traversal(curr.left)
|
||||
right = traversal(curr.right)
|
||||
|
||||
# Case 1:
|
||||
# 左右节点都有覆盖
|
||||
if left == 2 and right == 2:
|
||||
if left == 2 and right == 2:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Case 2:
|
||||
|
|
@ -388,7 +393,7 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
# left == 0 && right == 1 左节点有无覆盖,右节点摄像头
|
||||
# left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
|
||||
# left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
|
||||
elif left == 0 or right == 0:
|
||||
elif left == 0 or right == 0:
|
||||
result += 1
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -398,16 +403,17 @@ class Solution:
|
|||
# left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
|
||||
elif left == 1 or right == 1:
|
||||
return 2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 其他情况前段代码均已覆盖
|
||||
|
||||
if traversal(root) == 0:
|
||||
result += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
### Go
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
const inf = math.MaxInt64 / 2
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -437,7 +443,8 @@ func min(a, b int) int {
|
|||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
### Javascript
|
||||
|
||||
```Javascript
|
||||
var minCameraCover = function(root) {
|
||||
let result = 0
|
||||
|
|
@ -470,7 +477,7 @@ var minCameraCover = function(root) {
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -501,7 +508,7 @@ function minCameraCover(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
|||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### C
|
||||
### C
|
||||
|
||||
```c
|
||||
/*
|
||||
|
|
@ -576,7 +583,9 @@ object Solution {
|
|||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Rust
|
||||
|
||||
```Rust
|
||||
/// 版本一
|
||||
impl Solution {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
以这种方法绘制线条,并返回我们可以绘制的最大连线数。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 思路
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < stones.size(); i++) { // 遍历物品
|
|||
|
||||
举例,输入:[2,4,1,1],此时target = (2 + 4 + 1 + 1)/2 = 4 ,dp数组状态图如下:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
最后dp[target]里是容量为target的背包所能背的最大重量。
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ vector<vector<int>> dp(text1.size() + 1, vector<int>(text2.size() + 1, 0));
|
|||
|
||||
从递推公式,可以看出,有三个方向可以推出dp[i][j],如图:
|
||||
|
||||
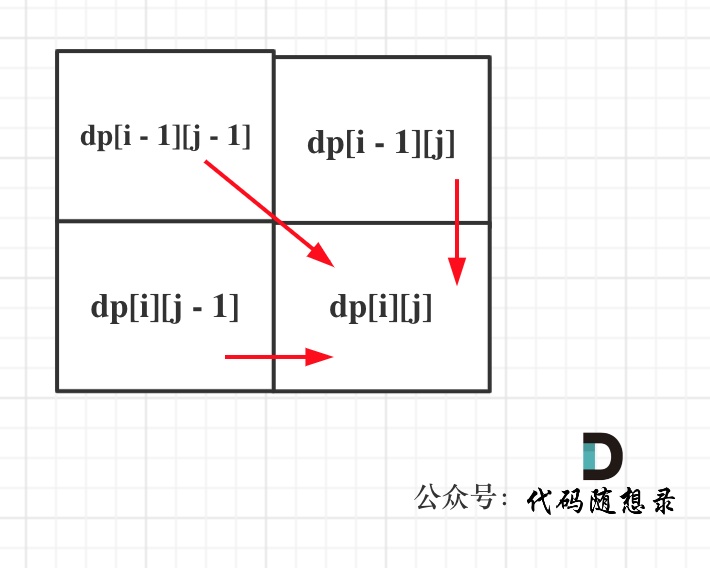
|
||||
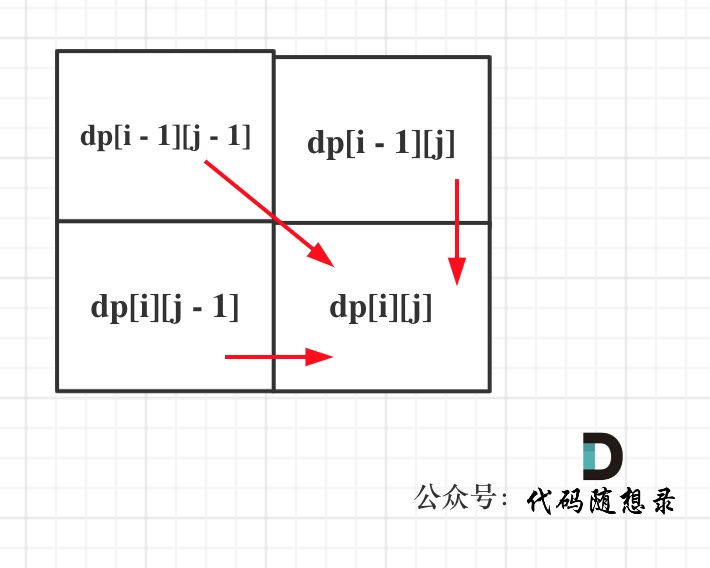
|
||||
|
||||
那么为了在递推的过程中,这三个方向都是经过计算的数值,所以要从前向后,从上到下来遍历这个矩阵。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,7 +99,8 @@ vector<vector<int>> dp(text1.size() + 1, vector<int>(text2.size() + 1, 0));
|
|||
|
||||
以输入:text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" 为例,dp状态如图:
|
||||
|
||||
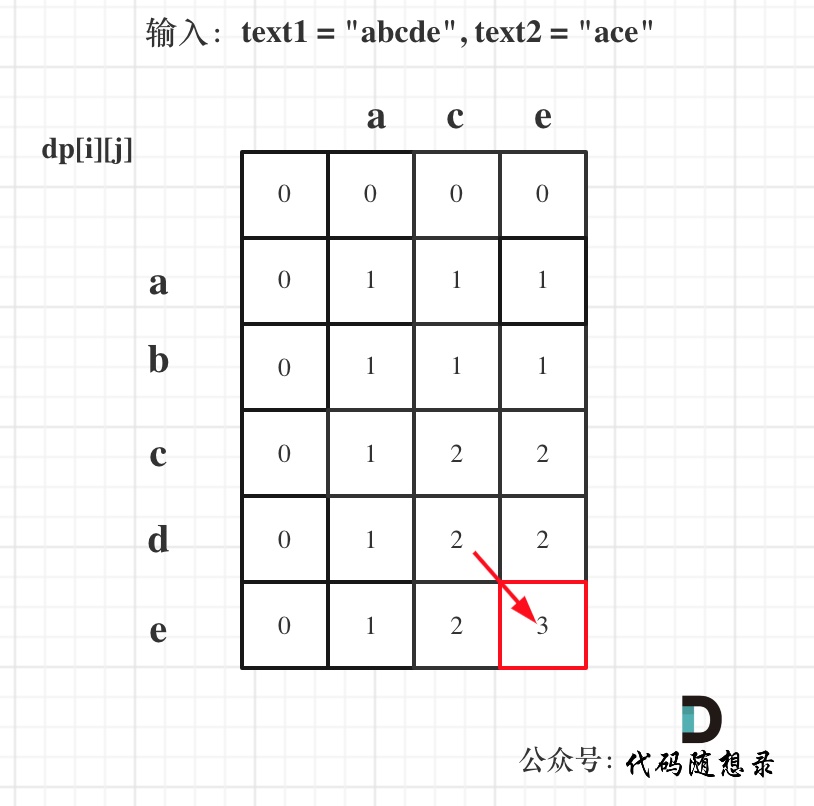
|
||||
|
||||
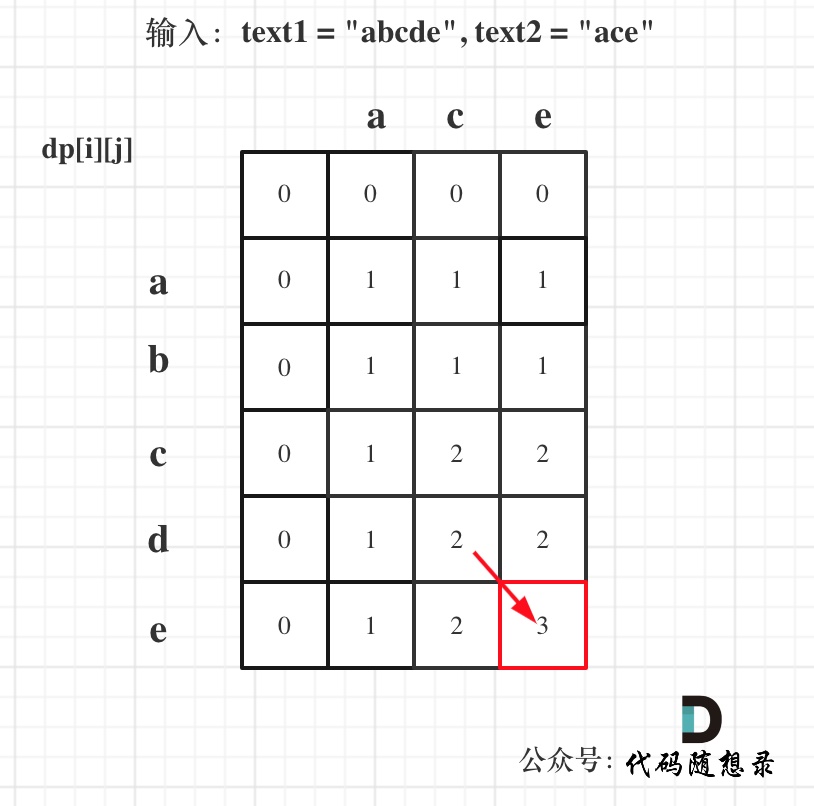
|
||||
|
||||
最后红框dp[text1.size()][text2.size()]为最终结果
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,18 +1,21 @@
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
# 程序提交之后为什么会超时?O(n)的算法会超时,n究竟是多大?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一些同学可能对计算机运行的速度还没有概念,就是感觉计算机运行速度应该会很快,那么在leetcode上做算法题目的时候为什么会超时呢?
|
||||
|
||||
计算机究竟1s可以执行多少次操作呢? 接下来探讨一下这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
# 超时是怎么回事
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
大家在leetcode上练习算法的时候应该都遇到过一种错误是“超时”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,6 +55,7 @@
|
|||
尽管有很多因素影响,但是还是可以对自己程序的运行时间有一个大体的评估的。
|
||||
|
||||
引用算法4里面的一段话:
|
||||
|
||||
* 火箭科学家需要大致知道一枚试射火箭的着陆点是在大海里还是在城市中;
|
||||
* 医学研究者需要知道一次药物测试是会杀死还是会治愈实验对象;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -103,6 +107,7 @@ void function3(long long n) {
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
来看一下这三个函数随着n的规模变化,耗时会产生多大的变化,先测function1 ,就把 function2 和 function3 注释掉
|
||||
|
||||
```CPP
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
long long n; // 数据规模
|
||||
|
|
@ -126,11 +131,11 @@ int main() {
|
|||
|
||||
来看一下运行的效果,如下图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
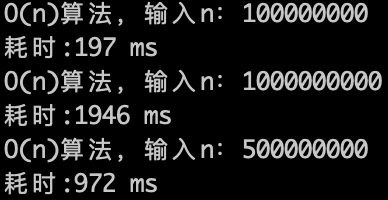
|
||||
|
||||
O(n)的算法,1s内大概计算机可以运行 5 * (10^8)次计算,可以推测一下O(n^2) 的算法应该1s可以处理的数量级的规模是 5 * (10^8)开根号,实验数据如下。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
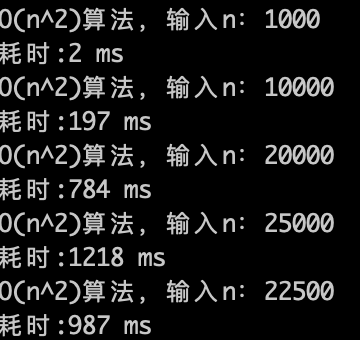
|
||||
|
||||
O(n^2)的算法,1s内大概计算机可以运行 22500次计算,验证了刚刚的推测。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -138,7 +143,7 @@ O(n^2)的算法,1s内大概计算机可以运行 22500次计算,验证了刚
|
|||
|
||||
理论上应该是比 O(n)少一个数量级,因为logn的复杂度 其实是很快,看一下实验数据。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
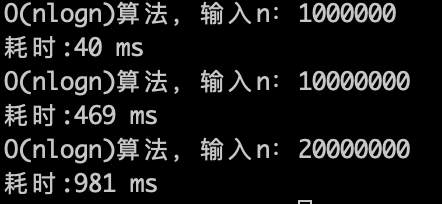
|
||||
|
||||
O(nlogn)的算法,1s内大概计算机可以运行 2 * (10^7)次计算,符合预期。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,7 +151,7 @@ O(nlogn)的算法,1s内大概计算机可以运行 2 * (10^7)次计算,符
|
|||
|
||||
**整体测试数据整理如下:**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
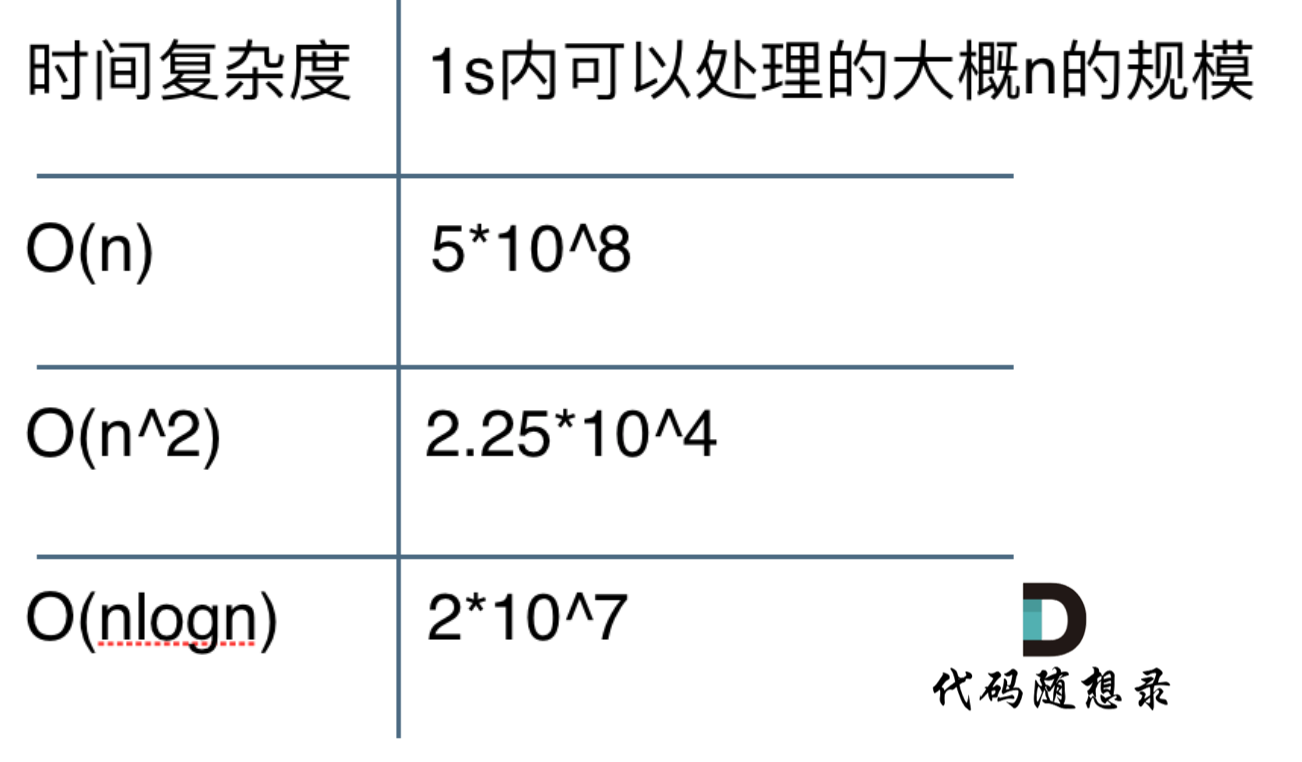
|
||||
|
||||
至于O(log n)和O(n^3) 等等这些时间复杂度在1s内可以处理的多大的数据规模,大家可以自己写一写代码去测一下了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue