 +
+ 
 -
- 
 +
+ 
+
+  +
+
# LeetCode 刷题攻略
@@ -111,14 +117,24 @@
(持续更新中.....)
+## 备战秋招
+
+1. [选择方向的时候,我也迷茫了](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZCzFiAHZHLqHPLJQXNm75g)
+2. [刷题就用库函数了,怎么了?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6K3_OSaudnHGq2Ey8vqYfg)
+3. [关于实习,大家可能有点迷茫!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xcxzi7c78kQGjvZ8hh7taA)
+4. [马上秋招了,慌得很!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7q7W8Cb2-a5U5atZdOnOFA)
+5. [Carl看了上百份简历,总结了这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sJa87MZD28piCOVMFkIbwQ)
+6. [面试中遇到了发散性问题.....](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/SSonDxi2pjkSVwHNzZswng)
+
## 数组
1. [数组过于简单,但你该了解这些!](./problems/数组理论基础.md)
2. [数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
3. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
-4. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
-5. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
-6. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
+4. [数组:有序数组的平方,还有序么?](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
+5. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
+6. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
+7. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
## 链表
@@ -169,10 +185,9 @@
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
-9. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
-10. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
-11. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
-12. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
+9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
+10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
+11. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
## 栈与队列
@@ -292,6 +307,7 @@
动态规划专题已经开始啦,来不及解释了,小伙伴们上车别掉队!
+
+
+
# LeetCode 刷题攻略
@@ -111,14 +117,24 @@
(持续更新中.....)
+## 备战秋招
+
+1. [选择方向的时候,我也迷茫了](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZCzFiAHZHLqHPLJQXNm75g)
+2. [刷题就用库函数了,怎么了?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6K3_OSaudnHGq2Ey8vqYfg)
+3. [关于实习,大家可能有点迷茫!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xcxzi7c78kQGjvZ8hh7taA)
+4. [马上秋招了,慌得很!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7q7W8Cb2-a5U5atZdOnOFA)
+5. [Carl看了上百份简历,总结了这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sJa87MZD28piCOVMFkIbwQ)
+6. [面试中遇到了发散性问题.....](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/SSonDxi2pjkSVwHNzZswng)
+
## 数组
1. [数组过于简单,但你该了解这些!](./problems/数组理论基础.md)
2. [数组:每次遇到二分法,都是一看就会,一写就废](./problems/0704.二分查找.md)
3. [数组:就移除个元素很难么?](./problems/0027.移除元素.md)
-4. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
-5. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
-6. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
+4. [数组:有序数组的平方,还有序么?](./problems/0977.有序数组的平方.md)
+5. [数组:滑动窗口拯救了你](./problems/0209.长度最小的子数组.md)
+6. [数组:这个循环可以转懵很多人!](./problems/0059.螺旋矩阵II.md)
+7. [数组:总结篇](./problems/数组总结篇.md)
## 链表
@@ -169,10 +185,9 @@
6. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
7. [链表:链表相交](./problems/面试题02.07.链表相交.md)
8. [链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](./problems/0142.环形链表II.md)
-9. [链表:删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](./problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md)
-10. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
-11. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
-12. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
+9. [哈希表:解决了两数之和,那么能解决三数之和么?](./problems/0015.三数之和.md)
+10. [双指针法:一样的道理,能解决四数之和](./problems/0018.四数之和.md)
+11. [双指针法:总结篇!](./problems/双指针总结.md)
## 栈与队列
@@ -292,6 +307,7 @@
动态规划专题已经开始啦,来不及解释了,小伙伴们上车别掉队!
+ 1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -305,7 +321,8 @@
背包问题系列:
-
1. [关于动态规划,你该了解这些!](./problems/动态规划理论基础.md)
2. [动态规划:斐波那契数](./problems/0509.斐波那契数.md)
3. [动态规划:爬楼梯](./problems/0070.爬楼梯.md)
@@ -305,7 +321,8 @@
背包问题系列:
-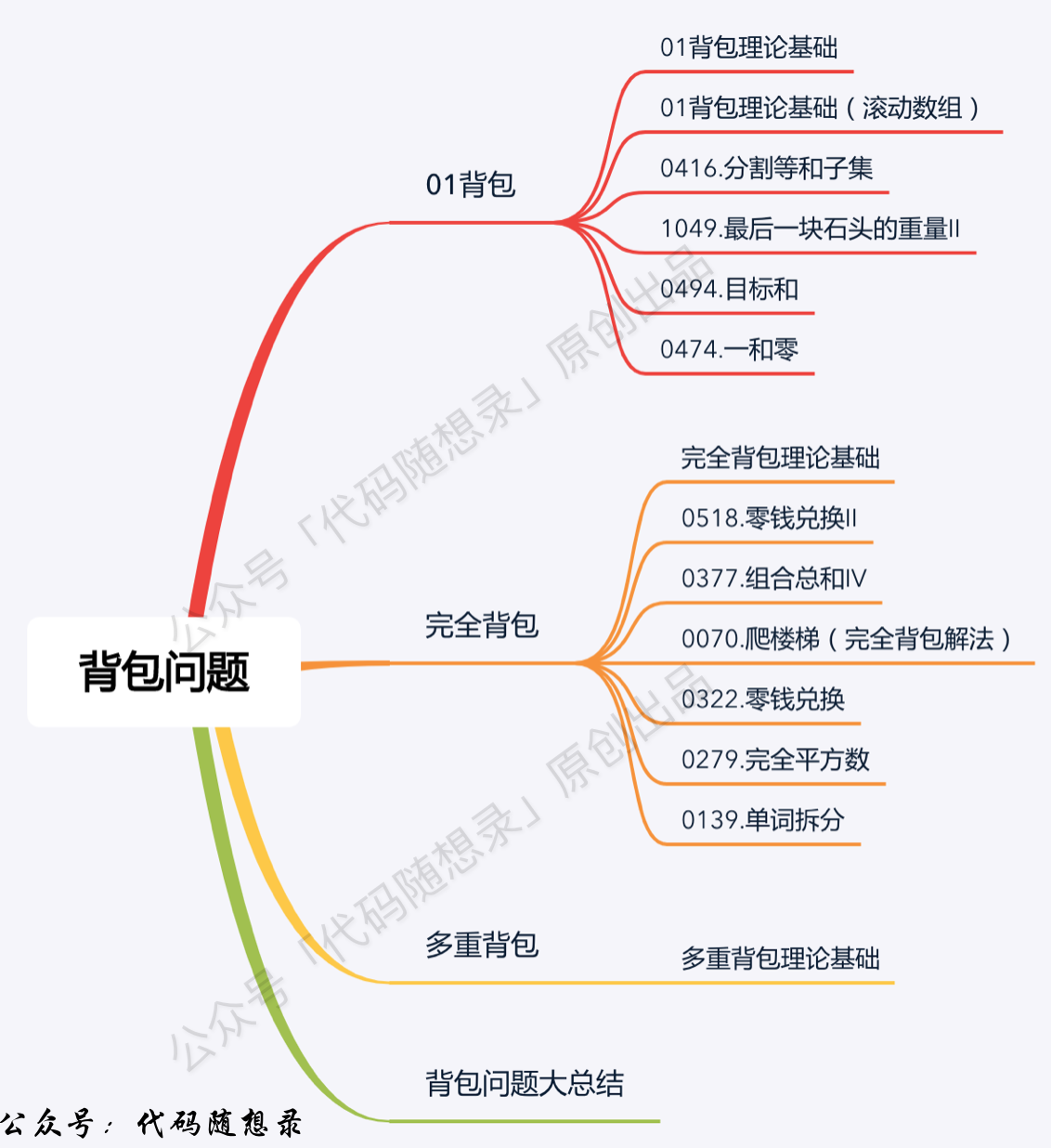 +
+ +
11. [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
12. [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
@@ -334,7 +351,8 @@
股票系列:
-
+
11. [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-1.md)
12. [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](./problems/背包理论基础01背包-2.md)
@@ -334,7 +351,8 @@
股票系列:
- +
+ +
32. [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
33. [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列六)](./problems/周总结/20210225动规周末总结.md)
@@ -348,6 +366,9 @@
子序列系列:
+
+
32. [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机](./problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md)
33. [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列六)](./problems/周总结/20210225动规周末总结.md)
@@ -348,6 +366,9 @@
子序列系列:
+ +
+
40. [动态规划:最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
41. [动态规划:最长连续递增序列](./problems/0674.最长连续递增序列.md)
42. [动态规划:最长重复子数组](./problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md)
@@ -361,10 +382,14 @@
52. [为了绝杀编辑距离,Carl做了三步铺垫,你都知道么?](./problems/为了绝杀编辑距离,卡尔做了三步铺垫.md)
53. [动态规划:回文子串](./problems/0647.回文子串.md)
54. [动态规划:最长回文子序列](./problems/0516.最长回文子序列.md)
-
+55. [动态规划总结篇](./problems/动态规划总结篇.md)
(持续更新中....)
+## 单调栈
+
+1. [每日温度](./problems/0739.每日温度.md)
+
## 图论
## 十大排序
@@ -385,12 +410,7 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-# 备战秋招
-1. [技术比较弱,也对技术不感兴趣,如何选择方向?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZCzFiAHZHLqHPLJQXNm75g)
-2. [刷题就用库函数了,怎么了?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6K3_OSaudnHGq2Ey8vqYfg)
-3. [关于实习,大家可能有点迷茫!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xcxzi7c78kQGjvZ8hh7taA)
-4. [马上秋招了,慌得很!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7q7W8Cb2-a5U5atZdOnOFA)
# B站算法视频讲解
@@ -409,6 +429,10 @@
(持续更新中....)
+# 贡献者
+
+你可以[点此链接](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢你们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,ACM 校赛、黑龙江省赛、东北四省赛金牌、亚洲区域赛铜牌获得者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -420,7 +444,7 @@
+
+
40. [动态规划:最长递增子序列](./problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md)
41. [动态规划:最长连续递增序列](./problems/0674.最长连续递增序列.md)
42. [动态规划:最长重复子数组](./problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md)
@@ -361,10 +382,14 @@
52. [为了绝杀编辑距离,Carl做了三步铺垫,你都知道么?](./problems/为了绝杀编辑距离,卡尔做了三步铺垫.md)
53. [动态规划:回文子串](./problems/0647.回文子串.md)
54. [动态规划:最长回文子序列](./problems/0516.最长回文子序列.md)
-
+55. [动态规划总结篇](./problems/动态规划总结篇.md)
(持续更新中....)
+## 单调栈
+
+1. [每日温度](./problems/0739.每日温度.md)
+
## 图论
## 十大排序
@@ -385,12 +410,7 @@
[各类基础算法模板](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode/blob/master/problems/算法模板.md)
-# 备战秋招
-1. [技术比较弱,也对技术不感兴趣,如何选择方向?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZCzFiAHZHLqHPLJQXNm75g)
-2. [刷题就用库函数了,怎么了?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6K3_OSaudnHGq2Ey8vqYfg)
-3. [关于实习,大家可能有点迷茫!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xcxzi7c78kQGjvZ8hh7taA)
-4. [马上秋招了,慌得很!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/7q7W8Cb2-a5U5atZdOnOFA)
# B站算法视频讲解
@@ -409,6 +429,10 @@
(持续更新中....)
+# 贡献者
+
+你可以[点此链接](https://github.com/youngyangyang04/leetcode-master/graphs/contributors)查看LeetCode-Master的所有贡献者。感谢你们补充了LeetCode-Master的其他语言版本,让更多的读者收益于此项目。
+
# 关于作者
大家好,我是程序员Carl,哈工大师兄,ACM 校赛、黑龙江省赛、东北四省赛金牌、亚洲区域赛铜牌获得者,先后在腾讯和百度从事后端技术研发,CSDN博客专家。对算法和C++后端技术有一定的见解,利用工作之余重新刷leetcode。
@@ -420,7 +444,7 @@
 -# 我的公众号
+# 公众号
更多精彩文章持续更新,微信搜索:「代码随想录」第一时间围观,关注后回复:「666」可以获得所有算法专题原创PDF。
diff --git a/problems/0001.两数之和.md b/problems/0001.两数之和.md
index 21f798a9..02e9996f 100644
--- a/problems/0001.两数之和.md
+++ b/problems/0001.两数之和.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-# 我的公众号
+# 公众号
更多精彩文章持续更新,微信搜索:「代码随想录」第一时间围观,关注后回复:「666」可以获得所有算法专题原创PDF。
diff --git a/problems/0001.两数之和.md b/problems/0001.两数之和.md
index 21f798a9..02e9996f 100644
--- a/problems/0001.两数之和.md
+++ b/problems/0001.两数之和.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 1. 两数之和 @@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/ 很明显暴力的解法是两层for循环查找,时间复杂度是O(n^2)。 建议大家做这道题目之前,先做一下这两道 -* [242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vM6OszkM6L1Mx2Ralm9Dig) -* [349. 两个数组的交集](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/N9iqAchXreSVW7zXUS4BVA) +* [242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ffS8jaVFNUWyfn_8T31IdA) +* [349. 两个数组的交集](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/aMSA5zrp3jJcLjuSB0Es2Q) -[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vM6OszkM6L1Mx2Ralm9Dig) 这道题目是用数组作为哈希表来解决哈希问题,[349. 两个数组的交集](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/N9iqAchXreSVW7zXUS4BVA)这道题目是通过set作为哈希表来解决哈希问题。 +[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ffS8jaVFNUWyfn_8T31IdA) 这道题目是用数组作为哈希表来解决哈希问题,[349. 两个数组的交集](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/aMSA5zrp3jJcLjuSB0Es2Q)这道题目是通过set作为哈希表来解决哈希问题。 本题呢,则要使用map,那么来看一下使用数组和set来做哈希法的局限。 @@ -51,13 +51,14 @@ C++中map,有三种类型: std::unordered_map 底层实现为哈希表,std::map 和std::multimap 的底层实现是红黑树。 -同理,std::map 和std::multimap 的key也是有序的(这个问题也经常作为面试题,考察对语言容器底层的理解)。 更多哈希表的理论知识请看[关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g8N6WmoQmsCUw3_BaWxHZA)。 +同理,std::map 和std::multimap 的key也是有序的(这个问题也经常作为面试题,考察对语言容器底层的理解)。 更多哈希表的理论知识请看[关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RSUANESA_tkhKhYe3ZR8Jg)。 **这道题目中并不需要key有序,选择std::unordered_map 效率更高!** 解题思路动画如下: - + + C++代码: @@ -134,6 +135,21 @@ func twoSum(nums []int, target int) []int { } ``` +```go +// 使用map方式解题,降低时间复杂度 +func twoSum(nums []int, target int) []int { + m := make(map[int]int) + for index, val := range nums { + if preIndex, ok := m[target-val]; ok { + return []int{preIndex, index} + } else { + m[val] = index + } + } + return []int{} +} +``` + Rust ```rust @@ -156,6 +172,21 @@ impl Solution { } ``` +Javascript + +```javascript +var twoSum = function (nums, target) { + let hash = {}; + for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { + if (hash[target - nums[i]] !== undefined) { + return [i, hash[target - nums[i]]]; + } + hash[nums[i]] = i; + } + return []; +}; +``` + @@ -163,4 +194,4 @@ impl Solution { * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -105,8 +105,7 @@ public: 时间复杂度:O(n^2)。 - -## 双指针法C++代码 +C++代码代码如下: ```C++ class Solution { @@ -163,13 +162,14 @@ public: # 思考题 -既然三数之和可以使用双指针法,我们之前讲过的[两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/uVAtjOHSeqymV8FeQbliJQ),可不可以使用双指针法呢? + +既然三数之和可以使用双指针法,我们之前讲过的[1.两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vaMsLnH-f7_9nEK4Cuu3KQ),可不可以使用双指针法呢? 如果不能,题意如何更改就可以使用双指针法呢? **大家留言说出自己的想法吧!** -两数之和 就不能使用双指针法,因为[两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/uVAtjOHSeqymV8FeQbliJQ)要求返回的是索引下表, 而双指针法一定要排序,一旦排序之后原数组的索引就被改变了。 +两数之和 就不能使用双指针法,因为[1.两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vaMsLnH-f7_9nEK4Cuu3KQ)要求返回的是索引下表, 而双指针法一定要排序,一旦排序之后原数组的索引就被改变了。 -如果[两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/uVAtjOHSeqymV8FeQbliJQ)要求返回的是数值的话,就可以使用双指针法了。 +如果[1.两数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vaMsLnH-f7_9nEK4Cuu3KQ)要求返回的是数值的话,就可以使用双指针法了。 @@ -218,8 +218,33 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```Python +class Solution: + def threeSum(self, nums): + ans = [] + n = len(nums) + nums.sort() + for i in range(n): + left = i + 1 + right = n - 1 + if nums[i] > 0: + break + if i >= 1 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: + continue + while left < right: + total = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] + if total > 0: + right -= 1 + elif total < 0: + left += 1 + else: + ans.append([nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]]) + while left != right and nums[left] == nums[left + 1]: left += 1 + while left != right and nums[right] == nums[right - 1]: right -= 1 + left += 1 + right -= 1 + return ans +``` Go: ```Go func threeSum(nums []int)[][]int{ @@ -256,8 +281,78 @@ func threeSum(nums []int)[][]int{ } ``` +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {number[]} nums + * @return {number[][]} + */ + +// 循环内不考虑去重 +var threeSum = function(nums) { + const len = nums.length; + if(len < 3) return []; + nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); + const resSet = new Set(); + for(let i = 0; i < len - 2; i++) { + if(nums[i] > 0) break; + let l = i + 1, r = len - 1; + while(l < r) { + const sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]; + if(sum < 0) { l++; continue }; + if(sum > 0) { r--; continue }; + resSet.add(`${nums[i]},${nums[l]},${nums[r]}`); + l++; + r--; + } + } + return Array.from(resSet).map(i => i.split(",")); +}; + +// 去重优化 +var threeSum = function(nums) { + const len = nums.length; + if(len < 3) return []; + nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); + const res = []; + for(let i = 0; i < len - 2; i++) { + if(nums[i] > 0) break; + // a去重 + if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue; + let l = i + 1, r = len - 1; + while(l < r) { + const sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]; + if(sum < 0) { l++; continue }; + if(sum > 0) { r--; continue }; + res.push([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]]) + // b c 去重 + while(l < r && nums[l] === nums[++l]); + while(l < r && nums[r] === nums[--r]); + } + } + return res; +}; +``` +ruby: +```ruby +def is_valid(strs) + symbol_map = {')' => '(', '}' => '{', ']' => '['} + stack = [] + strs.size.times {|i| + c = strs[i] + if symbol_map.has_key?(c) + top_e = stack.shift + return false if symbol_map[c] != top_e + else + stack.unshift(c) + end + } + stack.empty? +end +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) diff --git a/problems/0017.电话号码的字母组合.md b/problems/0017.电话号码的字母组合.md index f06ed80a..aefee698 100644 --- a/problems/0017.电话号码的字母组合.md +++ b/problems/0017.电话号码的字母组合.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 17.电话号码的字母组合 @@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ for (int i = 0; i < letters.size(); i++) { 关键地方都讲完了,按照[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gjSgJbNbd1eAA5WkA-HeWw)中的回溯法模板,不难写出如下C++代码: -``` +```c++ // 版本一 class Solution { private: @@ -183,7 +183,7 @@ public: 一些写法,是把回溯的过程放在递归函数里了,例如如下代码,我可以写成这样:(注意注释中不一样的地方) -``` +```c++ // 版本二 class Solution { private: @@ -272,7 +272,7 @@ class Solution { String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0']; for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { temp.append(str.charAt(i)); - //回溯 + //c backTracking(digits, numString, num + 1); //剔除末尾的继续尝试 temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1); @@ -283,9 +283,92 @@ class Solution { Python: +```Python +class Solution: + ans = [] + s = '' + letterMap = { + '2': 'abc', + '3': 'def', + '4': 'ghi', + '5': 'jkl', + '6': 'mno', + '7': 'pqrs', + '8': 'tuv', + '9': 'wxyz' + } + + def letterCombinations(self, digits): + self.ans.clear() + if digits == '': + return self.ans + self.backtracking(digits, 0) + return self.ans + + def backtracking(self, digits, index): + if index == len(digits): + self.ans.append(self.s) + return + else: + letters = self.letterMap[digits[index]] # 取出数字对应的字符集 + for letter in letters: + self.s = self.s + letter # 处理 + self.backtracking(digits, index + 1) + self.s = self.s[:-1] # 回溯 +``` + +python3: + +```py +class Solution: + def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]: + self.s = "" + res = [] + letterMap = ["","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"] + if len(digits) == 0: return res + def backtrack(digits,index): + if index == len(digits): + return res.append(self.s) + digit = int(digits[index]) #将index指向的数字转为int + letters = letterMap[digit] #取数字对应的字符集 + for i in range(len(letters)): + self.s += letters[i] + backtrack(digits,index + 1) #递归,注意index+1,一下层要处理下一个数字 + self.s = self.s[:-1] #回溯 + backtrack(digits,0) + return res +``` + Go: +javaScript: + +```js +var letterCombinations = function(digits) { + const k = digits.length; + const map = ["","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"]; + if(!k) return []; + if(k === 1) return map[digits].split(""); + + const res = [], path = []; + backtracking(digits, k, 0); + return res; + + function backtracking(n, k, a) { + if(path.length === k) { + res.push(path.join("")); + return; + } + for(const v of map[n[a]]) { + path.push(v); + backtracking(n, k, a + 1); + path.pop(); + } + + } +}; +``` diff --git a/problems/0018.四数之和.md b/problems/0018.四数之和.md index ff441bf7..0caf12be 100644 --- a/problems/0018.四数之和.md +++ b/problems/0018.四数之和.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 一样的道理,能解决四数之和 @@ -31,38 +31,39 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/ # 思路 -四数之和,和[三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r5cgZFu0tv4grBAexdcd8A)是一个思路,都是使用双指针法, 基本解法就是在[三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r5cgZFu0tv4grBAexdcd8A) 的基础上再套一层for循环。 +四数之和,和[15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QfTNEByq1YlNSXRKEumwHg)是一个思路,都是使用双指针法, 基本解法就是在[15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QfTNEByq1YlNSXRKEumwHg) 的基础上再套一层for循环。 但是有一些细节需要注意,例如: 不要判断`nums[k] > target` 就返回了,三数之和 可以通过 `nums[i] > 0` 就返回了,因为 0 已经是确定的数了,四数之和这道题目 target是任意值。(大家亲自写代码就能感受出来) -[三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r5cgZFu0tv4grBAexdcd8A)的双指针解法是一层for循环num[i]为确定值,然后循环内有left和right下表作为双指针,找到nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == 0。 +[15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QfTNEByq1YlNSXRKEumwHg)的双指针解法是一层for循环num[i]为确定值,然后循环内有left和right下表作为双指针,找到nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == 0。 四数之和的双指针解法是两层for循环nums[k] + nums[i]为确定值,依然是循环内有left和right下表作为双指针,找出nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == target的情况,三数之和的时间复杂度是O(n^2),四数之和的时间复杂度是O(n^3) 。 那么一样的道理,五数之和、六数之和等等都采用这种解法。 -对于[三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r5cgZFu0tv4grBAexdcd8A)双指针法就是将原本暴力O(n^3)的解法,降为O(n^2)的解法,四数之和的双指针解法就是将原本暴力O(n^4)的解法,降为O(n^3)的解法。 +对于[15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QfTNEByq1YlNSXRKEumwHg)双指针法就是将原本暴力O(n^3)的解法,降为O(n^2)的解法,四数之和的双指针解法就是将原本暴力O(n^4)的解法,降为O(n^3)的解法。 -之前我们讲过哈希表的经典题目:[四数相加II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ue8pKKU5hw_m-jPgwlHcbA),相对于本题简单很多,因为本题是要求在一个集合中找出四个数相加等于target,同时四元组不能重复。 +之前我们讲过哈希表的经典题目:[454.四数相加II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/12g_w6RzHuEpFts1pT6BWw),相对于本题简单很多,因为本题是要求在一个集合中找出四个数相加等于target,同时四元组不能重复。 -而[四数相加II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Ue8pKKU5hw_m-jPgwlHcbA)是四个独立的数组,只要找到A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0就可以,不用考虑有重复的四个元素相加等于0的情况,所以相对于本题还是简单了不少! +而[454.四数相加II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/12g_w6RzHuEpFts1pT6BWw)是四个独立的数组,只要找到A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0就可以,不用考虑有重复的四个元素相加等于0的情况,所以相对于本题还是简单了不少! 我们来回顾一下,几道题目使用了双指针法。 双指针法将时间复杂度O(n^2)的解法优化为 O(n)的解法。也就是降一个数量级,题目如下: -* [0027.移除元素](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wj0T-Xs88_FHJFwayElQlA) -* [15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r5cgZFu0tv4grBAexdcd8A) + +* [27.移除元素](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RMkulE4NIb6XsSX83ra-Ww) +* [15.三数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QfTNEByq1YlNSXRKEumwHg) * [18.四数之和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/nQrcco8AZJV1pAOVjeIU_g) -双指针来记录前后指针实现链表反转: -* [206.反转链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pnvVP-0ZM7epB8y3w_Njwg) +操作链表: -使用双指针来确定有环: +* [206.反转链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ckEvIVGcNLfrz6OLOMoT0A) +* [19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gxu65X1343xW_sBrkTz0Eg) +* [面试题 02.07. 链表相交](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BhfFfaGvt9Zs7UmH4YehZw) +* [142题.环形链表II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gt_VH3hQTqNxyWcl1ECSbQ) -* [142题.环形链表II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_QVP3IkRZWx9zIpQRgajzA) - -双指针法在数组和链表中还有很多应用,后面还会介绍到。 +双指针法在字符串题目中还有很多应用,后面还会介绍到。 C++代码 @@ -165,11 +166,75 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: +```python +class Solution(object): + def fourSum(self, nums, target): + """ + :type nums: List[int] + :type target: int + :rtype: List[List[int]] + """ + # use a dict to store value:showtimes + hashmap = dict() + for n in nums: + if n in hashmap: + hashmap[n] += 1 + else: + hashmap[n] = 1 + + # good thing about using python is you can use set to drop duplicates. + ans = set() + for i in range(len(nums)): + for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)): + for k in range(j + 1, len(nums)): + val = target - (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]) + if val in hashmap: + # make sure no duplicates. + count = (nums[i] == val) + (nums[j] == val) + (nums[k] == val) + if hashmap[val] > count: + ans.add(tuple(sorted([nums[i], nums[j], nums[k], val]))) + else: + continue + return ans + +``` Go: +javaScript: +```js +/** + * @param {number[]} nums + * @param {number} target + * @return {number[][]} + */ +var fourSum = function(nums, target) { + const len = nums.length; + if(len < 4) return []; + nums.sort((a, b) => a - b); + const res = []; + for(let i = 0; i < len - 3; i++) { + // 去重i + if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i - 1]) continue; + for(let j = i + 1; j < len - 2; j++) { + // 去重j + if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] === nums[j - 1]) continue; + let l = j + 1, r = len - 1; + while(l < r) { + const sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]; + if(sum < target) { l++; continue} + if(sum > target) { r--; continue} + res.push([nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]]); + while(l < r && nums[l] === nums[++l]); + while(l < r && nums[r] === nums[--r]); + } + } + } + return res; +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md b/problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md index 3b89dabd..52735794 100644 --- a/problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md +++ b/problems/0019.删除链表的倒数第N个节点.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -112,29 +112,79 @@ class Solution { } } ``` + +Python: +```python +# Definition for singly-linked list. +# class ListNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): +# self.val = val +# self.next = next +class Solution: + def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode: + head_dummy = ListNode() + head_dummy.next = head + + slow, fast = head_dummy, head_dummy + while(n!=0): #fast先往前走n步 + fast = fast.next + n -= 1 + while(fast.next!=None): + slow = slow.next + fast = fast.next + #fast 走到结尾后,slow的下一个节点为倒数第N个节点 + slow.next = slow.next.next #删除 + return head_dummy.next +``` Go: ```Go +/** + * Definition for singly-linked list. + * type ListNode struct { + * Val int + * Next *ListNode + * } + */ func removeNthFromEnd(head *ListNode, n int) *ListNode { - result:=&ListNode{} - result.Next=head - var pre *ListNode - cur:=result - - i:=1 - for head!=nil{ - if i>=n{ - pre=cur - cur=cur.Next + dummyHead := &ListNode{} + dummyHead.Next = head + cur := head + prev := dummyHead + i := 1 + for cur != nil { + cur = cur.Next + if i > n { + prev = prev.Next } - head=head.Next i++ } - pre.Next=pre.Next.Next - return result.Next - + prev.Next = prev.Next.Next + return dummyHead.Next } ``` +JavaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {ListNode} head + * @param {number} n + * @return {ListNode} + */ +var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) { + let ret = new ListNode(0, head), + slow = fast = ret; + while(n--) fast = fast.next; + if(!fast) return ret.next; + while (fast.next) { + fast = fast.next; + slow = slow.next + }; + slow.next = slow.next.next; + return ret.next; +}; +``` + ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) diff --git a/problems/0020.有效的括号.md b/problems/0020.有效的括号.md index 77c6e10a..dae84354 100644 --- a/problems/0020.有效的括号.md +++ b/problems/0020.有效的括号.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -162,6 +162,33 @@ class Solution { return deque.isEmpty(); } } +// 方法2 +class Solution { + public boolean isValid(String s) { + + Stack欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+ ## 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 @@ -87,10 +87,116 @@ public: Java: +```Java +// 递归版本 +class Solution { + public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { + // base case 退出提交 + if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; + // 获取当前节点的下一个节点 + ListNode next = head.next; + // 进行递归 + ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next); + // 这里进行交换 + next.next = head; + head.next = newNode; + + return next; + } +} +``` + +```java +// 虚拟头结点 +class Solution { + public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { + + ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0); + dummyNode.next = head; + ListNode prev = dummyNode; + + while (prev.next != null && prev.next.next != null) { + ListNode temp = head.next.next; // 缓存 next + prev.next = head.next; // 将 prev 的 next 改为 head 的 next + head.next.next = head; // 将 head.next(prev.next) 的next,指向 head + head.next = temp; // 将head 的 next 接上缓存的temp + prev = head; // 步进1位 + head = head.next; // 步进1位 + } + return dummyNode.next; + } +} +``` Python: +```python +class Solution: + def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: + dummy = ListNode(0) #设置一个虚拟头结点 + dummy.next = head + cur = dummy + while cur.next and cur.next.next: + tmp = cur.next #记录临时节点 + tmp1 = cur.next.next.next #记录临时节点 + + cur.next = cur.next.next #步骤一 + cur.next.next = tmp #步骤二 + cur.next.next.next = tmp1 #步骤三 + + cur = cur.next.next #cur移动两位,准备下一轮交换 + return dummy.next +``` Go: +```go +func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode { + dummy := &ListNode{ + Next: head, + } + //head=list[i] + //pre=list[i-1] + pre := dummy + for head != nil && head.Next != nil { + pre.Next = head.Next + next := head.Next.Next + head.Next.Next = head + head.Next = next + //pre=list[(i+2)-1] + pre = head + //head=list[(i+2)] + head = next + } + return dummy.Next +} +``` + +```go +// 递归版本 +func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode { + if head == nil || head.Next == nil { + return head + } + next := head.Next + head.Next = swapPairs(next.Next) + next.Next = head + return next +} +``` + +Javascript: +```javascript +var swapPairs = function (head) { + let ret = new ListNode(0, head), temp = ret; + while (temp.next && temp.next.next) { + let cur = temp.next.next, pre = temp.next; + pre.next = cur.next; + cur.next = pre; + temp.next = cur; + temp = pre; + } + return ret.next; +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0027.移除元素.md b/problems/0027.移除元素.md index 9481af1f..f1187db7 100644 --- a/problems/0027.移除元素.md +++ b/problems/0027.移除元素.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 27. 移除元素 @@ -186,6 +186,36 @@ var removeElement = (nums, val) => { }; ``` +Ruby: +```ruby +def remove_element(nums, val) + i = 0 + nums.each_index do |j| + if nums[j] != val + nums[i] = nums[j] + i+=1 + end + end + i +end +``` +Rust: +```rust +pub fn remove_element(nums: &mut Vec欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 在一个串中查找是否出现过另一个串,这是KMP的看家本领。 @@ -61,11 +61,6 @@ KMP的经典思想就是:**当出现字符串不匹配时,可以记录一部 读完本篇可以顺便,把leetcode上28.实现strStr()题目做了。 -如果文字实在看不下去,就看我在B站上的视频吧,如下: - -* [帮你把KMP算法学个通透!(理论篇)B站](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PD4y1o7nd/) -* [帮你把KMP算法学个通透!(求next数组代码篇)B站](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx/) - # 什么是KMP @@ -726,10 +721,98 @@ class Solution: Go: +```go +// 方法一:前缀表使用减1实现 + +// getNext 构造前缀表next +// params: +// next 前缀表数组 +// s 模式串 +func getNext(next []int, s string) { + j := -1 // j表示 最长相等前后缀长度 + next[0] = j + + for i := 1; i < len(s); i++ { + for j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j+1] { + j = next[j] // 回退前一位 + } + if s[i] == s[j+1] { + j++ + } + next[i] = j // next[i]是i(包括i)之前的最长相等前后缀长度 + } +} +func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int { + if len(needle) == 0 { + return 0 + } + next := make([]int, len(needle)) + getNext(next, needle) + j := -1 // 模式串的起始位置 next为-1 因此也为-1 + for i := 0; i < len(haystack); i++ { + for j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j+1] { + j = next[j] // 寻找下一个匹配点 + } + if haystack[i] == needle[j+1] { + j++ + } + if j == len(needle)-1 { // j指向了模式串的末尾 + return i - len(needle) + 1 + } + } + return -1 +} +``` + +```go +// 方法二: 前缀表无减一或者右移 + +// getNext 构造前缀表next +// params: +// next 前缀表数组 +// s 模式串 +func getNext(next []int, s string) { + j := 0 + next[0] = j + for i := 1; i < len(s); i++ { + for j > 0 && s[i] != s[j] { + j = next[j-1] + } + if s[i] == s[j] { + j++ + } + next[i] = j + } +} +func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int { + n := len(needle) + if n == 0 { + return 0 + } + j := 0 + next := make([]int, n) + getNext(next, needle) + for i := 0; i < len(haystack); i++ { + for j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j] { + j = next[j-1] // 回退到j的前一位 + } + if haystack[i] == needle[j] { + j++ + } + if j == n { + return i - n + 1 + } + } + return -1 +} +``` + + + ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ public: **大家要仔细看注释,思考为什么要写while(left <= right), 为什么要写right = middle - 1**。 -``` +```C++ class Solution { public: int searchInsert(vector欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
如果对回溯法理论还不清楚的同学,可以先看这个视频[视频来了!!带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/wDd5azGIYWjbU0fdua_qBg) @@ -287,11 +287,97 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def solveSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None: + """ + Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead. + """ + def backtrack(board): + for i in range(len(board)): #遍历行 + for j in range(len(board[0])): #遍历列 + if board[i][j] != ".": continue + for k in range(1,10): #(i, j) 这个位置放k是否合适 + if isValid(i,j,k,board): + board[i][j] = str(k) #放置k + if backtrack(board): return True #如果找到合适一组立刻返回 + board[i][j] = "." #回溯,撤销k + return False #9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false + return True #遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了 + def isValid(row,col,val,board): + for i in range(9): #判断行里是否重复 + if board[row][i] == str(val): + return False + for j in range(9): #判断列里是否重复 + if board[j][col] == str(val): + return False + startRow = (row // 3) * 3 + startcol = (col // 3) * 3 + for i in range(startRow,startRow + 3): #判断9方格里是否重复 + for j in range(startcol,startcol + 3): + if board[i][j] == str(val): + return False + return True + backtrack(board) +``` Go: +Javascript: +```Javascript +var solveSudoku = function(board) { + function isValid(row, col, val, board) { + let len = board.length + // 行不能重复 + for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) { + if(board[row][i] === val) { + return false + } + } + // 列不能重复 + for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) { + if(board[i][col] === val) { + return false + } + } + let startRow = Math.floor(row / 3) * 3 + let startCol = Math.floor(col / 3) * 3 + for(let i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++) { + for(let j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++) { + if(board[i][j] === val) { + return false + } + } + } + + return true + } + + function backTracking() { + for(let i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { + for(let j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) { + if(board[i][j] !== '.') continue + for(let val = 1; val <= 9; val++) { + if(isValid(i, j, `${val}`, board)) { + board[i][j] = `${val}` + if (backTracking()) { + return true + } + + board[i][j] = `.` + } + } + return false + } + } + return true + } + backTracking(board) + return board + +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0039.组合总和.md b/problems/0039.组合总和.md index ab118ee0..e3e4a117 100644 --- a/problems/0039.组合总和.md +++ b/problems/0039.组合总和.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 39. 组合总和 @@ -237,45 +237,81 @@ public: Java: ```Java +// 剪枝优化 class Solution { - List欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 这篇可以说是全网把组合问题如何去重,讲的最清晰的了! @@ -292,13 +292,61 @@ class Solution { } } ``` - Python: - - +```py +class Solution: + def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]: + res = [] + path = [] + def backtrack(candidates,target,sum,startIndex): + if sum == target: res.append(path[:]) + for i in range(startIndex,len(candidates)): #要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过 + if sum + candidates[i] > target: return + if i > startIndex and candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]: continue #直接用startIndex来去重,要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过 + sum += candidates[i] + path.append(candidates[i]) + backtrack(candidates,target,sum,i+1) #i+1:每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次 + sum -= candidates[i] #回溯 + path.pop() #回溯 + candidates = sorted(candidates) #首先把给candidates排序,让其相同的元素都挨在一起。 + backtrack(candidates,target,0,0) + return res +``` Go: +javaScript: +```js +/** + * @param {number[]} candidates + * @param {number} target + * @return {number[][]} + */ +var combinationSum2 = function(candidates, target) { + const res = []; path = [], len = candidates.length; + candidates.sort(); + backtracking(0, 0); + return res; + function backtracking(sum, i) { + if (sum > target) return; + if (sum === target) { + res.push(Array.from(path)); + return; + } + let f = -1; + for(let j = i; j < len; j++) { + const n = candidates[j]; + if(n > target - sum || n === f) continue; + path.push(n); + sum += n; + f = n; + backtracking(sum, j + 1); + path.pop(); + sum -= n; + } + } +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0045.跳跃游戏II.md b/problems/0045.跳跃游戏II.md index b8e369e6..4128da4c 100644 --- a/problems/0045.跳跃游戏II.md +++ b/problems/0045.跳跃游戏II.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 相对于[贪心算法:跳跃游戏](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/606_N9j8ACKCODoCbV1lSA)难了不少,做好心里准备! @@ -175,9 +175,64 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def jump(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) == 1: return 0 + ans = 0 + curDistance = 0 + nextDistance = 0 + for i in range(len(nums)): + nextDistance = max(i + nums[i], nextDistance) + if i == curDistance: + if curDistance != len(nums) - 1: + ans += 1 + curDistance = nextDistance + if nextDistance >= len(nums) - 1: break + return ans +``` Go: +```Go +func jump(nums []int) int { + dp:=make([]int ,len(nums)) + dp[0]=0 + + for i:=1;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 46.全排列 @@ -149,6 +149,7 @@ public: Java: ```java class Solution { + List欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 排列问题(二) ## 47.全排列 II @@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ public: path.clear(); sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 排序 vector欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 第51题. N皇后 @@ -430,6 +430,65 @@ func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string { } ``` +Javascript: +```Javascript +var solveNQueens = function(n) { + function isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n) { + + for(let i = 0; i < row; i++) { + if(chessBoard[i][col] === 'Q') { + return false + } + } + + for(let i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) { + if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') { + return false + } + } + + for(let i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) { + if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') { + return false + } + } + return true + } + + function transformChessBoard(chessBoard) { + let chessBoardBack = [] + chessBoard.forEach(row => { + let rowStr = '' + row.forEach(value => { + rowStr += value + }) + chessBoardBack.push(rowStr) + }) + + return chessBoardBack + } + + let result = [] + function backtracing(row,chessBoard) { + if(row === n) { + result.push(transformChessBoard(chessBoard)) + return + } + for(let col = 0; col < n; col++) { + if(isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n)) { + chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q' + backtracing(row + 1,chessBoard) + chessBoard[row][col] = '.' + } + } + } + let chessBoard = new Array(n).fill([]).map(() => new Array(n).fill('.')) + backtracing(0,chessBoard) + return result + +}; +``` + ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0053.最大子序和.md b/problems/0053.最大子序和.md index 6474d01f..81e0b35a 100644 --- a/problems/0053.最大子序和.md +++ b/problems/0053.最大子序和.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 53. 最大子序和 @@ -175,29 +175,39 @@ class Solution: ``` Go: -```Go -func maxSubArray(nums []int) int { - if len(nums)<1{ - return 0 - } - dp:=make([]int,len(nums)) - result:=nums[0] - dp[0]=nums[0] - for i:=1;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 53. 最大子序和 @@ -95,10 +95,47 @@ public: Java: +```java + /** + * 1.dp[i]代表当前下标对应的最大值 + * 2.递推公式 dp[i] = max (dp[i-1]+nums[i],nums[i]) res = max(res,dp[i]) + * 3.初始化 都为 0 + * 4.遍历方向,从前往后 + * 5.举例推导结果。。。 + * + * @param nums + * @return + */ + public static int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { + if (nums.length == 0) { + return 0; + } + int res = nums[0]; + int[] dp = new int[nums.length]; + dp[0] = nums[0]; + for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { + dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i], nums[i]); + res = res > dp[i] ? res : dp[i]; + } + return res; + } +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) == 0: + return 0 + dp = [0] * len(nums) + dp[0] = nums[0] + result = dp[0] + for i in range(1, len(nums)): + dp[i] = max(dp[i-1] + nums[i], nums[i]) #状态转移公式 + result = max(result, dp[i]) #result 保存dp[i]的最大值 + return result +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0055.跳跃游戏.md b/problems/0055.跳跃游戏.md index a25c831a..8618515e 100644 --- a/problems/0055.跳跃游戏.md +++ b/problems/0055.跳跃游戏.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 55. 跳跃游戏 @@ -122,8 +122,39 @@ class Solution: ``` Go: +```Go +func canJUmp(nums []int) bool { + if len(nums)<=1{ + return true + } + dp:=make([]bool,len(nums)) + dp[0]=true + for i:=1;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 56. 合并区间 @@ -141,16 +141,7 @@ Java: class Solution { public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) { List

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -224,6 +224,88 @@ class Solution: return matrix ``` +javaScript + +```js + +/** + * @param {number} n + * @return {number[][]} + */ +var generateMatrix = function(n) { + // new Array(n).fill(new Array(n)) + // 使用fill --> 填充的是同一个数组地址 + const res = Array.from({length: n}).map(() => new Array(n)); + let loop = n >> 1, i = 0, //循环次数 + count = 1, + startX = startY = 0; // 起始位置 + while(++i <= loop) { + // 定义行列 + let row = startX, column = startY; + // [ startY, n - i) + while(column < n - i) { + res[row][column++] = count++; + } + // [ startX, n - i) + while(row < n - i) { + res[row++][column] = count++; + } + // [n - i , startY) + while(column > startY) { + res[row][column--] = count++; + } + // [n - i , startX) + while(row > startX) { + res[row--][column] = count++; + } + startX = ++startY; + } + if(n & 1) { + res[startX][startY] = count; + } + return res; +}; +``` + +Go: + +```go +func generateMatrix(n int) [][]int { + top, bottom := 0, n-1 + left, right := 0, n-1 + num := 1 + tar := n * n + matrix := make([][]int, n) + for i := 0; i < n; i++ { + matrix[i] = make([]int, n) + } + for num <= tar { + for i := left; i <= right; i++ { + matrix[top][i] = num + num++ + } + top++ + for i := top; i <= bottom; i++ { + matrix[i][right] = num + num++ + } + right-- + for i := right; i >= left; i-- { + matrix[bottom][i] = num + num++ + } + bottom-- + for i := bottom; i >= top; i-- { + matrix[i][left] = num + num++ + } + left++ + } + return matrix +} +``` + + ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0062.不同路径.md b/problems/0062.不同路径.md index e3a6da8c..47cb41af 100644 --- a/problems/0062.不同路径.md +++ b/problems/0062.不同路径.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 62.不同路径 @@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ public: ### 动态规划 -机器人从(0 , 0) 位置触发,到(m - 1, n - 1)终点。 +机器人从(0 , 0) 位置出发,到(m - 1, n - 1)终点。 按照动规五部曲来分析: @@ -243,14 +243,92 @@ public: Java: +```java + /** + * 1. 确定dp数组下表含义 dp[i][j] 到每一个坐标可能的路径种类 + * 2. 递推公式 dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] dp[i][j-1] + * 3. 初始化 dp[i][0]=1 dp[0][i]=1 初始化横竖就可 + * 4. 遍历顺序 一行一行遍历 + * 5. 推导结果 。。。。。。。。 + * + * @param m + * @param n + * @return + */ + public static int uniquePaths(int m, int n) { + int[][] dp = new int[m][n]; + //初始化 + for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { + dp[i][0] = 1; + } + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { + dp[0][i] = 1; + } + for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) { + for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) { + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1]; + } + } + return dp[m-1][n-1]; + } + +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: # 动态规划 + def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int: + dp = [[0 for i in range(n)] for j in range(m)] + for i in range(m): dp[i][0] = 1 + for j in range(n): dp[0][j] = 1 + for i in range(1, m): + for j in range(1, n): + dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j] + return dp[m - 1][n - 1] +``` Go: +```Go +func uniquePaths(m int, n int) int { + dp := make([][]int, m) + for i := range dp { + dp[i] = make([]int, n) + dp[i][0] = 1 + } + for j := 0; j < n; j++ { + dp[0][j] = 1 + } + for i := 1; i < m; i++ { + for j := 1; j < n; j++ { + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1] + } + } + return dp[m-1][n-1] +} +``` - +Javascript: +```Javascript +var uniquePaths = function(m, n) { + const dp = Array(m).fill().map(item => Array(n)) + + for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) { + dp[i][0] = 1 + } + + for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { + dp[0][i] = 1 + } + + for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i) { + for (let j = 1; j < n; ++j) { + dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1] + } + } + return dp[m - 1][n - 1] +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0063.不同路径II.md b/problems/0063.不同路径II.md index 311f712e..52f00322 100644 --- a/problems/0063.不同路径II.md +++ b/problems/0063.不同路径II.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 63. 不同路径 II @@ -157,8 +157,6 @@ public: * 时间复杂度O(n * m) n m 分别为obstacleGrid 长度和宽度 * 空间复杂度O(n * m) -至于能不能优化空间降为一维dp数组,我感觉不太行,因为要考虑障碍,如果把这些障碍压缩到一行,结果一定就不一样了。 - ## 总结 本题是[62.不同路径](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/MGgGIt4QCpFMROE9X9he_A)的障碍版,整体思路大体一致。 @@ -237,7 +235,74 @@ class Solution: Go: +```go +func uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) int { + m,n:= len(obstacleGrid),len(obstacleGrid[0]) + // 定义一个dp数组 + dp := make([][]int,m) + for i,_ := range dp { + dp[i] = make([]int,n) + } + // 初始化 + for i:=0;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 70. 爬楼梯 +题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/ -假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。 +假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢? @@ -212,7 +213,45 @@ public: Java: +```Java +class Solution { + public int climbStairs(int n) { + // 跟斐波那契数列一样 + if(n <= 2) return n; + int a = 1, b = 2, sum = 0; + + for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++){ + sum = a + b; + a = b; + b = sum; + } + return b; + } +} +``` +```java +// 常规方式 +public int climbStairs(int n) { + int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; + dp[0] = 1; + dp[1] = 1; + for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { + dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; + } + return dp[n]; +} +// 用变量记录代替数组 +public int climbStairs(int n) { + int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0; // 默认需要1次 + for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { + c = a + b; // f(i - 1) + f(n - 2) + a = b; // 记录上一轮的值 + b = c; // 向后步进1个数 + } + return c; +} +``` Python: diff --git a/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md b/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md index f92e6716..b3e7eb73 100644 --- a/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md +++ b/problems/0070.爬楼梯完全背包版本.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:以前我没得选,现在我选择再爬一次! 之前讲这道题目的时候,因为还没有讲背包问题,所以就只是讲了一下爬楼梯最直接的动规方法(斐波那契)。 @@ -149,13 +149,48 @@ class Solution { Python: -Go: +```python3 +class Solution: + def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int: + dp = [0]*(n + 1) + dp[0] = 1 + m = 2 + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(n + 1): + # 遍历物品 + for step in range(1, m + 1): + if j >= step: + dp[j] += dp[j - step] + return dp[n] +``` +Go: +```go +func climbStairs(n int) int { + //定义 + dp := make([]int, n+1) + //初始化 + dp[0] = 1 + // 本题物品只有两个1,2 + m := 2 + // 遍历顺序 + for j := 1; j <= n; j++ { //先遍历背包 + for i := 1; i <= m; i++ { //再遍历物品 + if j >= i { + dp[j] += dp[j-i] + } + //fmt.Println(dp) + } + } + return dp[n] +} +``` + ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 72. 编辑距离 +https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/ + 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。 你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作: @@ -16,23 +18,23 @@ * 删除一个字符 * 替换一个字符 -示例 1: -输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros" -输出:3 -解释: -horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r') -rorse -> rose (删除 'r') -rose -> ros (删除 'e') +示例 1: +输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros" +输出:3 +解释: +horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r') +rorse -> rose (删除 'r') +rose -> ros (删除 'e') -示例 2: -输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution" -输出:5 -解释: -intention -> inention (删除 't') -inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e') -enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x') -exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c') -exection -> execution (插入 'u') +示例 2: +输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution" +输出:5 +解释: +intention -> inention (删除 't') +inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e') +enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x') +exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c') +exection -> execution (插入 'u') 提示: @@ -198,10 +200,50 @@ public: Java: - +```java +public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) { + int m = word1.length(); + int n = word2.length(); + int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; + // 初始化 + for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { + dp[i][0] = i; + } + for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { + dp[0][j] = j; + } + for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { + for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { + // 因为dp数组有效位从1开始 + // 所以当前遍历到的字符串的位置为i-1 | j-1 + if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) { + dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1]; + } else { + dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j]) + 1; + } + } + } + return dp[m][n]; +} +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int: + dp = [[0] * (len(word2)+1) for _ in range(len(word1)+1)] + for i in range(len(word1)+1): + dp[i][0] = i + for j in range(len(word2)+1): + dp[0][j] = j + for i in range(1, len(word1)+1): + for j in range(1, len(word2)+1): + if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]: + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + else: + dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) + 1 + return dp[-1][-1] +``` Go: ```Go diff --git a/problems/0077.组合.md b/problems/0077.组合.md index f31766e0..0b289a40 100644 --- a/problems/0077.组合.md +++ b/problems/0077.组合.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -370,11 +370,70 @@ class Solution { Python: - - +```python3 +class Solution: + def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]: + res=[] #存放符合条件结果的集合 + path=[] #用来存放符合条件结果 + def backtrack(n,k,startIndex): + if len(path) == k: + res.append(path[:]) + return + for i in range(startIndex,n+1): + path.append(i) #处理节点 + backtrack(n,k,i+1) #递归 + path.pop() #回溯,撤销处理的节点 + backtrack(n,k,1) + return res +``` +javascript +```javascript +let result = [] +let path = [] +var combine = function(n, k) { + result = [] + combineHelper(n, k, 1) + return result +}; +const combineHelper = (n, k, startIndex) => { + if (path.length === k) { + result.push([...path]) + return + } + for (let i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.length) + 1; ++i) { + path.push(i) + combineHelper(n, k, i + 1) + path.pop() + } +} +``` Go: - - +```Go +var res [][]int +func combine(n int, k int) [][]int { + res=[][]int{} + if n <= 0 || k <= 0 || k > n { + return res + } + backtrack(n, k, 1, []int{}) + return res +} +func backtrack(n,k,start int,track []int){ + if len(track)==k{ + temp:=make([]int,k) + copy(temp,track) + res=append(res,temp) + } + if len(track)+n-start+1 < k { + return + } + for i:=start;i<=n;i++{ + track=append(track,i) + backtrack(n,k,i+1,track) + track=track[:len(track)-1] + } +} +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0077.组合优化.md b/problems/0077.组合优化.md index a8a17858..d3e82f09 100644 --- a/problems/0077.组合优化.md +++ b/problems/0077.组合优化.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ public: Java: -``` +```java class Solution { List欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 第78题. 子集 @@ -186,7 +186,6 @@ class Solution { result.add(new ArrayList<>()); return result; } - Arrays.sort(nums); subsetsHelper(nums, 0); return result; } @@ -206,7 +205,20 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]: + res = [] + path = [] + def backtrack(nums,startIndex): + res.append(path[:]) #收集子集,要放在终止添加的上面,否则会漏掉自己 + for i in range(startIndex,len(nums)): #当startIndex已经大于数组的长度了,就终止了,for循环本来也结束了,所以不需要终止条件 + path.append(nums[i]) + backtrack(nums,i+1) #递归 + path.pop() #回溯 + backtrack(nums,0) + return res +``` Go: ```Go diff --git a/problems/0090.子集II.md b/problems/0090.子集II.md index 941e3eca..71aef5c7 100644 --- a/problems/0090.子集II.md +++ b/problems/0090.子集II.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 第90题.子集II @@ -208,7 +208,23 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]: + res = [] #存放符合条件结果的集合 + path = [] #用来存放符合条件结果 + def backtrack(nums,startIndex): + res.append(path[:]) + for i in range(startIndex,len(nums)): + if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: #我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过 + continue + path.append(nums[i]) + backtrack(nums,i+1) #递归 + path.pop() #回溯 + nums = sorted(nums) #去重需要排序 + backtrack(nums,0) + return res +``` Go: ```Go diff --git a/problems/0093.复原IP地址.md b/problems/0093.复原IP地址.md index 4cea7a3a..a8b9a215 100644 --- a/problems/0093.复原IP地址.md +++ b/problems/0093.复原IP地址.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -338,6 +338,35 @@ class Solution(object): return ans``` ``` +JavaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {string} s + * @return {string[]} + */ +var restoreIpAddresses = function(s) { + const res = [], path = []; + backtracking(0, 0) + return res; + function backtracking(i) { + const len = path.length; + if(len > 4) return; + if(len === 4 && i === s.length) { + res.push(path.join(".")); + return; + } + for(let j = i; j < s.length; j++) { + const str = s.substr(i, j - i + 1); + if(str.length > 3 || +str > 255) break; + if(str.length > 1 && str[0] === "0") break; + path.push(str); + backtracking(j + 1); + path.pop() + } + } +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) diff --git a/problems/0096.不同的二叉搜索树.md b/problems/0096.不同的二叉搜索树.md index 7dea8fb0..a9631315 100644 --- a/problems/0096.不同的二叉搜索树.md +++ b/problems/0096.不同的二叉搜索树.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 96.不同的二叉搜索树 @@ -186,10 +186,30 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def numTrees(self, n: int) -> int: + dp = [0] * (n + 1) + dp[0], dp[1] = 1, 1 + for i in range(2, n + 1): + for j in range(1, i + 1): + dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j] + return dp[-1] +``` Go: - +```Go +func numTrees(n int)int{ + dp:=make([]int,n+1) + dp[0]=1 + for i:=1;i<=n;i++{ + for j:=1;j<=i;j++{ + dp[i]+=dp[j-1]*dp[i-j] + } + } + return dp[n] +} +``` diff --git a/problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md b/problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md index f246c21a..eb877abb 100644 --- a/problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md +++ b/problems/0098.验证二叉搜索树.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 98.验证二叉搜索树 @@ -304,11 +304,58 @@ class Solution { return true; } } + +// 简洁实现·递归解法 +class Solution { + public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { + return validBST(Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE, root); + } + boolean validBST(long lower, long upper, TreeNode root) { + if (root == null) return true; + if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) return false; + return validBST(lower, root.val, root.left) && validBST(root.val, upper, root.right); + } +} +// 简洁实现·中序遍历 +class Solution { + private long prev = Long.MIN_VALUE; + public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { + if (root == null) { + return true; + } + if (!isValidBST(root.left)) { + return false; + } + if (root.val <= prev) { // 不满足二叉搜索树条件 + return false; + } + prev = root.val; + return isValidBST(root.right); + } +} ``` Python: - - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法 +class Solution: + def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + res = [] //把二叉搜索树按中序遍历写成list + def buildalist(root): + if not root: return + buildalist(root.left) //左 + res.append(root.val) //中 + buildalist(root.right) //右 + return res + buildalist(root) + return res == sorted(res) and len(set(res)) == len(res) //检查list里的数有没有重复元素,以及是否按从小到大排列 +``` Go: ```Go import "math" @@ -336,4 +383,4 @@ func isBST(root *TreeNode, min, max int) bool { * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 101. 对称二叉树 @@ -360,9 +360,129 @@ Java: Python: +> 递归法 +```python +class Solution: + def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + if not root: + return True + return self.compare(root.left, root.right) + + def compare(self, left, right): + #首先排除空节点的情况 + if left == None and right != None: return False + elif left != None and right == None: return False + elif left == None and right == None: return True + #排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况 + elif left.val != right.val: return False + + #此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况 + #此时才做递归,做下一层的判断 + outside = self.compare(left.left, right.right) #左子树:左、 右子树:右 + inside = self.compare(left.right, right.left) #左子树:右、 右子树:左 + isSame = outside and inside #左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理) + return isSame +``` + +> 迭代法: 使用队列 +```python +import collections +class Solution: + def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + if not root: + return True + queue = collections.deque() + queue.append(root.left) #将左子树头结点加入队列 + queue.append(root.right) #将右子树头结点加入队列 + while queue: #接下来就要判断这这两个树是否相互翻转 + leftNode = queue.popleft() + rightNode = queue.popleft() + if not leftNode and not rightNode: #左节点为空、右节点为空,此时说明是对称的 + continue + + #左右一个节点不为空,或者都不为空但数值不相同,返回false + if not leftNode or not rightNode or leftNode.val != rightNode.val: + return False + queue.append(leftNode.left) #加入左节点左孩子 + queue.append(rightNode.right) #加入右节点右孩子 + queue.append(leftNode.right) #加入左节点右孩子 + queue.append(rightNode.left) #加入右节点左孩子 + return True +``` + +> 迭代法:使用栈 +```python +class Solution: + def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + if not root: + return True + st = [] #这里改成了栈 + st.append(root.left) + st.append(root.right) + while st: + leftNode = st.pop() + rightNode = st.pop() + if not leftNode and not rightNode: + continue + if not leftNode or not rightNode or leftNode.val != rightNode.val: + return False + st.append(leftNode.left) + st.append(rightNode.right) + st.append(leftNode.right) + st.append(rightNode.left) + return True +``` Go: +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +// 递归 +func defs(left *TreeNode, right *TreeNode) bool { + if left == nil && right == nil { + return true; + }; + if left == nil || right == nil { + return false; + }; + if left.Val != right.Val { + return false; + } + return defs(left.Left, right.Right) && defs(right.Left, left.Right); +} +func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool { + return defs(root.Left, root.Right); +} + +// 迭代 +func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool { + var queue []*TreeNode; + if root != nil { + queue = append(queue, root.Left, root.Right); + } + for len(queue) > 0 { + left := queue[0]; + right := queue[1]; + queue = queue[2:]; + if left == nil && right == nil { + continue; + } + if left == nil || right == nil || left.Val != right.Val { + return false; + }; + queue = append(queue, left.Left, right.Right, right.Left, left.Right); + } + return true; +} +``` + JavaScript ```javascript @@ -379,6 +499,90 @@ const check = (leftPtr, rightPtr) => { return leftPtr.val === rightPtr.val && check(leftPtr.left, rightPtr.right) && check(leftPtr.right, rightPtr.left) } ``` +JavaScript: + +递归判断是否为对称二叉树: +```javascript +var isSymmetric = function(root) { + //使用递归遍历左右子树 递归三部曲 + // 1. 确定递归的参数 root.left root.right和返回值true false + const compareNode=function(left,right){ + //2. 确定终止条件 空的情况 + if(left===null&&right!==null||left!==null&&right===null){ + return false; + }else if(left===null&&right===null){ + return true; + }else if(left.val!==right.val){ + return false; + } + //3. 确定单层递归逻辑 + let outSide=compareNode(left.left,right.right); + let inSide=compareNode(left.right,right.left); + return outSide&&inSide; + } + if(root===null){ + return true; + } + return compareNode(root.left,root.right); +}; +``` +队列实现迭代判断是否为对称二叉树: +```javascript +var isSymmetric = function(root) { + //迭代方法判断是否是对称二叉树 + //首先判断root是否为空 + if(root===null){ + return true; + } + let queue=[]; + queue.push(root.left); + queue.push(root.right); + while(queue.length){ + let leftNode=queue.shift();//左节点 + let rightNode=queue.shift();//右节点 + if(leftNode===null&&rightNode===null){ + continue; + } + if(leftNode===null||rightNode===null||leftNode.val!==rightNode.val){ + return false; + } + queue.push(leftNode.left);//左节点左孩子入队 + queue.push(rightNode.right);//右节点右孩子入队 + queue.push(leftNode.right);//左节点右孩子入队 + queue.push(rightNode.left);//右节点左孩子入队 + } + return true; +}; +``` +栈实现迭代判断是否为对称二叉树: +```javascript +var isSymmetric = function(root) { + //迭代方法判断是否是对称二叉树 + //首先判断root是否为空 + if(root===null){ + return true; + } + let stack=[]; + stack.push(root.left); + stack.push(root.right); + while(stack.length){ + let rightNode=stack.pop();//左节点 + let leftNode=stack.pop();//右节点 + if(leftNode===null&&rightNode===null){ + continue; + } + if(leftNode===null||rightNode===null||leftNode.val!==rightNode.val){ + return false; + } + stack.push(leftNode.left);//左节点左孩子入队 + stack.push(rightNode.right);//右节点右孩子入队 + stack.push(leftNode.right);//左节点右孩子入队 + stack.push(rightNode.left);//右节点左孩子入队 + } + return true; +}; +``` + ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md b/problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md index 9b5f9ed5..89d0dda7 100644 --- a/problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md +++ b/problems/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 二叉树的层序遍历 @@ -79,6 +79,67 @@ public: return result; } }; +``` +python代码: + +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]: + if not root: + return [] + + quene = [root] + out_list = [] + + while quene: + length = len(queue) # 这里一定要先求出队列的长度,不能用range(len(queue)),因为queue长度是变化的 + in_list = [] + for _ in range(length): + curnode = queue.pop(0) # (默认移除列表最后一个元素)这里需要移除队列最头上的那个 + in_list.append(curnode.val) + if curnode.left: queue.append(curnode.left) + if curnode.right: queue.append(curnode.right) + out_list.append(in_list) + + return out_list +``` + + + +javascript代码: + +```javascript +var levelOrder = function(root) { + //二叉树的层序遍历 + let res=[],queue=[]; + queue.push(root); + if(root===null){ + return res; + } + while(queue.length!==0){ + // 记录当前层级节点数 + let length=queue.length; + //存放每一层的节点 + let curLevel=[]; + for(let i=0;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
看完本篇可以一起做了如下两道题目: @@ -193,40 +193,6 @@ public: }; ``` -使用栈来模拟后序遍历依然可以 - -```C++ -class Solution { -public: - int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { - stack

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
看完本文,可以一起解决如下两道题目 @@ -580,8 +580,10 @@ tree2 的前序遍历是[1 2 3], 后序遍历是[3 2 1]。 ## 其他语言版本 - Java: + +106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 + ```java class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) { @@ -617,9 +619,79 @@ class Solution { } ``` +105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 + +```java +class Solution { + public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { + return helper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1); + } + + public TreeNode helper(int[] preorder, int preLeft, int preRight, + int[] inorder, int inLeft, int inRight) { + // 递归终止条件 + if (inLeft > inRight || preLeft > preRight) return null; + + // val 为前序遍历第一个的值,也即是根节点的值 + // idx 为根据根节点的值来找中序遍历的下标 + int idx = inLeft, val = preorder[preLeft]; + TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val); + for (int i = inLeft; i <= inRight; i++) { + if (inorder[i] == val) { + idx = i; + break; + } + } + + // 根据 idx 来递归找左右子树 + root.left = helper(preorder, preLeft + 1, preLeft + (idx - inLeft), + inorder, inLeft, idx - 1); + root.right = helper(preorder, preLeft + (idx - inLeft) + 1, preRight, + inorder, idx + 1, inRight); + return root; + } +} +``` + Python: +105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法 +class Solution: + def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode: + if not preorder: return None //特殊情况 + root = TreeNode(preorder[0]) //新建父节点 + p=inorder.index(preorder[0]) //找到父节点在中序遍历的位置(因为没有重复的元素,才可以这样找) + root.left = self.buildTree(preorder[1:p+1],inorder[:p]) //注意左节点时分割中序数组和前续数组的开闭环 + root.right = self.buildTree(preorder[p+1:],inorder[p+1:]) //分割中序数组和前续数组 + return root +``` +106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法 +class Solution: + def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode: + if not postorder: return None //特殊情况 + root = TreeNode(postorder[-1]) //新建父节点 + p=inorder.index(postorder[-1]) //找到父节点在中序遍历的位置*因为没有重复的元素,才可以这样找 + root.left = self.buildTree(inorder[:p],postorder[:p]) //分割中序数组和后续数组 + root.right = self.buildTree(inorder[p+1:],postorder[p:-1]) //注意右节点时分割中序数组和后续数组的开闭环 + return root +``` Go: @@ -643,4 +715,4 @@ var buildTree = function(inorder, postorder) { * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 构造二叉搜索树,一不小心就平衡了 @@ -233,7 +233,27 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +#递归法 +class Solution: + def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode: + def buildaTree(left,right): + if left > right: return None #左闭右闭的区间,当区间 left > right的时候,就是空节点,当left = right的时候,不为空 + mid = left + (right - left) // 2 #保证数据不会越界 + val = nums[mid] + root = TreeNode(val) + root.left = buildaTree(left,mid - 1) + root.right = buildaTree(mid + 1,right) + return root + root = buildaTree(0,len(nums) - 1) #左闭右闭区间 + return root +``` Go: @@ -244,4 +264,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 求高度还是求深度,你搞懂了不? @@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ int getDepth(TreeNode* node) 2. 明确终止条件 -递归的过程中依然是遇到空节点了为终止,返回0,表示当前节点为根节点的书高度为0 +递归的过程中依然是遇到空节点了为终止,返回0,表示当前节点为根节点的树高度为0 代码如下: @@ -498,6 +498,62 @@ class Solution { Python: +> 递归法: +```python +class Solution: + def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + return True if self.getDepth(root) != -1 else False + + #返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是二叉搜索树了则返回-1 + def getDepth(self, node): + if not node: + return 0 + leftDepth = self.getDepth(node.left) + if leftDepth == -1: return -1 #说明左子树已经不是二叉平衡树 + rightDepth = self.getDepth(node.right) + if rightDepth == -1: return -1 #说明右子树已经不是二叉平衡树 + return -1 if abs(leftDepth - rightDepth)>1 else 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth) +``` + +> 迭代法: +```python +class Solution: + def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: + st = [] + if not root: + return True + st.append(root) + while st: + node = st.pop() #中 + if abs(self.getDepth(node.left) - self.getDepth(node.right)) > 1: + return False + if node.right: + st.append(node.right) #右(空节点不入栈) + if node.left: + st.append(node.left) #左(空节点不入栈) + return True + + def getDepth(self, cur): + st = [] + if cur: + st.append(cur) + depth = 0 + result = 0 + while st: + node = st.pop() + if node: + st.append(node) #中 + st.append(None) + depth += 1 + if node.right: st.append(node.right) #右 + if node.left: st.append(node.left) #左 + else: + node = st.pop() + depth -= 1 + result = max(result, depth) + return result +``` + Go: ```Go @@ -534,7 +590,34 @@ func abs(a int)int{ return a } ``` - +JavaScript: +```javascript +var isBalanced = function(root) { + //还是用递归三部曲 + 后序遍历 左右中 当前左子树右子树高度相差大于1就返回-1 + // 1. 确定递归函数参数以及返回值 + const getDepth=function(node){ + // 2. 确定递归函数终止条件 + if(node===null){ + return 0; + } + // 3. 确定单层递归逻辑 + let leftDepth=getDepth(node.left);//左子树高度 + if(leftDepth===-1){ + return -1; + } + let rightDepth=getDepth(node.right);//右子树高度 + if(rightDepth===-1){ + return -1; + } + if(Math.abs(leftDepth-rightDepth)>1){ + return -1; + }else{ + return 1+Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth); + } + } + return getDepth(root)===-1?false:true; +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md b/problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md index 01b6c89c..48795722 100644 --- a/problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md +++ b/problems/0111.二叉树的最小深度.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 和求最大深度一个套路? @@ -301,6 +301,111 @@ class Solution: Go: +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +func min(a, b int) int { + if a < b { + return a; + } + return b; +} +// 递归 +func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int { + if root == nil { + return 0; + } + if root.Left == nil && root.Right != nil { + return 1 + minDepth(root.Right); + } + if root.Right == nil && root.Left != nil { + return 1 + minDepth(root.Left); + } + return min(minDepth(root.Left), minDepth(root.Right)) + 1; +} + +// 迭代 + +func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int { + dep := 0; + queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0); + if root != nil { + queue = append(queue, root); + } + for l := len(queue); l > 0; { + dep++; + for ; l > 0; l-- { + node := queue[0]; + if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil { + return dep; + } + if node.Left != nil { + queue = append(queue, node.Left); + } + if node.Right != nil { + queue = append(queue, node.Right); + } + queue = queue[1:]; + } + l = len(queue); + } + return dep; +} +``` + + +JavaScript: + +递归法: + +```javascript +/** + * @param {TreeNode} root + * @return {number} + */ +var minDepth1 = function(root) { + if(!root) return 0; + // 到叶子节点 返回 1 + if(!root.left && !root.right) return 1; + // 只有右节点时 递归右节点 + if(!root.left) return 1 + minDepth(root.right);、 + // 只有左节点时 递归左节点 + if(!root.right) return 1 + minDepth(root.left); + return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1; +}; +``` + +迭代法: + +```javascript +/** +* @param {TreeNode} root +* @return {number} +*/ +var minDepth = function(root) { + if(!root) return 0; + const queue = [root]; + let dep = 0; + while(true) { + let size = queue.length; + dep++; + while(size--){ + const node = queue.shift(); + // 到第一个叶子节点 返回 当前深度 + if(!node.left && !node.right) return dep; + node.left && queue.push(node.left); + node.right && queue.push(node.right); + } + } +}; +``` + diff --git a/problems/0112.路径总和.md b/problems/0112.路径总和.md index 1b75113e..54f79d1d 100644 --- a/problems/0112.路径总和.md +++ b/problems/0112.路径总和.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 递归函数什么时候需要返回值 @@ -332,13 +332,246 @@ class Solution { } } +// LC112 简洁方法 +class Solution { + public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { + + if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出 + + // 叶子节点判断是否符合 + if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetSum; + + // 求两侧分支的路径和 + return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); + } +} +``` +迭代 +```java +class Solution { + public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { + if(root==null)return false; + Stack

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 115.不同的子序列 @@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ 题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。 - + 提示: @@ -148,7 +148,22 @@ Java: Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def numDistinct(self, s: str, t: str) -> int: + dp = [[0] * (len(t)+1) for _ in range(len(s)+1)] + for i in range(len(s)): + dp[i][0] = 1 + for j in range(1, len(t)): + dp[0][j] = 0 + for i in range(1, len(s)+1): + for j in range(1, len(t)+1): + if s[i-1] == t[j-1]: + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + dp[i-1][j] + else: + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + return dp[-1][-1] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md b/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md index 3d564892..259fff34 100644 --- a/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md +++ b/problems/0121.买卖股票的最佳时机.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机 @@ -16,14 +16,14 @@ 返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。 -示例 1: -输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4] -输出:5 +示例 1: +输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4] +输出:5 解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。 -示例 2: -输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] -输出:0 +示例 2: +输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] +输出:0 解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。 @@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ 这道题目最直观的想法,就是暴力,找最优间距了。 -``` +```C++ class Solution { public: int maxProfit(vector欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II @@ -133,9 +133,10 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: + ```java +// 贪心思路 class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { int sum = 0; @@ -153,6 +154,29 @@ class Solution { } ``` +```java +class Solution { // 动态规划 + public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { + // [天数][是否持有股票] + int[][] dp = new int[prices.length][2]; + + // bad case + dp[0][0] = 0; + dp[0][1] = -prices[0]; + + for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { + // dp公式 + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]); + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]); + } + + return dp[prices.length - 1][0]; + } +} +``` + + + Python: ```python class Solution: @@ -166,10 +190,20 @@ class Solution: Go: - +Javascript: +```Javascript +// 贪心 +var maxProfit = function(prices) { + let result = 0 + for(let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { + result += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0) + } + return result +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II @@ -133,10 +133,71 @@ public: Java: +```java +// 动态规划 +class Solution + // 实现1:二维数组存储 + // 可以将每天持有与否的情况分别用 dp[i][0] 和 dp[i][1] 来进行存储 + // 时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度O(n) + public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { + int n = prices.length; + int[][] dp = new int[n][2]; // 创建二维数组存储状态 + dp[0][0] = 0; // 初始状态 + dp[0][1] = -prices[0]; + for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]); // 第 i 天,没有股票 + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]); // 第 i 天,持有股票 + } + return dp[n - 1][0]; // 卖出股票收益高于持有股票收益,因此取[0] + } + // 实现2:变量存储 + // 第一种方法需要用二维数组存储,有空间开销,其实关心的仅仅是前一天的状态,不关注更多的历史信息 + // 因此,可以仅保存前一天的信息存入 dp0、dp1 这 2 个变量即可 + // 时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度O(1) + public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { + int n = prices.length; + int dp0 = 0, dp1 = -prices[0]; // 定义变量,存储初始状态 + for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { + int newDp0 = Math.max(dp0, dp1 + prices[i]); // 第 i 天,没有股票 + int newDp1 = Math.max(dp1, dp0 - prices[i]); // 第 i 天,持有股票 + dp0 = newDp0; + dp1 = newDp1; + } + return dp0; + } +} +``` Python: +> 版本一: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: + length = len(prices) + dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(length)] + dp[0][0] = -prices[0] + dp[0][1] = 0 + for i in range(1, length): + dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i]) #注意这里是和121. 买卖股票的最佳时机唯一不同的地方 + dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]) + return dp[-1][1] +``` + +> 版本二: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: + length = len(prices) + dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(2)] #注意这里只开辟了一个2 * 2大小的二维数组 + dp[0][0] = -prices[0] + dp[0][1] = 0 + for i in range(1, length): + dp[i % 2][0] = max(dp[(i-1) % 2][0], dp[(i-1) % 2][1] - prices[i]) + dp[i % 2][1] = max(dp[(i-1) % 2][1], dp[(i-1) % 2][0] + prices[i]) + return dp[(length-1) % 2][1] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md b/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md index 0e718cf1..fccb187d 100644 --- a/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md +++ b/problems/0123.买卖股票的最佳时机III.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III @@ -101,9 +101,9 @@ dp[i][4] = max(dp[i - 1][4], dp[i - 1][3] + prices[i]); 所以dp[0][2] = 0; -第0天第二次买入操作,初始值应该是多少呢? +第0天第二次买入操作,初始值应该是多少呢?应该不少同学疑惑,第一次还没买入呢,怎么初始化第二次买入呢? -不用管第几次,现在手头上没有现金,只要买入,现金就做相应的减少。 +第二次买入依赖于第一次卖出的状态,其实相当于第0天第一次买入了,第一次卖出了,然后在买入一次(第二次买入),那么现在手头上没有现金,只要买入,现金就做相应的减少。 所以第二次买入操作,初始化为:dp[0][3] = -prices[0]; @@ -190,12 +190,79 @@ dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]); 如果dp[1]取dp[1],即保持买入股 ## 其他语言版本 - Java: +```java +class Solution { // 动态规划 + public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { + // 可交易次数 + int k = 2; + + // [天数][交易次数][是否持有股票] + int[][][] dp = new int[prices.length][k + 1][2]; + + // badcase + dp[0][0][0] = 0; + dp[0][0][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; + dp[0][1][0] = 0; + dp[0][1][1] = -prices[0]; + dp[0][2][0] = 0; + dp[0][2][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; + + for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { + for (int j = 2; j >= 1; j--) { + // dp公式 + dp[i][j][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j][0], dp[i - 1][j][1] + prices[i]); + dp[i][j][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j][1], dp[i - 1][j - 1][0] - prices[i]); + } + } + + int res = 0; + for (int i = 1; i < 3; i++) { + res = Math.max(res, dp[prices.length - 1][i][0]); + } + return res; + } +} +``` + Python: +> 版本一: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: + if len(prices) == 0: + return 0 + dp = [[0] * 5 for _ in range(len(prices))] + dp[0][1] = -prices[0] + dp[0][3] = -prices[0] + for i in range(1, len(prices)): + dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] - prices[i]) + dp[i][2] = max(dp[i-1][2], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i]) + dp[i][3] = max(dp[i-1][3], dp[i-1][2] - prices[i]) + dp[i][4] = max(dp[i-1][4], dp[i-1][3] + prices[i]) + return dp[-1][4] +``` + +> 版本二: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: + if len(prices) == 0: + return 0 + dp = [0] * 5 + dp[1] = -prices[0] + dp[3] = -prices[0] + for i in range(1, len(prices)): + dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i]) + dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i]) + dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i]) + dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i]) + return dp[4] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0131.分割回文串.md b/problems/0131.分割回文串.md index 9c86a3bc..9d23fd13 100644 --- a/problems/0131.分割回文串.md +++ b/problems/0131.分割回文串.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 切割问题其实是一种组合问题! @@ -292,11 +292,59 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```py +class Solution: + def partition(self, s: str) -> List[List[str]]: + res = [] + path = [] #放已经回文的子串 + def backtrack(s,startIndex): + if startIndex >= len(s): #如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了 + return res.append(path[:]) + for i in range(startIndex,len(s)): + p = s[startIndex:i+1] #获取[startIndex,i+1]在s中的子串 + if p == p[::-1]: path.append(p) #是回文子串 + else: continue #不是回文,跳过 + backtrack(s,i+1) #寻找i+1为起始位置的子串 + path.pop() #回溯过程,弹出本次已经填在path的子串 + backtrack(s,0) + return res + +``` Go: +javaScript: +```js +/** + * @param {string} s + * @return {string[][]} + */ +const isPalindrome = (s, l, r) => { + for (let i = l, j = r; i < j; i++, j--) { + if(s[i] !== s[j]) return false; + } + return true; +} + +var partition = function(s) { + const res = [], path = [], len = s.length; + backtracking(0); + return res; + function backtracking(i) { + if(i >= len) { + res.push(Array.from(path)); + return; + } + for(let j = i; j < len; j++) { + if(!isPalindrome(s, i, j)) continue; + path.push(s.substr(i, j - i + 1)); + backtracking(j + 1); + path.pop(); + } + } +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0134.加油站.md b/problems/0134.加油站.md index 393e4627..dfed2d96 100644 --- a/problems/0134.加油站.md +++ b/problems/0134.加油站.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 134. 加油站 @@ -223,15 +223,50 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int: + start = 0 + curSum = 0 + totalSum = 0 + for i in range(len(gas)): + curSum += gas[i] - cost[i] + totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i] + if curSum < 0: + curSum = 0 + start = i + 1 + if totalSum < 0: return -1 + return start +``` Go: +Javascript: +```Javascript +var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) { + const gasLen = gas.length + let start = 0 + let curSum = 0 + let totalSum = 0 + for(let i = 0; i < gasLen; i++) { + curSum += gas[i] - cost[i] + totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i] + if(curSum < 0) { + curSum = 0 + start = i + 1 + } + } + + if(totalSum < 0) return -1 + + return start +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 135. 分发糖果 @@ -161,15 +161,49 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def candy(self, ratings: List[int]) -> int: + candyVec = [1] * len(ratings) + for i in range(1, len(ratings)): + if ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]: + candyVec[i] = candyVec[i - 1] + 1 + for j in range(len(ratings) - 2, -1, -1): + if ratings[j] > ratings[j + 1]: + candyVec[j] = max(candyVec[j], candyVec[j + 1] + 1) + return sum(candyVec) +``` Go: +Javascript: +```Javascript +var candy = function(ratings) { + let candys = new Array(ratings.length).fill(1) + for(let i = 1; i < ratings.length; i++) { + if(ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) { + candys[i] = candys[i - 1] + 1 + } + } + + for(let i = ratings.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) { + if(ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) { + candys[i] = Math.max(candys[i], candys[i + 1] + 1) + } + } + + let count = candys.reduce((a, b) => { + return a + b + }) + + return count +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:单词拆分 ## 139.单词拆分 @@ -252,9 +252,44 @@ class Solution { Python: +```python3 +class Solution: + def wordBreak(self, s: str, wordDict: List[str]) -> bool: + '''排列''' + dp = [False]*(len(s) + 1) + dp[0] = True + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(1, len(s) + 1): + # 遍历单词 + for word in wordDict: + if j >= len(word): + dp[j] = dp[j] or (dp[j - len(word)] and word == s[j - len(word):j]) + return dp[len(s)] +``` + + + Go: - +```Go +func wordBreak(s string,wordDict []string) bool { + wordDictSet:=make(map[string]bool) + for _,w:=range wordDict{ + wordDictSet[w]=true + } + dp:=make([]bool,len(s)+1) + dp[0]=true + for i:=1;i<=len(s);i++{ + for j:=0;j \ No newline at end of file
+
\ No newline at end of file
+
欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -234,6 +234,67 @@ class Solution: ``` Go: +```go +func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode { + slow, fast := head, head + for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil { + slow = slow.Next + fast = fast.Next.Next + if slow == fast { + for slow != head { + slow = slow.Next + head = head.Next + } + return head + } + } + return nil +} +``` + +javaScript + +```js +// 两种循环实现方式 +/** + * @param {ListNode} head + * @return {ListNode} + */ +// 先判断是否是环形链表 +var detectCycle = function(head) { + if(!head || !head.next) return null; + let slow =head.next, fast = head.next.next; + while(fast && fast.next && fast!== slow) { + slow = slow.next; + fast = fast.next.next; + } + if(!fast || !fast.next ) return null; + slow = head; + while (fast !== slow) { + slow = slow.next; + fast = fast.next; + } + return slow; +}; + +var detectCycle = function(head) { + if(!head || !head.next) return null; + let slow =head.next, fast = head.next.next; + while(fast && fast.next) { + slow = slow.next; + fast = fast.next.next; + if(fast == slow) { + slow = head; + while (fast !== slow) { + slow = slow.next; + fast = fast.next; + } + return slow; + } + } + return null; +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md b/problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md index 4e7365f7..c8b0da08 100644 --- a/problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md +++ b/problems/0150.逆波兰表达式求值.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -170,8 +170,75 @@ public class EvalRPN { } ``` +Go: +```Go +func evalRPN(tokens []string) int { + stack := []int{} + for _, token := range tokens { + val, err := strconv.Atoi(token) + if err == nil { + stack = append(stack, val) + } else { + num1, num2 := stack[len(stack)-2], stack[(len(stack))-1] + stack = stack[:len(stack)-2] + switch token { + case "+": + stack = append(stack, num1+num2) + case "-": + stack = append(stack, num1-num2) + case "*": + stack = append(stack, num1*num2) + case "/": + stack = append(stack, num1/num2) + } + } + } + return stack[0] +} +``` +javaScript: +```js + +/** + * @param {string[]} tokens + * @return {number} + */ +var evalRPN = function(tokens) { + const s = new Map([ + ["+", (a, b) => a * 1 + b * 1], + ["-", (a, b) => b - a], + ["*", (a, b) => b * a], + ["/", (a, b) => (b / a) | 0] + ]); + const stack = []; + for (const i of tokens) { + if(!s.has(i)) { + stack.push(i); + continue; + } + stack.push(s.get(i)(stack.pop(),stack.pop())) + } + return stack.pop(); +}; +``` + +python3 + +```python +def evalRPN(tokens) -> int: + stack = list() + for i in range(len(tokens)): + if tokens[i] not in ["+", "-", "*", "/"]: + stack.append(tokens[i]) + else: + tmp1 = stack.pop() + tmp2 = stack.pop() + res = eval(tmp2+tokens[i]+tmp1) + stack.append(str(int(res))) + return stack[-1] +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md b/problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md index 1c567f84..d76734e4 100644 --- a/problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md +++ b/problems/0151.翻转字符串里的单词.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -183,7 +183,7 @@ public: int end = 0; // 反转的单词在字符串里终止位置 bool entry = false; // 标记枚举字符串的过程中是否已经进入了单词区间 for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { // 开始反转单词 - if ((!entry) || (s[i] != ' ' && s[i - 1] == ' ')) { + if (!entry) { start = i; // 确定单词起始位置 entry = true; // 进入单词区间 } @@ -318,9 +318,61 @@ class Solution { Python: - Go: +```go +import ( + "fmt" +) + +func reverseWords(s string) string { + //1.使用双指针删除冗余的空格 + slowIndex, fastIndex := 0, 0 + b := []byte(s) + //删除头部冗余空格 + for len(b) > 0 && fastIndex < len(b) && b[fastIndex] == ' ' { + fastIndex++ + } + //删除单词间冗余空格 + for ; fastIndex < len(b); fastIndex++ { + if fastIndex-1 > 0 && b[fastIndex-1] == b[fastIndex] && b[fastIndex] == ' ' { + continue + } + b[slowIndex] = b[fastIndex] + slowIndex++ + } + //删除尾部冗余空格 + if slowIndex-1 > 0 && b[slowIndex-1] == ' ' { + b = b[:slowIndex-1] + } else { + b = b[:slowIndex] + } + //2.反转整个字符串 + reverse(&b, 0, len(b)-1) + //3.反转单个单词 i单词开始位置,j单词结束位置 + i := 0 + for i < len(b) { + j := i + for ; j < len(b) && b[j] != ' '; j++ { + } + reverse(&b, i, j-1) + i = j + i++ + } + return string(b) +} + +func reverse(b *[]byte, left, right int) { + for left < right { + (*b)[left], (*b)[right] = (*b)[right], (*b)[left] + left++ + right-- + } +} +``` + + + diff --git a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md index 11c5805b..431c292b 100644 --- a/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md +++ b/problems/0188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV @@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ 输入:k = 2, prices = [3,2,6,5,0,3] 输出:7 解释:在第 2 天 (股票价格 = 2) 的时候买入,在第 3 天 (股票价格 = 6) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 6-2 = 4。随后,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 0) 的时候买入,在第 6 天 (股票价格 = 3) 的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 3-0 = 3 。 - + 提示: @@ -167,12 +167,65 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: +```java +class Solution { //动态规划 + public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) { + if (prices == null || prices.length < 2 || k == 0) { + return 0; + } + + // [天数][交易次数][是否持有股票] + int[][][] dp = new int[prices.length][k + 1][2]; + + // bad case + dp[0][0][0] = 0; + dp[0][0][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; + dp[0][1][0] = 0; + dp[0][1][1] = -prices[0]; + // dp[0][j][0] 都均为0 + // dp[0][j][1] 异常值都取Integer.MIN_VALUE; + for (int i = 2; i < k + 1; i++) { + dp[0][i][0] = 0; + dp[0][i][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; + } + + for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { + for (int j = k; j >= 1; j--) { + // dp公式 + dp[i][j][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j][0], dp[i - 1][j][1] + prices[i]); + dp[i][j][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j][1], dp[i - 1][j - 1][0] - prices[i]); + } + } + + int res = 0; + for (int i = 1; i < k + 1; i++) { + res = Math.max(res, dp[prices.length - 1][i][0]); + } + + return res; + } +} +``` + Python: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, k: int, prices: List[int]) -> int: + if len(prices) == 0: + return 0 + dp = [[0] * (2*k+1) for _ in range(len(prices))] + for j in range(1, 2*k, 2): + dp[0][j] = -prices[0] + for i in range(1, len(prices)): + for j in range(0, 2*k-1, 2): + dp[i][j+1] = max(dp[i-1][j+1], dp[i-1][j] - prices[i]) + dp[i][j+2] = max(dp[i-1][j+2], dp[i-1][j+1] + prices[i]) + return dp[-1][2*k] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0198.打家劫舍.md b/problems/0198.打家劫舍.md index c64648ad..63a68c36 100644 --- a/problems/0198.打家劫舍.md +++ b/problems/0198.打家劫舍.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 198.打家劫舍 @@ -111,10 +111,40 @@ public: Java: +```Java +// 动态规划 +class Solution { + public int rob(int[] nums) { + if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; + if (nums.length == 1) return nums[0]; + int[] dp = new int[nums.length]; + dp[0] = nums[0]; + dp[1] = Math.max(dp[0], nums[1]); + for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) { + dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]); + } + + return dp[nums.length - 1]; + } +} +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def rob(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) == 0: + return 0 + if len(nums) == 1: + return nums[0] + dp = [0] * len(nums) + dp[0] = nums[0] + dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]) + for i in range(2, len(nums)): + dp[i] = max(dp[i-2]+nums[i], dp[i-1]) + return dp[-1] +``` Go: ```Go diff --git a/problems/0202.快乐数.md b/problems/0202.快乐数.md index 8c0dd1e7..d1bccd64 100644 --- a/problems/0202.快乐数.md +++ b/problems/0202.快乐数.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -22,13 +22,13 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/ **示例:** -输入:19 -输出:true -解释: -1^2 + 9^2 = 82 -8^2 + 2^2 = 68 -6^2 + 8^2 = 100 -1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1 +输入:19 +输出:true +解释: +1^2 + 9^2 = 82 +8^2 + 2^2 = 68 +6^2 + 8^2 = 100 +1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1 # 思路 @@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/ 题目中说了会 **无限循环**,那么也就是说**求和的过程中,sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!** -正如:[关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g8N6WmoQmsCUw3_BaWxHZA)中所说,**当我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法了。** +正如:[关于哈希表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RSUANESA_tkhKhYe3ZR8Jg)中所说,**当我们遇到了要快速判断一个元素是否出现集合里的时候,就要考虑哈希法了。** 所以这道题目使用哈希法,来判断这个sum是否重复出现,如果重复了就是return false, 否则一直找到sum为1为止。 @@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ public: -## 其他语言版本 +# 其他语言版本 Java: @@ -108,10 +108,84 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool: + set_ = set() + while 1: + sum_ = self.getSum(n) + if sum_ == 1: + return True + #如果这个sum曾经出现过,说明已经陷入了无限循环了,立刻return false + if sum_ in set_: + return False + else: + set_.add(sum_) + n = sum_ + + #取数值各个位上的单数之和 + def getSum(self, n): + sum_ = 0 + while n > 0: + sum_ += (n%10) * (n%10) + n //= 10 + return sum_ +``` Go: +```go +func isHappy(n int) bool { + m := make(map[int]bool) + for n != 1 && !m[n] { + n, m[n] = getSum(n), true + } + return n == 1 +} +func getSum(n int) int { + sum := 0 + for n > 0 { + sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10) + n = n / 10 + } + return sum +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js +function getN(n) { + if (n == 1 || n == 0) return n; + let res = 0; + while (n) { + res += (n % 10) * (n % 10); + n = parseInt(n / 10); + } + return res; +} + +var isHappy = function(n) { + const sumSet = new Set(); + while (n != 1 && !sumSet.has(n)) { + sumSet.add(n); + n = getN(n); + } + return n == 1; +}; + +// 使用环形链表的思想 说明出现闭环 退出循环 +var isHappy = function(n) { + if (getN(n) == 1) return true; + let a = getN(n), b = getN(getN(n)); + // 如果 a === b + while (b !== 1 && getN(b) !== 1 && a !== b) { + a = getN(a); + b = getN(getN(b)); + } + return b === 1 || getN(b) === 1 ; +}; +``` diff --git a/problems/0203.移除链表元素.md b/problems/0203.移除链表元素.md index 9fca1ee0..cac9f233 100644 --- a/problems/0203.移除链表元素.md +++ b/problems/0203.移除链表元素.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 链表操作中,可以使用原链表来直接进行删除操作,也可以设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作,接下来看一看哪种方式更方便。 @@ -15,7 +15,18 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/ 题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。 - +示例 1: +输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 +输出:[1,2,3,4,5] + +示例 2: +输入:head = [], val = 1 +输出:[] + +示例 3: +输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 +输出:[] + # 思路 @@ -197,10 +208,71 @@ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { ``` Python: - +```python +# Definition for singly-linked list. +# class ListNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): +# self.val = val +# self.next = next +class Solution: + def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode: + dummy_head = ListNode(next=head) #添加一个虚拟节点 + cur = dummy_head + while(cur.next!=None): + if(cur.next.val == val): + cur.next = cur.next.next #删除cur.next节点 + else: + cur = cur.next + return dummy_head.next +``` Go: +```go +/** + * Definition for singly-linked list. + * type ListNode struct { + * Val int + * Next *ListNode + * } + */ +func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode { + dummyHead := &ListNode{} + dummyHead.Next = head + cur := dummyHead + for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil { + if cur.Next.Val == val { + cur.Next = cur.Next.Next + } else { + cur = cur.Next + } + } + return dummyHead.Next +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {ListNode} head + * @param {number} val + * @return {ListNode} + */ +var removeElements = function(head, val) { + const ret = new ListNode(0, head); + let cur = ret; + while(cur.next) { + if(cur.next.val === val) { + cur.next = cur.next.next; + continue; + } + cur = cur.next; + } + return ret.next; +}; +``` + diff --git a/problems/0206.翻转链表.md b/problems/0206.翻转链表.md index 886bbfcd..7c002382 100644 --- a/problems/0206.翻转链表.md +++ b/problems/0206.翻转链表.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。 @@ -143,10 +143,112 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +#双指针 +# Definition for singly-linked list. +# class ListNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): +# self.val = val +# self.next = next +class Solution: + def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: + cur = head + pre = None + while(cur!=None): + temp = cur.next # 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next + cur.next = pre #反转 + #更新pre、cur指针 + pre = cur + cur = temp + return pre +``` Go: +```go +//双指针 +func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode { + var pre *ListNode + cur := head + for cur != nil { + next := cur.Next + cur.Next = pre + pre = cur + cur = next + } + return pre +} + +//递归 +func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode { + return help(nil, head) +} + +func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{ + if head == nil { + return pre + } + next := head.Next + head.Next = pre + return help(head, next) +} + +``` +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {ListNode} head + * @return {ListNode} + */ + +// 双指针: +var reverseList = function(head) { + if(!head || !head.next) return head; + let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head; + while(cur) { + temp = cur.next; + cur.next = pre; + pre = cur; + cur = temp; + } + // temp = cur = null; + return pre; +}; + +// 递归: +var reverse = function(pre, head) { + if(!head) return pre; + const temp = head.next; + head.next = pre; + pre = head + return reverse(pre, temp); +} + +var reverseList = function(head) { + return reverse(null, head); +}; + +// 递归2 +var reverse = function(head) { + if(!head || !head.next) return head; + // 从后往前翻 + const pre = reverse(head.next); + head.next = pre.next; + pre.next = head; + return head; +} + +var reverseList = function(head) { + let cur = head; + while(cur && cur.next) { + cur = cur.next; + } + reverse(head); + return cur; +}; +``` + @@ -154,4 +256,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 209.长度最小的子数组 @@ -116,26 +116,6 @@ public: 不要以为for里放一个while就以为是$O(n^2)$啊, 主要是看每一个元素被操作的次数,每个元素在滑动窗后进来操作一次,出去操作一次,每个元素都是被被操作两次,所以时间复杂度是2 * n 也就是$O(n)$。 -## 其他语言补充 - -python: - -```python -class Solution: - def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int: - # 定义一个无限大的数 - res = float("inf") - Sum = 0 - index = 0 - for i in range(len(nums)): - Sum += nums[i] - while Sum >= s: - res = min(res, i-index+1) - Sum -= nums[index] - index += 1 - return 0 if res==float("inf") else res -``` - ## 相关题目推荐 * 904.水果成篮 @@ -170,24 +150,69 @@ class Solution { Python: +```python +class Solution: + def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int: + # 定义一个无限大的数 + res = float("inf") + Sum = 0 + index = 0 + for i in range(len(nums)): + Sum += nums[i] + while Sum >= s: + res = min(res, i-index+1) + Sum -= nums[index] + index += 1 + return 0 if res==float("inf") else res +``` + Go: +```go +func minSubArrayLen(target int, nums []int) int { + i := 0 + l := len(nums) // 数组长度 + sum := 0 // 子数组之和 + result := l + 1 // 初始化返回长度为l+1,目的是为了判断“不存在符合条件的子数组,返回0”的情况 + for j := 0; j < l; j++ { + sum += nums[j] + for sum >= target { + subLength := j - i + 1 + if subLength < result { + result = subLength + } + sum -= nums[i] + i++ + } + } + if result == l+1 { + return 0 + } else { + return result + } +} +``` JavaScript: -``` -var minSubArrayLen = (target, nums) => { - let left = 0, right = 0,win = Infinity,sum = 0; - while(right < nums.length){ - sum += nums[right]; - while(sum >= target){ - win = right - left + 1 < win? right - left + 1 : win; - sum -= nums[left]; - left++; - } - right++; + +```js + +var minSubArrayLen = function(target, nums) { + // 长度计算一次 + const len = nums.length; + let l = r = sum = 0, + res = len + 1; // 子数组最大不会超过自身 + while(r < len) { + sum += nums[r++]; + // 窗口滑动 + while(sum >= target) { + // r始终为开区间 [l, r) + res = res < r - l ? res : r - l; + sum-=nums[l++]; + } } - return win === Infinity? 0:win; + return res > len ? 0 : res; }; ``` @@ -195,4 +220,4 @@ var minSubArrayLen = (target, nums) => { * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 213.打家劫舍II @@ -98,11 +98,73 @@ public: Java: +```Java +class Solution { + public int rob(int[] nums) { + if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) + return 0; + int len = nums.length; + if (len == 1) + return nums[0]; + return Math.max(robAction(nums, 0, len - 1), robAction(nums, 1, len)); + } + int robAction(int[] nums, int start, int end) { + int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0; + for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { + y = z; + z = Math.max(y, x + nums[i]); + x = y; + } + return z; + } +} +``` Python: +```Python +class Solution: + def rob(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if (n := len(nums)) == 0: + return 0 + if n == 1: + return nums[0] + result1 = self.robRange(nums, 0, n - 2) + result2 = self.robRange(nums, 1, n - 1) + return max(result1 , result2) + def robRange(self, nums: List[int], start: int, end: int) -> int: + if end == start: return nums[start] + dp = [0] * len(nums) + dp[start] = nums[start] + dp[start + 1] = max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]) + for i in range(start + 2, end + 1): + dp[i] = max(dp[i -2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]) + return dp[end] +``` +javascipt: +```javascript +var rob = function(nums) { + const n = nums.length + if (n === 0) return 0 + if (n === 1) return nums[0] + const result1 = robRange(nums, 0, n - 2) + const result2 = robRange(nums, 1, n - 1) + return Math.max(result1, result2) +}; + +const robRange = (nums, start, end) => { + if (end === start) return nums[start] + const dp = Array(nums.length).fill(0) + dp[start] = nums[start] + dp[start + 1] = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]) + for (let i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) { + dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]) + } + return dp[end] +} +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0216.组合总和III.md b/problems/0216.组合总和III.md index 21230e0f..9f75b23d 100644 --- a/problems/0216.组合总和III.md +++ b/problems/0216.组合总和III.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ void backtracking(int targetSum, int k, int sum, int startIndex) 所以 终止代码如下: -``` +```C++ if (path.size() == k) { if (sum == targetSum) result.push_back(path); return; // 如果path.size() == k 但sum != targetSum 直接返回 @@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ if (path.size() == k) { 代码如下: -``` +```C++ for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++) { sum += i; path.push_back(i); @@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++) { 参照[关于回溯算法,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gjSgJbNbd1eAA5WkA-HeWw)中的模板,不难写出如下C++代码: -``` +```C++ class Solution { private: vector

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 222.完全二叉树的节点个数 @@ -240,9 +240,171 @@ class Solution { Python: +> 递归法: +```python +class Solution: + def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + return self.getNodesNum(root) + + def getNodesNum(self, cur): + if not cur: + return 0 + leftNum = self.getNodesNum(cur.left) #左 + rightNum = self.getNodesNum(cur.right) #右 + treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1 #中 + return treeNum +``` + +> 递归法:精简版 +```python +class Solution: + def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + if not root: + return 0 + return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right) +``` + +> 迭代法: +```python +import collections +class Solution: + def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + queue = collections.deque() + if root: + queue.append(root) + result = 0 + while queue: + size = len(queue) + for i in range(size): + node = queue.popleft() + result += 1 #记录节点数量 + if node.left: + queue.append(node.left) + if node.right: + queue.append(node.right) + return result +``` + +> 完全二叉树 +```python +class Solution: + def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + if not root: + return 0 + left = root.left + right = root.right + leftHeight = 0 #这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便 + rightHeight = 0 + while left: #求左子树深度 + left = left.left + leftHeight += 1 + while right: #求右子树深度 + right = right.right + rightHeight += 1 + if leftHeight == rightHeight: + return (2 << leftHeight) - 1 #注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftHeight初始为0 + return self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right) + 1 +``` Go: +递归版本 + +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +//本题直接就是求有多少个节点,无脑存进数组算长度就行了。 +func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int { + if root == nil { + return 0 + } + res := 1 + if root.Right != nil { + res += countNodes(root.Right) + } + if root.Left != nil { + res += countNodes(root.Left) + } + return res +} +``` + + + +JavaScript: + +递归版本 +```javascript +var countNodes = function(root) { + //递归法计算二叉树节点数 + // 1. 确定递归函数参数 + const getNodeSum=function(node){ + //2. 确定终止条件 + if(node===null){ + return 0; + } + //3. 确定单层递归逻辑 + let leftNum=getNodeSum(node.left); + let rightNum=getNodeSum(node.right); + return leftNum+rightNum+1; + } + return getNodeSum(root); +}; +``` + +迭代(层序遍历)版本 +```javascript +var countNodes = function(root) { + //层序遍历 + let queue=[]; + if(root===null){ + return 0; + } + queue.push(root); + let nodeNums=0; + while(queue.length){ + let length=queue.length; + while(length--){ + let node=queue.shift(); + nodeNums++; + node.left&&queue.push(node.left); + node.right&&queue.push(node.right); + } + } + return nodeNums; +}; +``` + +利用完全二叉树性质 +```javascript +var countNodes = function(root) { + //利用完全二叉树的特点 + if(root===null){ + return 0; + } + let left=root.left; + let right=root.right; + let leftHeight=0,rightHeight=0; + while(left){ + left=left.left; + leftHeight++; + } + while(right){ + right=right.right; + rightHeight++; + } + if(leftHeight==rightHeight){ + return Math.pow(2,leftHeight+1)-1; + } + return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1; +}; +``` @@ -250,4 +412,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -156,6 +156,7 @@ public: Java: +使用两个 Queue 实现 ```java class MyStack { @@ -205,7 +206,94 @@ class MyStack { * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */ ``` +使用两个 Deque 实现 +```java +class MyStack { + // Deque 接口继承了 Queue 接口 + // 所以 Queue 中的 add、poll、peek等效于 Deque 中的 addLast、pollFirst、peekFirst + Deque

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 226.翻转二叉树 @@ -230,6 +230,56 @@ class Solution { Python: +> 递归法:前序遍历 +```python +class Solution: + def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: + if not root: + return None + root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left #中 + self.invertTree(root.left) #左 + self.invertTree(root.right) #右 + return root +``` + +> 迭代法:深度优先遍历(前序遍历) +```python +class Solution: + def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: + if not root: + return root + st = [] + st.append(root) + while st: + node = st.pop() + node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left #中 + if node.right: + st.append(node.right) #右 + if node.left: + st.append(node.left) #左 + return root +``` + +> 迭代法:广度优先遍历(层序遍历) +```python +import collections +class Solution: + def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: + queue = collections.deque() #使用deque() + if root: + queue.append(root) + while queue: + size = len(queue) + for i in range(size): + node = queue.popleft() + node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left #节点处理 + if node.left: + queue.append(node.left) + if node.right: + queue.append(node.right) + return root +``` + Go: ```Go func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { @@ -247,10 +297,100 @@ func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { } ``` +JavaScript: +使用递归版本的前序遍历 +```javascript +var invertTree = function(root) { + //1. 首先使用递归版本的前序遍历实现二叉树翻转 + //交换节点函数 + const inverNode=function(left,right){ + let temp=left; + left=right; + right=temp; + //需要重新给root赋值一下 + root.left=left; + root.right=right; + } + //确定递归函数的参数和返回值inverTree=function(root) + //确定终止条件 + if(root===null){ + return root; + } + //确定节点处理逻辑 交换 + inverNode(root.left,root.right); + invertTree(root.left); + invertTree(root.right); + return root; +}; +``` +使用迭代版本(统一模板))的前序遍历: +```javascript +var invertTree = function(root) { + //我们先定义节点交换函数 + const invertNode=function(root,left,right){ + let temp=left; + left=right; + right=temp; + root.left=left; + root.right=right; + } + //使用迭代方法的前序遍历 + let stack=[]; + if(root===null){ + return root; + } + stack.push(root); + while(stack.length){ + let node=stack.pop(); + if(node!==null){ + //前序遍历顺序中左右 入栈顺序是前序遍历的倒序右左中 + node.right&&stack.push(node.right); + node.left&&stack.push(node.left); + stack.push(node); + stack.push(null); + }else{ + node=stack.pop(); + //节点处理逻辑 + invertNode(node,node.left,node.right); + } + } + return root; +}; +``` +使用层序遍历: +```javascript +var invertTree = function(root) { + //我们先定义节点交换函数 + const invertNode=function(root,left,right){ + let temp=left; + left=right; + right=temp; + root.left=left; + root.right=right; + } + //使用层序遍历 + let queue=[]; + if(root===null){ + return root; + } + queue.push(root); + while(queue.length){ + let length=queue.length; + while(length--){ + let node=queue.shift(); + //节点处理逻辑 + invertNode(node,node.left,node.right); + node.left&&queue.push(node.left); + node.right&&queue.push(node.right); + } + } + return root; +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 工作上一定没人这么搞,但是考察对栈、队列理解程度的好题 @@ -131,6 +131,101 @@ public: Java: +使用Stack(堆栈)同名方法: +```java +class MyQueue { + // java中的 Stack 有设计上的缺陷,官方推荐使用 Deque(双端队列) 代替 Stack + Deque

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 @@ -247,8 +247,23 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, x): +# self.val = x +# self.left = None +# self.right = None - +class Solution: + def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode': + if not root: return root //中 + if root.val >p.val and root.val > q.val: + return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q) //左 + elif root.val < p.val and root.val < q.val: + return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q) //右 + else: return root +``` Go: @@ -258,4 +273,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 本来是打算将二叉树和二叉搜索树的公共祖先问题一起讲,后来发现篇幅过长了,只能先说一说二叉树的公共祖先问题。 @@ -263,10 +263,53 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, x): +# self.val = x +# self.left = None +# self.right = None +//递归 +class Solution: + def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode': + if not root or root == p or root == q: return root //找到了节点p或者q,或者遇到空节点 + left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q) //左 + right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q) //右 + if left and right: return root //中: left和right不为空,root就是最近公共节点 + elif left and not right: return left //目标节点是通过left返回的 + elif not left and right: return right //目标节点是通过right返回的 + else: return None //没找到 +``` Go: +```Go +func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode { + // check + if root == nil { + return root + } + // 相等 直接返回root节点即可 + if root == p || root == q { + return root + } + // Divide + left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q) + right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q) + // Conquer + // 左右两边都不为空,则根节点为祖先 + if left != nil && right != nil { + return root + } + if left != nil { + return left + } + if right != nil { + return right + } + return nil +} +``` @@ -274,4 +317,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -263,11 +263,159 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: +```python +class MyQueue: #单调队列(从大到小 + def __init__(self): + self.queue = [] #使用list来实现单调队列 + + #每次弹出的时候,比较当前要弹出的数值是否等于队列出口元素的数值,如果相等则弹出。 + #同时pop之前判断队列当前是否为空。 + def pop(self, value): + if self.queue and value == self.queue[0]: + self.queue.pop(0)#list.pop()时间复杂度为O(n),这里可以使用collections.deque() + + #如果push的数值大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列后端的数值弹出,直到push的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止。 + #这样就保持了队列里的数值是单调从大到小的了。 + def push(self, value): + while self.queue and value > self.queue[-1]: + self.queue.pop() + self.queue.append(value) + + #查询当前队列里的最大值 直接返回队列前端也就是front就可以了。 + def front(self): + return self.queue[0] + +class Solution: + def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]: + que = MyQueue() + result = [] + for i in range(k): #先将前k的元素放进队列 + que.push(nums[i]) + result.append(que.front()) #result 记录前k的元素的最大值 + for i in range(k, len(nums)): + que.pop(nums[i - k]) #滑动窗口移除最前面元素 + que.push(nums[i]) #滑动窗口前加入最后面的元素 + result.append(que.front()) #记录对应的最大值 + return result +``` Go: +```go +func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int { + var queue []int + var rtn []int + for f := 0; f < len(nums); f++ { + //维持队列递减, 将 k 插入合适的位置, queue中 <=k 的 元素都不可能是窗口中的最大值, 直接弹出 + for len(queue) > 0 && nums[f] > nums[queue[len(queue)-1]] { + queue = queue[:len(queue)-1] + } + // 等大的后来者也应入队 + if len(queue) == 0 || nums[f] <= nums[queue[len(queue)-1]] { + queue = append(queue, f) + } + + if f >= k - 1 { + rtn = append(rtn, nums[queue[0]]) + //弹出离开窗口的队首 + if f - k + 1 == queue[0] { + queue = queue[1:] + } + } + } + + return rtn + +} + +``` + +```go +// 封装单调队列的方式解题 +type MyQueue struct { + queue []int +} + +func NewMyQueue() *MyQueue { + return &MyQueue{ + queue: make([]int, 0), + } +} + +func (m *MyQueue) Front() int { + return m.queue[0] +} + +func (m *MyQueue) Back() int { + return m.queue[len(m.queue)-1] +} + +func (m *MyQueue) Empty() bool { + return len(m.queue) == 0 +} + +func (m *MyQueue) Push(val int) { + for !m.Empty() && val > m.Back() { + m.queue = m.queue[:len(m.queue)-1] + } + m.queue = append(m.queue, val) +} + +func (m *MyQueue) Pop(val int) { + if !m.Empty() && val == m.Front() { + m.queue = m.queue[1:] + } +} + +func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int { + queue := NewMyQueue() + length := len(nums) + res := make([]int, 0) + // 先将前k个元素放入队列 + for i := 0; i < k; i++ { + queue.Push(nums[i]) + } + // 记录前k个元素的最大值 + res = append(res, queue.Front()) + + for i := k; i < length; i++ { + // 滑动窗口移除最前面的元素 + queue.Pop(nums[i-k]) + // 滑动窗口添加最后面的元素 + queue.Push(nums[i]) + // 记录最大值 + res = append(res, queue.Front()) + } + return res +} +``` + +Javascript: +```javascript +var maxSlidingWindow = function (nums, k) { + // 队列数组(存放的是元素下标,为了取值方便) + const q = []; + // 结果数组 + const ans = []; + for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { + // 若队列不为空,且当前元素大于等于队尾所存下标的元素,则弹出队尾 + while (q.length && nums[i] >= nums[q[q.length - 1]]) { + q.pop(); + } + // 入队当前元素下标 + q.push(i); + // 判断当前最大值(即队首元素)是否在窗口中,若不在便将其出队 + while (q[0] <= i - k) { + q.shift(); + } + // 当达到窗口大小时便开始向结果中添加数据 + if (i >= k - 1) ans.push(nums[q[0]]); + } + return ans; +}; +``` ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md b/problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md index 1927f476..ba942f70 100644 --- a/problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md +++ b/problems/0242.有效的字母异位词.md @@ -1,26 +1,33 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 数组就是简单的哈希表,但是数组的大小可不是无限开辟的 -# 242.有效的字母异位词 +## 242.有效的字母异位词 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/ 给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。 - +示例 1: +输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" +输出: true + +示例 2: +输入: s = "rat", t = "car" +输出: false + **说明:** 你可以假设字符串只包含小写字母。 -# 思路 +## 思路 先看暴力的解法,两层for循环,同时还要记录字符是否重复出现,很明显时间复杂度是 O(n^2)。 @@ -52,7 +59,6 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/ 时间复杂度为O(n),空间上因为定义是的一个常量大小的辅助数组,所以空间复杂度为O(1)。 -看完这篇哈希表总结:[哈希表:总结篇!(每逢总结必经典)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/1s91yXtarL-PkX07BfnwLg),详细就可以哈希表的各种用法非常清晰了。 C++ 代码如下: ```C++ @@ -107,7 +113,22 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool: + record = [0] * 26 + for i in range(len(s)): + #并不需要记住字符a的ASCII,只要求出一个相对数值就可以了 + record[ord(s[i]) - ord("a")] += 1 + print(record) + for i in range(len(t)): + record[ord(t[i]) - ord("a")] -= 1 + for i in range(26): + if record[i] != 0: + #record数组如果有的元素不为零0,说明字符串s和t 一定是谁多了字符或者谁少了字符。 + return False + return True +``` Go: ```go @@ -134,9 +155,38 @@ func isAnagram(s string, t string) bool { } ``` +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {string} s + * @param {string} t + * @return {boolean} + */ +var isAnagram = function(s, t) { + if(s.length !== t.length) return false; + const resSet = new Array(26).fill(0); + const base = "a".charCodeAt(); + for(const i of s) { + resSet[i.charCodeAt() - base]++; + } + for(const i of t) { + if(!resSet[i.charCodeAt() - base]) return false; + resSet[i.charCodeAt() - base]--; + } + return true; +}; +``` + +## 相关题目 + +* 383.赎金信 +* 49.字母异位词分组 +* 438.找到字符串中所有字母异位词 + ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 以为只用了递归,其实还用了回溯 @@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) { 这里我们先使用vector

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:一样的套路,再求一次完全平方数 ## 279.完全平方数 @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ 输入:n = 13 输出:2 解释:13 = 4 + 9 - + 提示: * 1 <= n <= 10^4 @@ -184,9 +184,89 @@ class Solution { Python: +```python3 +class Solution: + def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int: + '''版本一''' + # 初始化 + nums = [i**2 for i in range(1, n + 1) if i**2 <= n] + dp = [10**4]*(n + 1) + dp[0] = 0 + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(1, n + 1): + # 遍历物品 + for num in nums: + if j >= num: + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - num] + 1) + return dp[n] + + def numSquares1(self, n: int) -> int: + '''版本二''' + # 初始化 + nums = [i**2 for i in range(1, n + 1) if i**2 <= n] + dp = [10**4]*(n + 1) + dp[0] = 0 + # 遍历物品 + for num in nums: + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(num, n + 1) + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - num] + 1) + return dp[n] +``` + + + Go: +```go +// 版本一,先遍历物品, 再遍历背包 +func numSquares1(n int) int { + //定义 + dp := make([]int, n+1) + // 初始化 + dp[0] = 0 + for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { + dp[i] = math.MaxInt32 + } + // 遍历物品 + for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { + // 遍历背包 + for j := i*i; j <= n; j++ { + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-i*i]+1) + } + } + return dp[n] +} + +// 版本二,先遍历背包, 再遍历物品 +func numSquares2(n int) int { + //定义 + dp := make([]int, n+1) + // 初始化 + dp[0] = 0 + // 遍历背包 + for j := 1; j <= n; j++ { + //初始化 + dp[j] = math.MaxInt32 + // 遍历物品 + for i := 1; i <= n; i++ { + if j >= i*i { + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-i*i]+1) + } + } + } + + return dp[n] +} + +func min(a, b int) int { + if a < b { + return a + } + return b +} +``` diff --git a/problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md b/problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md index 2bc5cf9c..8b4ad5b1 100644 --- a/problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md +++ b/problems/0300.最长上升子序列.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 300.最长递增子序列 @@ -98,8 +98,6 @@ public: }; ``` -杨老师的这个专栏很不错,他本身也是Oracle 首席工程师,对Java有极其深刻的理解,讲的内容很硬核,适合使用Java语言的录友们用来进阶!作为面试突击手册非常合适, 所以推荐给大家!现在下单输入口令:javahexin,可以省40元那[机智] - ## 总结 本题最关键的是要想到dp[i]由哪些状态可以推出来,并取最大值,那么很自然就能想到递推公式:dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1); @@ -110,14 +108,71 @@ public: Java: - +```Java +class Solution { + public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) { + int[] dp = new int[nums.length]; + Arrays.fill(dp, 1); + for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { + for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { + if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { + dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1); + } + } + } + int res = 0; + for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { + res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); + } + return res; + } +} +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) <= 1: + return len(nums) + dp = [1] * len(nums) + result = 0 + for i in range(1, len(nums)): + for j in range(0, i): + if nums[i] > nums[j]: + dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1) + result = max(result, dp[i]) #取长的子序列 + return result +``` Go: - - +```go +func lengthOfLIS(nums []int ) int { + dp := []int{} + for _, num := range nums { + if len(dp) ==0 || dp[len(dp) - 1] < num { + dp = append(dp, num) + } else { + l, r := 0, len(dp) - 1 + pos := r + for l <= r { + mid := (l + r) >> 1 + if dp[mid] >= num { + pos = mid; + r = mid - 1 + } else { + l = mid + 1 + } + } + dp[pos] = num + }//二分查找 + } + return len(dp) +} +``` +*复杂度分析* +- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)。数组 nums 的长度为 n,我们依次用数组中的元素去更新 dp 数组,相当于插入最后递增的元素,而更新 dp 数组时需要进行 O(logn) 的二分搜索,所以总时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)。 +- 空间复杂度:O(n),需要额外使用长度为 n 的 dp 数组。 ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期.md b/problems/0309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期.md index 15bba0b7..4667c122 100644 --- a/problems/0309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期.md +++ b/problems/0309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期 @@ -159,12 +159,51 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: +```java +class Solution { + public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { + if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) { + return 0; + } + int[][] dp = new int[prices.length][2]; + + // bad case + dp[0][0] = 0; + dp[0][1] = -prices[0]; + dp[1][0] = Math.max(dp[0][0], dp[0][1] + prices[1]); + dp[1][1] = Math.max(dp[0][1], -prices[1]); + + for (int i = 2; i < prices.length; i++) { + // dp公式 + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]); + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 2][0] - prices[i]); + } + + return dp[prices.length - 1][0]; + } +} +``` + Python: +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: + n = len(prices) + if n == 0: + return 0 + dp = [[0] * 4 for _ in range(n)] + dp[0][0] = -prices[0] #持股票 + for i in range(1, n): + dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], max(dp[i-1][3], dp[i-1][1]) - prices[i]) + dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][3]) + dp[i][2] = dp[i-1][0] + prices[i] + dp[i][3] = dp[i-1][2] + return max(dp[n-1][3], dp[n-1][1], dp[n-1][2]) +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0322.零钱兑换.md b/problems/0322.零钱兑换.md index e67695d8..cf537088 100644 --- a/problems/0322.零钱兑换.md +++ b/problems/0322.零钱兑换.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划: 给我个机会,我再兑换一次零钱 ## 322. 零钱兑换 @@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ 示例 5: 输入:coins = [1], amount = 2 输出:2 - + 提示: * 1 <= coins.length <= 12 @@ -209,9 +209,100 @@ class Solution { Python: +```python3 +class Solution: + def coinChange(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int: + '''版本一''' + # 初始化 + dp = [amount + 1]*(amount + 1) + dp[0] = 0 + # 遍历物品 + for coin in coins: + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(coin, amount + 1): + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - coin] + 1) + return dp[amount] if dp[amount] < amount + 1 else -1 + + def coinChange1(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int: + '''版本二''' + # 初始化 + dp = [amount + 1]*(amount + 1) + dp[0] = 0 + # 遍历物品 + for j in range(1, amount + 1): + # 遍历背包 + for coin in coins: + if j >= coin: + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - coin] + 1) + return dp[amount] if dp[amount] < amount + 1 else -1 +``` + + + Go: +```go +// 版本一, 先遍历物品,再遍历背包 +func coinChange1(coins []int, amount int) int { + dp := make([]int, amount+1) + // 初始化dp[0] + dp[0] = 0 + // 初始化为math.MaxInt32 + for j := 1; j <= amount; j++ { + dp[j] = math.MaxInt32 + } + // 遍历物品 + for i := 0; i < len(coins); i++ { + // 遍历背包 + for j := coins[i]; j <= amount; j++ { + if dp[j-coins[i]] != math.MaxInt32 { + // 推导公式 + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-coins[i]]+1) + //fmt.Println(dp,j,i) + } + } + } + // 没找到能装满背包的, 就返回-1 + if dp[amount] == math.MaxInt32 { + return -1 + } + return dp[amount] +} + +// 版本二,先遍历背包,再遍历物品 +func coinChange2(coins []int, amount int) int { + dp := make([]int, amount+1) + // 初始化dp[0] + dp[0] = 0 + // 遍历背包,从1开始 + for j := 1; j <= amount; j++ { + // 初始化为math.MaxInt32 + dp[j] = math.MaxInt32 + // 遍历物品 + for i := 0; i < len(coins); i++ { + if j >= coins[i] && dp[j-coins[i]] != math.MaxInt32 { + // 推导公式 + dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j-coins[i]]+1) + //fmt.Println(dp) + } + } + } + // 没找到能装满背包的, 就返回-1 + if dp[amount] == math.MaxInt32 { + return -1 + } + return dp[amount] +} + +func min(a, b int) int { + if a < b { + return a + } + return b +} + +``` diff --git a/problems/0332.重新安排行程.md b/problems/0332.重新安排行程.md index 756ecc86..97059e4a 100644 --- a/problems/0332.重新安排行程.md +++ b/problems/0332.重新安排行程.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 这也可以用回溯法? 其实深搜和回溯也是相辅相成的,毕竟都用递归。 @@ -399,6 +399,49 @@ char ** findItinerary(char *** tickets, int ticketsSize, int* ticketsColSize, in } ``` +Javascript: +```Javascript + +var findItinerary = function(tickets) { + let result = ['JFK'] + let map = {} + + for (const tickt of tickets) { + const [from, to] = tickt + if (!map[from]) { + map[from] = [] + } + map[from].push(to) + } + + for (const city in map) { + // 对到达城市列表排序 + map[city].sort() + } + function backtracing() { + if (result.length === tickets.length + 1) { + return true + } + if (!map[result[result.length - 1]] || !map[result[result.length - 1]].length) { + return false + } + for(let i = 0 ; i < map[result[result.length - 1]].length; i++) { + let city = map[result[result.length - 1]][i] + // 删除已走过航线,防止死循环 + map[result[result.length - 1]].splice(i, 1) + result.push(city) + if (backtracing()) { + return true + } + result.pop() + map[result[result.length - 1]].splice(i, 0, city) + } + } + backtracing() + return result +}; + +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) diff --git a/problems/0337.打家劫舍III.md b/problems/0337.打家劫舍III.md index 50b06e22..0a4b752b 100644 --- a/problems/0337.打家劫舍III.md +++ b/problems/0337.打家劫舍III.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 337.打家劫舍 III @@ -218,10 +218,94 @@ public: Java: +```Java +class Solution { + // 1.递归去偷,超时 + public int rob(TreeNode root) { + if (root == null) + return 0; + int money = root.val; + if (root.left != null) { + money += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right); + } + if (root.right != null) { + money += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right); + } + return Math.max(money, rob(root.left) + rob(root.right)); + } + // 2.递归去偷,记录状态 + // 执行用时:3 ms , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 56.24% 的用户 + public int rob1(TreeNode root) { + Map欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 343. 整数拆分 +题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/integer-break/ + 给定一个正整数 n,将其拆分为至少两个正整数的和,并使这些整数的乘积最大化。 返回你可以获得的最大乘积。 示例 1: @@ -49,11 +51,14 @@ dp[i]的定义讲贯彻整个解题过程,下面哪一步想不懂了,就想 **那有同学问了,j怎么就不拆分呢?** -j是从1开始遍历,拆分j的情况,在遍历j的过程中其实都计算过了。 +j是从1开始遍历,拆分j的情况,在遍历j的过程中其实都计算过了。那么从1遍历j,比较(i - j) * j和dp[i - j] * j 取最大的。递推公式:dp[i] = max(dp[i], max((i - j) * j, dp[i - j] * j)); -那么从1遍历j,比较(i - j) * j和dp[i - j] * j 取最大的。 +也可以这么理解,j * (i - j) 是单纯的把整数拆分为两个数相乘,而j * dp[i - j]是拆分成两个以及两个以上的个数相乘。 + +如果定义dp[i - j] * dp[j] 也是默认将一个数强制拆成4份以及4份以上了。 + +所以递推公式:dp[i] = max({dp[i], (i - j) * j, dp[i - j] * j}); -递推公式:dp[i] = max(dp[i], max((i - j) * j, dp[i - j] * j)); 3. dp的初始化 @@ -185,11 +190,38 @@ public: Java: - +```Java +class Solution { + public int integerBreak(int n) { + //dp[i]为正整数i拆分结果的最大乘积 + int[] dp = new int[n+1]; + dp[2] = 1; + for (int i = 3; i <= n; ++i) { + for (int j = 1; j < i - 1; ++j) { + //j*(i-j)代表把i拆分为j和i-j两个数相乘 + //j*dp[i-j]代表把i拆分成j和继续把(i-j)这个数拆分,取(i-j)拆分结果中的最大乘积与j相乘 + dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), j * dp[i - j])); + } + } + return dp[n]; + } +} +``` Python: - - +```python +class Solution: + def integerBreak(self, n: int) -> int: + dp = [0] * (n + 1) + dp[2] = 1 + for i in range(3, n + 1): + # 假设对正整数 i 拆分出的第一个正整数是 j(1 <= j < i),则有以下两种方案: + # 1) 将 i 拆分成 j 和 i−j 的和,且 i−j 不再拆分成多个正整数,此时的乘积是 j * (i-j) + # 2) 将 i 拆分成 j 和 i−j 的和,且 i−j 继续拆分成多个正整数,此时的乘积是 j * dp[i-j] + for j in range(1, i - 1): + dp[i] = max(dp[i], max(j * (i - j), j * dp[i - j])) + return dp[n] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0344.反转字符串.md b/problems/0344.反转字符串.md index b4c843b7..1b86e847 100644 --- a/problems/0344.反转字符串.md +++ b/problems/0344.反转字符串.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -157,7 +157,18 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def reverseString(self, s: List[str]) -> None: + """ + Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead. + """ + left, right = 0, len(s) - 1 + while(left < right): + s[left], s[right] = s[right], s[left] + left += 1 + right -= 1 +``` Go: ```Go @@ -172,6 +183,26 @@ func reverseString(s []byte) { } ``` +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {character[]} s + * @return {void} Do not return anything, modify s in-place instead. + */ +var reverseString = function(s) { + return s.reverse(); +}; + +var reverseString = function(s) { + let l = -1, r = s.length; + while(++l < --r) [s[l], s[r]] = [s[r], s[l]]; + return s; +}; +``` + + + diff --git a/problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md b/problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md index 0e70f553..71af618e 100644 --- a/problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md +++ b/problems/0347.前K个高频元素.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -162,7 +162,33 @@ class Solution { Python: - +```python +#时间复杂度:O(nlogk) +#空间复杂度:O(n) +import heapq +class Solution: + def topKFrequent(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]: + #要统计元素出现频率 + map_ = {} #nums[i]:对应出现的次数 + for i in range(len(nums)): + map_[nums[i]] = map_.get(nums[i], 0) + 1 + + #对频率排序 + #定义一个小顶堆,大小为k + pri_que = [] #小顶堆 + + #用固定大小为k的小顶堆,扫面所有频率的数值 + for key, freq in map_.items(): + heapq.heappush(pri_que, (freq, key)) + if len(pri_que) > k: #如果堆的大小大于了K,则队列弹出,保证堆的大小一直为k + heapq.heappop(pri_que) + + #找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒叙来输出到数组 + result = [0] * k + for i in range(k-1, -1, -1): + result[i] = heapq.heappop(pri_que)[1] + return result +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md b/problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md index b5116ee1..090480a4 100644 --- a/problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md +++ b/problems/0349.两个数组的交集.md @@ -1,17 +1,18 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 如果哈希值比较少、特别分散、跨度非常大,使用数组就造成空间的极大浪费! -# 349. 两个数组的交集 + +## 349. 两个数组的交集 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/ @@ -23,7 +24,7 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/ 输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。 我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。 -# 思路 +## 思路 这道题目,主要要学会使用一种哈希数据结构:unordered_set,这个数据结构可以解决很多类似的问题。 @@ -31,7 +32,7 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/ 这道题用暴力的解法时间复杂度是O(n^2),那来看看使用哈希法进一步优化。 -那么用数组来做哈希表也是不错的选择,例如[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vM6OszkM6L1Mx2Ralm9Dig),[0383.赎金信](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sYZIR4dFBrw_lr3eJJnteQ) +那么用数组来做哈希表也是不错的选择,例如[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ffS8jaVFNUWyfn_8T31IdA) 但是要注意,**使用数组来做哈希的题目,是因为题目都限制了数值的大小。** @@ -52,6 +53,7 @@ std::set和std::multiset底层实现都是红黑树,std::unordered_set的底  C++代码如下: + ```C++ class Solution { public: @@ -69,6 +71,13 @@ public: }; ``` +## 拓展 + +那有同学可能问了,遇到哈希问题我直接都用set不就得了,用什么数组啊。 + +直接使用set 不仅占用空间比数组大,而且速度要比数组慢,set把数值映射到key上都要做hash计算的。 + +不要小瞧 这个耗时,在数据量大的情况,差距是很明显的。 ## 其他语言版本 @@ -109,11 +118,70 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: +```python3 +class Solution: + def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]: + result_set = set() + + set1 = set(nums1) + for num in nums2: + if num in set1: + result_set.add(num) # set1里出现的nums2元素 存放到结果 + return result_set +``` Go: +```go +func intersection(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) []int { + m := make(map[int]int) + for _, v := range nums1 { + m[v] = 1 + } + var res []int + // 利用count>0,实现重复值只拿一次放入返回结果中 + for _, v := range nums2 { + if count, ok := m[v]; ok && count > 0 { + res = append(res, v) + m[v]-- + } + } + return res +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {number[]} nums1 + * @param {number[]} nums2 + * @return {number[]} + */ +var intersection = function(nums1, nums2) { + // 根据数组大小交换操作的数组 + if(nums1.length < nums2.length) { + const _ = nums1; + nums1 = nums2; + nums2 = _; + } + const nums1Set = new Set(nums1); + const resSet = new Set(); + // for(const n of nums2) { + // nums1Set.has(n) && resSet.add(n); + // } + // 循环 比 迭代器快 + for(let i = nums2.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { + nums1Set.has(nums2[i]) && resSet.add(nums2[i]); + } + return Array.from(resSet); +}; +``` +## 相关题目 + +* 350.两个数组的交集 II ----------------------- diff --git a/problems/0376.摆动序列.md b/problems/0376.摆动序列.md index fa90142d..4d283eb0 100644 --- a/problems/0376.摆动序列.md +++ b/problems/0376.摆动序列.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 本周讲解了[贪心理论基础](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/O935TaoHE9Eexwe_vSbRAg),以及第一道贪心的题目:[贪心算法:分发饼干](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YSuLIAYyRGlyxbp9BNC1uw),可能会给大家一种贪心算法比较简单的错觉,好了,接下来几天的题目难度要上来了,哈哈。 @@ -138,12 +138,38 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def wiggleMaxLength(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + preC,curC,res = 0,0,1 #题目里nums长度大于等于1,当长度为1时,其实到不了for循环里去,所以不用考虑nums长度 + for i in range(len(nums) - 1): + curC = nums[i + 1] - nums[i] + if curC * preC <= 0 and curC !=0: #差值为0时,不算摆动 + res += 1 + preC = curC #如果当前差值和上一个差值为一正一负时,才需要用当前差值替代上一个差值 + return res +``` Go: - +Javascript: +```Javascript +var wiggleMaxLength = function(nums) { + if(nums.length <= 1) return nums.length + let result = 1 + let preDiff = 0 + let curDiff = 0 + for(let i = 0; i <= nums.length; i++) { + curDiff = nums[i + 1] - nums[i] + if((curDiff > 0 && preDiff <= 0) || (curDiff < 0 && preDiff >= 0)) { + result++ + preDiff = curDiff + } + } + return result +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) diff --git a/problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md b/problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md index eca9a13b..d0394706 100644 --- a/problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md +++ b/problems/0377.组合总和Ⅳ.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:Carl称它为排列总和! ## 377. 组合总和 Ⅳ @@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ class Solution { return dp[target]; } } - +``` Python: @@ -183,7 +183,23 @@ class Solution: Go: - +```go +func combinationSum4(nums []int, target int) int { + //定义dp数组 + dp := make([]int, target+1) + // 初始化 + dp[0] = 1 + // 遍历顺序, 先遍历背包,再循环遍历物品 + for j:=0;j<=target;j++ { + for i:=0 ;i < len(nums);i++ { + if j >= nums[i] { + dp[j] += dp[j-nums[i]] + } + } + } + return dp[target] +} +``` @@ -191,4 +207,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -22,13 +22,13 @@ https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ransom-note/ 你可以假设两个字符串均只含有小写字母。 -canConstruct("a", "b") -> false -canConstruct("aa", "ab") -> false -canConstruct("aa", "aab") -> true +canConstruct("a", "b") -> false +canConstruct("aa", "ab") -> false +canConstruct("aa", "aab") -> true -# 思路 +## 思路 -这道题目和[242.有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vM6OszkM6L1Mx2Ralm9Dig)很像,[242.有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vM6OszkM6L1Mx2Ralm9Dig)相当于求 字符串a 和 字符串b 是否可以相互组成 ,而这道题目是求 字符串a能否组成字符串b,而不用管字符串b 能不能组成字符串a。 +这道题目和[242.有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ffS8jaVFNUWyfn_8T31IdA)很像,[242.有效的字母异位词](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ffS8jaVFNUWyfn_8T31IdA)相当于求 字符串a 和 字符串b 是否可以相互组成 ,而这道题目是求 字符串a能否组成字符串b,而不用管字符串b 能不能组成字符串a。 本题判断第一个字符串ransom能不能由第二个字符串magazines里面的字符构成,但是这里需要注意两点。 @@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ canConstruct("aa", "aab") -> true * 第二点 “你可以假设两个字符串均只含有小写字母。” *说明只有小写字母*,这一点很重要 -# 暴力解法 +## 暴力解法 那么第一个思路其实就是暴力枚举了,两层for循环,不断去寻找,代码如下: @@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ public: 这里时间复杂度是比较高的,而且里面还有一个字符串删除也就是erase的操作,也是费时的,当然这段代码也可以过这道题。 -# 哈希解法 +## 哈希解法 因为题目所只有小写字母,那可以采用空间换取时间的哈希策略, 用一个长度为26的数组还记录magazine里字母出现的次数。 @@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ public: 依然是数组在哈希法中的应用。 -一些同学可能想,用数组干啥,都用map完事了,**其实在本题的情况下,使用map的空间消耗要比数组大一些的,因为map要维护红黑树或者哈希表,而且还要做哈希函数。 所以数组更加简单直接有效!** +一些同学可能想,用数组干啥,都用map完事了,**其实在本题的情况下,使用map的空间消耗要比数组大一些的,因为map要维护红黑树或者哈希表,而且还要做哈希函数,是费时的!数据量大的话就能体现出来差别了。 所以数组更加简单直接有效!** 代码如下: @@ -105,8 +105,6 @@ public: - - ## 其他语言版本 @@ -138,10 +136,74 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```py +class Solution(object): + def canConstruct(self, ransomNote, magazine): + """ + :type ransomNote: str + :type magazine: str + :rtype: bool + """ + + # use a dict to store the number of letter occurance in ransomNote + hashmap = dict() + for s in ransomNote: + if s in hashmap: + hashmap[s] += 1 + else: + hashmap[s] = 1 + + # check if the letter we need can be found in magazine + for l in magazine: + if l in hashmap: + hashmap[l] -= 1 + + for key in hashmap: + if hashmap[key] > 0: + return False + + return True +``` Go: +```go +func canConstruct(ransomNote string, magazine string) bool { + record := make([]int, 26) + for _, v := range magazine { + record[v-'a']++ + } + for _, v := range ransomNote { + record[v-'a']-- + if record[v-'a'] < 0 { + return false + } + } + return true +} +``` +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {string} ransomNote + * @param {string} magazine + * @return {boolean} + */ +var canConstruct = function(ransomNote, magazine) { + const strArr = new Array(26).fill(0), + base = "a".charCodeAt(); + for(const s of magazine) { + strArr[s.charCodeAt() - base]++; + } + for(const s of ransomNote) { + const index = s.charCodeAt() - base; + if(!strArr[index]) return false; + strArr[index]--; + } + return true; +}; +``` diff --git a/problems/0392.判断子序列.md b/problems/0392.判断子序列.md index 95e0b124..9048ac44 100644 --- a/problems/0392.判断子序列.md +++ b/problems/0392.判断子序列.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 392.判断子序列 @@ -144,7 +144,20 @@ Java: Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def isSubsequence(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool: + dp = [[0] * (len(t)+1) for _ in range(len(s)+1)] + for i in range(1, len(s)+1): + for j in range(1, len(t)+1): + if s[i-1] == t[j-1]: + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 + else: + dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1] + if dp[-1][-1] == len(s): + return True + return False +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0404.左叶子之和.md b/problems/0404.左叶子之和.md index 0290dccd..aa758367 100644 --- a/problems/0404.左叶子之和.md +++ b/problems/0404.左叶子之和.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 404.左叶子之和 @@ -205,10 +205,139 @@ class Solution { Python: - - +```Python +**递归** +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + self.res=0 + def areleftleaves(root): + if not root:return + if root.left and (not root.left.left) and (not root.left.right):self.res+=root.left.val + areleftleaves(root.left) + areleftleaves(root.right) + areleftleaves(root) + return self.res +``` Go: +> 递归法 + +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int { + var res int + findLeft(root,&res) + return res +} +func findLeft(root *TreeNode,res *int){ + //左节点 + if root.Left!=nil&&root.Left.Left==nil&&root.Left.Right==nil{ + *res=*res+root.Left.Val + } + if root.Left!=nil{ + findLeft(root.Left,res) + } + if root.Right!=nil{ + findLeft(root.Right,res) + } +} +``` + +> 迭代法 + +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int { + var res int + queue:=list.New() + queue.PushBack(root) + for queue.Len()>0{ + length:=queue.Len() + for i:=0;i -
diff --git a/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md b/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
index 2ef0a2fd..9aca5b94 100644
--- a/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
+++ b/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-
-
diff --git a/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md b/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
index 2ef0a2fd..9aca5b94 100644
--- a/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
+++ b/problems/0406.根据身高重建队列.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 406.根据身高重建队列 @@ -211,15 +211,44 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def reconstructQueue(self, people: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: + people.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], -x[1]), reverse=True) + que = [] + for p in people: + if p[1] > len(que): + que.append(p) + else: + que.insert(p[1], p) + return que +``` Go: +Javascript: +```Javascript +var reconstructQueue = function(people) { + let queue = [] + people.sort((a, b ) => { + if(b[0] !== a[0]) { + return b[0] - a[0] + } else { + return a[1] - b[1] + } + + }) + for(let i = 0; i < people.length; i++) { + queue.splice(people[i][1], 0, people[i]) + } + return queue +}; +``` ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
-# 动态规划:分割等和子集可以用01背包! +欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 416. 分割等和子集 @@ -29,6 +28,10 @@ 输出: false 解释: 数组不能分割成两个元素和相等的子集. +提示: +* 1 <= nums.length <= 200 +* 1 <= nums[i] <= 100 + ## 思路 这道题目初步看,是如下两题几乎是一样的,大家可以用回溯法,解决如下两题 @@ -174,7 +177,7 @@ public: 这道题目就是一道01背包应用类的题目,需要我们拆解题目,然后套入01背包的场景。 -01背包相对于本题,主要要理解,题目中物品是nums[i],重量是nums[i]i,价值也是nums[i],背包体积是sum/2。 +01背包相对于本题,主要要理解,题目中物品是nums[i],重量是nums[i],价值也是nums[i],背包体积是sum/2。 看代码的话,就可以发现,基本就是按照01背包的写法来的。 @@ -222,8 +225,18 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python +class Solution: + def canPartition(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool: + taraget = sum(nums) + if taraget % 2 == 1: return False + taraget //= 2 + dp = [0] * 10001 + for i in range(len(nums)): + for j in range(taraget, nums[i] - 1, -1): + dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]) + return taraget == dp[taraget] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0435.无重叠区间.md b/problems/0435.无重叠区间.md index 4341f3b8..248526a1 100644 --- a/problems/0435.无重叠区间.md +++ b/problems/0435.无重叠区间.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 435. 无重叠区间 @@ -212,7 +212,19 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int: + if len(intervals) == 0: return 0 + intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[1]) + count = 1 # 记录非交叉区间的个数 + end = intervals[0][1] # 记录区间分割点 + for i in range(1, len(intervals)): + if end <= intervals[i][0]: + count += 1 + end = intervals[i][1] + return len(intervals) - count +``` Go: @@ -223,4 +235,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 二叉搜索树删除节点就涉及到结构调整了 @@ -281,7 +281,43 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def deleteNode(self, root: TreeNode, key: int) -> TreeNode: + if not root: return root #第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了 + if root.val == key: + if not root.left and not root.right: #第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点 + del root + return None + if not root.left and root.right: #第三种情况:其左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位 ,返回右孩子为根节点 + tmp = root + root = root.right + del tmp + return root + if root.left and not root.right: #第四种情况:其右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点 + tmp = root + root = root.left + del tmp + return root + else: #第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子的位置 + v = root.right + while v.left: + v = v.left + v.left = root.left + tmp = root + root = root.right + del tmp + return root + if root.val > key: root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left,key) #左递归 + if root.val < key: root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right,key) #右递归 + return root +``` Go: ```Go @@ -330,4 +366,4 @@ func deleteNode1(root *TreeNode)*TreeNode{ * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球 @@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ 其实都可以!只不过对应的遍历顺序不同,我就按照气球的起始位置排序了。 -既然按照其实位置排序,那么就从前向后遍历气球数组,靠左尽可能让气球重复。 +既然按照起始位置排序,那么就从前向后遍历气球数组,靠左尽可能让气球重复。 从前向后遍历遇到重叠的气球了怎么办? @@ -142,16 +142,8 @@ Java: ```java class Solution { public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) { - Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 需要哈希的地方都能找到map的身影 # 第454题.四数相加II + https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/ 给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0。 @@ -24,10 +25,8 @@ A = [ 1, 2] B = [-2,-1] C = [-1, 2] D = [ 0, 2] - 输出: 2 - **解释:** 两个元组如下: 1. (0, 0, 0, 1) -> A[0] + B[0] + C[0] + D[1] = 1 + (-2) + (-1) + 2 = 0 @@ -121,8 +120,88 @@ class Solution { Python: +``` +class Solution(object): + def fourSumCount(self, nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4): + """ + :type nums1: List[int] + :type nums2: List[int] + :type nums3: List[int] + :type nums4: List[int] + :rtype: int + """ + # use a dict to store the elements in nums1 and nums2 and their sum + hashmap = dict() + for n1 in nums1: + for n2 in nums2: + if n1 + n2 in hashmap: + hashmap[n1+n2] += 1 + else: + hashmap[n1+n2] = 1 + + # if the -(a+b) exists in nums3 and nums4, we shall add the count + count = 0 + for n3 in nums3: + for n4 in nums4: + key = - n3 - n4 + if key in hashmap: + count += hashmap[key] + return count + + +``` + Go: +```go +func fourSumCount(nums1 []int, nums2 []int, nums3 []int, nums4 []int) int { + m := make(map[int]int) + count := 0 + for _, v1 := range nums1 { + for _, v2 := range nums2 { + m[v1+v2]++ + } + } + for _, v3 := range nums3 { + for _, v4 := range nums4 { + count += m[-v3-v4] + } + } + return count +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js +/** + * @param {number[]} nums1 + * @param {number[]} nums2 + * @param {number[]} nums3 + * @param {number[]} nums4 + * @return {number} + */ +var fourSumCount = function(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4) { + const twoSumMap = new Map(); + let count = 0; + + for(const n1 of nums1) { + for(const n2 of nums2) { + const sum = n1 + n2; + twoSumMap.set(sum, (twoSumMap.get(sum) || 0) + 1) + } + } + + for(const n3 of nums3) { + for(const n4 of nums4) { + const sum = n3 + n4; + count += (twoSumMap.get(0 - sum) || 0) + } + } + + return count; +}; +``` diff --git a/problems/0455.分发饼干.md b/problems/0455.分发饼干.md index f57a7fa6..4814d414 100644 --- a/problems/0455.分发饼干.md +++ b/problems/0455.分发饼干.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 455.分发饼干 @@ -134,15 +134,41 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python3 +class Solution: + def findContentChildren(self, g: List[int], s: List[int]) -> int: + g.sort() + s.sort() + res = 0 + for i in range(len(s)): + if res

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -149,15 +149,151 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: +```java +class Solution { + public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { + if (s.equals("")) return false; + + int len = s.length(); + // 原串加个空格(哨兵),使下标从1开始,这样j从0开始,也不用初始化了 + s = " " + s; + char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); + int[] next = new int[len + 1]; + + // 构造 next 数组过程,j从0开始(空格),i从2开始 + for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= len; i++) { + // 匹配不成功,j回到前一位置 next 数组所对应的值 + while (j > 0 && chars[i] != chars[j + 1]) j = next[j]; + // 匹配成功,j往后移 + if (chars[i] == chars[j + 1]) j++; + // 更新 next 数组的值 + next[i] = j; + } + + // 最后判断是否是重复的子字符串,这里 next[len] 即代表next数组末尾的值 + if (next[len] > 0 && len % (len - next[len]) == 0) { + return true; + } + return false; + } +} +``` + Python: +这里使用了前缀表统一减一的实现方式 + +```python +class Solution: + def repeatedSubstringPattern(self, s: str) -> bool: + if len(s) == 0: + return False + nxt = [0] * len(s) + self.getNext(nxt, s) + if nxt[-1] != -1 and len(s) % (len(s) - (nxt[-1] + 1)) == 0: + return True + return False + + def getNext(self, nxt, s): + nxt[0] = -1 + j = -1 + for i in range(1, len(s)): + while j >= 0 and s[i] != s[j+1]: + j = nxt[j] + if s[i] == s[j+1]: + j += 1 + nxt[i] = j + return nxt +``` + +前缀表(不减一)的代码实现 + +```python +class Solution: + def repeatedSubstringPattern(self, s: str) -> bool: + if len(s) == 0: + return False + nxt = [0] * len(s) + self.getNext(nxt, s) + if nxt[-1] != 0 and len(s) % (len(s) - nxt[-1]) == 0: + return True + return False + + def getNext(self, nxt, s): + nxt[0] = 0 + j = 0 + for i in range(1, len(s)): + while j > 0 and s[i] != s[j]: + j = nxt[j - 1] + if s[i] == s[j]: + j += 1 + nxt[i] = j + return nxt +``` Go: +这里使用了前缀表统一减一的实现方式 + +```go +func repeatedSubstringPattern(s string) bool { + n := len(s) + if n == 0 { + return false + } + next := make([]int, n) + j := -1 + next[0] = j + for i := 1; i < n; i++ { + for j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j+1] { + j = next[j] + } + if s[i] == s[j+1] { + j++ + } + next[i] = j + } + // next[n-1]+1 最长相同前后缀的长度 + if next[n-1] != -1 && n%(n-(next[n-1]+1)) == 0 { + return true + } + return false +} +``` + +前缀表(不减一)的代码实现 + +```go +func repeatedSubstringPattern(s string) bool { + n := len(s) + if n == 0 { + return false + } + j := 0 + next := make([]int, n) + next[0] = j + for i := 1; i < n; i++ { + for j > 0 && s[i] != s[j] { + j = next[j-1] + } + if s[i] == s[j] { + j++ + } + next[i] = j + } + // next[n-1] 最长相同前后缀的长度 + if next[n-1] != 0 && n%(n-next[n-1]) == 0 { + return true + } + return false +} +``` + + + @@ -165,4 +301,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:一和零! ## 474.一和零 @@ -190,10 +190,59 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def findMaxForm(self, strs: List[str], m: int, n: int) -> int: + dp = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)] # 默认初始化0 + # 遍历物品 + for str in strs: + ones = str.count('1') + zeros = str.count('0') + # 遍历背包容量且从后向前遍历! + for i in range(m, zeros - 1, -1): + for j in range(n, ones - 1, -1): + dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeros][j - ones] + 1) + return dp[m][n] +``` Go: +```go +func findMaxForm(strs []string, m int, n int) int { + // 定义数组 + dp := make([][]int, m+1) + for i,_ := range dp { + dp[i] = make([]int, n+1 ) + } + // 遍历 + for i:=0;i欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 和子集问题有点像,但又处处是陷阱 @@ -229,10 +229,59 @@ class Solution { Python: - +```python3 +class Solution: + def findSubsequences(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]: + res = [] + path = [] + def backtrack(nums,startIndex): + repeat = [] #这里使用数组来进行去重操作 + if len(path) >=2: + res.append(path[:]) #注意这里不要加return,要取树上的节点 + for i in range(startIndex,len(nums)): + if nums[i] in repeat: + continue + if len(path) >= 1: + if nums[i] < path[-1]: + continue + repeat.append(nums[i]) #记录这个元素在本层用过了,本层后面不能再用了 + path.append(nums[i]) + backtrack(nums,i+1) + path.pop() + backtrack(nums,0) + return res +``` Go: +Javascript: + +```Javascript + +var findSubsequences = function(nums) { + let result = [] + let path = [] + function backtracing(startIndex) { + if(path.length > 1) { + result.push(path.slice()) + } + let uset = [] + for(let i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) { + if((path.length > 0 && nums[i] < path[path.length - 1]) || uset[nums[i] + 100]) { + continue + } + uset[nums[i] + 100] = true + path.push(nums[i]) + backtracing(i + 1) + path.pop() + } + } + backtracing(0) + return result +}; + +``` + @@ -240,4 +289,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:目标和! ## 494. 目标和 @@ -19,15 +19,15 @@ 示例: -输入:nums: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S: 3 -输出:5 -解释: +输入:nums: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S: 3 +输出:5 --1+1+1+1+1 = 3 -+1-1+1+1+1 = 3 -+1+1-1+1+1 = 3 -+1+1+1-1+1 = 3 -+1+1+1+1-1 = 3 +解释: +-1+1+1+1+1 = 3 ++1-1+1+1+1 = 3 ++1+1-1+1+1 = 3 ++1+1+1-1+1 = 3 ++1+1+1+1-1 = 3 一共有5种方法让最终目标和为3。 @@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ dp[j] 表示:填满j(包括j)这么大容积的包,有dp[i]种方法 有哪些来源可以推出dp[j]呢? -不考虑nums[i]的情况下,填满容量为j - nums[i]的背包,有dp[j - nums[i]]中方法。 +不考虑nums[i]的情况下,填满容量为j - nums[i]的背包,有dp[j - nums[i]]种方法。 那么只要搞到nums[i]的话,凑成dp[j]就有dp[j - nums[i]] 种方法。 @@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ public: 是的,如果仅仅是求个数的话,就可以用dp,但[回溯算法:39. 组合总和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FLg8G6EjVcxBjwCbzpACPw)要求的是把所有组合列出来,还是要使用回溯法爆搜的。 -本地还是有点难度,大家也可以记住,在求装满背包有几种方法的情况下,递推公式一般为: +本题还是有点难度,大家也可以记住,在求装满背包有几种方法的情况下,递推公式一般为: ``` dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]; @@ -261,10 +261,50 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int: + sumValue = sum(nums) + if target > sumValue or (sumValue + target) % 2 == 1: return 0 + bagSize = (sumValue + target) // 2 + dp = [0] * (bagSize + 1) + dp[0] = 1 + for i in range(len(nums)): + for j in range(bagSize, nums[i] - 1, -1): + dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]] + return dp[bagSize] +``` Go: - +```go +func findTargetSumWays(nums []int, target int) int { + sum := 0 + for _, v := range nums { + sum += v + } + if target > sum { + return 0 + } + if (sum+target)%2 == 1 { + return 0 + } + // 计算背包大小 + bag := (sum + target) / 2 + // 定义dp数组 + dp := make([]int, bag+1) + // 初始化 + dp[0] = 1 + // 遍历顺序 + for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ { + for j := bag; j >= nums[i]; j-- { + //推导公式 + dp[j] += dp[j-nums[i]] + //fmt.Println(dp) + } + } + return dp[bag] +} +``` @@ -272,4 +312,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 二叉树上应该怎么求,二叉搜索树上又应该怎么求? @@ -394,8 +394,39 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法 +class Solution: + def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]: + if not root: return + self.pre = root + self.count = 0 //统计频率 + self.countMax = 0 //最大频率 + self.res = [] + def findNumber(root): + if not root: return None // 第一个节点 + findNumber(root.left) //左 + if self.pre.val == root.val: //中: 与前一个节点数值相同 + self.count += 1 + else: // 与前一个节点数值不同 + self.pre = root + self.count = 1 + if self.count > self.countMax: // 如果计数大于最大值频率 + self.countMax = self.count // 更新最大频率 + self.res = [root.val] //更新res + elif self.count == self.countMax: // 如果和最大值相同,放进res中 + self.res.append(root.val) + findNumber(root.right) //右 + return + findNumber(root) + return self.res +``` Go: @@ -405,4 +436,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 509. 斐波那契数 @@ -171,12 +171,55 @@ public: Java: - +```Java +class Solution { + public int fib(int n) { + if (n < 2) return n; + int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0; + for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { + c = a + b; + a = b; + b = c; + } + return c; + } +} +``` Python: +```python3 +class Solution: + def fib(self, n: int) -> int: + if n < 2: + return n + a, b, c = 0, 1, 0 + for i in range(1, n): + c = a + b + a, b = b, c + return c +# 递归实现 +class Solution: + def fib(self, n: int) -> int: + if n < 2: + return n + return self.fib(n - 1) + self.fib(n - 2) +``` Go: +```Go +func fib(n int) int { + if n < 2 { + return n + } + a, b, c := 0, 1, 0 + for i := 1; i < n; i++ { + c = a + b + a, b = b, c + } + return c +} +``` diff --git a/problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md b/problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md index ac21dc68..e252ccd3 100644 --- a/problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md +++ b/problems/0513.找树左下角的值.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 513.找树左下角的值 @@ -274,10 +274,151 @@ class Solution { Python: - - +```python +//递归法 +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def findBottomLeftValue(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + depth=0 + self.res=[] + def level(root,depth): + if not root:return + if depth==len(self.res): + self.res.append([]) + self.res[depth].append(root.val) + level(root.left,depth+1) + level(root.right,depth+1) + level(root,depth) + return self.res[-1][0] +``` Go: +> 递归法 + +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ + var maxDeep int // 全局变量 深度 + var value int //全局变量 最终值 +func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int { + if root.Left==nil&&root.Right==nil{//需要提前判断一下(不要这个if的话提交结果会出错,但执行代码不会。防止这种情况出现,故先判断是否只有一个节点) + return root.Val + } + findLeftValue (root,maxDeep) + return value +} +func findLeftValue (root *TreeNode,deep int){ + //最左边的值在左边 + if root.Left==nil&&root.Right==nil{ + if deep>maxDeep{ + value=root.Val + maxDeep=deep + } + } + //递归 + if root.Left!=nil{ + deep++ + findLeftValue(root.Left,deep) + deep--//回溯 + } + if root.Right!=nil{ + deep++ + findLeftValue(root.Right,deep) + deep--//回溯 + } +} +``` + +> 迭代法 + +```go +/** + * Definition for a binary tree node. + * type TreeNode struct { + * Val int + * Left *TreeNode + * Right *TreeNode + * } + */ +func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int { + queue:=list.New() + var gradation int + queue.PushBack(root) + for queue.Len()>0{ + length:=queue.Len() + for i:=0;i \ No newline at end of file
+
\ No newline at end of file
+
欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 516.最长回文子序列 题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence/ @@ -170,9 +170,49 @@ public class Solution { Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def longestPalindromeSubseq(self, s: str) -> int: + dp = [[0] * len(s) for _ in range(len(s))] + for i in range(len(s)): + dp[i][i] = 1 + for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1): + for j in range(i+1, len(s)): + if s[i] == s[j]: + dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j-1] + 2 + else: + dp[i][j] = max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j-1]) + return dp[0][-1] +``` Go: +```Go +func longestPalindromeSubseq(s string) int { + lenth:=len(s) + dp:=make([][]int,lenth) + for i:=0;i +
+ 
 -
- 
 +
+  -
-欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 动态规划:给你一些零钱,你要怎么凑? ## 518. 零钱兑换 II @@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ 示例 3: 输入: amount = 10, coins = [10] 输出: 1 - + 注意,你可以假设: * 0 <= amount (总金额) <= 5000 @@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ dp[j] (考虑coins[i]的组合总和) 就是所有的dp[j - coins[i]](不 而本题要求凑成总和的组合数,元素之间要求没有顺序。 -所以纯完全背包是能凑成总结就行,不用管怎么凑的。 +所以纯完全背包是能凑成总和就行,不用管怎么凑的。 本题是求凑出来的方案个数,且每个方案个数是为组合数。 @@ -208,10 +208,42 @@ class Solution { Python: -Go: +```python3 +class Solution: + def change(self, amount: int, coins: List[int]) -> int: + dp = [0]*(amount + 1) + dp[0] = 1 + # 遍历物品 + for i in range(len(coins)): + # 遍历背包 + for j in range(coins[i], amount + 1): + dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]] + return dp[amount] +``` +Go: +```go +func change(amount int, coins []int) int { + // 定义dp数组 + dp := make([]int, amount+1) + // 初始化,0大小的背包, 当然是不装任何东西了, 就是1种方法 + dp[0] = 1 + // 遍历顺序 + // 遍历物品 + for i := 0 ;i < len(coins);i++ { + // 遍历背包 + for j:= coins[i] ; j <= amount ;j++ { + // 推导公式 + dp[j] += dp[j-coins[i]] + } + } + return dp[amount] +} +``` + + ----------------------- * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) diff --git a/problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md b/problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md index 903ebf78..03c48d9c 100644 --- a/problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md +++ b/problems/0530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 利用二叉搜索树的特性搞起! @@ -151,7 +151,30 @@ public: Java: - +递归 +```java +class Solution { + TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点 + int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; + public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) { + if(root==null)return 0; + traversal(root); + return result; + } + public void traversal(TreeNode root){ + if(root==null)return; + //左 + traversal(root.left); + //中 + if(pre!=null){ + result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val); + } + pre = root; + //右 + traversal(root.right); + } +} +``` ```Java class Solution { TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点 @@ -177,8 +200,29 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def getMinimumDifference(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: + res = [] + r = float("inf") + def buildaList(root): //把二叉搜索树转换成有序数组 + if not root: return None + if root.left: buildaList(root.left) //左 + res.append(root.val) //中 + if root.right: buildaList(root.right) //右 + return res + + buildaList(root) + for i in range(len(res)-1): // 统计有序数组的最小差值 + r = min(abs(res[i]-res[i+1]),r) + return r +``` Go: @@ -188,4 +232,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 @@ -196,8 +196,26 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - - +```python3 +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +#递归法 +class Solution: + def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: + def buildalist(root): + if not root: return None + buildalist(root.right) #右中左遍历 + root.val += self.pre + self.pre = root.val + buildalist(root.left) + self.pre = 0 #记录前一个节点的数值 + buildalist(root) + return root +``` Go: @@ -207,4 +225,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
@@ -106,27 +106,24 @@ Java: class Solution { public String reverseStr(String s, int k) { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); - - for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i += (2 * k)) { + int length = s.length(); + int start = 0; + while (start < length) { + // 找到k处和2k处 StringBuffer temp = new StringBuffer(); - // 剩余字符大于 k 个,每隔 2k 个字符的前 k 个字符进行反转 - if (i + k <= s.length()) { - // 反转前 k 个字符 - temp.append(s.substring(i, i + k)); - res.append(temp.reverse()); + // 与length进行判断,如果大于length了,那就将其置为length + int firstK = (start + k > length) ? length : start + k; + int secondK = (start + (2 * k) > length) ? length : start + (2 * k); - // 反转完前 k 个字符之后,如果紧接着还有 k 个字符,则直接加入这 k 个字符 - if (i + 2 * k <= s.length()) { - res.append(s.substring(i + k, i + 2 * k)); - // 不足 k 个字符,则直接加入剩下所有字符 - } else { - res.append(s.substring(i + k, s.length())); - } - continue; - } - // 剩余字符少于 k 个,则将剩余字符全部反转。 - temp.append(s.substring(i, s.length())); + //无论start所处位置,至少会反转一次 + temp.append(s.substring(start, firstK)); res.append(temp.reverse()); + + // 如果firstK到secondK之间有元素,这些元素直接放入res里即可。 + if (firstK < secondK) { //此时剩余长度一定大于k。 + res.append(s.substring(firstK, secondK)); + } + start += (2 * k); } return res.toString(); } @@ -134,10 +131,84 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: +```python + +class Solution(object): + def reverseStr(self, s, k): + """ + :type s: str + :type k: int + :rtype: str + """ + from functools import reduce + # turn s into a list + s = list(s) + + # another way to simply use a[::-1], but i feel this is easier to understand + def reverse(s): + left, right = 0, len(s) - 1 + while left < right: + s[left], s[right] = s[right], s[left] + left += 1 + right -= 1 + return s + + # make sure we reverse each 2k elements + for i in range(0, len(s), 2*k): + s[i:(i+k)] = reverse(s[i:(i+k)]) + + # combine list into str. + return reduce(lambda a, b: a+b, s) + +``` Go: +```go +func reverseStr(s string, k int) string { + ss := []byte(s) + length := len(s) + for i := 0; i < length; i += 2 * k { + if i + k <= length { + reverse(ss[i:i+k]) + } else { + reverse(ss[i:length]) + } + } + return string(ss) +} +func reverse(b []byte) { + left := 0 + right := len(b) - 1 + for left < right { + b[left], b[right] = b[right], b[left] + left++ + right-- + } +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js + +/** + * @param {string} s + * @param {number} k + * @return {string} + */ +var reverseStr = function(s, k) { + const len = s.length; + let resArr = s.split(""); + for(let i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * k) { + let l = i - 1, r = i + k > len ? len : i + k; + while(++l < --r) [resArr[l], resArr[r]] = [resArr[r], resArr[l]]; + } + return resArr.join(""); +}; + +``` diff --git a/problems/0583.两个字符串的删除操作.md b/problems/0583.两个字符串的删除操作.md index 9679347a..0b32d129 100644 --- a/problems/0583.两个字符串的删除操作.md +++ b/problems/0583.两个字符串的删除操作.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 583. 两个字符串的删除操作 @@ -107,7 +107,22 @@ Java: Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def minDistance(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int: + dp = [[0] * (len(word2)+1) for _ in range(len(word1)+1)] + for i in range(len(word1)+1): + dp[i][0] = i + for j in range(len(word2)+1): + dp[0][j] = j + for i in range(1, len(word1)+1): + for j in range(1, len(word2)+1): + if word1[i-1] == word2[j-1]: + dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + else: + dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1] + 2, dp[i-1][j] + 1, dp[i][j-1] + 1) + return dp[-1][-1] +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0617.合并二叉树.md b/problems/0617.合并二叉树.md index 848454de..d65275f0 100644 --- a/problems/0617.合并二叉树.md +++ b/problems/0617.合并二叉树.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 617.合并二叉树 @@ -312,7 +312,23 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法*前序遍历 +class Solution: + def mergeTrees(self, root1: TreeNode, root2: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: + if not root1: return root2 // 如果t1为空,合并之后就应该是t2 + if not root2: return root1 // 如果t2为空,合并之后就应该是t1 + root1.val = root1.val + root2.val //中 + root1.left = self.mergeTrees(root1.left , root2.left) //左 + root1.right = self.mergeTrees(root1.right , root2.right) //右 + return root1 //root1修改了结构和数值 +``` Go: @@ -323,4 +339,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 647. 回文子串 @@ -219,14 +219,147 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: +动态规划: + +```java +class Solution { + public int countSubstrings(String s) { + int len, ans = 0; + if (s == null || (len = s.length()) < 1) return 0; + //dp[i][j]:s字符串下标i到下标j的字串是否是一个回文串,即s[i, j] + boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len]; + for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { + for (int i = 0; i <= j; i++) { + //当两端字母一样时,才可以两端收缩进一步判断 + if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { + //i++,j--,即两端收缩之后i,j指针指向同一个字符或者i超过j了,必然是一个回文串 + if (j - i < 3) { + dp[i][j] = true; + } else { + //否则通过收缩之后的字串判断 + dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1]; + } + } else {//两端字符不一样,不是回文串 + dp[i][j] = false; + } + } + } + //遍历每一个字串,统计回文串个数 + for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { + for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { + if (dp[i][j]) ans++; + } + } + return ans; + } +} +``` + +中心扩散法: + +```java +class Solution { + public int countSubstrings(String s) { + int len, ans = 0; + if (s == null || (len = s.length()) < 1) return 0; + //总共有2 * len - 1个中心点 + for (int i = 0; i < 2 * len - 1; i++) { + //通过遍历每个回文中心,向两边扩散,并判断是否回文字串 + //有两种情况,left == right,right = left + 1,这两种回文中心是不一样的 + int left = i / 2, right = left + i % 2; + while (left >= 0 && right < len && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) { + //如果当前是一个回文串,则记录数量 + ans++; + left--; + right++; + } + } + return ans; + } +} +``` + Python: +> 动态规划: +```python +class Solution: + def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int: + dp = [[False] * len(s) for _ in range(len(s))] + result = 0 + for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1): #注意遍历顺序 + for j in range(i, len(s)): + if s[i] == s[j]: + if j - i <= 1: #情况一 和 情况二 + result += 1 + dp[i][j] = True + elif dp[i+1][j-1]: #情况三 + result += 1 + dp[i][j] = True + return result +``` + +> 动态规划:简洁版 +```python +class Solution: + def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int: + dp = [[False] * len(s) for _ in range(len(s))] + result = 0 + for i in range(len(s)-1, -1, -1): #注意遍历顺序 + for j in range(i, len(s)): + if s[i] == s[j] and (j - i <= 1 or dp[i+1][j-1]): + result += 1 + dp[i][j] = True + return result +``` + +> 双指针法: +```python +class Solution: + def countSubstrings(self, s: str) -> int: + result = 0 + for i in range(len(s)): + result += self.extend(s, i, i, len(s)) #以i为中心 + result += self.extend(s, i, i+1, len(s)) #以i和i+1为中心 + return result + + def extend(self, s, i, j, n): + res = 0 + while i >= 0 and j < n and s[i] == s[j]: + i -= 1 + j += 1 + res += 1 + return res +``` Go: +```Go +func countSubstrings(s string) int { + res:=0 + dp:=make([][]bool,len(s)) + for i:=0;i +
+ 
 -
- 
 +
+  -
-欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 654.最大二叉树 @@ -256,7 +256,25 @@ class Solution { ``` Python: - +```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +//递归法 +class Solution: + def constructMaximumBinaryTree(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode: + if not nums: return None //终止条件 + root = TreeNode(max(nums)) //新建节点 + p = nums.index(root.val) //找到最大值位置 + if p > 0: //保证有左子树 + root.left = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[:p]) //递归 + if p < len(nums): //保证有右子树 + root.right = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[p+1:]) //递归 + return root +``` Go: @@ -267,4 +285,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 如果不对递归有深刻的理解,本题有点难 @@ -266,7 +266,25 @@ class Solution { Python: +```python3 +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right +class Solution: + def trimBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> TreeNode: + if not root: return root + if root.val < low: + return self.trimBST(root.right,low,high) // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点 + if root.val > high: + return self.trimBST(root.left,low,high) // 寻找符合区间[low, high]的节点 + root.left = self.trimBST(root.left,low,high) // root->left接入符合条件的左孩子 + root.right = self.trimBST(root.right,low,high) // root->right接入符合条件的右孩子 + return root +``` Go: @@ -276,4 +294,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 674. 最长连续递增序列 @@ -156,10 +156,65 @@ public: Java: - +```java + /** + * 1.dp[i] 代表当前下表最大连续值 + * 2.递推公式 if(nums[i+1]>nums[i]) dp[i+1] = dp[i]+1 + * 3.初始化 都为1 + * 4.遍历方向,从其那往后 + * 5.结果推导 。。。。 + * @param nums + * @return + */ + public static int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) { + int[] dp = new int[nums.length]; + for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) { + dp[i] = 1; + } + int res = 1; + for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) { + if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { + dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1; + } + res = res > dp[i + 1] ? res : dp[i + 1]; + } + return res; + } +``` Python: +> 动态规划: +```python +class Solution: + def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) == 0: + return 0 + result = 1 + dp = [1] * len(nums) + for i in range(len(nums)-1): + if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录 + dp[i+1] = dp[i] + 1 + result = max(result, dp[i+1]) + return result +``` + +> 贪心法: +```python +class Solution: + def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: + if len(nums) == 0: + return 0 + result = 1 #连续子序列最少也是1 + count = 1 + for i in range(len(nums)-1): + if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录 + count += 1 + else: #不连续,count从头开始 + count = 1 + result = max(result, count) + return result +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md b/problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md index 277ef681..25a06617 100644 --- a/problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md +++ b/problems/0700.二叉搜索树中的搜索.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 700.二叉搜索树中的搜索 @@ -212,13 +212,18 @@ Python: 递归法: ```python +# Definition for a binary tree node. +# class TreeNode: +# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): +# self.val = val +# self.left = left +# self.right = right class Solution: def searchBST(self, root: TreeNode, val: int) -> TreeNode: - if root is None: - return None - if val < root.val: return self.searchBST(root.left, val) - elif val > root.val: return self.searchBST(root.right, val) - else: return root + if not root or root.val == val: return root //为空或者已经找到都是直接返回root,所以合并了 + if root.val > val: return self.searchBST(root.left,val) //注意一定要加return + else: return self.searchBST(root.right,val) + ``` 迭代法: @@ -243,4 +248,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作 @@ -271,6 +271,20 @@ class Solution: Go: +```Go +func insertIntoBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode { + if root == nil { + root = &TreeNode{Val: val} + return root + } + if root.Val > val { + root.Left = insertIntoBST(root.Left, val) + } else { + root.Right = insertIntoBST(root.Right, val) + } + return root +} +``` @@ -279,4 +293,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 704. 二分查找 @@ -13,18 +13,23 @@ 给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。 +示例 1: -示例 1: -输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9 -输出: 4 -解释: 9 出现在 nums 中并且下标为 4 +``` +输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9 +输出: 4 +解释: 9 出现在 nums 中并且下标为 4 +``` -示例 2: -输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2 -输出: -1 -解释: 2 不存在 nums 中因此返回 -1 +示例 2: -提示: +``` +输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 2 +输出: -1 +解释: 2 不存在 nums 中因此返回 -1 +``` + +提示: * 你可以假设 nums 中的所有元素是不重复的。 * n 将在 [1, 10000]之间。 @@ -146,13 +151,17 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 -Java: +**Java:** (版本一)左闭右闭区间 ```java class Solution { public int search(int[] nums, int target) { + // 避免当 target 小于nums[0] nums[nums.length - 1]时多次循环运算 + if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) { + return -1; + } int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1; while (left <= right) { int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1); @@ -188,9 +197,11 @@ class Solution { } ``` -Python: +**Python:** -```python3 +(版本一)左闭右闭区间 + +```python class Solution: def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int: left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1 @@ -207,8 +218,104 @@ class Solution: return -1 ``` +(版本二)左闭右开区间 + +```python +class Solution: + def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int: + left,right =0, len(nums) + while left < right: + mid = (left + right) // 2 + if nums[mid] < target: + left = mid+1 + elif nums[mid] > target: + right = mid + else: + return mid + return -1 +``` + + + +**Go:** + +(版本一)左闭右闭区间 + +```go +func search(nums []int, target int) int { + high := len(nums)-1 + low := 0 + for low <= high { + mid := low + (high-low)/2 + if nums[mid] == target { + return mid + } else if nums[mid] > target { + high = mid-1 + } else { + low = mid+1 + } + } + return -1 +} +``` + +(版本二)左闭右开区间 + +```go +func search(nums []int, target int) int { + high := len(nums) + low := 0 + for low < high { + mid := low + (high-low)/2 + if nums[mid] == target { + return mid + } else if nums[mid] > target { + high = mid + } else { + low = mid+1 + } + } + return -1 +} +``` + +**javaScript:** + +```js + +// (版本一)左闭右闭区间 + +var search = function(nums, target) { + let l = 0, r = nums.length - 1; + // 区间 [l, r] + while(l <= r) { + let mid = (l + r) >> 1; + if(nums[mid] === target) return mid; + let isSmall = nums[mid] < target; + l = isSmall ? mid + 1 : l; + r = isSmall ? r : mid - 1; + } + return -1; +}; + +// (版本二)左闭右开区间 + +var search = function(nums, target) { + let l = 0, r = nums.length; + // 区间 [l, r) + while(l < r) { + let mid = (l + r) >> 1; + if(nums[mid] === target) return mid; + let isSmall = nums[mid] < target; + l = isSmall ? mid + 1 : l; + // 所以 mid 不会被取到 + r = isSmall ? r : mid; + } + return -1; +}; + +``` -Go: @@ -217,4 +324,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 听说这道题目把链表常见的五个操作都覆盖了? @@ -158,6 +158,14 @@ private: Java: ```Java +class ListNode { +int val; +ListNode next; +ListNode(){} +ListNode(int val) { +this.val=val; +} +} class MyLinkedList { //size存储链表元素的个数 int size; @@ -231,10 +239,425 @@ class MyLinkedList { ``` Python: +```python3 +# 单链表 +class Node: + + def __init__(self, val): + self.val = val + self.next = None +class MyLinkedList: + + def __init__(self): + self._head = Node(0) # 虚拟头部节点 + self._count = 0 # 添加的节点数 + + def get(self, index: int) -> int: + """ + Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. + """ + if 0 <= index < self._count: + node = self._head + for _ in range(index + 1): + node = node.next + return node.val + else: + return -1 + + def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None: + """ + Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. + """ + self.addAtIndex(0, val) + + def addAtTail(self, val: int) -> None: + """ + Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. + """ + self.addAtIndex(self._count, val) + + def addAtIndex(self, index: int, val: int) -> None: + """ + Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. + """ + if index < 0: + index = 0 + elif index > self._count: + return + + # 计数累加 + self._count += 1 + + add_node = Node(val) + prev_node, current_node = None, self._head + for _ in range(index + 1): + prev_node, current_node = current_node, current_node.next + else: + prev_node.next, add_node.next = add_node, current_node + + def deleteAtIndex(self, index: int) -> None: + """ + Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. + """ + if 0 <= index < self._count: + # 计数-1 + self._count -= 1 + prev_node, current_node = None, self._head + for _ in range(index + 1): + prev_node, current_node = current_node, current_node.next + else: + prev_node.next, current_node.next = current_node.next, None + + +# 双链表 +# 相对于单链表, Node新增了prev属性 +class Node: + + def __init__(self, val): + self.val = val + self.prev = None + self.next = None + + +class MyLinkedList: + + def __init__(self): + self._head, self._tail = Node(0), Node(0) # 虚拟节点 + self._head.next, self._tail.prev = self._tail, self._head + self._count = 0 # 添加的节点数 + + def _get_node(self, index: int) -> Node: + # 当index小于_count//2时, 使用_head查找更快, 反之_tail更快 + if index >= self._count // 2: + # 使用prev往前找 + node = self._tail + for _ in range(self._count - index): + node = node.prev + else: + # 使用next往后找 + node = self._head + for _ in range(index + 1): + node = node.next + return node + + def get(self, index: int) -> int: + """ + Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. + """ + if 0 <= index < self._count: + node = self._get_node(index) + return node.val + else: + return -1 + + def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None: + """ + Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. + """ + self._update(self._head, self._head.next, val) + + def addAtTail(self, val: int) -> None: + """ + Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. + """ + self._update(self._tail.prev, self._tail, val) + + def addAtIndex(self, index: int, val: int) -> None: + """ + Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. + """ + if index < 0: + index = 0 + elif index > self._count: + return + node = self._get_node(index) + self._update(node.prev, node, val) + + def _update(self, prev: Node, next: Node, val: int) -> None: + """ + 更新节点 + :param prev: 相对于更新的前一个节点 + :param next: 相对于更新的后一个节点 + :param val: 要添加的节点值 + """ + # 计数累加 + self._count += 1 + node = Node(val) + prev.next, next.prev = node, node + node.prev, node.next = prev, next + + def deleteAtIndex(self, index: int) -> None: + """ + Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. + """ + if 0 <= index < self._count: + node = self._get_node(index) + # 计数-1 + self._count -= 1 + node.prev.next, node.next.prev = node.next, node.prev +``` + Go: +```go +//循环双链表 +type MyLinkedList struct { + dummy *Node +} + +type Node struct { + Val int + Next *Node + Pre *Node +} + +//仅保存哑节点,pre-> rear, next-> head +/** Initialize your data structure here. */ +func Constructor() MyLinkedList { + rear := &Node{ + Val: -1, + Next: nil, + Pre: nil, + } + rear.Next = rear + rear.Pre = rear + return MyLinkedList{rear} +} + +/** Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. */ +func (this *MyLinkedList) Get(index int) int { + head := this.dummy.Next + //head == this, 遍历完全 + for head != this.dummy && index > 0 { + index-- + head = head.Next + } + //否则, head == this, 索引无效 + if 0 != index { + return -1 + } + return head.Val +} + +/** Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. */ +func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtHead(val int) { + dummy := this.dummy + node := &Node{ + Val: val, + //head.Next指向原头节点 + Next: dummy.Next, + //head.Pre 指向哑节点 + Pre: dummy, + } + + //更新原头节点 + dummy.Next.Pre = node + //更新哑节点 + dummy.Next = node + //以上两步不能反 +} + +/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */ +func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtTail(val int) { + dummy := this.dummy + rear := &Node{ + Val: val, + //rear.Next = dummy(哑节点) + Next: dummy, + //rear.Pre = ori_rear + Pre: dummy.Pre, + } + + //ori_rear.Next = rear + dummy.Pre.Next = rear + //update dummy + dummy.Pre = rear + //以上两步不能反 +} + +/** Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. */ +func (this *MyLinkedList) AddAtIndex(index int, val int) { + head := this.dummy.Next + //head = MyLinkedList[index] + for head != this.dummy && index > 0 { + head = head.Next + index-- + } + node := &Node{ + Val: val, + //node.Next = MyLinkedList[index] + Next: head, + //node.Pre = MyLinkedList[index-1] + Pre: head.Pre, + } + //MyLinkedList[index-1].Next = node + head.Pre.Next = node + //MyLinkedList[index].Pre = node + head.Pre = node + //以上两步不能反 +} + +/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */ +func (this *MyLinkedList) DeleteAtIndex(index int) { + //链表为空 + if this.dummy.Next == this.dummy { + return + } + head := this.dummy.Next + //head = MyLinkedList[index] + for head.Next != this.dummy && index > 0 { + head = head.Next + index-- + } + //验证index有效 + if index == 0 { + //MyLinkedList[index].Pre = index[index-2] + head.Next.Pre = head.Pre + //MyLinedList[index-2].Next = index[index] + head.Pre.Next = head.Next + //以上两步顺序无所谓 + } +} +``` + +javaScript: + +```js + +class LinkNode { + constructor(val, next) { + this.val = val; + this.next = next; + } +} + +/** + * Initialize your data structure here. + * 单链表 储存头尾节点 和 节点数量 + */ +var MyLinkedList = function() { + this._size = 0; + this._tail = null; + this._head = null; +}; + +/** + * Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. + * @param {number} index + * @return {number} + */ +MyLinkedList.prototype.getNode = function(index) { + if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return null; + // 创建虚拟头节点 + let cur = new LinkNode(0, this._head); + // 0 -> head + while(index-- >= 0) { + cur = cur.next; + } + return cur; +}; +MyLinkedList.prototype.get = function(index) { + if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return -1; + // 获取当前节点 + return this.getNode(index).val; +}; + +/** + * Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. + * @param {number} val + * @return {void} + */ +MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtHead = function(val) { + const node = new LinkNode(val, this._head); + this._head = node; + this._size++; + if(!this._tail) { + this._tail = node; + } +}; + +/** + * Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. + * @param {number} val + * @return {void} + */ +MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtTail = function(val) { + const node = new LinkNode(val, null); + this._size++; + if(this._tail) { + this._tail.next = node; + this._tail = node; + return; + } + this._tail = node; + this._head = node; +}; + +/** + * Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. + * @param {number} index + * @param {number} val + * @return {void} + */ +MyLinkedList.prototype.addAtIndex = function(index, val) { + if(index > this._size) return; + if(index <= 0) { + this.addAtHead(val); + return; + } + if(index === this._size) { + this.addAtTail(val); + return; + } + // 获取目标节点的上一个的节点 + const node = this.getNode(index - 1); + node.next = new LinkNode(val, node.next); + this._size++; +}; + +/** + * Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. + * @param {number} index + * @return {void} + */ +MyLinkedList.prototype.deleteAtIndex = function(index) { + if(index < 0 || index >= this._size) return; + if(index === 0) { + this._head = this._head.next; + this._size--; + return; + } + // 获取目标节点的上一个的节点 + const node = this.getNode(index - 1); + node.next = node.next.next; + // 处理尾节点 + if(index === this._size - 1) { + this._tail = node; + } + this._size--; +}; + +// MyLinkedList.prototype.out = function() { +// let cur = this._head; +// const res = []; +// while(cur) { +// res.push(cur.val); +// cur = cur.next; +// } +// }; +/** + * Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such: + * var obj = new MyLinkedList() + * var param_1 = obj.get(index) + * obj.addAtHead(val) + * obj.addAtTail(val) + * obj.addAtIndex(index,val) + * obj.deleteAtIndex(index) + */ +``` + diff --git a/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费.md b/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费.md index 86954c14..abd20625 100644 --- a/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费.md +++ b/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 @@ -154,9 +154,9 @@ public: ## 其他语言版本 - Java: ```java +// 贪心思路 class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) { int buy = prices[0] + fee; @@ -174,8 +174,46 @@ class Solution { } ``` -Python: +```java +class Solution { // 动态规划 + public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) { + if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) { + return 0; + } + int[][] dp = new int[prices.length][2]; + + // bad case + dp[0][0] = 0; + dp[0][1] = -prices[0]; + + for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i] - fee); + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i]); + } + + return dp[prices.length - 1][0]; + } +} +``` + + +Python: +```python +class Solution: # 贪心思路 + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int: + result = 0 + minPrice = prices[0] + for i in range(1, len(prices)): + if prices[i] < minPrice: + minPrice = prices[i] + elif prices[i] >= minPrice and prices[i] <= minPrice + fee: + continue + else: + result += prices[i] - minPrice - fee + minPrice = prices[i] - fee + return result +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md b/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md index 3926643d..5eb3453b 100644 --- a/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md +++ b/problems/0714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费(动态规划).md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 @@ -95,10 +95,61 @@ public: Java: +```java +/** + * 卖出时支付手续费 + * @param prices + * @param fee + * @return + */ +public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) { + int len = prices.length; + // 0 : 持股(买入) + // 1 : 不持股(售出) + // dp 定义第i天持股/不持股 所得最多现金 + int[][] dp = new int[len][2]; + dp[0][0] = -prices[0]; + for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]); + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i] - fee, dp[i - 1][1]); + } + return Math.max(dp[len - 1][0], dp[len - 1][1]); +} +/** + * 买入时支付手续费 + * @param prices + * @param fee + * @return + */ +public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) { + int len = prices.length; + // 0 : 持股(买入) + // 1 : 不持股(售出) + // dp 定义第i天持股/不持股 所得最多现金 + int[][] dp = new int[len][2]; + // 考虑买入的时候就支付手续费 + dp[0][0] = -prices[0] - fee; + for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { + dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i] - fee); + dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]); + } + return Math.max(dp[len - 1][0], dp[len - 1][1]); +} +``` Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int: + n = len(prices) + dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(n)] + dp[0][0] = -prices[0] #持股票 + for i in range(1, n): + dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i]) + dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] + prices[i] - fee) + return max(dp[-1][0], dp[-1][1]) +``` Go: diff --git a/problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md b/problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md index c20ea79f..bef616d3 100644 --- a/problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md +++ b/problems/0718.最长重复子数组.md @@ -1,10 +1,10 @@ -欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 718. 最长重复子数组 @@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ public: **此时遍历B数组的时候,就要从后向前遍历,这样避免重复覆盖**。 -``` +```C++ class Solution { public: int findLength(vector欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
## 738.单调递增的数字 +题目链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/monotone-increasing-digits/ 给定一个非负整数 N,找出小于或等于 N 的最大的整数,同时这个整数需要满足其各个位数上的数字是单调递增。 @@ -30,7 +31,7 @@ ## 暴力解法 -题意很简单,那么首先想的就是暴力解法了,来我提大家暴力一波,结果自然是超时! +题意很简单,那么首先想的就是暴力解法了,来我替大家暴力一波,结果自然是超时! 代码如下: ```C++ @@ -146,7 +147,19 @@ class Solution { Python: - +```python +class Solution: + def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int: + strNum = list(str(n)) + flag = len(strNum) + for i in range(len(strNum) - 1, 0, -1): + if int(strNum[i]) < int(strNum[i - 1]): + strNum[i - 1] = str(int(strNum[i - 1]) - 1) + flag = i + for i in range(flag, len(strNum)): + strNum[i] = '9' + return int("".join(strNum)) +``` Go: @@ -157,4 +170,4 @@ Go: * 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw) * B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321) * 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ) -

欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
+ +# 739. 每日温度 + + +https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/daily-temperatures/ + +请根据每日 气温 列表,重新生成一个列表。对应位置的输出为:要想观测到更高的气温,至少需要等待的天数。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。 + +例如,给定一个列表 temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 69, 72, 76, 73],你的输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。 + +提示:气温 列表长度的范围是 [1, 30000]。每个气温的值的均为华氏度,都是在 [30, 100] 范围内的整数。 + + +## 思路 + +首先想到的当然是暴力解法,两层for循环,把至少需要等待的天数就搜出来了。时间复杂度是O(n^2) + +那么接下来在来看看使用单调栈的解法。 + +那有同学就问了,我怎么能想到用单调栈呢? 什么时候用单调栈呢? + +**通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了**。 + +时间复杂度为O(n)。 + +例如本题其实就是找找到一个元素右边第一个比自己大的元素。 + +此时就应该想到用单调栈了。 + +那么单调栈的原理是什么呢?为什么时间复杂度是O(n)就可以找到每一个元素的右边第一个比它大的元素位置呢? + +单调栈的本质是空间换时间,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元素的元素,优点是只需要遍历一次。 + + +在使用单调栈的时候首先要明确如下几点: + +1. 单调栈里存放的元素是什么? + +单调栈里只需要存放元素的下标i就可以了,如果需要使用对应的元素,直接T[i]就可以获取。 + +2. 单调栈里元素是递增呢? 还是递减呢? + +**注意一下顺序为 从栈头到栈底的顺序**,因为单纯的说从左到右或者从前到后,不说栈头朝哪个方向的话,大家一定会越看越懵。 + + +这里我们要使用递增循序(再强调一下是指从栈头到栈底的顺序),因为只有递增的时候,加入一个元素i,才知道栈顶元素在数组中右面第一个比栈顶元素大的元素是i。 + +文字描述理解起来有点费劲,接下来我画了一系列的图,来讲解单调栈的工作过程。 + +使用单调栈主要有三个判断条件。 + +* 当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 +* 当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 +* 当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 + +**把这三种情况分析清楚了,也就理解透彻了**。 + +接下来我们用temperatures = [73, 74, 75, 71, 71, 72, 76, 73]为例来逐步分析,输出应该是 [1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0]。 + +首先先将第一个遍历元素加入单调栈 + + +加入T[1] = 74,因为T[1] > T[0](当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),而我们要保持一个递增单调栈(从栈头到栈底),所以将T[0]弹出,T[1]加入,此时result数组可以记录了,result[0] = 1,即T[0]右面第一个比T[0]大的元素是T[1]。 + + +加入T[2],同理,T[1]弹出 + + + +加入T[3],T[3] < T[2] (当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),加T[3]加入单调栈。 + + + +加入T[4],T[4] == T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),此时依然要加入栈,不用计算距离,因为我们要求的是右面第一个大于本元素的位置,而不是大于等于! + + +加入T[5],T[5] > T[4] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[4]弹出,同时计算距离,更新result + + +T[4]弹出之后, T[5] > T[3] (当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况),将T[3]继续弹出,同时计算距离,更新result + + +直到发现T[5]小于T[st.top()],终止弹出,将T[5]加入单调栈 + + +加入T[6],同理,需要将栈里的T[5],T[2]弹出 + + +同理,继续弹出 + + +此时栈里只剩下了T[6] + + + +加入T[7], T[7] < T[6] 直接入栈,这就是最后的情况,result数组也更新完了。 + + + +此时有同学可能就疑惑了,那result[6] , result[7]怎么没更新啊,元素也一直在栈里。 + +其实定义result数组的时候,就应该直接初始化为0,如果result没有更新,说明这个元素右面没有更大的了,也就是为0。 + +以上在图解的时候,已经把,这三种情况都做了详细的分析。 + +* 情况一:当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 +* 情况二:当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 +* 情况三:当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况 + +C++代码如下: + +```C++ +// 版本一 +class Solution { +public: + vector
+ * 入站元素要和当前栈内栈首元素进行比较
+ * 若大于栈首则 则与元素下标做差
+ * 若大于等于则放入
+ *
+ * @param temperatures
+ * @return
+ */
+ public static int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
+ Stack 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益! 欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!









 -
-这棵二叉树为满二叉树,也可以说深度为 k,有 $(2^k)-1$ 个节点的二叉树。
-
-
-### 完全二叉树
-
-什么是完全二叉树?
-
-完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1 ~ $2^{(h-1)}$ 个节点。
-
-**大家要自己看完全二叉树的定义,很多同学对完全二叉树其实不是真正的懂了。**
-
-我来举一个典型的例子如题:
-
-
-
-这棵二叉树为满二叉树,也可以说深度为 k,有 $(2^k)-1$ 个节点的二叉树。
-
-
-### 完全二叉树
-
-什么是完全二叉树?
-
-完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1 ~ $2^{(h-1)}$ 个节点。
-
-**大家要自己看完全二叉树的定义,很多同学对完全二叉树其实不是真正的懂了。**
-
-我来举一个典型的例子如题:
-
- -
-相信不少同学最后一个二叉树是不是完全二叉树都中招了。
-
-**之前我们刚刚讲过优先级队列其实是一个堆,堆就是一棵完全二叉树,同时保证父子节点的顺序关系。**
-
-### 二叉搜索树
-
-前面介绍的书,都没有数值的,而二叉搜索树是有数值的了,**二叉搜索树是一个有序树**。
-
-
-* 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
-* 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
-* 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
-
-下面这两棵树都是搜索树
-
-
-相信不少同学最后一个二叉树是不是完全二叉树都中招了。
-
-**之前我们刚刚讲过优先级队列其实是一个堆,堆就是一棵完全二叉树,同时保证父子节点的顺序关系。**
-
-### 二叉搜索树
-
-前面介绍的书,都没有数值的,而二叉搜索树是有数值的了,**二叉搜索树是一个有序树**。
-
-
-* 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
-* 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
-* 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
-
-下面这两棵树都是搜索树
- -
-
-### 平衡二叉搜索树
-
-平衡二叉搜索树:又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
-
-如图:
-
-
-
-
-### 平衡二叉搜索树
-
-平衡二叉搜索树:又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
-
-如图:
-
-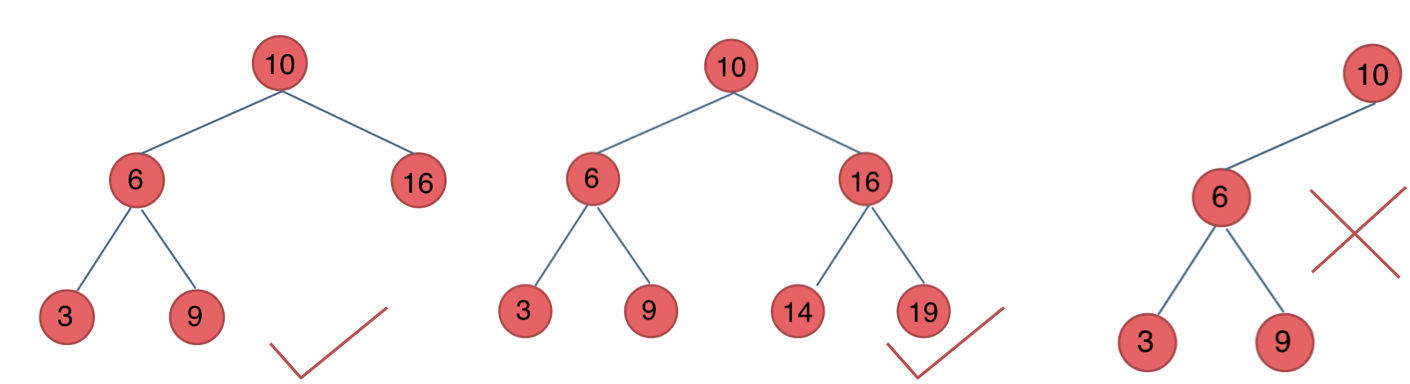 -
-最后一棵 不是平衡二叉树,因为它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值超过了1。
-
-**C++中map、set、multimap,multiset的底层实现都是平衡二叉搜索树**,所以map、set的增删操作时间时间复杂度是logn,注意我这里没有说unordered_map、unordered_set,unordered_map、unordered_map底层实现是哈希表。
-
-**所以大家使用自己熟悉的编程语言写算法,一定要知道常用的容器底层都是如何实现的,最基本的就是map、set等等,否则自己写的代码,自己对其性能分析都分析不清楚!**
-
-
-## 二叉树的存储方式
-
-**二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。**
-
-那么链式存储方式就用指针, 顺序存储的方式就是用数组。
-
-顾名思义就是顺序存储的元素在内存是连续分布的,而链式存储则是通过指针把分布在散落在各个地址的节点串联一起。
-
-链式存储如图:
-
-
-
-最后一棵 不是平衡二叉树,因为它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值超过了1。
-
-**C++中map、set、multimap,multiset的底层实现都是平衡二叉搜索树**,所以map、set的增删操作时间时间复杂度是logn,注意我这里没有说unordered_map、unordered_set,unordered_map、unordered_map底层实现是哈希表。
-
-**所以大家使用自己熟悉的编程语言写算法,一定要知道常用的容器底层都是如何实现的,最基本的就是map、set等等,否则自己写的代码,自己对其性能分析都分析不清楚!**
-
-
-## 二叉树的存储方式
-
-**二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。**
-
-那么链式存储方式就用指针, 顺序存储的方式就是用数组。
-
-顾名思义就是顺序存储的元素在内存是连续分布的,而链式存储则是通过指针把分布在散落在各个地址的节点串联一起。
-
-链式存储如图:
-
-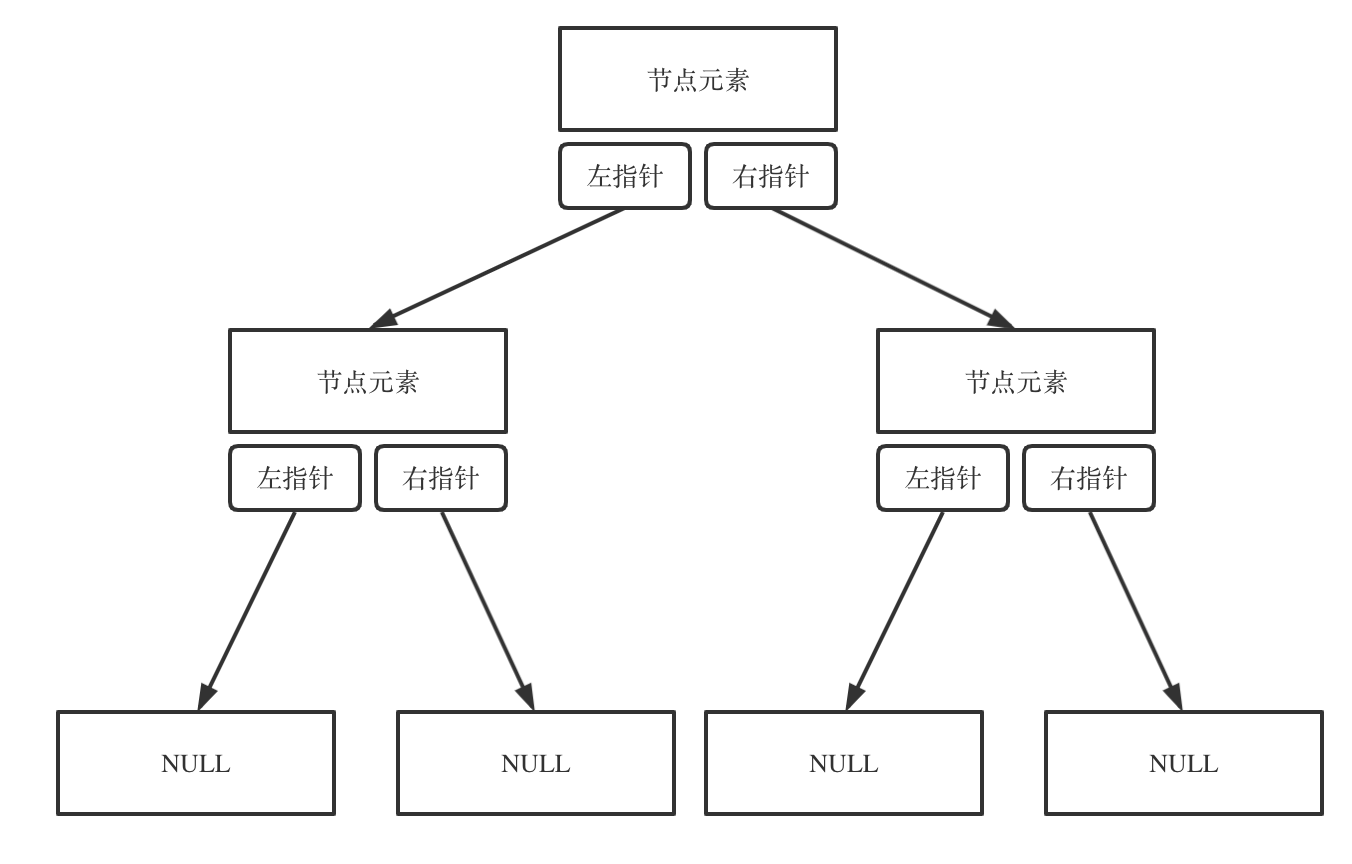 -
-链式存储是大家很熟悉的一种方式,那么我们来看看如何顺序存储呢?
-
-其实就是用数组来存储二叉树,顺序存储的方式如图:
-
-
-
-链式存储是大家很熟悉的一种方式,那么我们来看看如何顺序存储呢?
-
-其实就是用数组来存储二叉树,顺序存储的方式如图:
-
-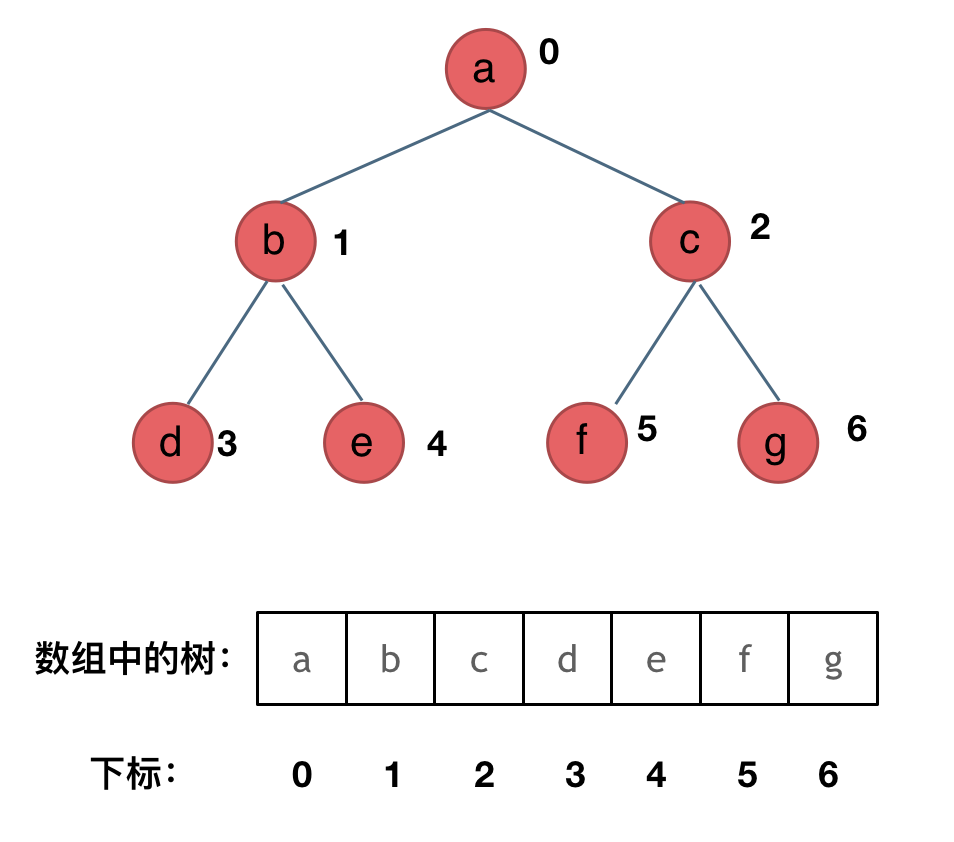 -
-用数组来存储二叉树如何遍历的呢?
-
-**如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i * 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i * 2 + 2。**
-
-但是用链式表示的二叉树,更有利于我们理解,所以一般我们都是用链式存储二叉树。
-
-**所以大家要了解,用数组依然可以表示二叉树。**
-
-## 二叉树的遍历方式
-
-关于二叉树的遍历方式,要知道二叉树遍历的基本方式都有哪些。
-
-一些同学用做了很多二叉树的题目了,可能知道前序、中序、后序遍历,可能知道层序遍历,但是却没有框架。
-
-我这里把二叉树的几种遍历方式列出来,大家就可以一一串起来了。
-
-二叉树主要有两种遍历方式:
-1. 深度优先遍历:先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走。
-2. 广度优先遍历:一层一层的去遍历。
-
-**这两种遍历是图论中最基本的两种遍历方式**,后面在介绍图论的时候 还会介绍到。
-
-那么从深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历进一步拓展,才有如下遍历方式:
-
-* 深度优先遍历
- * 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- * 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- * 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
-* 广度优先遍历
- * 层次遍历(迭代法)
-
-
-在深度优先遍历中:有三个顺序,前序、中序、后序遍历, 有同学总分不清这三个顺序,经常搞混,我这里教大家一个技巧。
-
-**这里前、中、后,其实指的就是中间节点的遍历顺序**,只要大家记住 前序、中序、后序指的就是中间节点的位置就可以了。
-
-看如下中间节点的顺序,就可以发现,中间节点的顺序就是所谓的遍历方式
-
-* 前序遍历:中左右
-* 中序遍历:左中右
-* 后序遍历:左右中
-
-大家可以对着如下图,看看自己理解的前后中序有没有问题。
-
-
-
-用数组来存储二叉树如何遍历的呢?
-
-**如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i * 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i * 2 + 2。**
-
-但是用链式表示的二叉树,更有利于我们理解,所以一般我们都是用链式存储二叉树。
-
-**所以大家要了解,用数组依然可以表示二叉树。**
-
-## 二叉树的遍历方式
-
-关于二叉树的遍历方式,要知道二叉树遍历的基本方式都有哪些。
-
-一些同学用做了很多二叉树的题目了,可能知道前序、中序、后序遍历,可能知道层序遍历,但是却没有框架。
-
-我这里把二叉树的几种遍历方式列出来,大家就可以一一串起来了。
-
-二叉树主要有两种遍历方式:
-1. 深度优先遍历:先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走。
-2. 广度优先遍历:一层一层的去遍历。
-
-**这两种遍历是图论中最基本的两种遍历方式**,后面在介绍图论的时候 还会介绍到。
-
-那么从深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历进一步拓展,才有如下遍历方式:
-
-* 深度优先遍历
- * 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- * 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- * 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
-* 广度优先遍历
- * 层次遍历(迭代法)
-
-
-在深度优先遍历中:有三个顺序,前序、中序、后序遍历, 有同学总分不清这三个顺序,经常搞混,我这里教大家一个技巧。
-
-**这里前、中、后,其实指的就是中间节点的遍历顺序**,只要大家记住 前序、中序、后序指的就是中间节点的位置就可以了。
-
-看如下中间节点的顺序,就可以发现,中间节点的顺序就是所谓的遍历方式
-
-* 前序遍历:中左右
-* 中序遍历:左中右
-* 后序遍历:左右中
-
-大家可以对着如下图,看看自己理解的前后中序有没有问题。
-
-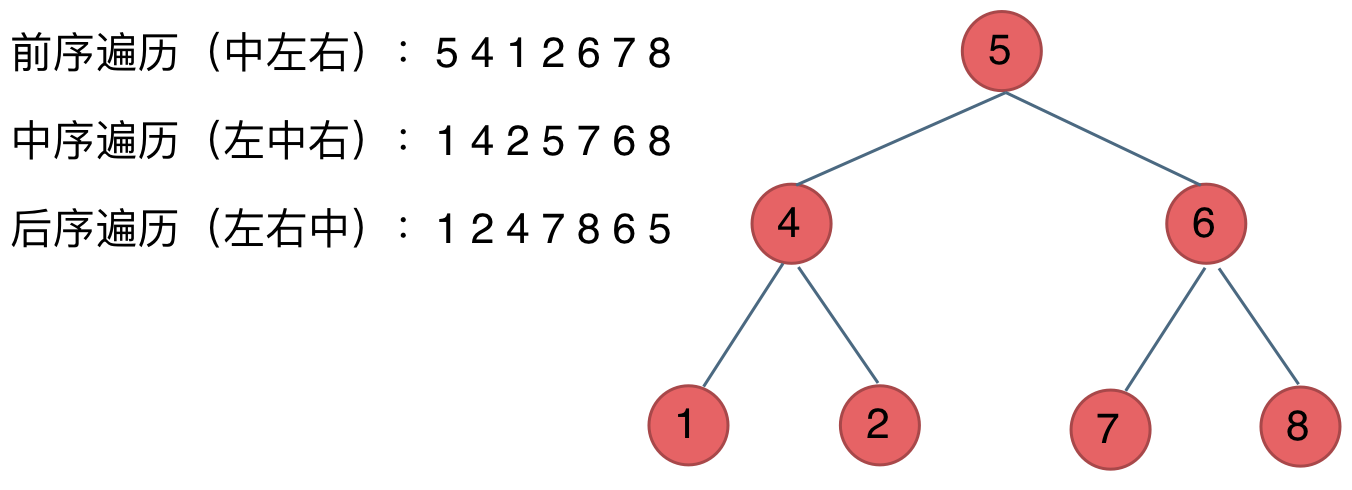 -
-最后再说一说二叉树中深度优先和广度优先遍历实现方式,我们做二叉树相关题目,经常会使用递归的方式来实现深度优先遍历,也就是实现前序、中序、后序遍历,使用递归是比较方便的。
-
-**之前我们讲栈与队列的时候,就说过栈其实就是递归的一种是实现结构**,也就说前序、中序、后序遍历的逻辑其实都是可以借助栈使用非递归的方式来实现的。
-
-而广度优先遍历的实现一般使用队列来实现,这也是队列先进先出的特点所决定的,因为需要先进先出的结构,才能一层一层的来遍历二叉树。
-
-**这里其实我们又了解了栈与队列的一个应用场景了。**
-
-具体的实现我们后面都会讲的,这里大家先要清楚这些理论基础。
-
-## 二叉树的定义
-
-刚刚我们说过了二叉树有两种存储方式顺序存储,和链式存储,顺序存储就是用数组来存,这个定义没啥可说的,我们来看看链式存储的二叉树节点的定义方式。
-
-
-C++代码如下:
-
-```
-struct TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode *left;
- TreeNode *right;
- TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
-};
-```
-
-大家会发现二叉树的定义 和链表是差不多的,相对于链表 ,二叉树的节点里多了一个指针, 有两个指针,指向左右孩子.
-
-这里要提醒大家要注意二叉树节点定义的书写方式。
-
-**在现场面试的时候 面试官可能要求手写代码,所以数据结构的定义以及简单逻辑的代码一定要锻炼白纸写出来。**
-
-因为我们在刷leetcode的时候,节点的定义默认都定义好了,真到面试的时候,需要自己写节点定义的时候,有时候会一脸懵逼!
-
-## 总结
-
-二叉树是一种基础数据结构,在算法面试中都是常客,也是众多数据结构的基石。
-
-本篇我们介绍了二叉树的种类、存储方式、遍历方式以及定义,比较全面的介绍了二叉树各个方面的重点,帮助大家扫一遍基础。
-
-**说道二叉树,就不得不说递归,很多同学对递归都是又熟悉又陌生,递归的代码一般很简短,但每次都是一看就会,一写就废。**
-
-
-
-## 其他语言版本
-
-
-Java:
-
-
-Python:
-
-
-Go:
-
-
-
-
------------------------
-* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
-* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
-* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)
-
-
-最后再说一说二叉树中深度优先和广度优先遍历实现方式,我们做二叉树相关题目,经常会使用递归的方式来实现深度优先遍历,也就是实现前序、中序、后序遍历,使用递归是比较方便的。
-
-**之前我们讲栈与队列的时候,就说过栈其实就是递归的一种是实现结构**,也就说前序、中序、后序遍历的逻辑其实都是可以借助栈使用非递归的方式来实现的。
-
-而广度优先遍历的实现一般使用队列来实现,这也是队列先进先出的特点所决定的,因为需要先进先出的结构,才能一层一层的来遍历二叉树。
-
-**这里其实我们又了解了栈与队列的一个应用场景了。**
-
-具体的实现我们后面都会讲的,这里大家先要清楚这些理论基础。
-
-## 二叉树的定义
-
-刚刚我们说过了二叉树有两种存储方式顺序存储,和链式存储,顺序存储就是用数组来存,这个定义没啥可说的,我们来看看链式存储的二叉树节点的定义方式。
-
-
-C++代码如下:
-
-```
-struct TreeNode {
- int val;
- TreeNode *left;
- TreeNode *right;
- TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
-};
-```
-
-大家会发现二叉树的定义 和链表是差不多的,相对于链表 ,二叉树的节点里多了一个指针, 有两个指针,指向左右孩子.
-
-这里要提醒大家要注意二叉树节点定义的书写方式。
-
-**在现场面试的时候 面试官可能要求手写代码,所以数据结构的定义以及简单逻辑的代码一定要锻炼白纸写出来。**
-
-因为我们在刷leetcode的时候,节点的定义默认都定义好了,真到面试的时候,需要自己写节点定义的时候,有时候会一脸懵逼!
-
-## 总结
-
-二叉树是一种基础数据结构,在算法面试中都是常客,也是众多数据结构的基石。
-
-本篇我们介绍了二叉树的种类、存储方式、遍历方式以及定义,比较全面的介绍了二叉树各个方面的重点,帮助大家扫一遍基础。
-
-**说道二叉树,就不得不说递归,很多同学对递归都是又熟悉又陌生,递归的代码一般很简短,但每次都是一看就会,一写就废。**
-
-
-
-## 其他语言版本
-
-
-Java:
-
-
-Python:
-
-
-Go:
-
-
-
-
------------------------
-* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
-* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
-* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)
-




















 +
+* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FwIiPPmR18_AJO5eiidT6w)
+* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/M4uHxNVKRKm5HPjkNZBnFA)
+* [动态规划:分割等和子集可以用01背包!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sYw3QtPPQ5HMZCJcT4EaLQ)
+* [动态规划:最后一块石头的重量 II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WbwAo3jaUaNJjvhHgq0BGg)
+* [动态规划:目标和!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2pWmaohX75gwxvBENS-NCw)
+* [动态规划:一和零!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/x-u3Dsp76DlYqtCe0xEKJw)
+* [动态规划:关于完全背包,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/akwyxlJ4TLvKcw26KB9uJw)
+* [动态规划:给你一些零钱,你要怎么凑?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PlowDsI4WMBOzf3q80AksQ)
+* [动态规划:Carl称它为排列总和!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Iixw0nahJWQgbqVNk8k6gA)
+* [动态规划:以前我没得选,现在我选择再爬一次!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/e_wacnELo-2PG76EjrUakA)
+* [动态规划: 给我个机会,我再兑换一次零钱](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dyk-xNilHzNtVdPPLObSeQ)
+* [动态规划:一样的套路,再求一次完全平方数](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VfJT78p7UGpDZsapKF_QJQ)
+* [动态规划:单词拆分](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3Spx1B6MbIYjS8YkVbByzA)
+* [动态规划:关于多重背包,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b-UUUmbvG7URWyCjQkiuuQ)
+* [听说背包问题很难? 这篇总结篇来拯救你了](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZOehl3U1mDiyOQjFG1wNJA)
+
+## 打家劫舍系列
+
+* [动态规划:开始打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UZ31WdLEEFmBegdgLkJ8Dw)
+* [动态规划:继续打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kKPx4HpH3RArbRcxAVHbeQ)
+* [动态规划:还要打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BOJ1lHsxbQxUZffXlgglEQ)
+
+## 股票系列
+
+
+
+* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FwIiPPmR18_AJO5eiidT6w)
+* [动态规划:关于01背包问题,你该了解这些!(滚动数组)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/M4uHxNVKRKm5HPjkNZBnFA)
+* [动态规划:分割等和子集可以用01背包!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sYw3QtPPQ5HMZCJcT4EaLQ)
+* [动态规划:最后一块石头的重量 II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WbwAo3jaUaNJjvhHgq0BGg)
+* [动态规划:目标和!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2pWmaohX75gwxvBENS-NCw)
+* [动态规划:一和零!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/x-u3Dsp76DlYqtCe0xEKJw)
+* [动态规划:关于完全背包,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/akwyxlJ4TLvKcw26KB9uJw)
+* [动态规划:给你一些零钱,你要怎么凑?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PlowDsI4WMBOzf3q80AksQ)
+* [动态规划:Carl称它为排列总和!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Iixw0nahJWQgbqVNk8k6gA)
+* [动态规划:以前我没得选,现在我选择再爬一次!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/e_wacnELo-2PG76EjrUakA)
+* [动态规划: 给我个机会,我再兑换一次零钱](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dyk-xNilHzNtVdPPLObSeQ)
+* [动态规划:一样的套路,再求一次完全平方数](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VfJT78p7UGpDZsapKF_QJQ)
+* [动态规划:单词拆分](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/3Spx1B6MbIYjS8YkVbByzA)
+* [动态规划:关于多重背包,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b-UUUmbvG7URWyCjQkiuuQ)
+* [听说背包问题很难? 这篇总结篇来拯救你了](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZOehl3U1mDiyOQjFG1wNJA)
+
+## 打家劫舍系列
+
+* [动态规划:开始打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UZ31WdLEEFmBegdgLkJ8Dw)
+* [动态规划:继续打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kKPx4HpH3RArbRcxAVHbeQ)
+* [动态规划:还要打家劫舍!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BOJ1lHsxbQxUZffXlgglEQ)
+
+## 股票系列
+
+ +
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/keWo5qYJY4zmHn3amfXdfQ)
+* [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列六)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GVu-6eF0iNkpVDKRXTPOTA)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/d4TRWFuhaY83HPa6t5ZL-w)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机III](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Sbs157mlVDtAR0gbLpdKzg)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机IV](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jtxZJWAo2y5sUsW647Z5cw)
+* [动态规划:最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/TczJGFAPnkjH9ET8kwH1OA)
+* [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列七)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vdzDlrEvhXWRzblTnOnzKg)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2Cd_uINjerZ25VHH0K2IBQ)
+* [动态规划:股票系列总结篇](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sC5XyEtDQWkonKnbCvZhDw)
+
+## 子序列系列
+
+
+
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/keWo5qYJY4zmHn3amfXdfQ)
+* [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列六)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GVu-6eF0iNkpVDKRXTPOTA)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机II](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/d4TRWFuhaY83HPa6t5ZL-w)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机III](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Sbs157mlVDtAR0gbLpdKzg)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机IV](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jtxZJWAo2y5sUsW647Z5cw)
+* [动态规划:最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/TczJGFAPnkjH9ET8kwH1OA)
+* [动态规划:本周我们都讲了这些(系列七)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vdzDlrEvhXWRzblTnOnzKg)
+* [动态规划:买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2Cd_uINjerZ25VHH0K2IBQ)
+* [动态规划:股票系列总结篇](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sC5XyEtDQWkonKnbCvZhDw)
+
+## 子序列系列
+
+ +
+* [动态规划:最长递增子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/f8nLO3JGfgriXep_gJQpqQ)
+* [动态规划:最长连续递增序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/c0Nn0TtjkTISVdqRsyMmyA)
+* [动态规划:最长重复子数组](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/U5WaWqBwdoxzQDotOdWqZg)
+* [动态规划:最长公共子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Qq0q4HaE4TyasCTj2WGFOg)
+* [动态规划:不相交的线](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/krfYzSYEO8jIoVfyHzR0rw)
+* [动态规划:最大子序和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2Xtyi2L4r8sM-BcxgUKmcA)
+* [动态规划:判断子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2pjT4B4fjfOx5iB6N6xyng)
+* [动态规划:不同的子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/1SULY2XVSROtk_hsoVLu8A)
+* [动态规划:两个字符串的删除操作](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/a8BerpqSf76DCqkPDJrpYg)
+* [动态规划:编辑距离](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8aG71XjSgZG6kZbiAdkJnQ)
+* [为了绝杀编辑距离,我做了三步铺垫,你都知道么?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kbs4kCUzg8gPFttF9H3Yyw)
+* [动态规划:回文子串](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2WetyP6IYQ6VotegepVpEw)
+* [动态规划:最长回文子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jbd3p4QPm5Kh1s2smTzWag)
+
+
+## 动规结束语
+
+关于动规,还有 树形DP(打家劫舍系列里有一道),数位DP,区间DP ,概率型DP,博弈型DP,状态压缩dp等等等,这些我就不去做讲解了,面试中出现的概率非常低。
+
+能把本篇中列举的题目都研究通透的话,你的动规水平就已经非常高了。 对付面试已经足够!
+
+这已经是全网对动规最深刻的讲解系列了。
+
+**其实大家去网上搜一搜也可以发现,能把动态规划讲清楚的资料挺少的,因为动规确实很难!要给别人讲清楚更难!**
+
+《剑指offer》上 动规的题目很少,经典的算法书籍《算法4》 没有讲 动规,而《算法导论》讲的动规基本属于劝退级别的。
+
+讲清楚一道题容易,讲清楚两道题也容易,但把整个动态规划的各个分支讲清楚,每道题目讲通透,并用一套方法论把整个动规贯彻始终就非常难了。
+
+所以Carl花费的这么大精力,把自己对动规算法理解 一五一十的全部分享给了录友们,帮助大家少走弯路!
+
+**至于动态规划PDF,即将在公众号「代码随想录」全网首发!**
+
+最后感谢录友们的一路支持,Carl才有继续更下去的动力[玫瑰],[撒花]
+
+
+-----------------------
+* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
+* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
+* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)
+
+
+* [动态规划:最长递增子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/f8nLO3JGfgriXep_gJQpqQ)
+* [动态规划:最长连续递增序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/c0Nn0TtjkTISVdqRsyMmyA)
+* [动态规划:最长重复子数组](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/U5WaWqBwdoxzQDotOdWqZg)
+* [动态规划:最长公共子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Qq0q4HaE4TyasCTj2WGFOg)
+* [动态规划:不相交的线](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/krfYzSYEO8jIoVfyHzR0rw)
+* [动态规划:最大子序和](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2Xtyi2L4r8sM-BcxgUKmcA)
+* [动态规划:判断子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2pjT4B4fjfOx5iB6N6xyng)
+* [动态规划:不同的子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/1SULY2XVSROtk_hsoVLu8A)
+* [动态规划:两个字符串的删除操作](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/a8BerpqSf76DCqkPDJrpYg)
+* [动态规划:编辑距离](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8aG71XjSgZG6kZbiAdkJnQ)
+* [为了绝杀编辑距离,我做了三步铺垫,你都知道么?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kbs4kCUzg8gPFttF9H3Yyw)
+* [动态规划:回文子串](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/2WetyP6IYQ6VotegepVpEw)
+* [动态规划:最长回文子序列](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jbd3p4QPm5Kh1s2smTzWag)
+
+
+## 动规结束语
+
+关于动规,还有 树形DP(打家劫舍系列里有一道),数位DP,区间DP ,概率型DP,博弈型DP,状态压缩dp等等等,这些我就不去做讲解了,面试中出现的概率非常低。
+
+能把本篇中列举的题目都研究通透的话,你的动规水平就已经非常高了。 对付面试已经足够!
+
+这已经是全网对动规最深刻的讲解系列了。
+
+**其实大家去网上搜一搜也可以发现,能把动态规划讲清楚的资料挺少的,因为动规确实很难!要给别人讲清楚更难!**
+
+《剑指offer》上 动规的题目很少,经典的算法书籍《算法4》 没有讲 动规,而《算法导论》讲的动规基本属于劝退级别的。
+
+讲清楚一道题容易,讲清楚两道题也容易,但把整个动态规划的各个分支讲清楚,每道题目讲通透,并用一套方法论把整个动规贯彻始终就非常难了。
+
+所以Carl花费的这么大精力,把自己对动规算法理解 一五一十的全部分享给了录友们,帮助大家少走弯路!
+
+**至于动态规划PDF,即将在公众号「代码随想录」全网首发!**
+
+最后感谢录友们的一路支持,Carl才有继续更下去的动力[玫瑰],[撒花]
+
+
+-----------------------
+* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
+* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
+* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)
+


 -
-
-首先slow进环的时候,fast一定是先进环来了。
-
-如果slow进环入口,fast也在环入口,那么把这个环展开成直线,就是如下图的样子:
-
-
-
-
-首先slow进环的时候,fast一定是先进环来了。
-
-如果slow进环入口,fast也在环入口,那么把这个环展开成直线,就是如下图的样子:
-
- -
-可以看出如果slow 和 fast同时在环入口开始走,一定会在环入口3相遇,slow走了一圈,fast走了两圈。
-
-重点来了,slow进环的时候,fast一定是在环的任意一个位置,如图:
-
-
-
-可以看出如果slow 和 fast同时在环入口开始走,一定会在环入口3相遇,slow走了一圈,fast走了两圈。
-
-重点来了,slow进环的时候,fast一定是在环的任意一个位置,如图:
-
- -
-那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。
-
-因为k是小于n的(图中可以看出),所以(k + n) / 2 一定小于n。
-
-**也就是说slow一定没有走到环入口3,而fast已经到环入口3了**。
-
-这说明什么呢?
-
-**在slow开始走的那一环已经和fast相遇了**。
-
-那有同学又说了,为什么fast不能跳过去呢? 在刚刚已经说过一次了,**fast相对于slow是一次移动一个节点,所以不可能跳过去**。
-
-好了,这次把为什么第一次在环中相遇,slow的 步数 是 x+y 而不是 x + 若干环的长度 + y ,用数学推理了一下,算是对[链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_QVP3IkRZWx9zIpQRgajzA)的补充。
-
-这次可以说把环形链表这道题目的各个细节,完完整整的证明了一遍,说这是全网最详细讲解不为过吧,哈哈。
-
-# 总结
+## 总结
考察链表的操作其实就是考察指针的操作,是面试中的常见类型。
链表篇中开头介绍[链表理论知识](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/slM1CH5Ew9XzK93YOQYSjA),然后分别通过经典题目介绍了如下知识点:
-* [虚拟头结点的技巧](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/slM1CH5Ew9XzK93YOQYSjA)
-* [链表的增删改查](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Cf95Lc6brKL4g2j8YyF3Mg)
-* [反转一个链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pnvVP-0ZM7epB8y3w_Njwg)
-* [有否环形,以及环的入口](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_QVP3IkRZWx9zIpQRgajzA)
+1. [关于链表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fDGMmLrW7ZHlzkzlf_dZkw)
+2. [虚拟头结点的技巧](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/L5aanfALdLEwVWGvyXPDqA)
+3. [链表的增删改查](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jnC_LAD0ZKCsj-FZc57F1g)
+4. [反转一个链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ckEvIVGcNLfrz6OLOMoT0A)
+5. [删除倒数第N个节点](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gxu65X1343xW_sBrkTz0Eg)
+6. [链表相交](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BhfFfaGvt9Zs7UmH4YehZw)
+7. [有否环形,以及环的入口](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gt_VH3hQTqNxyWcl1ECSbQ)
-虽然这几篇文章都是几个月前发的了,但在在文章留言区,可以看到很多录友都在从头打卡!
-
-如果希望从基础学起来的同学,也可以从头学起来,从头开始打卡,打卡的同时也总结自己的所学所思,一定进步飞快!
-
-
-
-## 其他语言版本
-
-
-Java:
-
-
-Python:
-
-
-Go:
diff --git a/problems/链表理论基础.md b/problems/链表理论基础.md
index 1dee1182..252247c7 100644
--- a/problems/链表理论基础.md
+++ b/problems/链表理论基础.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-
-
-那么fast指针走到环入口3的时候,已经走了k + n 个节点,slow相应的应该走了(k + n) / 2 个节点。
-
-因为k是小于n的(图中可以看出),所以(k + n) / 2 一定小于n。
-
-**也就是说slow一定没有走到环入口3,而fast已经到环入口3了**。
-
-这说明什么呢?
-
-**在slow开始走的那一环已经和fast相遇了**。
-
-那有同学又说了,为什么fast不能跳过去呢? 在刚刚已经说过一次了,**fast相对于slow是一次移动一个节点,所以不可能跳过去**。
-
-好了,这次把为什么第一次在环中相遇,slow的 步数 是 x+y 而不是 x + 若干环的长度 + y ,用数学推理了一下,算是对[链表:环找到了,那入口呢?](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_QVP3IkRZWx9zIpQRgajzA)的补充。
-
-这次可以说把环形链表这道题目的各个细节,完完整整的证明了一遍,说这是全网最详细讲解不为过吧,哈哈。
-
-# 总结
+## 总结
考察链表的操作其实就是考察指针的操作,是面试中的常见类型。
链表篇中开头介绍[链表理论知识](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/slM1CH5Ew9XzK93YOQYSjA),然后分别通过经典题目介绍了如下知识点:
-* [虚拟头结点的技巧](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/slM1CH5Ew9XzK93YOQYSjA)
-* [链表的增删改查](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Cf95Lc6brKL4g2j8YyF3Mg)
-* [反转一个链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/pnvVP-0ZM7epB8y3w_Njwg)
-* [有否环形,以及环的入口](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_QVP3IkRZWx9zIpQRgajzA)
+1. [关于链表,你该了解这些!](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fDGMmLrW7ZHlzkzlf_dZkw)
+2. [虚拟头结点的技巧](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/L5aanfALdLEwVWGvyXPDqA)
+3. [链表的增删改查](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jnC_LAD0ZKCsj-FZc57F1g)
+4. [反转一个链表](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ckEvIVGcNLfrz6OLOMoT0A)
+5. [删除倒数第N个节点](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gxu65X1343xW_sBrkTz0Eg)
+6. [链表相交](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BhfFfaGvt9Zs7UmH4YehZw)
+7. [有否环形,以及环的入口](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/gt_VH3hQTqNxyWcl1ECSbQ)
-虽然这几篇文章都是几个月前发的了,但在在文章留言区,可以看到很多录友都在从头打卡!
-
-如果希望从基础学起来的同学,也可以从头学起来,从头开始打卡,打卡的同时也总结自己的所学所思,一定进步飞快!
-
-
-
-## 其他语言版本
-
-
-Java:
-
-
-Python:
-
-
-Go:
diff --git a/problems/链表理论基础.md b/problems/链表理论基础.md
index 1dee1182..252247c7 100644
--- a/problems/链表理论基础.md
+++ b/problems/链表理论基础.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-