
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 763.划分字母区间
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-labels/)
字符串 S 由小写字母组成。我们要把这个字符串划分为尽可能多的片段,同一字母最多出现在一个片段中。返回一个表示每个字符串片段的长度的列表。
示例:
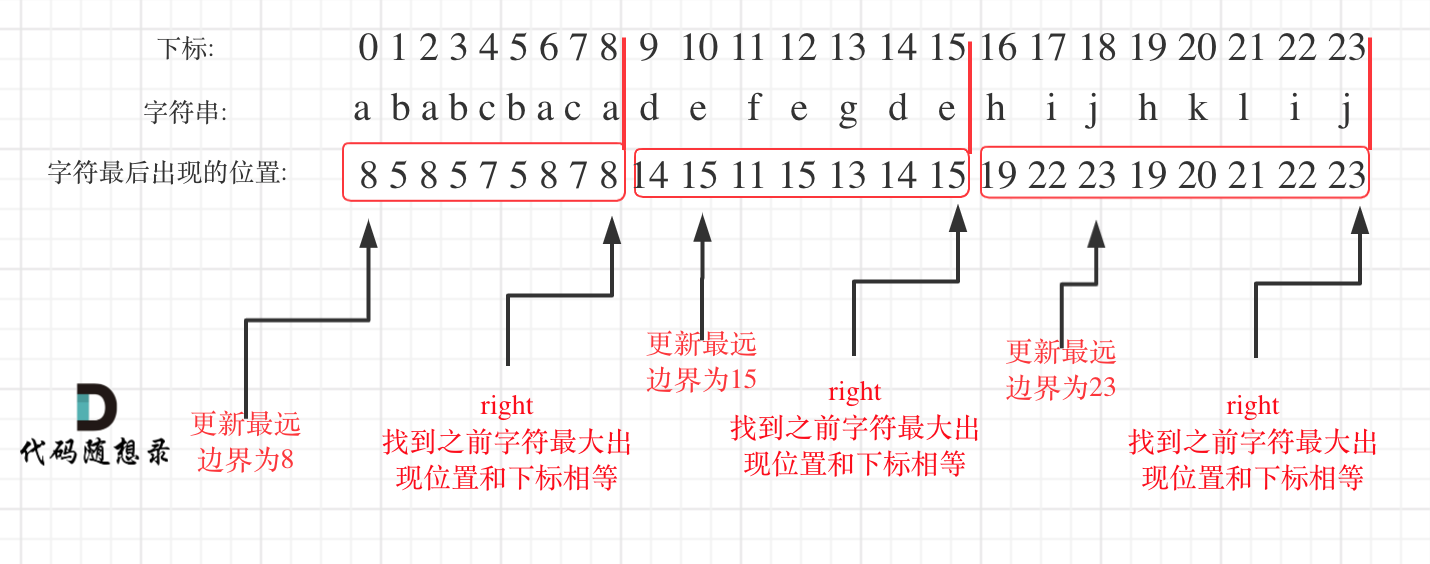
* 输入:S = "ababcbacadefegdehijhklij"
* 输出:[9,7,8]
解释:
划分结果为 "ababcbaca", "defegde", "hijhklij"。
每个字母最多出现在一个片段中。
像 "ababcbacadefegde", "hijhklij" 的划分是错误的,因为划分的片段数较少。
提示:
* S的长度在[1, 500]之间。
* S只包含小写字母 'a' 到 'z' 。
## 思路
一想到分割字符串就想到了回溯,但本题其实不用回溯去暴力搜索。
题目要求同一字母最多出现在一个片段中,那么如何把同一个字母的都圈在同一个区间里呢?
如果没有接触过这种题目的话,还挺有难度的。
在遍历的过程中相当于是要找每一个字母的边界,**如果找到之前遍历过的所有字母的最远边界,说明这个边界就是分割点了**。此时前面出现过所有字母,最远也就到这个边界了。
可以分为如下两步:
* 统计每一个字符最后出现的位置
* 从头遍历字符,并更新字符的最远出现下标,如果找到字符最远出现位置下标和当前下标相等了,则找到了分割点
如图:
明白原理之后,代码并不复杂,如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
vector partitionLabels(string S) {
int hash[27] = {0}; // i为字符,hash[i]为字符出现的最后位置
for (int i = 0; i < S.size(); i++) { // 统计每一个字符最后出现的位置
hash[S[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
vector result;
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < S.size(); i++) {
right = max(right, hash[S[i] - 'a']); // 找到字符出现的最远边界
if (i == right) {
result.push_back(right - left + 1);
left = i + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
};
```
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$,使用的hash数组是固定大小
## 总结
这道题目leetcode标记为贪心算法,说实话,我没有感受到贪心,找不出局部最优推出全局最优的过程。就是用最远出现距离模拟了圈字符的行为。
但这道题目的思路是很巧妙的,所以有必要介绍给大家做一做,感受一下。
## 补充
这里提供一种与[452.用最少数量的箭引爆气球](https://programmercarl.com/0452.用最少数量的箭引爆气球.html)、[435.无重叠区间](https://programmercarl.com/0435.无重叠区间.html)相同的思路。
统计字符串中所有字符的起始和结束位置,记录这些区间(实际上也就是[435.无重叠区间](https://programmercarl.com/0435.无重叠区间.html)题目里的输入),**将区间按左边界从小到大排序,找到边界将区间划分成组,互不重叠。找到的边界就是答案。**
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(vector &a, vector &b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
}
// 记录每个字母出现的区间
vector> countLabels(string s) {
vector> hash(26, vector(2, INT_MIN));
vector> hash_filter;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
if (hash[s[i] - 'a'][0] == INT_MIN) {
hash[s[i] - 'a'][0] = i;
}
hash[s[i] - 'a'][1] = i;
}
// 去除字符串中未出现的字母所占用区间
for (int i = 0; i < hash.size(); ++i) {
if (hash[i][0] != INT_MIN) {
hash_filter.push_back(hash[i]);
}
}
return hash_filter;
}
vector partitionLabels(string s) {
vector res;
// 这一步得到的 hash 即为无重叠区间题意中的输入样例格式:区间列表
// 只不过现在我们要求的是区间分割点
vector> hash = countLabels(s);
// 按照左边界从小到大排序
sort(hash.begin(), hash.end(), cmp);
// 记录最大右边界
int rightBoard = hash[0][1];
int leftBoard = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < hash.size(); ++i) {
// 由于字符串一定能分割,因此,
// 一旦下一区间左边界大于当前右边界,即可认为出现分割点
if (hash[i][0] > rightBoard) {
res.push_back(rightBoard - leftBoard + 1);
leftBoard = hash[i][0];
}
rightBoard = max(rightBoard, hash[i][1]);
}
// 最右端
res.push_back(rightBoard - leftBoard + 1);
return res;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
### Java
```java
class Solution {
public List partitionLabels(String S) {
List list = new LinkedList<>();
int[] edge = new int[26];
char[] chars = S.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
edge[chars[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
int idx = 0;
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
idx = Math.max(idx,edge[chars[i] - 'a']);
if (i == idx) {
list.add(i - last);
last = i;
}
}
return list;
}
}
class Solution{
/*解法二: 上述c++补充思路的Java代码实现*/
public int[][] findPartitions(String s) {
List temp = new ArrayList<>();
int[][] hash = new int[26][2];//26个字母2列 表示该字母对应的区间
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
//更新字符c对应的位置i
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (hash[c - 'a'][0] == 0) hash[c - 'a'][0] = i;
hash[c - 'a'][1] = i;
//第一个元素区别对待一下
hash[s.charAt(0) - 'a'][0] = 0;
}
List> h = new LinkedList<>();
//组装区间
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
//if (hash[i][0] != hash[i][1]) {
temp.clear();
temp.add(hash[i][0]);
temp.add(hash[i][1]);
//System.out.println(temp);
h.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
// }
}
// System.out.println(h);
// System.out.println(h.size());
int[][] res = new int[h.size()][2];
for (int i = 0; i < h.size(); i++) {
List list = h.get(i);
res[i][0] = list.get(0);
res[i][1] = list.get(1);
}
return res;
}
public List partitionLabels(String s) {
int[][] partitions = findPartitions(s);
List res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(partitions, (o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1[0], o2[0]));
int right = partitions[0][1];
int left = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < partitions.length; i++) {
if (partitions[i][0] > right) {
//左边界大于右边界即可纪委一次分割
res.add(right - left + 1);
left = partitions[i][0];
}
right = Math.max(right, partitions[i][1]);
}
//最右端
res.add(right - left + 1);
return res;
}
}
```
### Python
```python
class Solution:
def partitionLabels(self, s: str) -> List[int]:
hash = [0] * 26
for i in range(len(s)):
hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')] = i
result = []
left = 0
right = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
right = max(right, hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')])
if i == right:
result.append(right - left + 1)
left = i + 1
return result
```
### Go
```go
func partitionLabels(s string) []int {
var res []int;
var marks [26]int;
size, left, right := len(s), 0, 0;
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
marks[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
right = max(right, marks[s[i] - 'a']);
if i == right {
res = append(res, right - left + 1);
left = i + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
a = b;
}
return a;
}
```
### Javascript
```Javascript
var partitionLabels = function(s) {
let hash = {}
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
hash[s[i]] = i
}
let result = []
let left = 0
let right = 0
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
right = Math.max(right, hash[s[i]])
if(right === i) {
result.push(right - left + 1)
left = i + 1
}
}
return result
};
```
### TypeScript
```typescript
function partitionLabels(s: string): number[] {
const length: number = s.length;
const resArr: number[] = [];
const helperMap: Map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
helperMap.set(s[i], i);
}
let left: number = 0;
let right: number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
right = Math.max(helperMap.get(s[i])!, right);
if (i === right) {
resArr.push(i - left + 1);
left = i + 1;
}
}
return resArr;
};
```
### Scala
```scala
object Solution {
import scala.collection.mutable
def partitionLabels(s: String): List[Int] = {
var hash = new Array[Int](26)
for (i <- s.indices) {
hash(s(i) - 'a') = i
}
var res = mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
var (left, right) = (0, 0)
for (i <- s.indices) {
right = math.max(hash(s(i) - 'a'), right)
if (i == right) {
res.append(right - left + 1)
left = i + 1
}
}
res.toList
}
}
```
### Rust
```Rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
fn max (a: usize, b: usize) -> usize {
if a > b { a } else { b }
}
pub fn partition_labels(s: String) -> Vec {
let s = s.chars().collect::>();
let mut hash: HashMap = HashMap::new();
for i in 0..s.len() {
hash.insert(s[i], i);
}
let mut result: Vec = Vec::new();
let mut left: usize = 0;
let mut right: usize = 0;
for i in 0..s.len() {
right = Self::max(right, hash[&s[i]]);
if i == right {
result.push((right - left + 1) as i32);
left = i + 1;
}
}
result
}
}
```
-----------------------

