



欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
# 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
示例 1:
* 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
* 输出:6
示例 2:
* 输入:root = []
* 输出:0
示例 3:
* 输入:root = [1]
* 输出:1
提示:
* 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
* 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
* 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
# 思路
本篇给出按照普通二叉树的求法以及利用完全二叉树性质的求法。
## 普通二叉树
首先按照普通二叉树的逻辑来求。
这道题目的递归法和求二叉树的深度写法类似, 而迭代法,[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)遍历模板稍稍修改一下,记录遍历的节点数量就可以了。
递归遍历的顺序依然是后序(左右中)。
### 递归
如果对求二叉树深度还不熟悉的话,看这篇:[二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](https://programmercarl.com/0104.二叉树的最大深度.html)。
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回以该节点为根节点二叉树的节点数量,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
```
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
```
2. 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示节点数为0。
代码如下:
```
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
```
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的节点数量,再求的右子树的节点数量,最后取总和再加一 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的节点数量。
代码如下:
```
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur->left); // 左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur->right); // 右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; // 中
return treeNum;
```
所以整体C++代码如下:
```CPP
// 版本一
class Solution {
private:
int getNodesNum(TreeNode* cur) {
if (cur == 0) return 0;
int leftNum = getNodesNum(cur->left); // 左
int rightNum = getNodesNum(cur->right); // 右
int treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1; // 中
return treeNum;
}
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return getNodesNum(root);
}
};
```
代码精简之后C++代码如下:
```CPP
// 版本二
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
};
```
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O(logn),算上了递归系统栈占用的空间
**网上基本都是这个精简的代码版本,其实不建议大家照着这个来写,代码确实精简,但隐藏了一些内容,连遍历的顺序都看不出来,所以初学者建议学习版本一的代码,稳稳的打基础**。
### 迭代法
如果对求二叉树层序遍历还不熟悉的话,看这篇:[二叉树:层序遍历登场!](https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html)。
那么只要模板少做改动,加一个变量result,统计节点数量就可以了
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
queue que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int result = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
result++; // 记录节点数量
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return result;
}
};
```
* 时间复杂度:O(n)
* 空间复杂度:O(n)
## 完全二叉树
以上方法都是按照普通二叉树来做的,对于完全二叉树特性不了解的同学可以看这篇 [关于二叉树,你该了解这些!](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树理论基础.html),这篇详细介绍了各种二叉树的特性。
完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:就是满二叉树,情况二:最后一层叶子节点没有满。
对于情况一,可以直接用 2^树深度 - 1 来计算,注意这里根节点深度为1。
对于情况二,分别递归左孩子,和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,然后依然可以按照情况1来计算。
完全二叉树(一)如图:
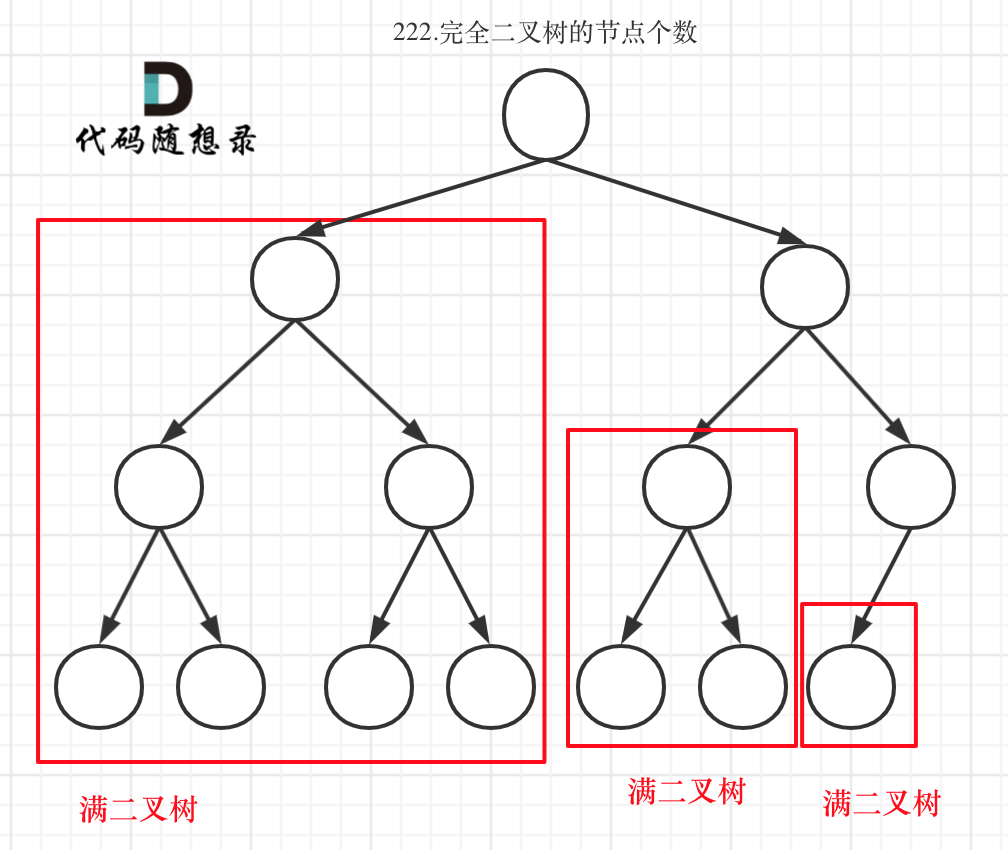
完全二叉树(二)如图:

可以看出如果整个树不是满二叉树,就递归其左右孩子,直到遇到满二叉树为止,用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量。
C++代码如下:
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftHeight = 0, rightHeight = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left) { // 求左子树深度
left = left->left;
leftHeight++;
}
while (right) { // 求右子树深度
right = right->right;
rightHeight++;
}
if (leftHeight == rightHeight) {
return (2 << leftHeight) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftHeight初始为0
}
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};
```
* 时间复杂度:O(logn * logn)
* 空间复杂度:O(logn)
# 其他语言版本
## Java
```java
class Solution {
// 通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
```
```java
class Solution {
// 迭代法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result++;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return result;
}
}
```
```java
class Solution {
/**
* 针对完全二叉树的解法
*
* 满二叉树的结点数为:2^depth - 1
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right);
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {// 左子树是满二叉树
// 2^leftDepth其实是 (2^leftDepth - 1) + 1 ,左子树 + 根结点
return (1 << leftDepth) + countNodes(root.right);
} else {// 右子树是满二叉树
return (1 << rightDepth) + countNodes(root.left);
}
}
private int getDepth(TreeNode root) {
int depth = 0;
while (root != null) {
root = root.left;
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
```
## Python
递归法:
```python
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
return self.getNodesNum(root)
def getNodesNum(self, cur):
if not cur:
return 0
leftNum = self.getNodesNum(cur.left) #左
rightNum = self.getNodesNum(cur.right) #右
treeNum = leftNum + rightNum + 1 #中
return treeNum
```
递归法:精简版
```python
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right)
```
迭代法:
```python
import collections
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
queue = collections.deque()
if root:
queue.append(root)
result = 0
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for i in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
result += 1 #记录节点数量
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return result
```
完全二叉树
```python
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left = root.left
right = root.right
leftHeight = 0 #这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
rightHeight = 0
while left: #求左子树深度
left = left.left
leftHeight += 1
while right: #求右子树深度
right = right.right
rightHeight += 1
if leftHeight == rightHeight:
return (2 << leftHeight) - 1 #注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftHeight初始为0
return self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right) + 1
```
## Go
递归版本
```go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
//本题直接就是求有多少个节点,无脑存进数组算长度就行了。
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
res := 1
if root.Right != nil {
res += countNodes(root.Right)
}
if root.Left != nil {
res += countNodes(root.Left)
}
return res
}
```
利用完全二叉树特性的递归解法
```go
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftH, rightH := 0, 0
leftNode := root.Left
rightNode := root.Right
for leftNode != nil {
leftNode = leftNode.Left
leftH++
}
for rightNode != nil {
rightNode = rightNode.Right
rightH++
}
if leftH == rightH {
return (2 << leftH) - 1
}
return countNodes(root.Left) + countNodes(root.Right) + 1
}
```
## JavaScript:
递归版本
```javascript
var countNodes = function(root) {
//递归法计算二叉树节点数
// 1. 确定递归函数参数
const getNodeSum=function(node){
//2. 确定终止条件
if(node===null){
return 0;
}
//3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let leftNum=getNodeSum(node.left);
let rightNum=getNodeSum(node.right);
return leftNum+rightNum+1;
}
return getNodeSum(root);
};
```
迭代(层序遍历)版本
```javascript
var countNodes = function(root) {
//层序遍历
let queue=[];
if(root===null){
return 0;
}
queue.push(root);
let nodeNums=0;
while(queue.length){
let length=queue.length;
while(length--){
let node=queue.shift();
nodeNums++;
node.left&&queue.push(node.left);
node.right&&queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return nodeNums;
};
```
利用完全二叉树性质
```javascript
var countNodes = function(root) {
//利用完全二叉树的特点
if(root===null){
return 0;
}
let left=root.left;
let right=root.right;
let leftHeight=0,rightHeight=0;
while(left){
left=left.left;
leftHeight++;
}
while(right){
right=right.right;
rightHeight++;
}
if(leftHeight==rightHeight){
return Math.pow(2,leftHeight+1)-1;
}
return countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right)+1;
};
```
-----------------------
* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)




