
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
# 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 同:160.链表相交 [力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/) 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。 图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交: 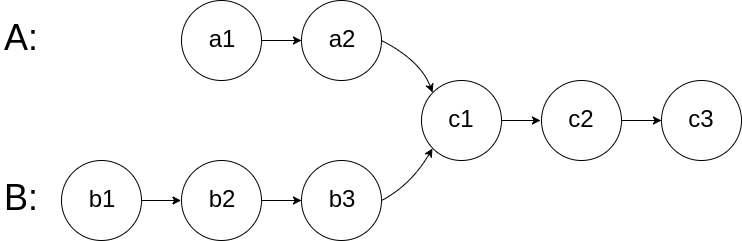 题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。 注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。 示例 1: 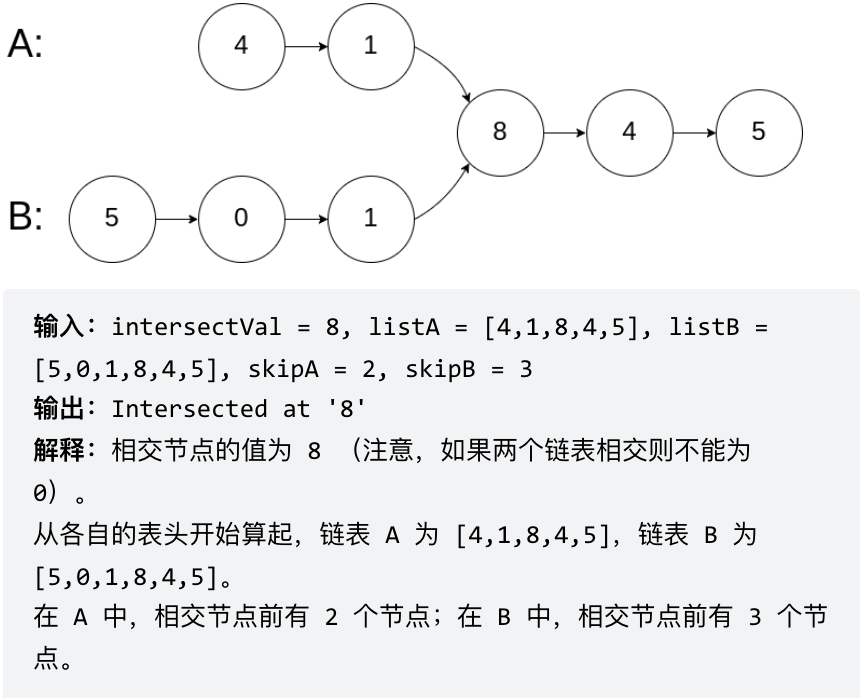 示例 2: 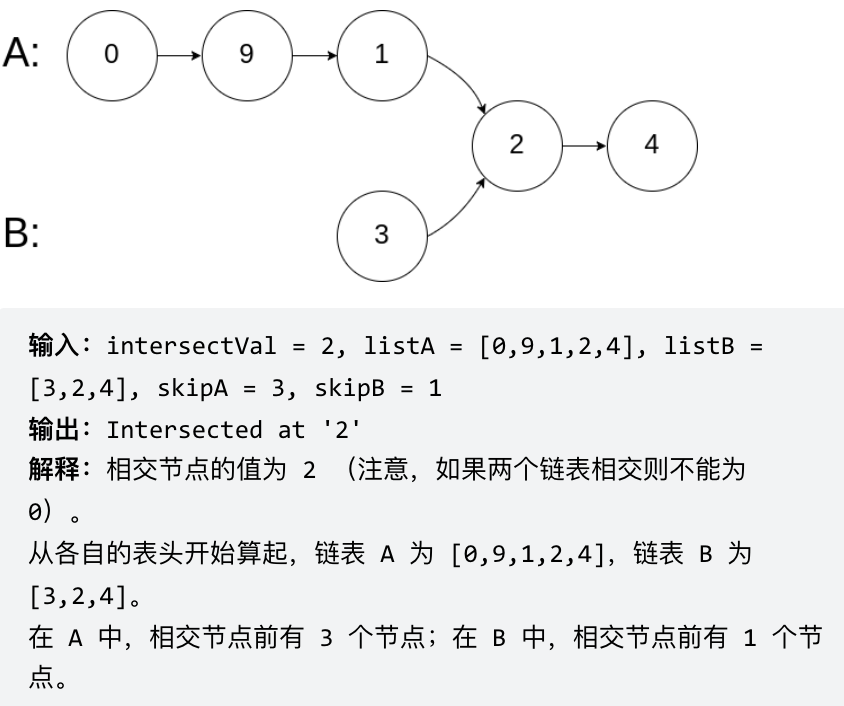 示例 3: 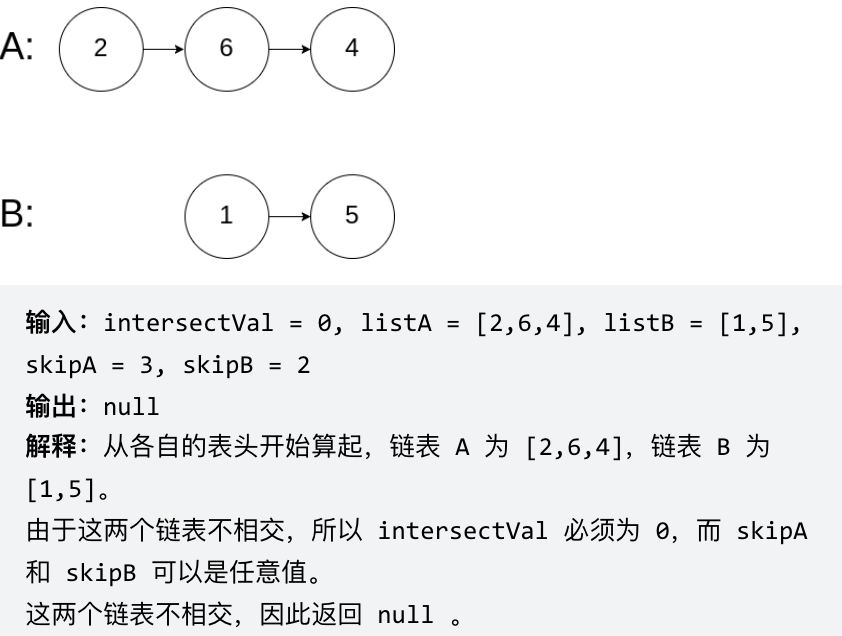 ## 思路 简单来说,就是求两个链表交点节点的**指针**。 这里同学们要注意,交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等。 为了方便举例,假设节点元素数值相等,则节点指针相等。 看如下两个链表,目前curA指向链表A的头结点,curB指向链表B的头结点:  我们求出两个链表的长度,并求出两个链表长度的差值,然后让curA移动到,和curB 末尾对齐的位置,如图:  此时我们就可以比较curA和curB是否相同,如果不相同,同时向后移动curA和curB,如果遇到curA == curB,则找到交点。 否则循环退出返回空指针。 C++代码如下: ```CPP class Solution { public: ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { ListNode* curA = headA; ListNode* curB = headB; int lenA = 0, lenB = 0; while (curA != NULL) { // 求链表A的长度 lenA++; curA = curA->next; } while (curB != NULL) { // 求链表B的长度 lenB++; curB = curB->next; } curA = headA; curB = headB; // 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度 if (lenB > lenA) { swap (lenA, lenB); swap (curA, curB); } // 求长度差 int gap = lenA - lenB; // 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐) while (gap--) { curA = curA->next; } // 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回 while (curA != NULL) { if (curA == curB) { return curA; } curA = curA->next; curB = curB->next; } return NULL; } }; ``` * 时间复杂度:O(n + m) * 空间复杂度:O(1) ## 其他语言版本 ### Java: ```Java (版本一)先行移动长链表实现同步移动 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode curA = headA; ListNode curB = headB; int lenA = 0, lenB = 0; while (curA != null) { // 求链表A的长度 lenA++; curA = curA.next; } while (curB != null) { // 求链表B的长度 lenB++; curB = curB.next; } curA = headA; curB = headB; // 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度 if (lenB > lenA) { //1. swap (lenA, lenB); int tmpLen = lenA; lenA = lenB; lenB = tmpLen; //2. swap (curA, curB); ListNode tmpNode = curA; curA = curB; curB = tmpNode; } // 求长度差 int gap = lenA - lenB; // 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐) while (gap-- > 0) { curA = curA.next; } // 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回 while (curA != null) { if (curA == curB) { return curA; } curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return null; } } (版本二) 合并链表实现同步移动 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { // p1 指向 A 链表头结点,p2 指向 B 链表头结点 ListNode p1 = headA, p2 = headB; while (p1 != p2) { // p1 走一步,如果走到 A 链表末尾,转到 B 链表 if (p1 == null) p1 = headB; else p1 = p1.next; // p2 走一步,如果走到 B 链表末尾,转到 A 链表 if (p2 == null) p2 = headA; else p2 = p2.next; } return p1; } } ``` ### Python: ```python (版本一)求长度,同时出发 class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: lenA, lenB = 0, 0 cur = headA while cur: # 求链表A的长度 cur = cur.next lenA += 1 cur = headB while cur: # 求链表B的长度 cur = cur.next lenB += 1 curA, curB = headA, headB if lenA > lenB: # 让curB为最长链表的头,lenB为其长度 curA, curB = curB, curA lenA, lenB = lenB, lenA for _ in range(lenB - lenA): # 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐) curB = curB.next while curA: # 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回 if curA == curB: return curA else: curA = curA.next curB = curB.next return None ``` ```python (版本二)求长度,同时出发 (代码复用) class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: lenA = self.getLength(headA) lenB = self.getLength(headB) # 通过移动较长的链表,使两链表长度相等 if lenA > lenB: headA = self.moveForward(headA, lenA - lenB) else: headB = self.moveForward(headB, lenB - lenA) # 将两个头向前移动,直到它们相交 while headA and headB: if headA == headB: return headA headA = headA.next headB = headB.next return None def getLength(self, head: ListNode) -> int: length = 0 while head: length += 1 head = head.next return length def moveForward(self, head: ListNode, steps: int) -> ListNode: while steps > 0: head = head.next steps -= 1 return head ``` ```python (版本三)求长度,同时出发 (代码复用 + 精简) class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: dis = self.getLength(headA) - self.getLength(headB) # 通过移动较长的链表,使两链表长度相等 if dis > 0: headA = self.moveForward(headA, dis) else: headB = self.moveForward(headB, abs(dis)) # 将两个头向前移动,直到它们相交 while headA and headB: if headA == headB: return headA headA = headA.next headB = headB.next return None def getLength(self, head: ListNode) -> int: length = 0 while head: length += 1 head = head.next return length def moveForward(self, head: ListNode, steps: int) -> ListNode: while steps > 0: head = head.next steps -= 1 return head ``` ```python (版本四)等比例法 # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: # 处理边缘情况 if not headA or not headB: return None # 在每个链表的头部初始化两个指针 pointerA = headA pointerB = headB # 遍历两个链表直到指针相交 while pointerA != pointerB: # 将指针向前移动一个节点 pointerA = pointerA.next if pointerA else headB pointerB = pointerB.next if pointerB else headA # 如果相交,指针将位于交点节点,如果没有交点,值为None return pointerA ``` ### Go: ```go func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { curA := headA curB := headB lenA, lenB := 0, 0 // 求A,B的长度 for curA != nil { curA = curA.Next lenA++ } for curB != nil { curB = curB.Next lenB++ } var step int var fast, slow *ListNode // 请求长度差,并且让更长的链表先走相差的长度 if lenA > lenB { step = lenA - lenB fast, slow = headA, headB } else { step = lenB - lenA fast, slow = headB, headA } for i:=0; i < step; i++ { fast = fast.Next } // 遍历两个链表遇到相同则跳出遍历 for fast != slow { fast = fast.Next slow = slow.Next } return fast } ``` 双指针 ```go func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { l1,l2 := headA, headB for l1 != l2 { if l1 != nil { l1 = l1.Next } else { l1 = headB } if l2 != nil { l2 = l2.Next } else { l2 = headA } } return l1 } ``` ### JavaScript: ```js var getListLen = function(head) { let len = 0, cur = head; while(cur) { len++; cur = cur.next; } return len; } var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) { let curA = headA,curB = headB, lenA = getListLen(headA), // 求链表A的长度 lenB = getListLen(headB); if(lenA < lenB) { // 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度 // 交换变量注意加 “分号” ,两个数组交换变量在同一个作用域下时 // 如果不加分号,下面两条代码等同于一条代码: [curA, curB] = [lenB, lenA] [curA, curB] = [curB, curA]; [lenA, lenB] = [lenB, lenA]; } let i = lenA - lenB; // 求长度差 while(i-- > 0) { // 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐) curA = curA.next; } while(curA && curA !== curB) { // 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回 curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return curA; }; ``` ### TypeScript: ```typescript function getIntersectionNode(headA: ListNode | null, headB: ListNode | null): ListNode | null { let sizeA: number = 0, sizeB: number = 0; let curA: ListNode | null = headA, curB: ListNode | null = headB; while (curA) { sizeA++; curA = curA.next; } while (curB) { sizeB++; curB = curB.next; } curA = headA; curB = headB; if (sizeA < sizeB) { [sizeA, sizeB] = [sizeB, sizeA]; [curA, curB] = [curB, curA]; } let gap = sizeA - sizeB; while (gap-- && curA) { curA = curA.next; } while (curA && curB) { if (curA === curB) { return curA; } curA = curA.next; curB = curB.next; } return null; }; ``` ### C: ```c ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { ListNode *l = NULL, *s = NULL; int lenA = 0, lenB = 0, gap = 0; // 求出两个链表的长度 s = headA; while (s) { lenA ++; s = s->next; } s = headB; while (s) { lenB ++; s = s->next; } // 求出两个链表长度差 if (lenA > lenB) { l = headA, s = headB; gap = lenA - lenB; } else { l = headB, s = headA; gap = lenB - lenA; } // 尾部对齐 while (gap--) l = l->next; // 移动,并检查是否有相同的元素 while (l) { if (l == s) return l; l = l->next, s = s->next; } return NULL; } ``` ### Scala: ```scala object Solution { def getIntersectionNode(headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode): ListNode = { var lenA = 0 // headA链表的长度 var lenB = 0 // headB链表的长度 var tmp = headA // 临时变量 // 统计headA的长度 while (tmp != null) { lenA += 1; tmp = tmp.next } // 统计headB的长度 tmp = headB // 临时变量赋值给headB while (tmp != null) { lenB += 1 tmp = tmp.next } // 因为传递过来的参数是不可变量,所以需要重新定义 var listA = headA var listB = headB // 两个链表的长度差 // 如果gap>0,lenA>lenB,headA(listA)链表往前移动gap步 // 如果gap<0,lenA