
参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
> 链表操作中,可以使用原链表来直接进行删除操作,也可以设置一个虚拟头结点再进行删除操作,接下来看一看哪种方式更方便。 # 203.移除链表元素 [力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/) 题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。 示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5] 示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[] 示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[] # 思路 为了方便大家理解,我特意录制了视频:[链表基础操作| LeetCode:203.移除链表元素](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18B4y1s7R9),结合视频在看本题解,事半功倍。 这里以链表 1 4 2 4 来举例,移除元素4。 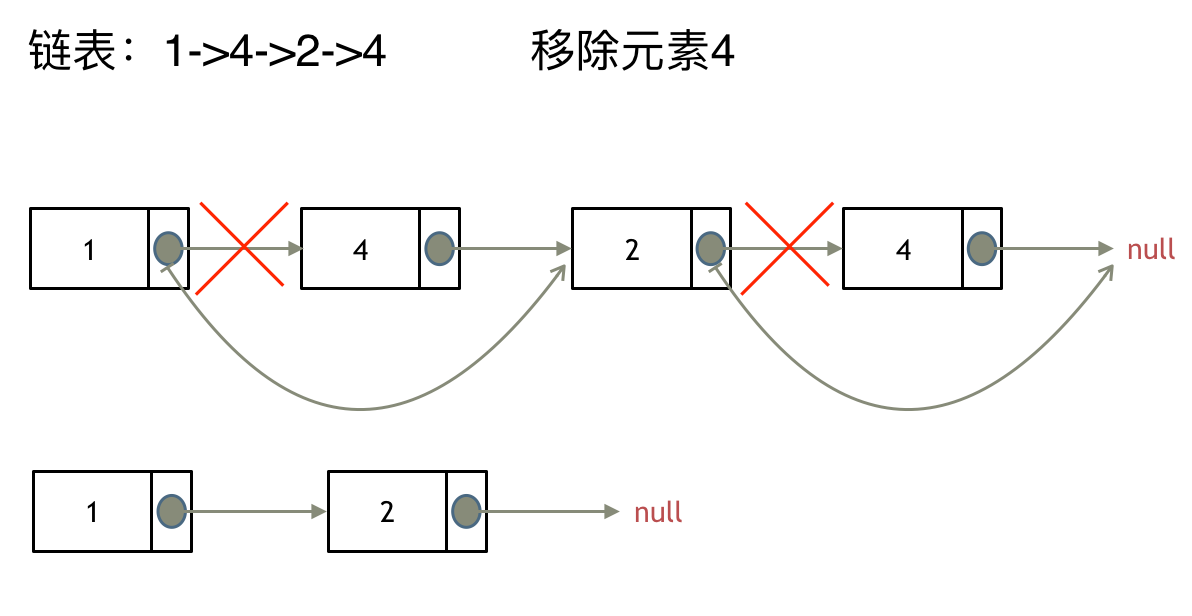 如果使用C,C++编程语言的话,不要忘了还要从内存中删除这两个移除的节点, 清理节点内存之后如图: 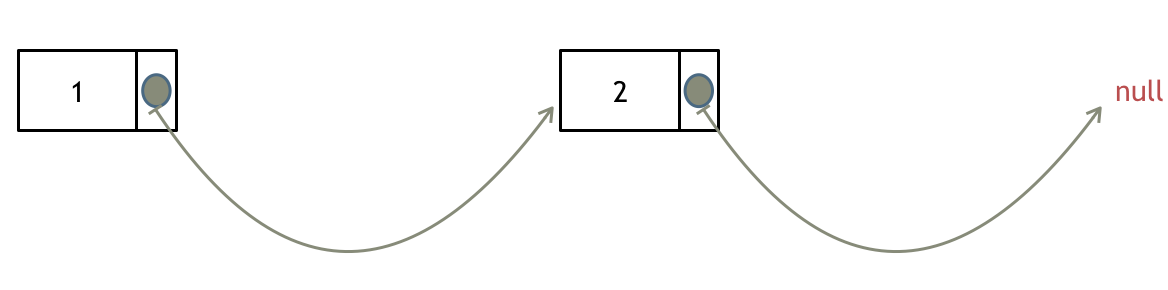 **当然如果使用java ,python的话就不用手动管理内存了。** 还要说明一下,就算使用C++来做leetcode,如果移除一个节点之后,没有手动在内存中删除这个节点,leetcode依然也是可以通过的,只不过,内存使用的空间大一些而已,但建议依然要养成手动清理内存的习惯。 这种情况下的移除操作,就是让节点next指针直接指向下下一个节点就可以了, 那么因为单链表的特殊性,只能指向下一个节点,刚刚删除的是链表的中第二个,和第四个节点,那么如果删除的是头结点又该怎么办呢? 这里就涉及如下链表操作的两种方式: * **直接使用原来的链表来进行删除操作。** * **设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。** 来看第一种操作:直接使用原来的链表来进行移除。 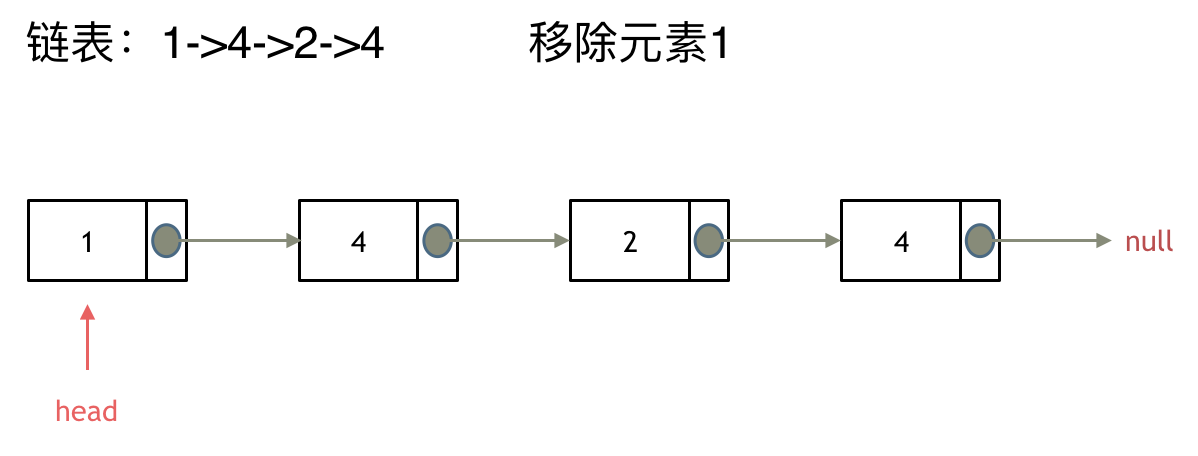 移除头结点和移除其他节点的操作是不一样的,因为链表的其他节点都是通过前一个节点来移除当前节点,而头结点没有前一个节点。 所以头结点如何移除呢,其实只要将头结点向后移动一位就可以,这样就从链表中移除了一个头结点。 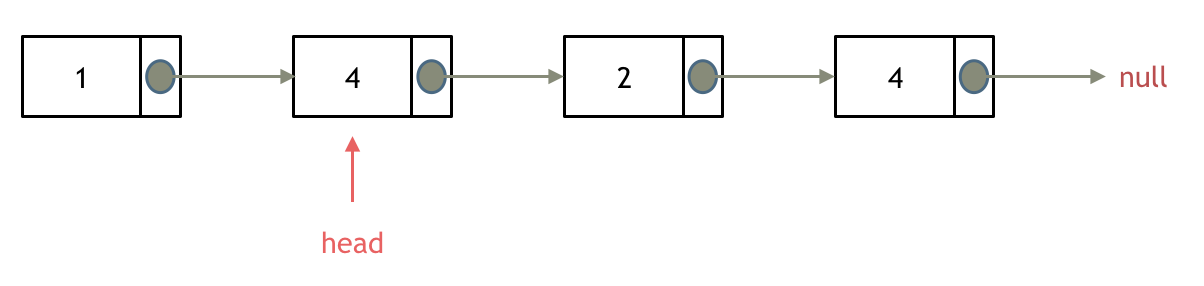 依然别忘将原头结点从内存中删掉。  这样移除了一个头结点,是不是发现,在单链表中移除头结点 和 移除其他节点的操作方式是不一样,其实在写代码的时候也会发现,需要单独写一段逻辑来处理移除头结点的情况。 那么可不可以 以一种统一的逻辑来移除 链表的节点呢。 其实**可以设置一个虚拟头结点**,这样原链表的所有节点就都可以按照统一的方式进行移除了。 来看看如何设置一个虚拟头。依然还是在这个链表中,移除元素1。 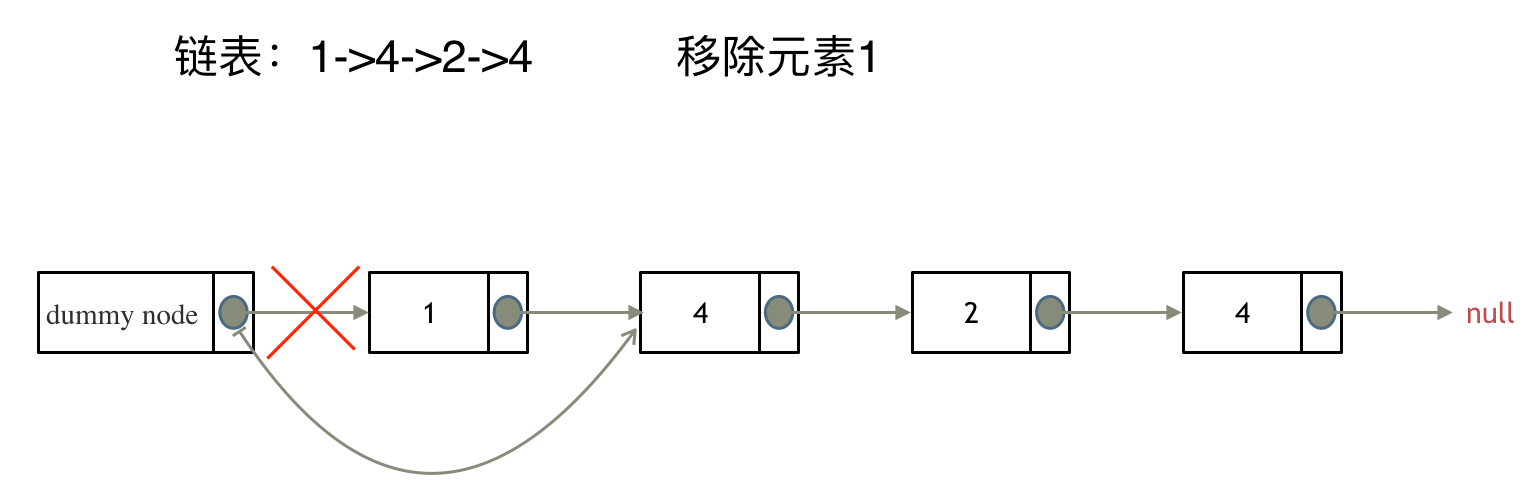 这里来给链表添加一个虚拟头结点为新的头结点,此时要移除这个旧头结点元素1。 这样是不是就可以使用和移除链表其他节点的方式统一了呢? 来看一下,如何移除元素1 呢,还是熟悉的方式,然后从内存中删除元素1。 最后呢在题目中,return 头结点的时候,别忘了 `return dummyNode->next;`, 这才是新的头结点 # C++代码 **直接使用原来的链表来进行移除节点操作:** ```CPP class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { // 删除头结点 while (head != NULL && head->val == val) { // 注意这里不是if ListNode* tmp = head; head = head->next; delete tmp; } // 删除非头结点 ListNode* cur = head; while (cur != NULL && cur->next!= NULL) { if (cur->next->val == val) { ListNode* tmp = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; delete tmp; } else { cur = cur->next; } } return head; } }; ``` * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) **设置一个虚拟头结点在进行移除节点操作:** ```CPP class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // 设置一个虚拟头结点 dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方面后面做删除操作 ListNode* cur = dummyHead; while (cur->next != NULL) { if(cur->next->val == val) { ListNode* tmp = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; delete tmp; } else { cur = cur->next; } } head = dummyHead->next; delete dummyHead; return head; } }; ``` * 时间复杂度: O(n) * 空间复杂度: O(1) ## 其他语言版本 C: 用原来的链表操作: ```c struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* temp; // 当头结点存在并且头结点的值等于val时 while(head && head->val == val) { temp = head; // 将新的头结点设置为head->next并删除原来的头结点 head = head->next; free(temp); } struct ListNode *cur = head; // 当cur存在并且cur->next存在时 // 此解法需要判断cur存在因为cur指向head。若head本身为NULL或者原链表中元素都为val的话,cur也会为NULL while(cur && (temp = cur->next)) { // 若cur->next的值等于val if(temp->val == val) { // 将cur->next设置为cur->next->next并删除cur->next cur->next = temp->next; free(temp); } // 若cur->next不等于val,则将cur后移一位 else cur = cur->next; } // 返回头结点 return head; } ``` 设置一个虚拟头结点: ```c /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */ struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ typedef struct ListNode ListNode; ListNode *shead; shead = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); shead->next = head; ListNode *cur = shead; while(cur->next != NULL){ if (cur->next->val == val){ ListNode *tmp = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; free(tmp); } else{ cur = cur->next; } } head = shead->next; free(shead); return head; } ``` Java: ```java /** * 添加虚节点方式 * 时间复杂度 O(n) * 空间复杂度 O(1) * @param head * @param val * @return */ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if (head == null) { return head; } // 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head); ListNode pre = dummy; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == val) { pre.next = cur.next; } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return dummy.next; } /** * 不添加虚拟节点方式 * 时间复杂度 O(n) * 空间复杂度 O(1) * @param head * @param val * @return */ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while (head != null && head.val == val) { head = head.next; } // 已经为null,提前退出 if (head == null) { return head; } // 已确定当前head.val != val ListNode pre = head; ListNode cur = head.next; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val == val) { pre.next = cur.next; } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return head; } /** * 不添加虚拟节点and pre Node方式 * 时间复杂度 O(n) * 空间复杂度 O(1) * @param head * @param val * @return */ public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while(head!=null && head.val==val){ head = head.next; } ListNode curr = head; while(curr!=null){ while(curr.next!=null && curr.next.val == val){ curr.next = curr.next.next; } curr = curr.next; } return head; } ``` Python: ```python # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode: dummy_head = ListNode(next=head) #添加一个虚拟节点 cur = dummy_head while(cur.next!=None): if(cur.next.val == val): cur.next = cur.next.next #删除cur.next节点 else: cur = cur.next return dummy_head.next ``` Go: ```go /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode { dummyHead := &ListNode{} dummyHead.Next = head cur := dummyHead for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil { if cur.Next.Val == val { cur.Next = cur.Next.Next } else { cur = cur.Next } } return dummyHead.Next } ``` javaScript: ```js /** * @param {ListNode} head * @param {number} val * @return {ListNode} */ var removeElements = function(head, val) { const ret = new ListNode(0, head); let cur = ret; while(cur.next) { if(cur.next.val === val) { cur.next = cur.next.next; continue; } cur = cur.next; } return ret.next; }; ``` TypeScript: 版本一(在原链表上直接删除): ```typescript /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */ function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null { // 删除头部节点 while (head !== null && head.val === val) { head = head.next; } if (head === null) return head; let pre: ListNode = head, cur: ListNode | null = head.next; // 删除非头部节点 while (cur) { if (cur.val === val) { pre.next = cur.next; } else { //此处不加类型断言时:编译器会认为pre类型为ListNode, pre.next类型为ListNode | null pre = pre.next as ListNode; } cur = cur.next; } return head; }; ``` 版本二(虚拟头节点): ```typescript function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null { // 添加虚拟节点 const data = new ListNode(0, head); let pre = data, cur = data.next; while (cur) { if (cur.val === val) { pre.next = cur.next } else { pre = cur; } cur = cur.next; } return data.next; }; ``` Swift: ```swift /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * public var val: Int * public var next: ListNode? * public init() { self.val = 0; self.next = nil; } * public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.next = nil; } * public init(_ val: Int, _ next: ListNode?) { self.val = val; self.next = next; } * } */ func removeElements(_ head: ListNode?, _ val: Int) -> ListNode? { let dummyNode = ListNode() dummyNode.next = head var currentNode = dummyNode while let curNext = currentNode.next { if curNext.val == val { currentNode.next = curNext.next } else { currentNode = curNext } } return dummyNode.next } ``` PHP: ```php /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */ // 虚拟头+双指针 func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode { dummyHead := &ListNode{} dummyHead.Next = head pred := dummyHead cur := head for cur != nil { if cur.Val == val { pred.Next = cur.Next } else { pred = cur } cur = cur.Next } return dummyHead.Next } ``` RUST: ```rust // Definition for singly-linked list. // #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)] // pub struct ListNode { // pub val: i32, // pub next: Option