 > 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。
# 206.反转链表
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
# 思路
如果再定义一个新的链表,实现链表元素的反转,其实这是对内存空间的浪费。
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:
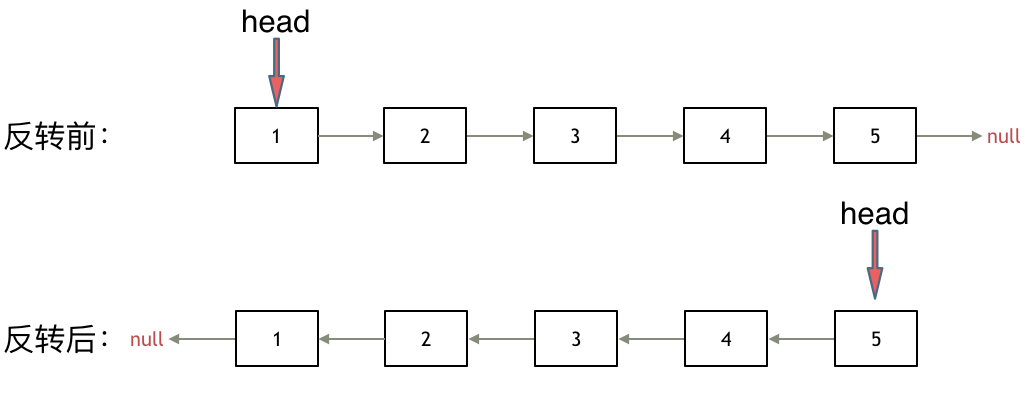
之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
那么接下来看一看是如何反转的呢?
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:

首先定义一个cur指针,指向头结点,再定义一个pre指针,初始化为null。
然后就要开始反转了,首先要把 cur->next 节点用tmp指针保存一下,也就是保存一下这个节点。
为什么要保存一下这个节点呢,因为接下来要改变 cur->next 的指向了,将cur->next 指向pre ,此时已经反转了第一个节点了。
接下来,就是循环走如下代码逻辑了,继续移动pre和cur指针。
最后,cur 指针已经指向了null,循环结束,链表也反转完毕了。 此时我们return pre指针就可以了,pre指针就指向了新的头结点。
# C++代码
## 双指针法
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur->next = pre; // 翻转操作
// 更新pre 和 cur指针
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
```
## 递归法
递归法相对抽象一些,但是其实和双指针法是一样的逻辑,同样是当cur为空的时候循环结束,不断将cur指向pre的过程。
关键是初始化的地方,可能有的同学会不理解, 可以看到双指针法中初始化 cur = head,pre = NULL,在递归法中可以从如下代码看出初始化的逻辑也是一样的,只不过写法变了。
具体可以看代码(已经详细注释),**双指针法写出来之后,理解如下递归写法就不难了,代码逻辑都是一样的。**
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};
```
我们可以发现,上面的递归写法和双指针法实质上都是从前往后翻转指针指向,其实还有另外一种与双指针法不同思路的递归写法:从后往前翻转指针指向。
具体代码如下(带详细注释):
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode *last = reverseList(head->next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head->next->next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head->next = NULL;
return last;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
Java:
```java
// 双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
```
```java
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
```
```java
// 从后向前递归
class Solution {
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head.next.next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
```
Python迭代法:
```python
#双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur.next = pre #反转
#更新pre、cur指针
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
```
Python递归法:
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(pre,cur):
if not cur:
return pre
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
return reverse(cur,tmp)
return reverse(None,head)
```
Go:
```go
//双指针
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
return help(nil, head)
}
func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{
if head == nil {
return pre
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = pre
return help(head, next)
}
```
javaScript:
```js
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 双指针:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// temp = cur = null;
return pre;
};
// 递归:
var reverse = function(pre, head) {
if(!head) return pre;
const temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head
return reverse(pre, temp);
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head);
};
// 递归2
var reverse = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
// 从后往前翻
const pre = reverse(head.next);
head.next = pre.next;
pre.next = head;
return head;
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
let cur = head;
while(cur && cur.next) {
cur = cur.next;
}
reverse(head);
return cur;
};
```
Ruby:
```ruby
# 双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
# return nil if head.nil? # 循环判断条件亦能起到相同作用因此不必单独判断
cur, per = head, nil
until cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = per
per = cur
cur = tem
end
per
end
# 递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
reverse(nil, head)
end
def reverse(pre, cur)
return pre if cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = pre
reverse(cur, tem) # 通过递归实现双指针法中的更新操作
end
```
Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
var pre: ListNode? = null
var cur = head
while (cur != null) {
val temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
```
Swift:
```swift
/// 双指针法 (迭代)
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
return head
}
var pre: ListNode? = nil
var cur: ListNode? = head
var temp: ListNode? = nil
while cur != nil {
temp = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
/// 递归
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList2(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return reverse(pre: nil, cur: head)
}
func reverse(pre: ListNode?, cur: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if cur == nil {
return pre
}
let temp: ListNode? = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
return reverse(pre: cur, cur: temp)
}
```
C:
双指针法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//保存cur的下一个结点
struct ListNode* temp;
//pre指针指向前一个当前结点的前一个结点
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
//用head代替cur,也可以再定义一个cur结点指向head。
while(head) {
//保存下一个结点的位置
temp = head->next;
//翻转操作
head->next = pre;
//更新结点
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}
```
递归法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* cur) {
if(!cur)
return pre;
struct ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
//将cur作为pre传入下一层
//将temp作为cur传入下一层,改变其指针指向当前cur
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
```
-----------------------
> 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。
# 206.反转链表
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
# 思路
如果再定义一个新的链表,实现链表元素的反转,其实这是对内存空间的浪费。
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:

之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
那么接下来看一看是如何反转的呢?
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:

首先定义一个cur指针,指向头结点,再定义一个pre指针,初始化为null。
然后就要开始反转了,首先要把 cur->next 节点用tmp指针保存一下,也就是保存一下这个节点。
为什么要保存一下这个节点呢,因为接下来要改变 cur->next 的指向了,将cur->next 指向pre ,此时已经反转了第一个节点了。
接下来,就是循环走如下代码逻辑了,继续移动pre和cur指针。
最后,cur 指针已经指向了null,循环结束,链表也反转完毕了。 此时我们return pre指针就可以了,pre指针就指向了新的头结点。
# C++代码
## 双指针法
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur->next = pre; // 翻转操作
// 更新pre 和 cur指针
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
```
## 递归法
递归法相对抽象一些,但是其实和双指针法是一样的逻辑,同样是当cur为空的时候循环结束,不断将cur指向pre的过程。
关键是初始化的地方,可能有的同学会不理解, 可以看到双指针法中初始化 cur = head,pre = NULL,在递归法中可以从如下代码看出初始化的逻辑也是一样的,只不过写法变了。
具体可以看代码(已经详细注释),**双指针法写出来之后,理解如下递归写法就不难了,代码逻辑都是一样的。**
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};
```
我们可以发现,上面的递归写法和双指针法实质上都是从前往后翻转指针指向,其实还有另外一种与双指针法不同思路的递归写法:从后往前翻转指针指向。
具体代码如下(带详细注释):
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode *last = reverseList(head->next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head->next->next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head->next = NULL;
return last;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
Java:
```java
// 双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
```
```java
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
```
```java
// 从后向前递归
class Solution {
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head.next.next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
```
Python迭代法:
```python
#双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur.next = pre #反转
#更新pre、cur指针
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
```
Python递归法:
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(pre,cur):
if not cur:
return pre
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
return reverse(cur,tmp)
return reverse(None,head)
```
Go:
```go
//双指针
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
return help(nil, head)
}
func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{
if head == nil {
return pre
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = pre
return help(head, next)
}
```
javaScript:
```js
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 双指针:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// temp = cur = null;
return pre;
};
// 递归:
var reverse = function(pre, head) {
if(!head) return pre;
const temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head
return reverse(pre, temp);
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head);
};
// 递归2
var reverse = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
// 从后往前翻
const pre = reverse(head.next);
head.next = pre.next;
pre.next = head;
return head;
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
let cur = head;
while(cur && cur.next) {
cur = cur.next;
}
reverse(head);
return cur;
};
```
Ruby:
```ruby
# 双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
# return nil if head.nil? # 循环判断条件亦能起到相同作用因此不必单独判断
cur, per = head, nil
until cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = per
per = cur
cur = tem
end
per
end
# 递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
reverse(nil, head)
end
def reverse(pre, cur)
return pre if cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = pre
reverse(cur, tem) # 通过递归实现双指针法中的更新操作
end
```
Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
var pre: ListNode? = null
var cur = head
while (cur != null) {
val temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
```
Swift:
```swift
/// 双指针法 (迭代)
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
return head
}
var pre: ListNode? = nil
var cur: ListNode? = head
var temp: ListNode? = nil
while cur != nil {
temp = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
/// 递归
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList2(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return reverse(pre: nil, cur: head)
}
func reverse(pre: ListNode?, cur: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if cur == nil {
return pre
}
let temp: ListNode? = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
return reverse(pre: cur, cur: temp)
}
```
C:
双指针法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//保存cur的下一个结点
struct ListNode* temp;
//pre指针指向前一个当前结点的前一个结点
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
//用head代替cur,也可以再定义一个cur结点指向head。
while(head) {
//保存下一个结点的位置
temp = head->next;
//翻转操作
head->next = pre;
//更新结点
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}
```
递归法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* cur) {
if(!cur)
return pre;
struct ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
//将cur作为pre传入下一层
//将temp作为cur传入下一层,改变其指针指向当前cur
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
```
-----------------------

 > 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。
# 206.反转链表
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
# 思路
如果再定义一个新的链表,实现链表元素的反转,其实这是对内存空间的浪费。
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:

之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
那么接下来看一看是如何反转的呢?
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:

首先定义一个cur指针,指向头结点,再定义一个pre指针,初始化为null。
然后就要开始反转了,首先要把 cur->next 节点用tmp指针保存一下,也就是保存一下这个节点。
为什么要保存一下这个节点呢,因为接下来要改变 cur->next 的指向了,将cur->next 指向pre ,此时已经反转了第一个节点了。
接下来,就是循环走如下代码逻辑了,继续移动pre和cur指针。
最后,cur 指针已经指向了null,循环结束,链表也反转完毕了。 此时我们return pre指针就可以了,pre指针就指向了新的头结点。
# C++代码
## 双指针法
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur->next = pre; // 翻转操作
// 更新pre 和 cur指针
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
```
## 递归法
递归法相对抽象一些,但是其实和双指针法是一样的逻辑,同样是当cur为空的时候循环结束,不断将cur指向pre的过程。
关键是初始化的地方,可能有的同学会不理解, 可以看到双指针法中初始化 cur = head,pre = NULL,在递归法中可以从如下代码看出初始化的逻辑也是一样的,只不过写法变了。
具体可以看代码(已经详细注释),**双指针法写出来之后,理解如下递归写法就不难了,代码逻辑都是一样的。**
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};
```
我们可以发现,上面的递归写法和双指针法实质上都是从前往后翻转指针指向,其实还有另外一种与双指针法不同思路的递归写法:从后往前翻转指针指向。
具体代码如下(带详细注释):
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode *last = reverseList(head->next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head->next->next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head->next = NULL;
return last;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
Java:
```java
// 双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
```
```java
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
```
```java
// 从后向前递归
class Solution {
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head.next.next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
```
Python迭代法:
```python
#双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur.next = pre #反转
#更新pre、cur指针
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
```
Python递归法:
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(pre,cur):
if not cur:
return pre
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
return reverse(cur,tmp)
return reverse(None,head)
```
Go:
```go
//双指针
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
return help(nil, head)
}
func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{
if head == nil {
return pre
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = pre
return help(head, next)
}
```
javaScript:
```js
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 双指针:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// temp = cur = null;
return pre;
};
// 递归:
var reverse = function(pre, head) {
if(!head) return pre;
const temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head
return reverse(pre, temp);
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head);
};
// 递归2
var reverse = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
// 从后往前翻
const pre = reverse(head.next);
head.next = pre.next;
pre.next = head;
return head;
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
let cur = head;
while(cur && cur.next) {
cur = cur.next;
}
reverse(head);
return cur;
};
```
Ruby:
```ruby
# 双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
# return nil if head.nil? # 循环判断条件亦能起到相同作用因此不必单独判断
cur, per = head, nil
until cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = per
per = cur
cur = tem
end
per
end
# 递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
reverse(nil, head)
end
def reverse(pre, cur)
return pre if cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = pre
reverse(cur, tem) # 通过递归实现双指针法中的更新操作
end
```
Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
var pre: ListNode? = null
var cur = head
while (cur != null) {
val temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
```
Swift:
```swift
/// 双指针法 (迭代)
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
return head
}
var pre: ListNode? = nil
var cur: ListNode? = head
var temp: ListNode? = nil
while cur != nil {
temp = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
/// 递归
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList2(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return reverse(pre: nil, cur: head)
}
func reverse(pre: ListNode?, cur: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if cur == nil {
return pre
}
let temp: ListNode? = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
return reverse(pre: cur, cur: temp)
}
```
C:
双指针法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//保存cur的下一个结点
struct ListNode* temp;
//pre指针指向前一个当前结点的前一个结点
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
//用head代替cur,也可以再定义一个cur结点指向head。
while(head) {
//保存下一个结点的位置
temp = head->next;
//翻转操作
head->next = pre;
//更新结点
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}
```
递归法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* cur) {
if(!cur)
return pre;
struct ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
//将cur作为pre传入下一层
//将temp作为cur传入下一层,改变其指针指向当前cur
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
```
-----------------------
> 反转链表的写法很简单,一些同学甚至可以背下来但过一阵就忘了该咋写,主要是因为没有理解真正的反转过程。
# 206.反转链表
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
# 思路
如果再定义一个新的链表,实现链表元素的反转,其实这是对内存空间的浪费。
其实只需要改变链表的next指针的指向,直接将链表反转 ,而不用重新定义一个新的链表,如图所示:

之前链表的头节点是元素1, 反转之后头结点就是元素5 ,这里并没有添加或者删除节点,仅仅是改变next指针的方向。
那么接下来看一看是如何反转的呢?
我们拿有示例中的链表来举例,如动画所示:

首先定义一个cur指针,指向头结点,再定义一个pre指针,初始化为null。
然后就要开始反转了,首先要把 cur->next 节点用tmp指针保存一下,也就是保存一下这个节点。
为什么要保存一下这个节点呢,因为接下来要改变 cur->next 的指向了,将cur->next 指向pre ,此时已经反转了第一个节点了。
接下来,就是循环走如下代码逻辑了,继续移动pre和cur指针。
最后,cur 指针已经指向了null,循环结束,链表也反转完毕了。 此时我们return pre指针就可以了,pre指针就指向了新的头结点。
# C++代码
## 双指针法
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* temp; // 保存cur的下一个节点
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur) {
temp = cur->next; // 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur->next = pre; // 翻转操作
// 更新pre 和 cur指针
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
```
## 递归法
递归法相对抽象一些,但是其实和双指针法是一样的逻辑,同样是当cur为空的时候循环结束,不断将cur指向pre的过程。
关键是初始化的地方,可能有的同学会不理解, 可以看到双指针法中初始化 cur = head,pre = NULL,在递归法中可以从如下代码看出初始化的逻辑也是一样的,只不过写法变了。
具体可以看代码(已经详细注释),**双指针法写出来之后,理解如下递归写法就不难了,代码逻辑都是一样的。**
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* pre,ListNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
// 可以和双指针法的代码进行对比,如下递归的写法,其实就是做了这两步
// pre = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 和双指针法初始化是一样的逻辑
// ListNode* cur = head;
// ListNode* pre = NULL;
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
};
```
我们可以发现,上面的递归写法和双指针法实质上都是从前往后翻转指针指向,其实还有另外一种与双指针法不同思路的递归写法:从后往前翻转指针指向。
具体代码如下(带详细注释):
```CPP
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode *last = reverseList(head->next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head->next->next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head->next = NULL;
return last;
}
};
```
## 其他语言版本
Java:
```java
// 双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
```
```java
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
// prev = cur;
// cur = temp;
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
}
```
```java
// 从后向前递归
class Solution {
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 边缘条件判断
if(head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return head;
// 递归调用,翻转第二个节点开始往后的链表
ListNode last = reverseList(head.next);
// 翻转头节点与第二个节点的指向
head.next.next = head;
// 此时的 head 节点为尾节点,next 需要指向 NULL
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
```
Python迭代法:
```python
#双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
pre = None
while(cur!=None):
temp = cur.next # 保存一下 cur的下一个节点,因为接下来要改变cur->next
cur.next = pre #反转
#更新pre、cur指针
pre = cur
cur = temp
return pre
```
Python递归法:
```python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(pre,cur):
if not cur:
return pre
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
return reverse(cur,tmp)
return reverse(None,head)
```
Go:
```go
//双指针
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode
cur := head
for cur != nil {
next := cur.Next
cur.Next = pre
pre = cur
cur = next
}
return pre
}
//递归
func reverseList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
return help(nil, head)
}
func help(pre, head *ListNode)*ListNode{
if head == nil {
return pre
}
next := head.Next
head.Next = pre
return help(head, next)
}
```
javaScript:
```js
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
// 双指针:
var reverseList = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let temp = null, pre = null, cur = head;
while(cur) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
// temp = cur = null;
return pre;
};
// 递归:
var reverse = function(pre, head) {
if(!head) return pre;
const temp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head
return reverse(pre, temp);
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
return reverse(null, head);
};
// 递归2
var reverse = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
// 从后往前翻
const pre = reverse(head.next);
head.next = pre.next;
pre.next = head;
return head;
}
var reverseList = function(head) {
let cur = head;
while(cur && cur.next) {
cur = cur.next;
}
reverse(head);
return cur;
};
```
Ruby:
```ruby
# 双指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
# return nil if head.nil? # 循环判断条件亦能起到相同作用因此不必单独判断
cur, per = head, nil
until cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = per
per = cur
cur = tem
end
per
end
# 递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
def reverse_list(head)
reverse(nil, head)
end
def reverse(pre, cur)
return pre if cur.nil?
tem = cur.next
cur.next = pre
reverse(cur, tem) # 通过递归实现双指针法中的更新操作
end
```
Kotlin:
```Kotlin
fun reverseList(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
var pre: ListNode? = null
var cur = head
while (cur != null) {
val temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
```
Swift:
```swift
/// 双指针法 (迭代)
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if head == nil || head?.next == nil {
return head
}
var pre: ListNode? = nil
var cur: ListNode? = head
var temp: ListNode? = nil
while cur != nil {
temp = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = temp
}
return pre
}
/// 递归
/// - Parameter head: 头结点
/// - Returns: 翻转后的链表头结点
func reverseList2(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
return reverse(pre: nil, cur: head)
}
func reverse(pre: ListNode?, cur: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
if cur == nil {
return pre
}
let temp: ListNode? = cur?.next
cur?.next = pre
return reverse(pre: cur, cur: temp)
}
```
C:
双指针法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
//保存cur的下一个结点
struct ListNode* temp;
//pre指针指向前一个当前结点的前一个结点
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
//用head代替cur,也可以再定义一个cur结点指向head。
while(head) {
//保存下一个结点的位置
temp = head->next;
//翻转操作
head->next = pre;
//更新结点
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}
```
递归法:
```c
struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* cur) {
if(!cur)
return pre;
struct ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
//将cur作为pre传入下一层
//将temp作为cur传入下一层,改变其指针指向当前cur
return reverse(cur, temp);
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
```
-----------------------
