347 lines
9.6 KiB
Markdown
347 lines
9.6 KiB
Markdown
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="./qita/join.md">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
# 110. 字符串接龙
|
||
|
||
[卡码网题目链接(ACM模式)](https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1183)
|
||
|
||
题目描述
|
||
|
||
字典 strList 中从字符串 beginStr 和 endStr 的转换序列是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
|
||
|
||
1. 序列中第一个字符串是 beginStr。
|
||
|
||
2. 序列中最后一个字符串是 endStr。
|
||
|
||
3. 每次转换只能改变一个字符。
|
||
|
||
4. 转换过程中的中间字符串必须是字典 strList 中的字符串。
|
||
|
||
给你两个字符串 beginStr 和 endStr 和一个字典 strList,找到从 beginStr 到 endStr 的最短转换序列中的字符串数目。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
|
||
|
||
输入描述
|
||
|
||
第一行包含一个整数 N,表示字典 strList 中的字符串数量。 第二行包含两个字符串,用空格隔开,分别代表 beginStr 和 endStr。 后续 N 行,每行一个字符串,代表 strList 中的字符串。
|
||
|
||
输出描述
|
||
|
||
输出一个整数,代表从 beginStr 转换到 endStr 需要的最短转换序列中的字符串数量。如果不存在这样的转换序列,则输出 0。
|
||
|
||
输入示例
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
6
|
||
abc def
|
||
efc
|
||
dbc
|
||
ebc
|
||
dec
|
||
dfc
|
||
yhn
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
输出示例
|
||
|
||
4
|
||
|
||
提示信息
|
||
|
||
从 startStr 到 endStr,在 strList 中最短的路径为 abc -> dbc -> dec -> def,所以输出结果为 4
|
||
|
||
数据范围:
|
||
|
||
2 <= N <= 500
|
||
|
||
<p>
|
||
<img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20240529121038.png" alt="" width="50%" />
|
||
</p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
以示例1为例,从这个图中可以看出 abc 到 def的路线 不止一条,但最短的一条路径上是4个节点。
|
||
|
||
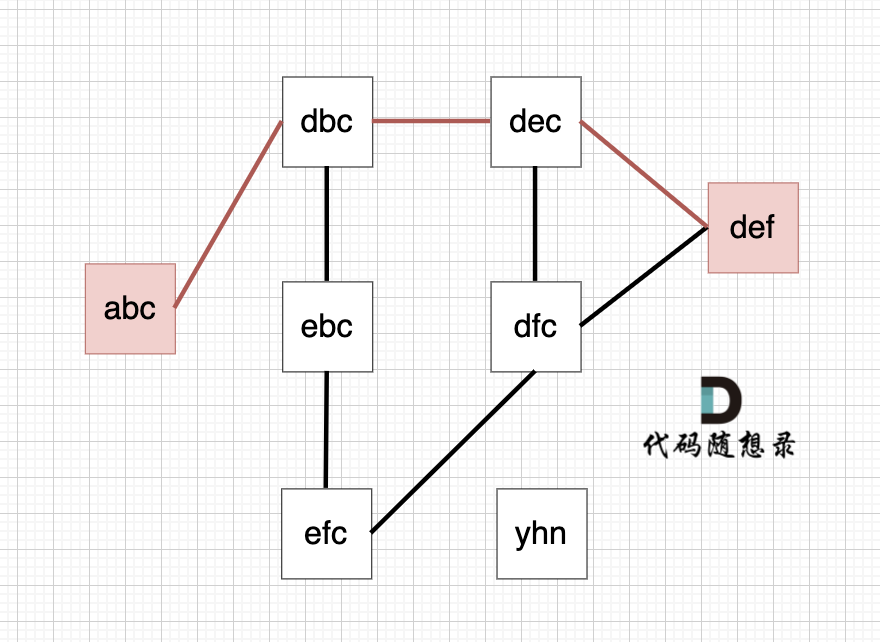
|
||
|
||
本题只需要求出最短路径的长度就可以了,不用找出具体路径。
|
||
|
||
所以这道题要解决两个问题:
|
||
|
||
* 图中的线是如何连在一起的
|
||
* 起点和终点的最短路径长度
|
||
|
||
首先题目中并没有给出点与点之间的连线,而是要我们自己去连,条件是字符只能差一个。
|
||
|
||
所以判断点与点之间的关系,需要判断是不是差一个字符,**如果差一个字符,那就是有链接**。
|
||
|
||
然后就是求起点和终点的最短路径长度,**这里无向图求最短路,广搜最为合适,广搜只要搜到了终点,那么一定是最短的路径**。因为广搜就是以起点中心向四周扩散的搜索。
|
||
|
||
**本题如果用深搜,会比较麻烦,要在到达终点的不同路径中选则一条最短路**。 而广搜只要达到终点,一定是最短路。
|
||
|
||
另外需要有一个注意点:
|
||
|
||
* 本题是一个无向图,需要用标记位,标记着节点是否走过,否则就会死循环!
|
||
* 使用set来检查字符串是否出现在字符串集合里更快一些
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:(详细注释)
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
#include <iostream>
|
||
#include <vector>
|
||
#include <string>
|
||
#include <unordered_set>
|
||
#include <unordered_map>
|
||
#include <queue>
|
||
using namespace std;
|
||
int main() {
|
||
string beginStr, endStr, str;
|
||
int n;
|
||
cin >> n;
|
||
unordered_set<string> strSet;
|
||
cin >> beginStr >> endStr;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
cin >> str;
|
||
strSet.insert(str);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 记录strSet里的字符串是否被访问过,同时记录路径长度
|
||
unordered_map<string, int> visitMap; // <记录的字符串,路径长度>
|
||
|
||
// 初始化队列
|
||
queue<string> que;
|
||
que.push(beginStr);
|
||
|
||
// 初始化visitMap
|
||
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(beginStr, 1));
|
||
|
||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||
string word = que.front();
|
||
que.pop();
|
||
int path = visitMap[word]; // 这个字符串在路径中的长度
|
||
|
||
// 开始在这个str中,挨个字符去替换
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < word.size(); i++) {
|
||
string newWord = word; // 用一个新字符串替换str,因为每次要置换一个字符
|
||
|
||
// 遍历26的字母
|
||
for (int j = 0 ; j < 26; j++) {
|
||
newWord[i] = j + 'a';
|
||
if (newWord == endStr) { // 发现替换字母后,字符串与终点字符串相同
|
||
cout << path + 1 << endl; // 找到了路径
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
// 字符串集合里出现了newWord,并且newWord没有被访问过
|
||
if (strSet.find(newWord) != strSet.end()
|
||
&& visitMap.find(newWord) == visitMap.end()) {
|
||
// 添加访问信息,并将新字符串放到队列中
|
||
visitMap.insert(pair<string, int>(newWord, path + 1));
|
||
que.push(newWord);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 没找到输出0
|
||
cout << 0 << endl;
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
当然本题也可以用双向BFS,就是从头尾两端进行搜索,大家感兴趣,可以自己去实现,这里就不再做详细讲解了。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
```Java
|
||
public class Main {
|
||
// BFS方法
|
||
public static int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
|
||
// 使用set作为查询容器,效率更高
|
||
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(wordList);
|
||
|
||
// 声明一个queue存储每次变更一个字符得到的且存在于容器中的新字符串
|
||
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
|
||
|
||
// 声明一个hashMap存储遍历到的字符串以及所走过的路径path
|
||
HashMap<String, Integer> visitMap = new HashMap<>();
|
||
queue.offer(beginWord);
|
||
visitMap.put(beginWord, 1);
|
||
|
||
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
|
||
String curWord = queue.poll();
|
||
int path = visitMap.get(curWord);
|
||
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < curWord.length(); i++) {
|
||
char[] ch = curWord.toCharArray();
|
||
// 每个位置尝试26个字母
|
||
for (char k = 'a'; k <= 'z'; k++) {
|
||
ch[i] = k;
|
||
|
||
String newWord = new String(ch);
|
||
if (newWord.equals(endWord)) return path + 1;
|
||
|
||
// 如果这个新字符串存在于容器且之前未被访问到
|
||
if (set.contains(newWord) && !visitMap.containsKey(newWord)) {
|
||
visitMap.put(newWord, path + 1);
|
||
queue.offer(newWord);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public static void main (String[] args) {
|
||
/* code */
|
||
// 接收输入
|
||
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
|
||
int N = sc.nextInt();
|
||
sc.nextLine();
|
||
String[] strs = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
|
||
|
||
List<String> wordList = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||
wordList.add(sc.nextLine());
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// wordList.add(strs[1]);
|
||
|
||
// 打印结果
|
||
int result = ladderLength(strs[0], strs[1], wordList);
|
||
System.out.println(result);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
```Python
|
||
def judge(s1,s2):
|
||
count=0
|
||
for i in range(len(s1)):
|
||
if s1[i]!=s2[i]:
|
||
count+=1
|
||
return count==1
|
||
|
||
if __name__=='__main__':
|
||
n=int(input())
|
||
beginstr,endstr=map(str,input().split())
|
||
if beginstr==endstr:
|
||
print(0)
|
||
exit()
|
||
strlist=[]
|
||
for i in range(n):
|
||
strlist.append(input())
|
||
|
||
# use bfs
|
||
visit=[False for i in range(n)]
|
||
queue=[[beginstr,1]]
|
||
while queue:
|
||
str,step=queue.pop(0)
|
||
if judge(str,endstr):
|
||
print(step+1)
|
||
exit()
|
||
for i in range(n):
|
||
if visit[i]==False and judge(strlist[i],str):
|
||
visit[i]=True
|
||
queue.append([strlist[i],step+1])
|
||
print(0)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go
|
||
|
||
### Rust
|
||
|
||
### Javascript
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
|
||
// 创建readline接口
|
||
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
|
||
// 创建异步迭代器
|
||
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
|
||
|
||
let N //输入字符串个数
|
||
let beginStr //开始字符串
|
||
let endStr //结束字符串
|
||
let strSet = new Set() //字符串集合
|
||
let visitedMap = new Map() //访问过的字符串
|
||
|
||
// 读取输入,初始化地图
|
||
const init = async () => {
|
||
let line = await readline();
|
||
line = line.trim()
|
||
N = Number(line);
|
||
|
||
line = await readline();
|
||
line = line.trim().split(' ')
|
||
beginStr = line[0]
|
||
endStr = line[1]
|
||
|
||
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
|
||
line = await readline()
|
||
line = line.trim()
|
||
strSet.add(line.trim())
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
(async function () {
|
||
|
||
// 读取输入,初始化数据
|
||
await init()
|
||
|
||
// 初始化队列
|
||
let queue = []
|
||
queue.push(beginStr)
|
||
|
||
// 初始化visitMap
|
||
visitedMap.set(beginStr, 1)
|
||
|
||
while (queue.length) {
|
||
let word = queue.shift()
|
||
let path = visitedMap.get(word)
|
||
|
||
// 遍历26个字母
|
||
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
|
||
let newWord = word.split('') // 用一个新字符串替换str,因为每次要置换一个字符
|
||
for (let j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
|
||
newWord[i] = String.fromCharCode('a'.charCodeAt() + j)
|
||
// 发现替换字母后,字符串与终点字符串相同
|
||
if (newWord.join('') === endStr) {
|
||
console.log(path + 1);
|
||
return 0; // 找到了路径
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 字符串集合里出现了newWord,并且newWord没有被访问过
|
||
if (strSet.has(newWord.join('')) && !visitedMap.has(newWord.join(''))) {
|
||
// 添加访问信息,并将新字符串放到队列中
|
||
queue.push(newWord.join(''))
|
||
visitedMap.set(newWord.join(''), path + 1)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
console.log(0);
|
||
})()
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### TypeScript
|
||
|
||
### PhP
|
||
|
||
### Swift
|
||
|
||
### Scala
|
||
|
||
### C#
|
||
|
||
### Dart
|
||
|
||
### C
|
||
|