mirror of https://github.com/doocs/leetcode.git
|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_EN.md | ||
| Solution.cpp | ||
| Solution.cs | ||
| Solution.go | ||
| Solution.java | ||
| Solution.py | ||
| Solution.ts | ||
README_EN.md
| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | Medium | https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/0200-0299/0223.Rectangle%20Area/README_EN.md |
|
223. Rectangle Area
Description
Given the coordinates of two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane, return the total area covered by the two rectangles.
The first rectangle is defined by its bottom-left corner (ax1, ay1) and its top-right corner (ax2, ay2).
The second rectangle is defined by its bottom-left corner (bx1, by1) and its top-right corner (bx2, by2).
Example 1:
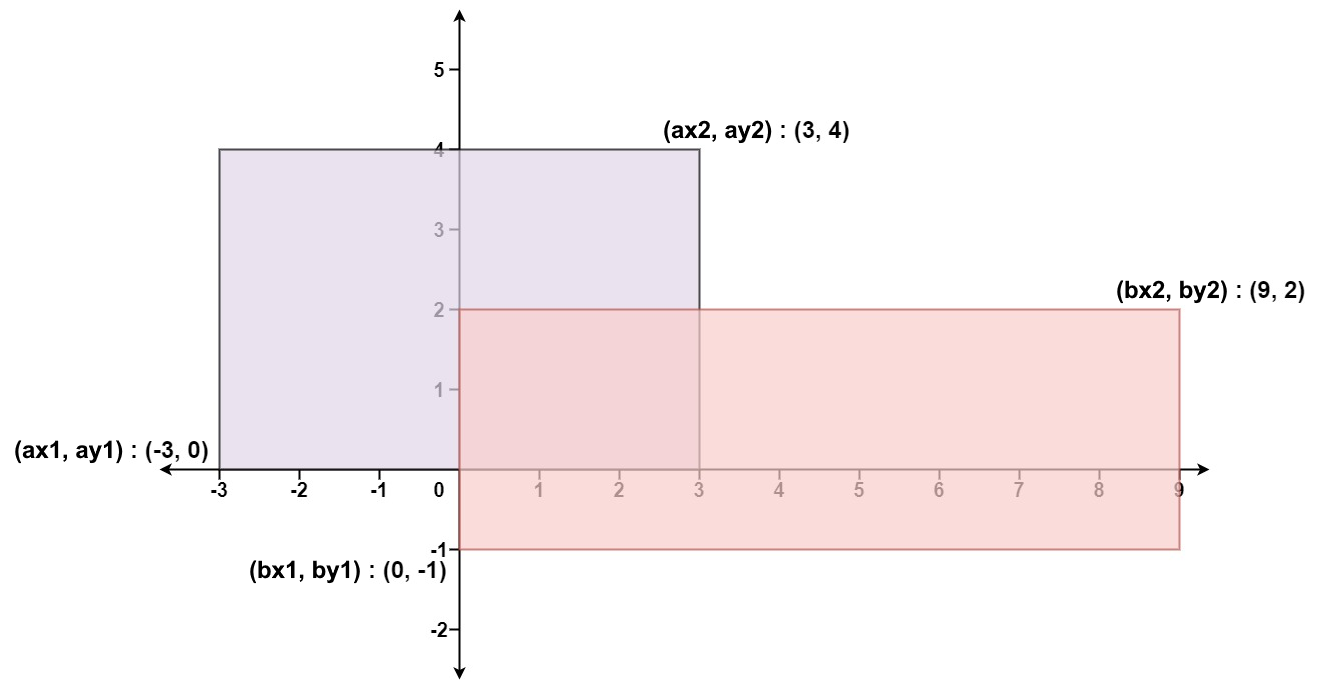
Input: ax1 = -3, ay1 = 0, ax2 = 3, ay2 = 4, bx1 = 0, by1 = -1, bx2 = 9, by2 = 2 Output: 45
Example 2:
Input: ax1 = -2, ay1 = -2, ax2 = 2, ay2 = 2, bx1 = -2, by1 = -2, bx2 = 2, by2 = 2 Output: 16
Constraints:
-104 <= ax1 <= ax2 <= 104-104 <= ay1 <= ay2 <= 104-104 <= bx1 <= bx2 <= 104-104 <= by1 <= by2 <= 104
Solutions
Solution 1: Calculate Overlapping Area
First, we calculate the area of the two rectangles separately, denoted as a and b. Then we calculate the overlapping width width and height height. The overlapping area is max(width, 0) \times max(height, 0). Finally, we subtract the overlapping area from a and b.
The time complexity is O(1), and the space complexity is O(1).
Python3
class Solution:
def computeArea(
self,
ax1: int,
ay1: int,
ax2: int,
ay2: int,
bx1: int,
by1: int,
bx2: int,
by2: int,
) -> int:
a = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1)
b = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1)
width = min(ax2, bx2) - max(ax1, bx1)
height = min(ay2, by2) - max(ay1, by1)
return a + b - max(height, 0) * max(width, 0)
Java
class Solution {
public int computeArea(int ax1, int ay1, int ax2, int ay2, int bx1, int by1, int bx2, int by2) {
int a = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1);
int b = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1);
int width = Math.min(ax2, bx2) - Math.max(ax1, bx1);
int height = Math.min(ay2, by2) - Math.max(ay1, by1);
return a + b - Math.max(height, 0) * Math.max(width, 0);
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int computeArea(int ax1, int ay1, int ax2, int ay2, int bx1, int by1, int bx2, int by2) {
int a = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1);
int b = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1);
int width = min(ax2, bx2) - max(ax1, bx1);
int height = min(ay2, by2) - max(ay1, by1);
return a + b - max(height, 0) * max(width, 0);
}
};
Go
func computeArea(ax1 int, ay1 int, ax2 int, ay2 int, bx1 int, by1 int, bx2 int, by2 int) int {
a := (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1)
b := (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1)
width := min(ax2, bx2) - max(ax1, bx1)
height := min(ay2, by2) - max(ay1, by1)
return a + b - max(height, 0)*max(width, 0)
}
TypeScript
function computeArea(
ax1: number,
ay1: number,
ax2: number,
ay2: number,
bx1: number,
by1: number,
bx2: number,
by2: number,
): number {
const a = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1);
const b = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1);
const width = Math.min(ax2, bx2) - Math.max(ax1, bx1);
const height = Math.min(ay2, by2) - Math.max(ay1, by1);
return a + b - Math.max(width, 0) * Math.max(height, 0);
}
C#
public class Solution {
public int ComputeArea(int ax1, int ay1, int ax2, int ay2, int bx1, int by1, int bx2, int by2) {
int a = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1);
int b = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1);
int width = Math.Min(ax2, bx2) - Math.Max(ax1, bx1);
int height = Math.Min(ay2, by2) - Math.Max(ay1, by1);
return a + b - Math.Max(height, 0) * Math.Max(width, 0);
}
}