mirror of https://github.com/doocs/leetcode.git
|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_EN.md | ||
| Solution.cpp | ||
| Solution.go | ||
| Solution.java | ||
| Solution.py | ||
| Solution.ts | ||
README_EN.md
| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | Easy | https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/0400-0499/0422.Valid%20Word%20Square/README_EN.md |
|
422. Valid Word Square 🔒
Description
Given an array of strings words, return true if it forms a valid word square.
A sequence of strings forms a valid word square if the kth row and column read the same string, where 0 <= k < max(numRows, numColumns).
Example 1:
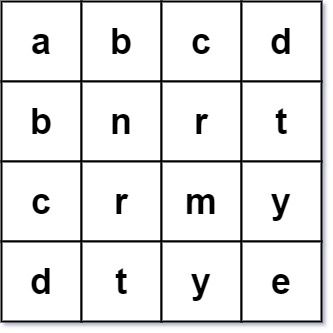
Input: words = ["abcd","bnrt","crmy","dtye"] Output: true Explanation: The 1st row and 1st column both read "abcd". The 2nd row and 2nd column both read "bnrt". The 3rd row and 3rd column both read "crmy". The 4th row and 4th column both read "dtye". Therefore, it is a valid word square.
Example 2:
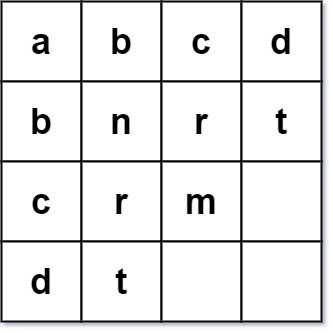
Input: words = ["abcd","bnrt","crm","dt"] Output: true Explanation: The 1st row and 1st column both read "abcd". The 2nd row and 2nd column both read "bnrt". The 3rd row and 3rd column both read "crm". The 4th row and 4th column both read "dt". Therefore, it is a valid word square.
Example 3:
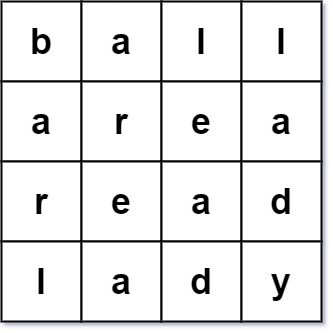
Input: words = ["ball","area","read","lady"] Output: false Explanation: The 3rd row reads "read" while the 3rd column reads "lead". Therefore, it is NOT a valid word square.
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 5001 <= words[i].length <= 500words[i]consists of only lowercase English letters.
Solutions
Solution 1: Iterative Check
We observe that if words[i][j] \neq words[j][i], we can directly return false.
Therefore, we only need to iterate through each row, and then check whether each row satisfies words[i][j] = words[j][i]. Note that if the index is out of bounds, we also directly return false.
The time complexity is O(n^2), where n is the length of words. The space complexity is $O(1)`.
Python3
class Solution:
def validWordSquare(self, words: List[str]) -> bool:
m = len(words)
for i, w in enumerate(words):
for j, c in enumerate(w):
if j >= m or i >= len(words[j]) or c != words[j][i]:
return False
return True
Java
class Solution {
public boolean validWordSquare(List<String> words) {
int m = words.size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int n = words.get(i).length();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (j >= m || i >= words.get(j).length()) {
return false;
}
if (words.get(i).charAt(j) != words.get(j).charAt(i)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool validWordSquare(vector<string>& words) {
int m = words.size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int n = words[i].size();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (j >= m || i >= words[j].size() || words[i][j] != words[j][i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
Go
func validWordSquare(words []string) bool {
m := len(words)
for i, w := range words {
for j := range w {
if j >= m || i >= len(words[j]) || w[j] != words[j][i] {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
TypeScript
function validWordSquare(words: string[]): boolean {
const m = words.length;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
const n = words[i].length;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (j >= m || i >= words[j].length || words[i][j] !== words[j][i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}