|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_EN.md | ||
| Solution.cpp | ||
| Solution.go | ||
| Solution.java | ||
| Solution.py | ||
| Solution.ts | ||
README_EN.md
| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | Easy | https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/0800-0899/0897.Increasing%20Order%20Search%20Tree/README_EN.md |
|
897. Increasing Order Search Tree
Description
Given the root of a binary search tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only one right child.
Example 1:
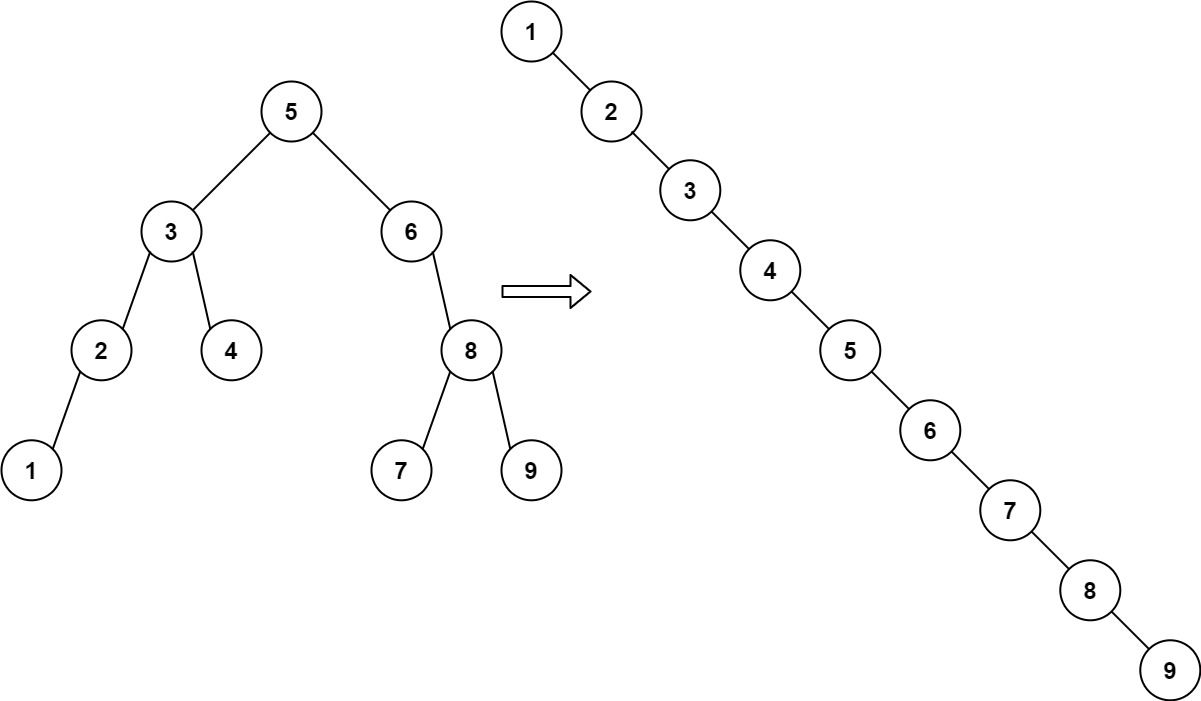
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
Example 2:
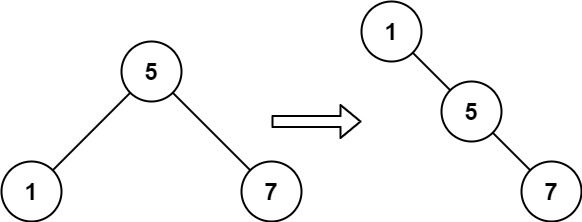
Input: root = [5,1,7] Output: [1,null,5,null,7]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS In-order Traversal
We define a virtual node dummy, initially the right child of dummy points to the root node root, and a pointer prev points to dummy.
We perform an in-order traversal on the binary search tree. During the traversal, each time we visit a node, we point the right child of prev to it, then set the left child of the current node to null, and assign the current node to prev for the next traversal.
After the traversal ends, the original binary search tree is modified into a singly linked list with only right child nodes. We then return the right child of the virtual node dummy.
The time complexity is O(n), and the space complexity is O(n). Here, n is the number of nodes in the binary search tree.
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def increasingBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return
nonlocal prev
dfs(root.left)
prev.right = root
root.left = None
prev = root
dfs(root.right)
dummy = prev = TreeNode(right=root)
dfs(root)
return dummy.right
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode prev;
public TreeNode increasingBST(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode dummy = new TreeNode(0, null, root);
prev = dummy;
dfs(root);
return dummy.right;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
prev.right = root;
root.left = null;
prev = root;
dfs(root.right);
}
}
C++
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* dummy = new TreeNode(0, nullptr, root);
TreeNode* prev = dummy;
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root->left);
prev->right = root;
root->left = nullptr;
prev = root;
dfs(root->right);
};
dfs(root);
return dummy->right;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func increasingBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
dummy := &TreeNode{Val: 0, Right: root}
prev := dummy
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Left)
prev.Right = root
root.Left = nil
prev = root
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return dummy.Right
}
TypeScript
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function increasingBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
const dummy = new TreeNode((right = root));
let prev = dummy;
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
prev.right = root;
root.left = null;
prev = root;
dfs(root.right);
};
dfs(root);
return dummy.right;
}