|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| README_EN.md | ||
| Solution.cpp | ||
| Solution.go | ||
| Solution.java | ||
| Solution.py | ||
| Solution.ts | ||
README_EN.md
| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | Hard | https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/1300-1399/1330.Reverse%20Subarray%20To%20Maximize%20Array%20Value/README_EN.md | 2481 | Biweekly Contest 18 Q4 |
|
1330. Reverse Subarray To Maximize Array Value
Description
You are given an integer array nums. The value of this array is defined as the sum of |nums[i] - nums[i + 1]| for all 0 <= i < nums.length - 1.
You are allowed to select any subarray of the given array and reverse it. You can perform this operation only once.
Find maximum possible value of the final array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,1,5,4] Output: 10 Explanation: By reversing the subarray [3,1,5] the array becomes [2,5,1,3,4] whose value is 10.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,9,24,2,1,10] Output: 68
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104-105 <= nums[i] <= 105- The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit integer.
Solutions
Solution 1: Classification Discussion + Enumeration
According to the problem description, we need to find the maximum value of the array \sum_{i=0}^{n-2} |a_i - a_{i+1}| when reversing a subarray once.
Next, we discuss the following cases:
- Do not reverse the subarray.
- Reverse the subarray, and the subarray "includes" the first element.
- Reverse the subarray, and the subarray "includes" the last element.
- Reverse the subarray, and the subarray "does not include" the first and last elements.
Let s be the array value when the subarray is not reversed, then s = \sum_{i=0}^{n-2} |a_i - a_{i+1}|. We can initialize the answer ans to s.
If we reverse the subarray and the subarray includes the first element, we can enumerate the last element a_i of the reversed subarray, where 0 \leq i < n-1. In this case, ans = \max(ans, s + |a_0 - a_{i+1}| - |a_i - a_{i+1}|).
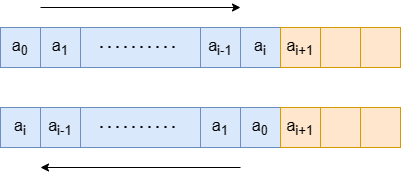
Similarly, if we reverse the subarray and the subarray includes the last element, we can enumerate the first element a_{i+1} of the reversed subarray, where 0 \leq i < n-1. In this case, ans = \max(ans, s + |a_{n-1} - a_i| - |a_i - a_{i+1}|).
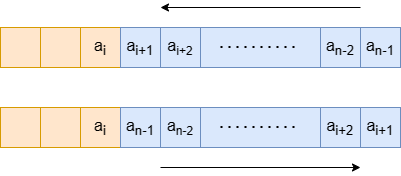
If we reverse the subarray and the subarray does not include the first and last elements, we consider any two adjacent elements in the array as a point pair (x, y). Let the first element of the reversed subarray be y_1, and its left adjacent element be x_1; let the last element of the reversed subarray be x_2, and its right adjacent element be y_2.
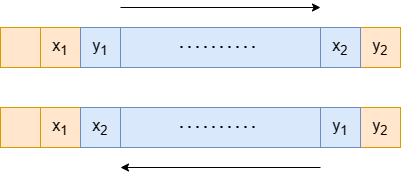
At this time, compared to not reversing the subarray, the change in the array value is |x_1 - x_2| + |y_1 - y_2| - |x_1 - y_1| - |x_2 - y_2|, where the first two terms can be expressed as:
\left | x_1 - x_2 \right | + \left | y_1 - y_2 \right | = \max \begin{cases} (x_1 + y_1) - (x_2 + y_2) \\ (x_1 - y_1) - (x_2 - y_2) \\ (-x_1 + y_1) - (-x_2 + y_2) \\ (-x_1 - y_1) - (-x_2 - y_2) \end{cases}
Then the change in the array value is:
\left | x_1 - x_2 \right | + \left | y_1 - y_2 \right | - \left | x_1 - y_1 \right | - \left | x_2 - y_2 \right | = \max \begin{cases} (x_1 + y_1) - \left |x_1 - y_1 \right | - \left ( (x_2 + y_2) + \left |x_2 - y_2 \right | \right ) \\ (x_1 - y_1) - \left |x_1 - y_1 \right | - \left ( (x_2 - y_2) + \left |x_2 - y_2 \right | \right ) \\ (-x_1 + y_1) - \left |x_1 - y_1 \right | - \left ( (-x_2 + y_2) + \left |x_2 - y_2 \right | \right ) \\ (-x_1 - y_1) - \left |x_1 - y_1 \right | - \left ( (-x_2 - y_2) + \left |x_2 - y_2 \right | \right ) \end{cases}
Therefore, we only need to find the maximum value mx of k_1 \times x + k_2 \times y, where k_1, k_2 \in \{-1, 1\}, and the corresponding minimum value mi of |x - y|. Then the maximum change in the array value is mx - mi. The answer is ans = \max(ans, s + \max(0, mx - mi)).
In the code implementation, we define an array of length 5, dirs=[1, -1, -1, 1, 1]. Each time we take two adjacent elements of the array as the values of k_1 and k_2, which can cover all cases of k_1, k_2 \in \{-1, 1\}.
The time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of the array nums. The space complexity is O(1).
Similar problems:
Python3
class Solution:
def maxValueAfterReverse(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
ans = s = sum(abs(x - y) for x, y in pairwise(nums))
for x, y in pairwise(nums):
ans = max(ans, s + abs(nums[0] - y) - abs(x - y))
ans = max(ans, s + abs(nums[-1] - x) - abs(x - y))
for k1, k2 in pairwise((1, -1, -1, 1, 1)):
mx, mi = -inf, inf
for x, y in pairwise(nums):
a = k1 * x + k2 * y
b = abs(x - y)
mx = max(mx, a - b)
mi = min(mi, a + b)
ans = max(ans, s + max(mx - mi, 0))
return ans
Java
class Solution {
public int maxValueAfterReverse(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
s += Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
}
int ans = s;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
ans = Math.max(
ans, s + Math.abs(nums[0] - nums[i + 1]) - Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]));
ans = Math.max(
ans, s + Math.abs(nums[n - 1] - nums[i]) - Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]));
}
int[] dirs = {1, -1, -1, 1, 1};
final int inf = 1 << 30;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int k1 = dirs[k], k2 = dirs[k + 1];
int mx = -inf, mi = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
int a = k1 * nums[i] + k2 * nums[i + 1];
int b = Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
mx = Math.max(mx, a - b);
mi = Math.min(mi, a + b);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, s + Math.max(0, mx - mi));
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxValueAfterReverse(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
s += abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
}
int ans = s;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
ans = max(ans, s + abs(nums[0] - nums[i + 1]) - abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]));
ans = max(ans, s + abs(nums[n - 1] - nums[i]) - abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]));
}
int dirs[5] = {1, -1, -1, 1, 1};
const int inf = 1 << 30;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int k1 = dirs[k], k2 = dirs[k + 1];
int mx = -inf, mi = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
int a = k1 * nums[i] + k2 * nums[i + 1];
int b = abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
mx = max(mx, a - b);
mi = min(mi, a + b);
}
ans = max(ans, s + max(0, mx - mi));
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxValueAfterReverse(nums []int) int {
s, n := 0, len(nums)
for i, x := range nums[:n-1] {
y := nums[i+1]
s += abs(x - y)
}
ans := s
for i, x := range nums[:n-1] {
y := nums[i+1]
ans = max(ans, s+abs(nums[0]-y)-abs(x-y))
ans = max(ans, s+abs(nums[n-1]-x)-abs(x-y))
}
dirs := [5]int{1, -1, -1, 1, 1}
const inf = 1 << 30
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
k1, k2 := dirs[k], dirs[k+1]
mx, mi := -inf, inf
for i, x := range nums[:n-1] {
y := nums[i+1]
a := k1*x + k2*y
b := abs(x - y)
mx = max(mx, a-b)
mi = min(mi, a+b)
}
ans = max(ans, s+max(mx-mi, 0))
}
return ans
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}
TypeScript
function maxValueAfterReverse(nums: number[]): number {
const n = nums.length;
let s = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
s += Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
}
let ans = s;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
const d = Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
ans = Math.max(ans, s + Math.abs(nums[0] - nums[i + 1]) - d);
ans = Math.max(ans, s + Math.abs(nums[n - 1] - nums[i]) - d);
}
const dirs = [1, -1, -1, 1, 1];
const inf = 1 << 30;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
let mx = -inf;
let mi = inf;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
const a = dirs[k] * nums[i] + dirs[k + 1] * nums[i + 1];
const b = Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]);
mx = Math.max(mx, a - b);
mi = Math.min(mi, a + b);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, s + Math.max(0, mx - mi));
}
return ans;
}