4.7 KiB
| title | description | keywords | redirect_from | ui_tabs | cli_tabs | next_steps | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deploy a workload to a Kubernetes cluster | Use Docker Enterprise Edition to deploy Kubernetes workloads from yaml files. | UCP, Docker EE, orchestration, Kubernetes, cluster |
|
|
|
|
{% if include.ui %} The Docker EE web UI enables deploying your Kubernetes YAML files. In most cases, no modifications are necessary to deploy on a cluster that's managed by Docker EE.
Deploy an NGINX server
In this example, a simple Kubernetes Deployment object for an NGINX server is defined in YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80
The YAML specifies an earlier version of NGINX, which will be updated in a later section.
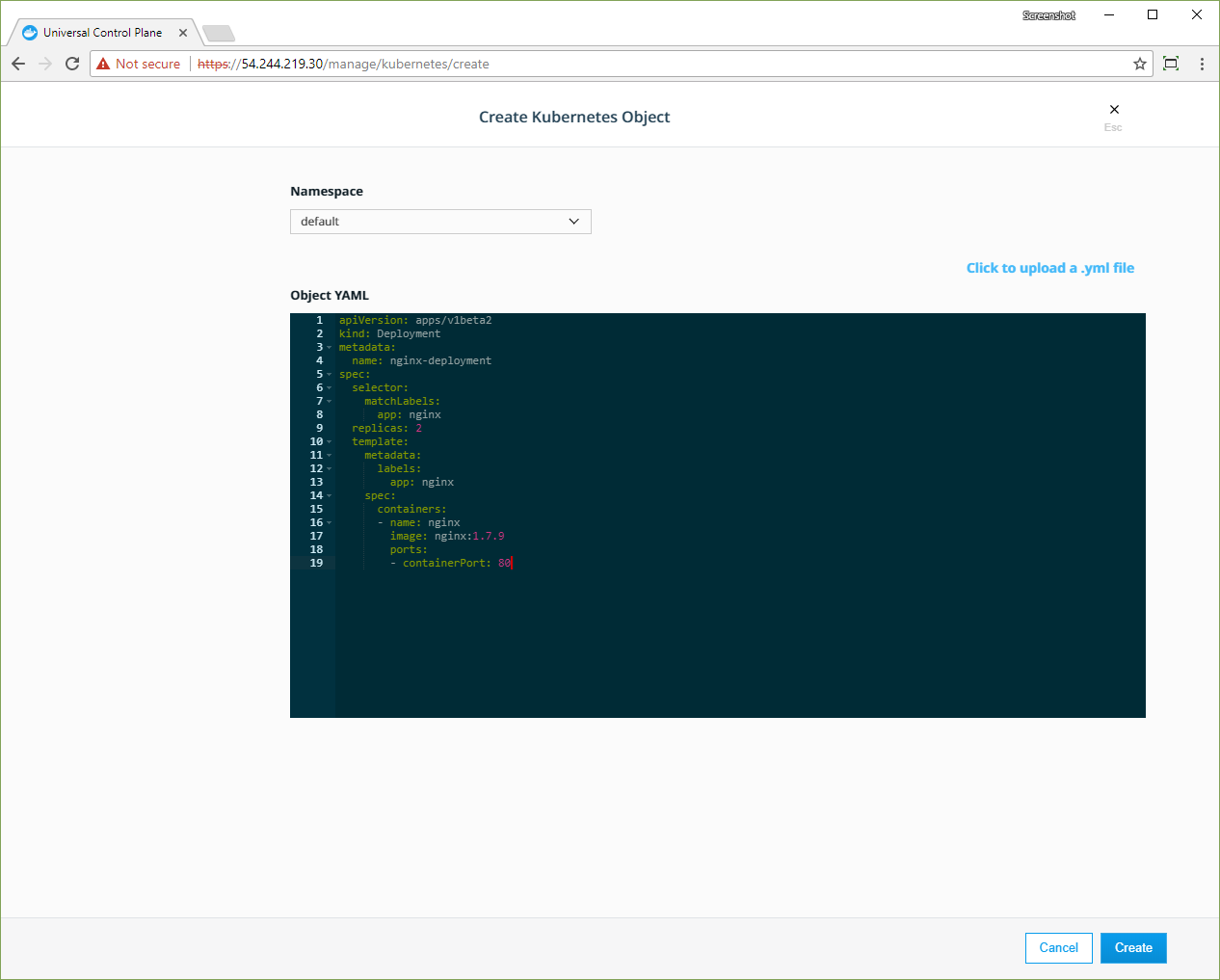
- Open the Docker EE web UI, and in the left pane, click Kubernetes.
- Click Create to open the Create Kubernetes Object page.
- In the Namespace dropdown, select default.
- In the Object YAML editor, paste the previous YAML.
- Click Create.
Inspect the deployment
The Docker EE web UI shows the status of your deployment when you click the links in the Kubernetes section of the left pane.
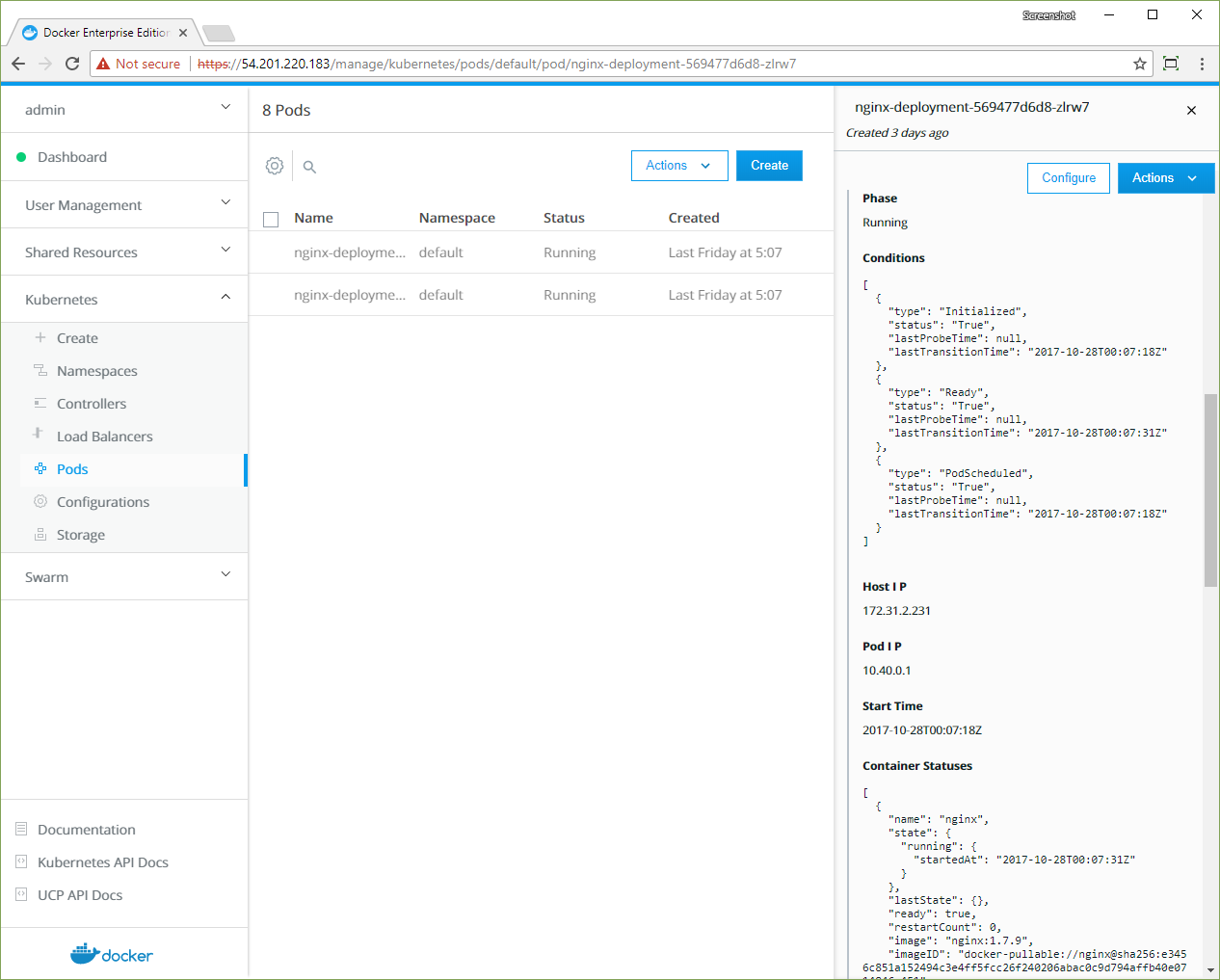
- In the left pane. click Controllers to see the resource controllers that Docker EE created for the NGINX server.
- Click the nginx-deployment controller, and in the details pane, scroll to the Template section. This shows the values that Docker EE used to create the deployment.
- In the left pane, click Pods to see the pods that are provisioned for the NGINX server. Click one of the pods, and in the details pane, scroll to the Status section to see that pod's phase, IP address, and other properties.
Update the deployment
Update an existing deployment by applying an updated YAML file. In this example, the server is scaled up to four replicas and updated to a later version of NGINX.
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 4
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- In the left pane, click Controllers and select the nginx-deployment controller.
- In the details pane, click Configure, and in the Edit Deployment page, paste the previous YAML.
- Click Edit to update the deployment with the new YAML.
{% endif %}
{% if include.cli %}
With Docker EE, you deploy your Kubernetes objects on the command line by using
kubectl. Install and set up kubectl.
Docker EE ensures that communication with the cluster is secure. When you run
kubectl commands on a Docker EE node, you need to authenticate your request
with a client certificate bundle. Get your client bundle by using the Docker EE web UI or the command line.
If you don't have the client bundle set up, you'll see an error when you run
kubectl commands:
The connection to the server localhost:8080 was refused - did you specify the right host or port?
When you have kubectl and the client bundle installed, you can deploy a
Kubernetes object from YAML.
Save the previous YAML to a file named "deployment.yaml", and use the following command to deploy the NGINX server:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Inspect the deployment
Use the describe deployment option to inspect the deployment:
kubectl describe deployment nginx-deployment
Also, you can use the Docker EE web UI to see the deployment's pods and controllers.
Update the deployment
Update an existing deployment by applying an updated YAML file.
Save the previous YAML to a file named "update.yaml", and use the following command to deploy the NGINX server:
kubectl apply -f update.yaml
{% endif %}