9.2 KiB
| title | description | keywords | ui_tabs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deploy an ingress controller for a Kubernetes app | Learn how to enable routing for a Kubernetes workload in Docker Enterprise Edition. | UCP, Docker EE, Kubernetes, ingress, routing |
|
{% if include.version=="ucp-3.0" %}
When you deploy your Kubernetes app on a Docker EE cluster, you may want to expose a service that enables external users to connect to it. Also, you may want network communication to reference named hosts, instead of IP addresses. Kubernetes provides ingress controllers to enable these functions.
Use an ingress controller when you want to:
- give your Kubernetes app an externally-reachable URL,
- load-balance traffic to your app, or
- offer name-based hosting.
Kubernetes provides an NGINX ingress controller that you can use in a Docker EE cluster, without modifications. Learn about ingress in Kubernetes.
Routing for Swarm apps
To enable similar features for Swarm apps, see Layer 7 routing. {: .important}
Create the Kubernetes namespace for the ingress controller
-
Navigate to the Namespaces page and click Create.
-
In the Object YAML editor, append the following text.
metadata: name: ingress-nginxThe finished YAML should look like this.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: ingress-nginx -
Click Create.
-
In the ingress-nginx namespace, click the More options icon, and in the context menu, select Set Context.
Create a grant
Docker EE 2.0 Beta2
In Beta2, default service accounts have limited or no permissions, and all other service accounts have full admin-scoped privileges. Instead of creating a grant, create a service account named
nginx-service-accountin theingress-nginxnamespace.apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: nginx-service-account namespace: ingress-nginxSkip to the Install the NGINX ingress controller procedure.
The default service account that's associated with the ingress-nginx
namespace needs access to Kubernetes resources, so create a grant with
Restricted Control permissions.
- Navigate to the Grants page and click Create Grant.
- In the left pane, click Resource Sets, and in the Type section, click Namespaces.
- Enable the Apply grant to all existing and new namespaces option.
- In the left pane, click Roles. In the Role dropdown, select Restricted Control.
- In the left pane, click Subjects, and select Service Account.
- In the Namespace dropdown, select ingress-nginx, and in the Service Account dropdown., select default.
- Click Create.
Ingress and role-based access control
Docker EE has an access control system that differs from Kubernetes RBAC. If your ingress controller has access control requirements, you need to create corresponding UCP grants. Learn to migrate Kubernetes roles to Docker EE authorization. {: .important}
Install the NGINX ingress controller
The cluster is ready for the ingress controller deployment, which has three main components:
- a simple HTTP server, named
default-http-backend, - an ingress controller, named
nginx-ingress-controller, and - a service that exposes the app, named
ingress-nginx.
Navigate to the Create Kubernetes Object page, and in the Object YAML editor, paste the following YAML.
Docker EE 2.0 Beta2
Uncomment
serviceAccountName: nginx-service-accountto use the service account that you created previously.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: default-http-backend
labels:
app: default-http-backend
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: default-http-backend
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 60
containers:
- name: default-http-backend
# Any image is permissable as long as:
# 1. It serves a 404 page at /
# 2. It serves 200 on a /healthz endpoint
image: gcr.io/google_containers/defaultbackend:1.4
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 8080
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 5
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
resources:
limits:
cpu: 10m
memory: 20Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 20Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: default-http-backend
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app: default-http-backend
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: default-http-backend
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: tcp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: udp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ingress-nginx
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: '10254'
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
spec:
# Beta2 only: Uncomment the following line
# serviceAccountName: nginx-service-account
initContainers:
- command:
- sh
- -c
- sysctl -w net.core.somaxconn=32768; sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range="1024 65535"
image: alpine:3.6
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: sysctl
securityContext:
privileged: true
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller:0.10.2
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --default-backend-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/default-http-backend
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --tcp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/tcp-services
- --udp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/udp-services
- --annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: ingress-nginx
Inspect the installation
The default-http-backend provides a simple service that serves a 404 page
at / and serves 200 on the /healthz endpoint.
-
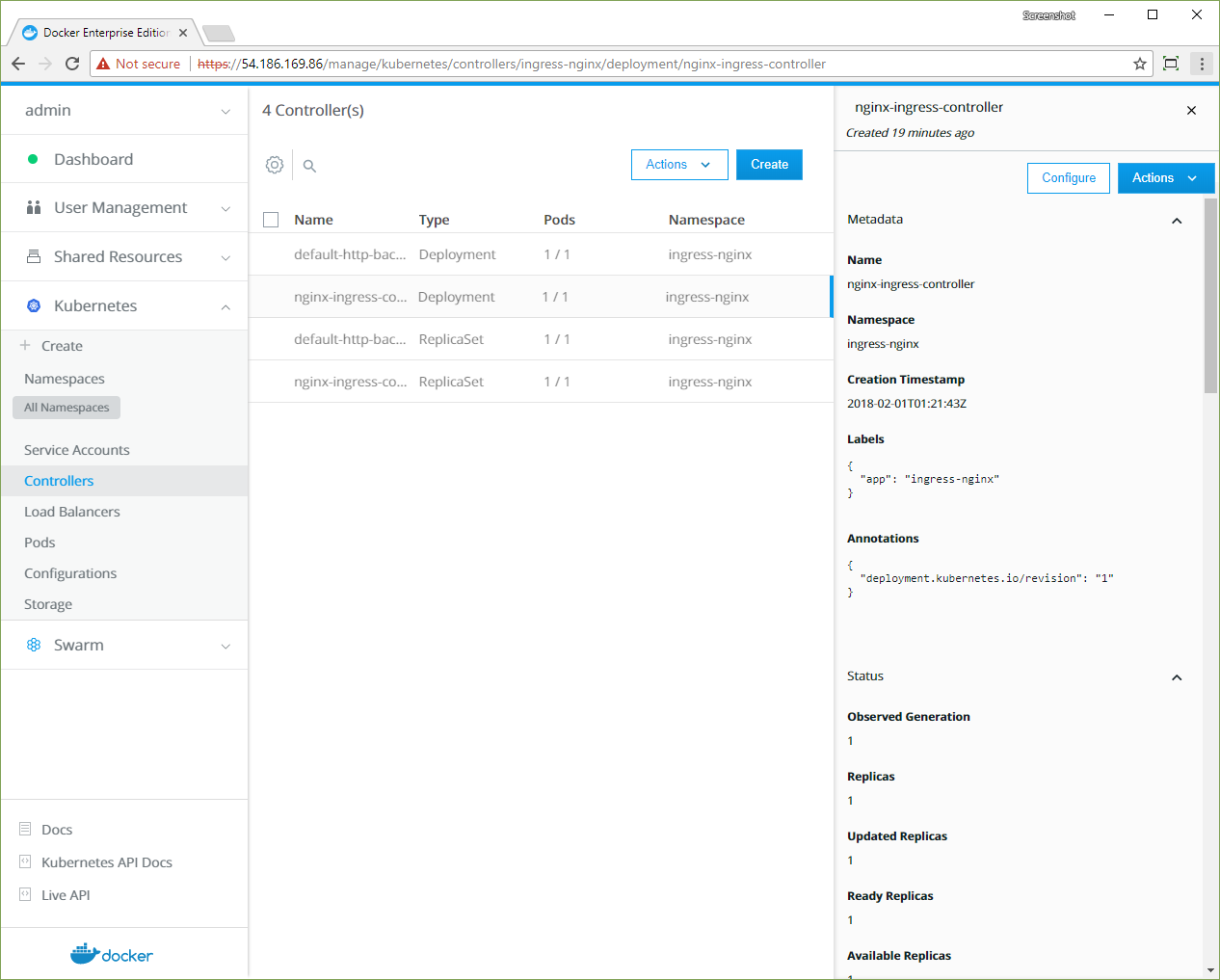
Navigate to the Controllers page and confirm that the default-http-backend and nginx-ingress-controller objects are scheduled.
Scheduling latency
It may take several seconds for the HTTP backend and the ingress controller's
DeploymentandReplicaSetobjects to be scheduled. { .important } -
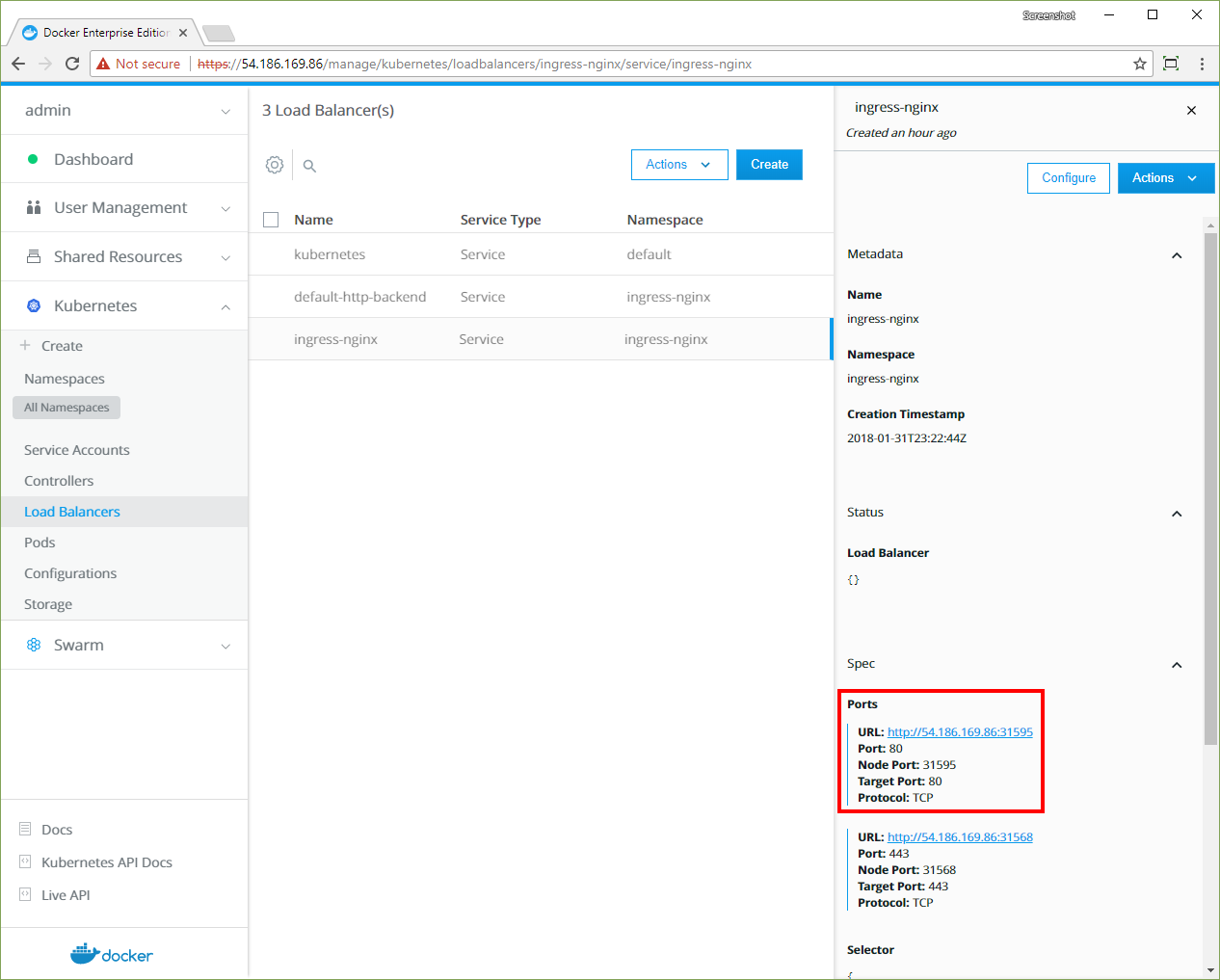
When the workload is running, navigate to the Load Balancers page and click the ingress-nginx service.
-
In the details pane, click the first URL in the Ports section.
A new page opens, displaying
default backend - 404.
Inspect the installation in the CLI
From the command line, confirm that the deployment is running by using
curl with the URL that's shown on the details pane of the ingress-nginx
service.
curl -I http://<ucp-ip>:<ingress port>/
This command returns the following result.
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Server: nginx/1.13.8
Test the server's health ping service by appending /healthz to the URL.
curl -I http://<ucp-ip>:<ingress port>/healthz
This command returns the following result.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.13.8
{% endif %}