11 KiB
Install Istio
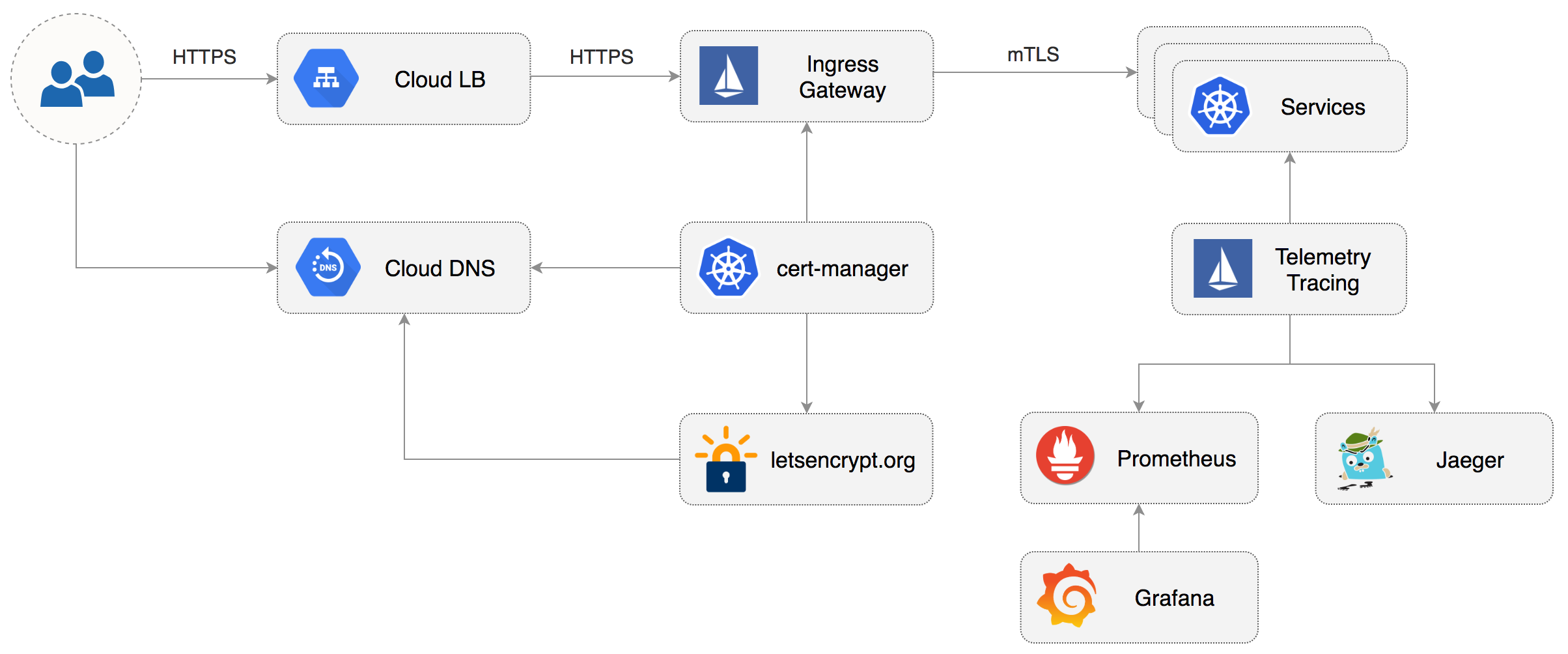
This guide walks you through setting up Istio with Jaeger, Prometheus, Grafana and Let’s Encrypt TLS for ingress gateway on Google Kubernetes Engine.
Prerequisites
You will be creating a cluster on Google’s Kubernetes Engine GKE,
if you don’t have an account you can sign up here for free credits.
Login into GCP, create a project and enable billing for it.
Install the gcloud command line utility and configure your project with gcloud init.
Set the default project replace `PROJECT_ID` with your own project:
gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
Set the default compute region and zone:
gcloud config set compute/region europe-west3
gcloud config set compute/zone europe-west3-a
Enable the Kubernetes and Cloud DNS services for your project:
gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable dns.googleapis.com
Install the kubectl command-line tool:
gcloud components install kubectl
Install the helm command-line tool:
brew install kubernetes-helm
GKE cluster setup
Create a cluster with three nodes using the latest Kubernetes version:
k8s_version=$(gcloud container get-server-config --format=json \
| jq -r '.validNodeVersions[0]')
gcloud container clusters create istio \
--cluster-version=${k8s_version} \
--zone=europe-west3-a \
--num-nodes=3 \
--machine-type=n1-highcpu-4 \
--preemptible \
--no-enable-cloud-logging \
--disk-size=30 \
--enable-autorepair \
--scopes=gke-default,compute-rw,storage-rw
The above command will create a default node pool consisting of n1-highcpu-4 vCPU: 4, RAM 3.60GB, DISK: 30GB
preemptible VMs. Preemptible VMs are up to 80% cheaper than regular instances and are terminated and replaced
after a maximum of 24 hours.
Set up credentials for kubectl:
gcloud container clusters get-credentials istio -z=europe-west3-a
Create a cluster admin role binding:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding "cluster-admin-$(whoami)" \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user="$(gcloud config get-value core/account)"
Validate your setup with:
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Cloud DNS setup
You will need an internet domain and access to the registrar to change the name servers to Google Cloud DNS.
Create a managed zone named istio in Cloud DNS replace `example.com` with your domain:
gcloud dns managed-zones create \
--dns-name="example.com." \
--description="Istio zone" "istio"
Look up your zone's name servers:
gcloud dns managed-zones describe istio
Update your registrar's name server records with the records returned by the above command.
Wait for the name servers to change replace `example.com` with your domain:
watch dig +short NS example.com
Create a static IP address named istio-gateway-ip in the same region as your GKE cluster:
gcloud compute addresses create istio-gateway-ip --region europe-west3
Find the static IP address:
gcloud compute addresses describe istio-gateway-ip --region europe-west3
Create the following DNS records replace `example.com` with your domain and set your Istio Gateway IP:
DOMAIN="example.com"
GATEWAYIP="35.198.98.90"
gcloud dns record-sets transaction start --zone=istio
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
--name="${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
--name="www.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
gcloud dns record-sets transaction add --zone=istio \
--name="*.${DOMAIN}" --ttl=300 --type=A ${GATEWAYIP}
gcloud dns record-sets transaction execute --zone istio
Verify that the wildcard DNS is working replace `example.com` with your domain:
watch host test.example.com
Install Istio with Helm
Download the latest Istio release:
curl -L https://git.io/getLatestIstio | sh -
Navigate to istio-x.x.x dir and copy the Istio CLI in your bin:
cd istio-x.x.x/
sudo cp ./bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
Apply the Istio CRDs:
kubectl apply -f ./install/kubernetes/helm/istio/templates/crds.yaml
Create a service account and a cluster role binding for Tiller:
kubectl apply -f ./install/kubernetes/helm/helm-service-account.yaml
Deploy Tiller in the kube-system namespace:
helm init --service-account tiller
Find the GKE IP ranges:
gcloud container clusters describe istio --zone=europe-west3-a \
| grep -e clusterIpv4Cidr -e servicesIpv4Cidr
You'll be using the IP ranges to allow unrestricted egress traffic for services running inside the service mesh.
Configure Istio with Prometheus, Jaeger, and cert-manager:
global:
nodePort: false
proxy:
# replace with your GKE IP ranges
includeIPRanges: "10.28.0.0/14,10.7.240.0/20"
sidecarInjectorWebhook:
enabled: true
enableNamespacesByDefault: false
gateways:
enabled: true
istio-ingressgateway:
replicaCount: 2
autoscaleMin: 2
autoscaleMax: 3
# replace with your Istio Gateway IP
loadBalancerIP: "35.198.98.90"
type: LoadBalancer
pilot:
enabled: true
replicaCount: 1
autoscaleMin: 1
autoscaleMax: 1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1024Mi
grafana:
enabled: true
security:
enabled: true
adminUser: admin
# change the password
adminPassword: admin
prometheus:
enabled: true
servicegraph:
enabled: true
tracing:
enabled: true
jaeger:
tag: 1.7
certmanager:
enabled: true
Save the above file as my-istio.yaml and install Istio with Helm:
helm upgrade --install istio ./install/kubernetes/helm/istio \
--namespace=istio-system \
-f ./my-istio.yaml
Verify that Istio workloads are running:
kubectl -n istio-system get pods
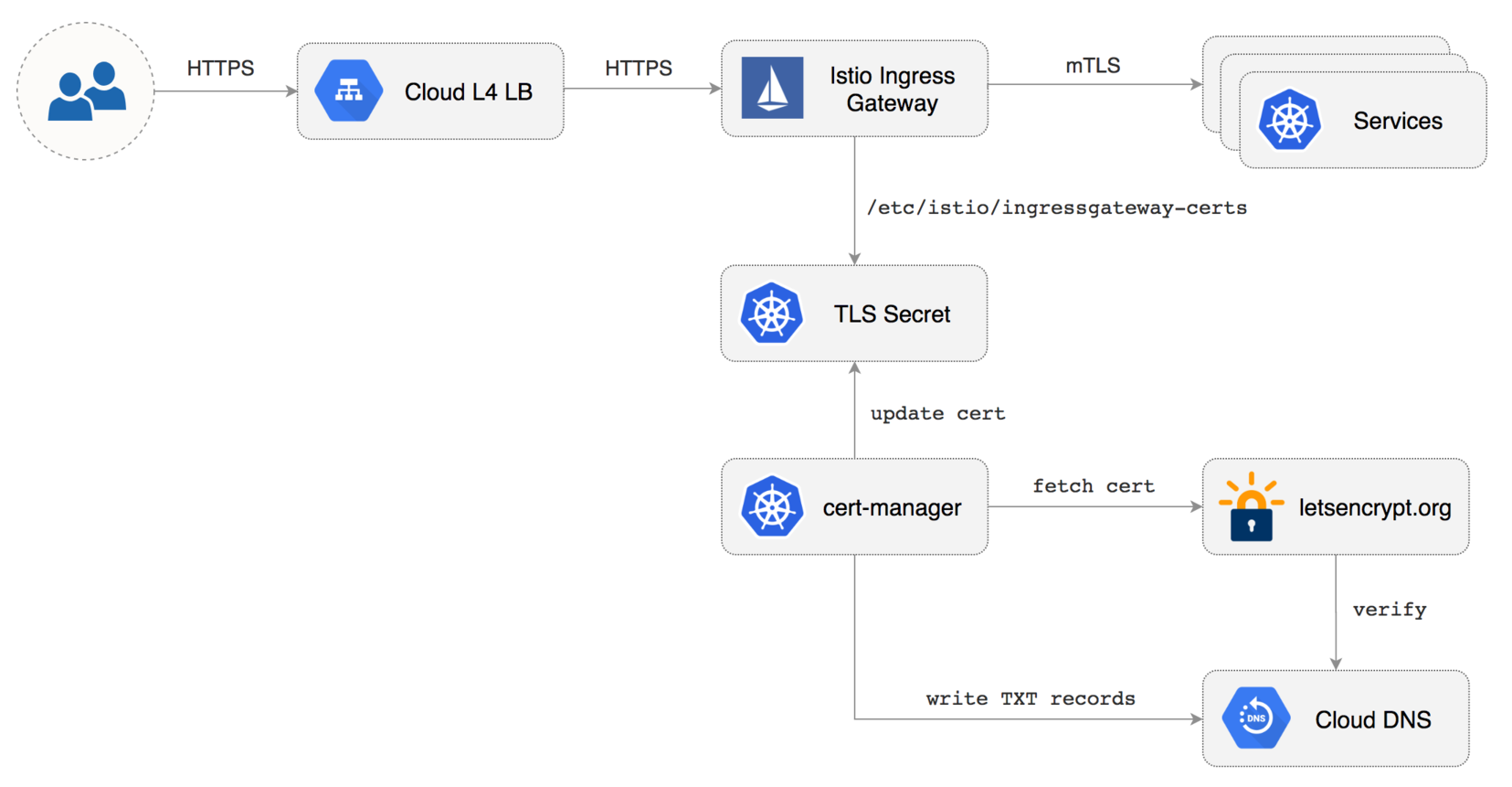
Configure Istio Gateway with LE TLS
Create a Istio Gateway in istio-system namespace with HTTPS redirect:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: public-gateway
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
tls:
httpsRedirect: true
- port:
number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
hosts:
- "*"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
privateKey: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.key
serverCertificate: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs/tls.crt
Save the above resource as istio-gateway.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./istio-gateway.yaml
Create a service account with Cloud DNS admin role replace `my-gcp-project` with your project ID:
GCP_PROJECT=my-gcp-project
gcloud iam service-accounts create dns-admin \
--display-name=dns-admin \
--project=${GCP_PROJECT}
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create ./gcp-dns-admin.json \
--iam-account=dns-admin@${GCP_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--project=${GCP_PROJECT}
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${GCP_PROJECT} \
--member=serviceAccount:dns-admin@${GCP_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role=roles/dns.admin
Create a Kubernetes secret with the GCP Cloud DNS admin key:
kubectl create secret generic cert-manager-credentials \
--from-file=./gcp-dns-admin.json \
--namespace=istio-system
Create a letsencrypt issuer for CloudDNS (replace email@example.com with a valid email address and
my-gcp-projectwith your project ID):
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
namespace: istio-system
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: email@example.com
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
dns01:
providers:
- name: cloud-dns
clouddns:
serviceAccountSecretRef:
name: cert-manager-credentials
key: gcp-dns-admin.json
project: my-gcp-project
Save the above resource as letsencrypt-issuer.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./letsencrypt-issuer.yaml
Create a wildcard certificate replace `example.com` with your domain:
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: istio-gateway
namespace: istio-system
spec:
secretname: istio-ingressgateway-certs
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
commonName: "*.example.com"
acme:
config:
- dns01:
provider: cloud-dns
domains:
- "*.example.com"
- "example.com"
Save the above resource as of-cert.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./of-cert.yaml
In a couple of seconds cert-manager should fetch a wildcard certificate from letsencrypt.org:
kubectl -n istio-system logs deployment/certmanager -f
Certificate issued successfully
Certificate istio-system/istio-gateway scheduled for renewal in 1438 hours
Recreate Istio ingress gateway pods:
kubectl -n istio-system delete pods -l istio=ingressgateway
Note that Istio gateway doesn't reload the certificates from the TLS secret on cert-manager renewal. Since the GKE cluster is made out of preemptible VMs the gateway pods will be replaced once every 24h, if your not using preemptible nodes then you need to manually kill the gateway pods every two months before the certificate expires.
Expose services outside the service mesh
In order to expose services via the Istio Gateway you have to create a Virtual Service attached to Istio Gateway.
Create a virtual service in istio-system namespace for Grafana replace `example.com` with your domain:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: grafana
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- "grafana.example.com"
gateways:
- public-gateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: grafana
timeout: 30s
Save the above resource as grafana-virtual-service.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./grafana-virtual-service.yaml
Navigate to http://grafana.example.com in your browser and you should be redirected to the HTTPS version.
Check that HTTP2 is enabled:
curl -I --http2 https://grafana.example.com
HTTP/2 200
content-type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3
server: envoy