1626 lines
49 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
1626 lines
49 KiB
Markdown
Executable File
* [做项目(多个C++、Java、Go、测开、前端项目)](https://www.programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html)
|
||
* [刷算法(两个月高强度学算法)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html)
|
||
* [背八股(40天挑战高频面试题)](https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/bagu.html)
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 112. 路径总和
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
|
||
|
||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
|
||
|
||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||
|
||
示例:
|
||
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
|
||
|
||
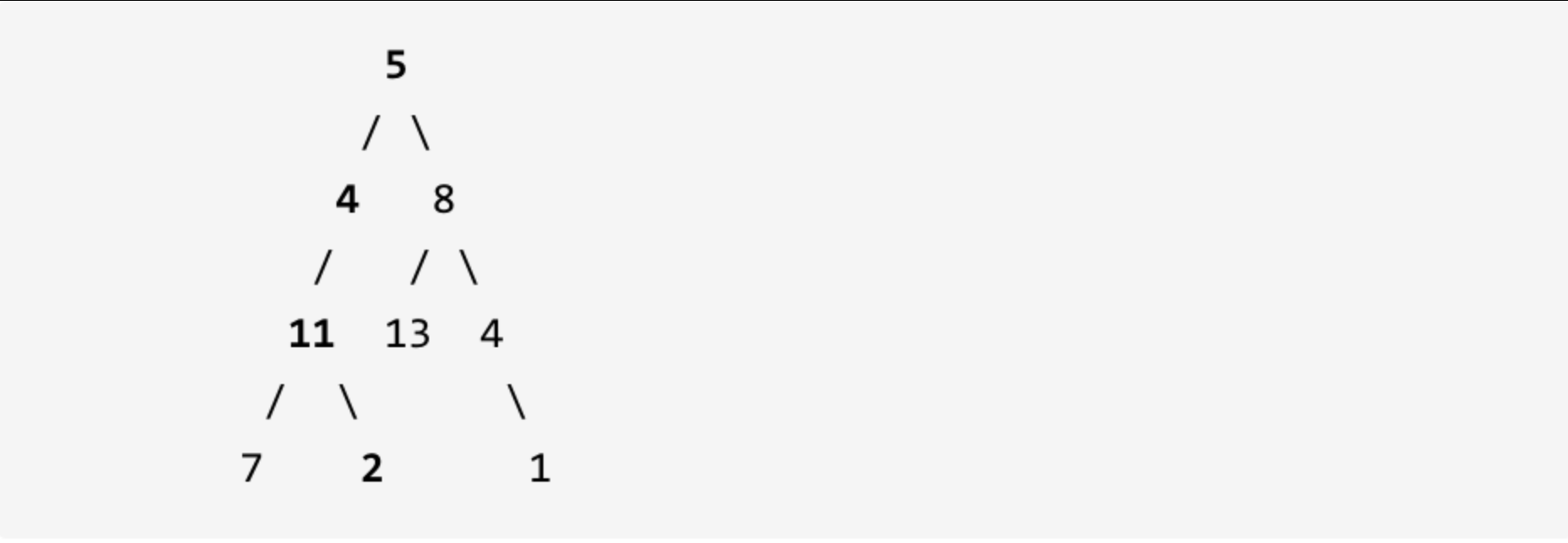
|
||
|
||
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
|
||
|
||
## 算法公开课
|
||
|
||
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html):[拿不准的遍历顺序,搞不清的回溯过程,我太难了! | LeetCode:112. 路径总和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19t4y1L7CR),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
相信很多同学都会疑惑,递归函数什么时候要有返回值,什么时候没有返回值,特别是有的时候递归函数返回类型为bool类型。
|
||
|
||
那么接下来我通过详细讲解如下两道题,来回答这个问题:
|
||
|
||
* [112.路径总和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/)
|
||
* [113.路径总和ii](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
|
||
|
||
这道题我们要遍历从根节点到叶子节点的路径看看总和是不是目标和。
|
||
|
||
### 递归
|
||
|
||
可以使用深度优先遍历的方式(本题前中后序都可以,无所谓,因为中节点也没有处理逻辑)来遍历二叉树
|
||
|
||
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回类型
|
||
|
||
参数:需要二叉树的根节点,还需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。
|
||
|
||
再来看返回值,递归函数什么时候需要返回值?什么时候不需要返回值?这里总结如下三点:
|
||
|
||
* 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(这种情况就是本文下半部分介绍的113.路径总和ii)
|
||
* 如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (这种情况我们在[236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://programmercarl.com/0236.二叉树的最近公共祖先.html)中介绍)
|
||
* 如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
|
||
|
||
而本题我们要找一条符合条件的路径,所以递归函数需要返回值,及时返回,那么返回类型是什么呢?
|
||
|
||
如图所示:
|
||
|
||
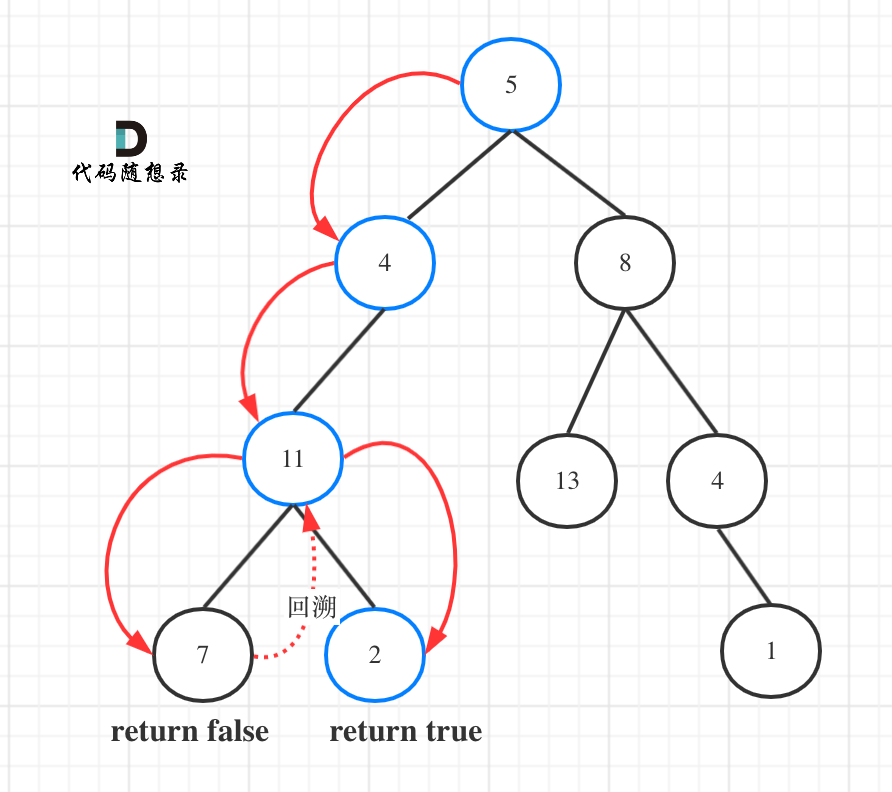
|
||
|
||
图中可以看出,遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
|
||
|
||
所以代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
bool traversal(treenode* cur, int count) // 注意函数的返回类型
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
2. 确定终止条件
|
||
|
||
首先计数器如何统计这一条路径的和呢?
|
||
|
||
不要去累加然后判断是否等于目标和,那么代码比较麻烦,可以用递减,让计数器count初始为目标和,然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值。
|
||
|
||
如果最后count == 0,同时到了叶子节点的话,说明找到了目标和。
|
||
|
||
如果遍历到了叶子节点,count不为0,就是没找到。
|
||
|
||
递归终止条件代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) return true; // 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) return false; // 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
|
||
|
||
因为终止条件是判断叶子节点,所以递归的过程中就不要让空节点进入递归了。
|
||
|
||
递归函数是有返回值的,如果递归函数返回true,说明找到了合适的路径,应该立刻返回。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
if (cur->left) { // 左 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
// 遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
|
||
if (traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val)) return true; // 注意这里有回溯的逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur->right) { // 右 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
// 遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
|
||
if (traversal(cur->right, count - cur->right->val)) return true; // 注意这里有回溯的逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
以上代码中是包含着回溯的,没有回溯,如何后撤重新找另一条路径呢。
|
||
|
||
回溯隐藏在`traversal(cur->left, count - cur->left->val)`这里, 因为把`count - cur->left->val` 直接作为参数传进去,函数结束,count的数值没有改变。
|
||
|
||
为了把回溯的过程体现出来,可以改为如下代码:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
if (cur->left) { // 左
|
||
count -= cur->left->val; // 递归,处理节点;
|
||
if (traversal(cur->left, count)) return true;
|
||
count += cur->left->val; // 回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur->right) { // 右
|
||
count -= cur->right->val;
|
||
if (traversal(cur->right, count)) return true;
|
||
count += cur->right->val;
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
bool traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) return true; // 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) return false; // 遇到叶子节点直接返回
|
||
|
||
if (cur->left) { // 左
|
||
count -= cur->left->val; // 递归,处理节点;
|
||
if (traversal(cur->left, count)) return true;
|
||
count += cur->left->val; // 回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur->right) { // 右
|
||
count -= cur->right->val; // 递归,处理节点;
|
||
if (traversal(cur->right, count)) return true;
|
||
count += cur->right->val; // 回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
|
||
if (root == NULL) return false;
|
||
return traversal(root, sum - root->val);
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
以上代码精简之后如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
|
||
if (!root) return false;
|
||
if (!root->left && !root->right && sum == root->val) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
return hasPathSum(root->left, sum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**是不是发现精简之后的代码,已经完全看不出分析的过程了,所以我们要把题目分析清楚之后,再追求代码精简。** 这一点我已经强调很多次了!
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 迭代
|
||
|
||
如果使用栈模拟递归的话,那么如果做回溯呢?
|
||
|
||
**此时栈里一个元素不仅要记录该节点指针,还要记录从头结点到该节点的路径数值总和。**
|
||
|
||
c++就我们用pair结构来存放这个栈里的元素。
|
||
|
||
定义为:`pair<TreeNode*, int>` pair<节点指针,路径数值>
|
||
|
||
这个为栈里的一个元素。
|
||
|
||
如下代码是使用栈模拟的前序遍历,如下:(详细注释)
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
class solution {
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
bool haspathsum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
|
||
if (root == null) return false;
|
||
// 此时栈里要放的是pair<节点指针,路径数值>
|
||
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int>> st;
|
||
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(root, root->val));
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
pair<TreeNode*, int> node = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
// 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
|
||
if (!node.first->left && !node.first->right && sum == node.second) return true;
|
||
|
||
// 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if (node.first->right) {
|
||
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->right, node.second + node.first->right->val));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if (node.first->left) {
|
||
st.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->left, node.second + node.first->left->val));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果大家完全理解了本题的递归方法之后,就可以顺便把leetcode上113. 路径总和ii做了。
|
||
|
||
## 相关题目推荐
|
||
|
||
### 113. 路径总和ii
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/)
|
||
|
||
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
|
||
|
||
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||
|
||
示例:
|
||
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
|
||
|
||
|
||
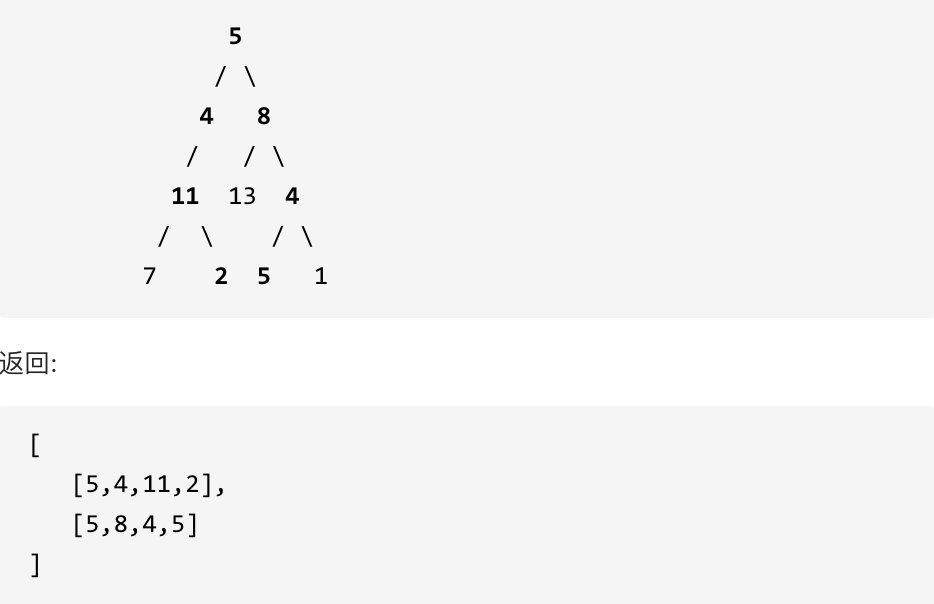
|
||
|
||
### 思路
|
||
|
||
|
||
113.路径总和ii要遍历整个树,找到所有路径,**所以递归函数不要返回值!**
|
||
|
||
如图:
|
||
|
||
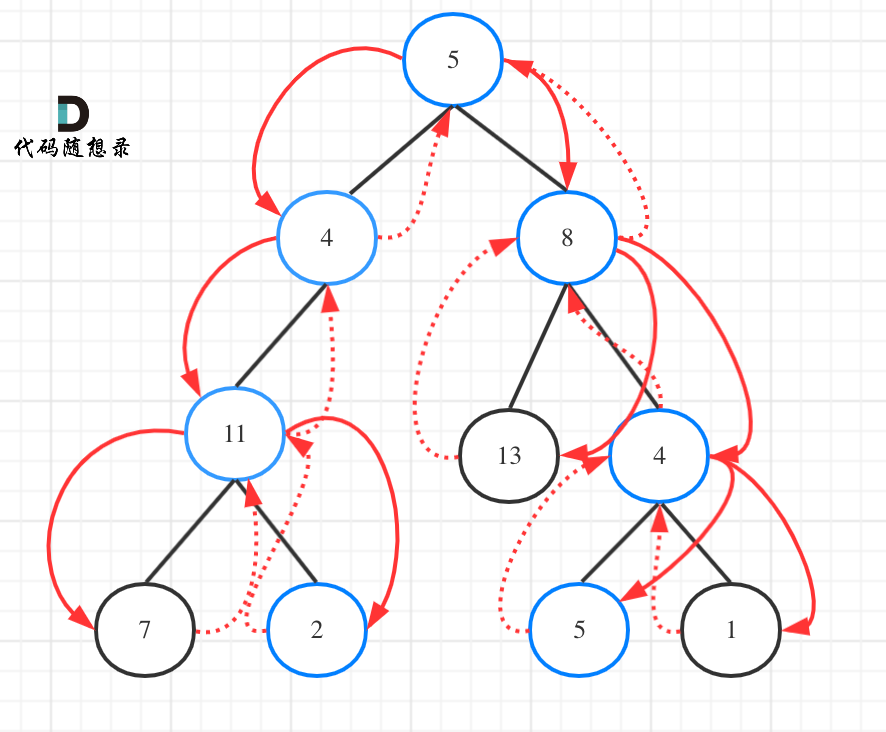
|
||
|
||
|
||
为了尽可能的把细节体现出来,我写出如下代码(**这份代码并不简洁,但是逻辑非常清晰**)
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
class solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
vector<vector<int>> result;
|
||
vector<int> path;
|
||
// 递归函数不需要返回值,因为我们要遍历整个树
|
||
void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) {
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right && count == 0) { // 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为sum的路径
|
||
result.push_back(path);
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if (!cur->left && !cur->right) return ; // 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||
|
||
if (cur->left) { // 左 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
path.push_back(cur->left->val);
|
||
count -= cur->left->val;
|
||
traversal(cur->left, count); // 递归
|
||
count += cur->left->val; // 回溯
|
||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur->right) { // 右 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
path.push_back(cur->right->val);
|
||
count -= cur->right->val;
|
||
traversal(cur->right, count); // 递归
|
||
count += cur->right->val; // 回溯
|
||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
return ;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
|
||
result.clear();
|
||
path.clear();
|
||
if (root == NULL) return result;
|
||
path.push_back(root->val); // 把根节点放进路径
|
||
traversal(root, sum - root->val);
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
至于113. 路径总和ii 的迭代法我并没有写,用迭代方式记录所有路径比较麻烦,也没有必要,如果大家感兴趣的话,可以再深入研究研究。
|
||
|
||
### 总结
|
||
|
||
本篇通过leetcode上112. 路径总和 和 113. 路径总和ii 详细的讲解了 递归函数什么时候需要返回值,什么不需要返回值。
|
||
|
||
这两道题目是掌握这一知识点非常好的题目,大家看完本篇文章再去做题,就会感受到搜索整棵树和搜索某一路径的差别。
|
||
|
||
对于112. 路径总和,我依然给出了递归法和迭代法,这种题目其实用迭代法会复杂一些,能掌握递归方式就够了!
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
if (root == null) {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
targetSum -= root.val;
|
||
// 叶子结点
|
||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
|
||
return targetSum == 0;
|
||
}
|
||
if (root.left != null) {
|
||
boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum);
|
||
if (left) { // 已经找到,提前返回
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (root.right != null) {
|
||
boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum);
|
||
if (right) { // 已经找到,提前返回
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// lc112 简洁方法
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
|
||
if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出
|
||
|
||
// 叶子节点判断是否符合
|
||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetSum;
|
||
|
||
// 求两侧分支的路径和
|
||
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
if(root == null) return false;
|
||
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
|
||
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
|
||
stack1.push(root);
|
||
stack2.push(root.val);
|
||
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
|
||
int size = stack1.size();
|
||
|
||
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||
TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
|
||
int sum = stack2.pop();
|
||
|
||
// 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
|
||
if(node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
// 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if(node.right != null){
|
||
stack1.push(node.right);
|
||
stack2.push(sum + node.right.val);
|
||
}
|
||
// 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if(node.left != null) {
|
||
stack1.push(node.left);
|
||
stack2.push(sum + node.left.val);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
```Java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
Stack<TreeNode> treeNodeStack = new Stack<>();
|
||
Stack<Integer> sumStack = new Stack<>();
|
||
|
||
if(root == null)
|
||
return false;
|
||
treeNodeStack.add(root);
|
||
sumStack.add(root.val);
|
||
|
||
while(!treeNodeStack.isEmpty()){
|
||
TreeNode curr = treeNodeStack.peek();
|
||
int tempsum = sumStack.pop();
|
||
if(curr != null){
|
||
treeNodeStack.pop();
|
||
treeNodeStack.add(curr);
|
||
treeNodeStack.add(null);
|
||
sumStack.add(tempsum);
|
||
if(curr.right != null){
|
||
treeNodeStack.add(curr.right);
|
||
sumStack.add(tempsum + curr.right.val);
|
||
}
|
||
if(curr.left != null){
|
||
treeNodeStack.add(curr.left);
|
||
sumStack.add(tempsum + curr.left.val);
|
||
}
|
||
}else{
|
||
treeNodeStack.pop();
|
||
TreeNode temp = treeNodeStack.pop();
|
||
if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null && tempsum == targetSum)
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
|
||
|
||
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
|
||
preOrderDfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public void preOrderDfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {
|
||
path.add(root.val);
|
||
// 遇到了叶子节点
|
||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
|
||
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
|
||
if (targetSum - root.val == 0) {
|
||
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
|
||
}
|
||
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if (root.left != null) {
|
||
preOrderDfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
|
||
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
if (root.right != null) {
|
||
preOrderDfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
|
||
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
// 解法2
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
List<List<Integer>> result;
|
||
LinkedList<Integer> path;
|
||
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root,int targetSum) {
|
||
result = new LinkedList<>();
|
||
path = new LinkedList<>();
|
||
travesal(root, targetSum);
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
private void travesal(TreeNode root, int count) {
|
||
if (root == null) return;
|
||
path.offer(root.val);
|
||
count -= root.val;
|
||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0) {
|
||
result.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
|
||
}
|
||
travesal(root.left, count);
|
||
travesal(root.right, count);
|
||
path.removeLast(); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
```java
|
||
// 解法3 DFS统一迭代法
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
Stack<TreeNode> nodeStack = new Stack<>();
|
||
Stack<Integer> sumStack = new Stack<>();
|
||
Stack<ArrayList<Integer>> pathStack = new Stack<>();
|
||
if(root == null)
|
||
return result;
|
||
nodeStack.add(root);
|
||
sumStack.add(root.val);
|
||
pathStack.add(new ArrayList<>());
|
||
|
||
while(!nodeStack.isEmpty()){
|
||
TreeNode currNode = nodeStack.peek();
|
||
int currSum = sumStack.pop();
|
||
ArrayList<Integer> currPath = pathStack.pop();
|
||
if(currNode != null){
|
||
nodeStack.pop();
|
||
nodeStack.add(currNode);
|
||
nodeStack.add(null);
|
||
sumStack.add(currSum);
|
||
currPath.add(currNode.val);
|
||
pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
|
||
if(currNode.right != null){
|
||
nodeStack.add(currNode.right);
|
||
sumStack.add(currSum + currNode.right.val);
|
||
pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
|
||
}
|
||
if(currNode.left != null){
|
||
nodeStack.add(currNode.left);
|
||
sumStack.add(currSum + currNode.left.val);
|
||
pathStack.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
|
||
}
|
||
}else{
|
||
nodeStack.pop();
|
||
TreeNode temp = nodeStack.pop();
|
||
if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null && currSum == targetSum)
|
||
result.add(new ArrayList(currPath));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
(版本一) 递归
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def traversal(self, cur: TreeNode, count: int) -> bool:
|
||
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0: # 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
|
||
return True
|
||
if not cur.left and not cur.right: # 遇到叶子节点直接返回
|
||
return False
|
||
|
||
if cur.left: # 左
|
||
count -= cur.left.val
|
||
if self.traversal(cur.left, count): # 递归,处理节点
|
||
return True
|
||
count += cur.left.val # 回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
|
||
if cur.right: # 右
|
||
count -= cur.right.val
|
||
if self.traversal(cur.right, count): # 递归,处理节点
|
||
return True
|
||
count += cur.right.val # 回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
|
||
return False
|
||
|
||
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
|
||
if root is None:
|
||
return False
|
||
return self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
(版本二) 递归 + 精简
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
|
||
if not root:
|
||
return False
|
||
if not root.left and not root.right and targetSum == root.val:
|
||
return True
|
||
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
(版本三) 迭代
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
|
||
if not root:
|
||
return False
|
||
# 此时栈里要放的是pair<节点指针,路径数值>
|
||
st = [(root, root.val)]
|
||
while st:
|
||
node, path_sum = st.pop()
|
||
# 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true
|
||
if not node.left and not node.right and path_sum == sum:
|
||
return True
|
||
# 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if node.right:
|
||
st.append((node.right, path_sum + node.right.val))
|
||
# 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来
|
||
if node.left:
|
||
st.append((node.left, path_sum + node.left.val))
|
||
return False
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||
|
||
(版本一) 递归
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
self.result = []
|
||
self.path = []
|
||
|
||
def traversal(self, cur, count):
|
||
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0: # 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为sum的路径
|
||
self.result.append(self.path[:])
|
||
return
|
||
|
||
if not cur.left and not cur.right: # 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||
return
|
||
|
||
if cur.left: # 左 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
self.path.append(cur.left.val)
|
||
count -= cur.left.val
|
||
self.traversal(cur.left, count) # 递归
|
||
count += cur.left.val # 回溯
|
||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||
|
||
if cur.right: # 右 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
self.path.append(cur.right.val)
|
||
count -= cur.right.val
|
||
self.traversal(cur.right, count) # 递归
|
||
count += cur.right.val # 回溯
|
||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||
|
||
return
|
||
|
||
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||
self.result.clear()
|
||
self.path.clear()
|
||
if not root:
|
||
return self.result
|
||
self.path.append(root.val) # 把根节点放进路径
|
||
self.traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
|
||
return self.result
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
(版本二) 递归 + 精简
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||
|
||
result = []
|
||
self.traversal(root, targetSum, [], result)
|
||
return result
|
||
def traversal(self,node, count, path, result):
|
||
if not node:
|
||
return
|
||
path.append(node.val)
|
||
count -= node.val
|
||
if not node.left and not node.right and count == 0:
|
||
result.append(list(path))
|
||
self.traversal(node.left, count, path, result)
|
||
self.traversal(node.right, count, path, result)
|
||
path.pop()
|
||
```
|
||
(版本三) 迭代
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||
if not root:
|
||
return []
|
||
stack = [(root, [root.val])]
|
||
res = []
|
||
while stack:
|
||
node, path = stack.pop()
|
||
if not node.left and not node.right and sum(path) == targetSum:
|
||
res.append(path)
|
||
if node.right:
|
||
stack.append((node.right, path + [node.right.val]))
|
||
if node.left:
|
||
stack.append((node.left, path + [node.left.val]))
|
||
return res
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
### Go
|
||
|
||
112. 路径总和
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
//递归法
|
||
/**
|
||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
* type TreeNode struct {
|
||
* Val int
|
||
* Left *TreeNode
|
||
* Right *TreeNode
|
||
* }
|
||
*/
|
||
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
|
||
if root == nil {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
return traversal(root, targetSum - root.Val)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func traversal(cur *TreeNode, count int) bool {
|
||
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil && count == 0 {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
if cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
if cur.Left != nil {
|
||
count -= cur.Left.Val
|
||
if traversal(cur.Left, count) {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
count += cur.Left.Val
|
||
}
|
||
if cur.Right != nil {
|
||
count -= cur.Right.Val
|
||
if traversal(cur.Right, count) {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
count += cur.Right.Val
|
||
}
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
//递归法精简
|
||
/**
|
||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
* type TreeNode struct {
|
||
* Val int
|
||
* Left *TreeNode
|
||
* Right *TreeNode
|
||
* }
|
||
*/
|
||
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
|
||
if root == nil {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
targetSum -= root.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
|
||
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
return hasPathSum(root.Left, targetSum) || hasPathSum(root.Right, targetSum) // 否则递归找
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
113. 路径总和 II
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
/**
|
||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
* type TreeNode struct {
|
||
* Val int
|
||
* Left *TreeNode
|
||
* Right *TreeNode
|
||
* }
|
||
*/
|
||
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) [][]int {
|
||
result := make([][]int, 0)
|
||
traverse(root, &result, new([]int), targetSum)
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func traverse(node *TreeNode, result *[][]int, currPath *[]int, targetSum int) {
|
||
if node == nil { // 这个判空也可以挪到递归遍历左右子树时去判断
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
targetSum -= node.Val // 将targetSum在遍历每层的时候都减去本层节点的值
|
||
*currPath = append(*currPath, node.Val) // 把当前节点放到路径记录里
|
||
|
||
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil && targetSum == 0 { // 如果剩余的targetSum为0, 则正好就是符合的结果
|
||
// 不能直接将currPath放到result里面, 因为currPath是共享的, 每次遍历子树时都会被修改
|
||
pathCopy := make([]int, len(*currPath))
|
||
for i, element := range *currPath {
|
||
pathCopy[i] = element
|
||
}
|
||
*result = append(*result, pathCopy) // 将副本放到结果集里
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
traverse(node.Left, result, currPath, targetSum)
|
||
traverse(node.Right, result, currPath, targetSum)
|
||
*currPath = (*currPath)[:len(*currPath)-1] // 当前节点遍历完成, 从路径记录里删除掉
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### JavaScript
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param {treenode} root
|
||
* @param {number} targetsum
|
||
* @return {boolean}
|
||
*/
|
||
let haspathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
||
// 递归法
|
||
const traversal = (node, cnt) => {
|
||
// 遇到叶子节点,并且计数为0
|
||
if (cnt === 0 && !node.left && !node.right) return true;
|
||
// 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边(计数不为0),直接返回
|
||
if (!node.left && !node.right) return false;
|
||
|
||
// 左(空节点不遍历).遇到叶子节点返回true,则直接返回true
|
||
if (node.left && traversal(node.left, cnt - node.left.val)) return true;
|
||
// 右(空节点不遍历)
|
||
if (node.right && traversal(node.right, cnt - node.right.val)) return true;
|
||
return false;
|
||
};
|
||
if (!root) return false;
|
||
return traversal(root, targetsum - root.val);
|
||
|
||
// 精简代码:
|
||
// if (!root) return false;
|
||
// if (!root.left && !root.right && targetsum === root.val) return true;
|
||
// return haspathsum(root.left, targetsum - root.val) || haspathsum(root.right, targetsum - root.val);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
let hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||
if(root === null) return false;
|
||
let nodeArr = [root];
|
||
let valArr = [0];
|
||
while(nodeArr.length) {
|
||
let curNode = nodeArr.shift();
|
||
let curVal = valArr.shift();
|
||
curVal += curNode.val;
|
||
// 为叶子结点,且和等于目标数,返回true
|
||
if (curNode.left === null && curNode.right === null && curVal === targetSum) {
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
// 左节点,将当前的数值也对应记录下来
|
||
if (curNode.left) {
|
||
nodeArr.push(curNode.left);
|
||
valArr.push(curVal);
|
||
}
|
||
// 右节点,将当前的数值也对应记录下来
|
||
if (curNode.right) {
|
||
nodeArr.push(curNode.right);
|
||
valArr.push(curVal);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
let pathsum = function (root, targetsum) {
|
||
// 递归法
|
||
// 要遍历整个树找到所有路径,所以递归函数不需要返回值, 与112不同
|
||
const res = [];
|
||
const travelsal = (node, cnt, path) => {
|
||
// 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为sum的路径
|
||
if (cnt === 0 && !node.left && !node.right) {
|
||
res.push([...path]); // 不能写res.push(path), 要深拷贝
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
if (!node.left && !node.right) return; // 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||
// 左 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
if (node.left) {
|
||
path.push(node.left.val);
|
||
travelsal(node.left, cnt - node.left.val, path); // 递归
|
||
path.pop(); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
// 右 (空节点不遍历)
|
||
if (node.right) {
|
||
path.push(node.right.val);
|
||
travelsal(node.right, cnt - node.right.val, path); // 递归
|
||
path.pop(); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
return;
|
||
};
|
||
if (!root) return res;
|
||
travelsal(root, targetsum - root.val, [root.val]); // 把根节点放进路径
|
||
return res;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**递归 精简版**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var pathsum = function(root, targetsum) {
|
||
//递归方法
|
||
let respath = [],curpath = [];
|
||
// 1. 确定递归函数参数
|
||
const traveltree = function(node,count) {
|
||
curpath.push(node.val);
|
||
count -= node.val;
|
||
if(node.left === null && node.right === null && count === 0) {
|
||
respath.push([...curpath]);
|
||
}
|
||
node.left && traveltree(node.left, count);
|
||
node.right && traveltree(node.right, count);
|
||
let cur = curpath.pop();
|
||
count -= cur;
|
||
}
|
||
if(root === null) {
|
||
return respath;
|
||
}
|
||
travelTree(root, targetSum);
|
||
return resPath;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
let pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
|
||
if(root === null) return [];
|
||
let nodeArr = [root];
|
||
let resArr = []; // 记录符合目标和的返回路径
|
||
let tempArr = [[]]; // 对应路径
|
||
let countArr = [0]; //对应和
|
||
while(nodeArr.length) {
|
||
let curNode = nodeArr.shift();
|
||
let curVal = countArr.shift();
|
||
let curNodeArr = tempArr.shift();
|
||
curVal += curNode.val;
|
||
curNodeArr.push(curNode.val);
|
||
// 为叶子结点,且和等于目标数,将此次结果数组push进返回数组中
|
||
if (curNode.left === null && curNode.right === null && curVal === targetSum) {
|
||
resArr.push(curNodeArr);
|
||
}
|
||
// 左节点,将当前的和及对应路径也对应记录下来
|
||
if (curNode.left) {
|
||
nodeArr.push(curNode.left);
|
||
countArr.push(curVal);
|
||
tempArr.push([...curNodeArr]);
|
||
}
|
||
// 右节点,将当前的和及对应路径也对应记录下来
|
||
if (curNode.right) {
|
||
nodeArr.push(curNode.right);
|
||
countArr.push(curVal);
|
||
tempArr.push([...curNodeArr]);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return resArr;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### TypeScript
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
**递归法:**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function hasPathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): boolean {
|
||
function recur(node: TreeNode, sum: number): boolean {
|
||
console.log(sum);
|
||
if (
|
||
node.left === null &&
|
||
node.right === null &&
|
||
sum === 0
|
||
) return true;
|
||
if (node.left !== null) {
|
||
sum -= node.left.val;
|
||
if (recur(node.left, sum) === true) return true;
|
||
sum += node.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
if (node.right !== null) {
|
||
sum -= node.right.val;
|
||
if (recur(node.right, sum) === true) return true;
|
||
sum += node.right.val;
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
if (root === null) return false;
|
||
return recur(root, targetSum - root.val);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**递归法(精简版):**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function hasPathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): boolean {
|
||
if (root === null) return false;
|
||
targetSum -= root.val;
|
||
if (
|
||
root.left === null &&
|
||
root.right === null &&
|
||
targetSum === 0
|
||
) return true;
|
||
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum) ||
|
||
hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代法:**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function hasPathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): boolean {
|
||
type Pair = {
|
||
node: TreeNode, // 当前节点
|
||
sum: number // 根节点到当前节点的路径数值总和
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
const helperStack: Pair[] = [];
|
||
if (root !== null) helperStack.push({ node: root, sum: root.val });
|
||
let tempPair: Pair;
|
||
while (helperStack.length > 0) {
|
||
tempPair = helperStack.pop()!;
|
||
if (
|
||
tempPair.node.left === null &&
|
||
tempPair.node.right === null &&
|
||
tempPair.sum === targetSum
|
||
) return true;
|
||
if (tempPair.node.right !== null) {
|
||
helperStack.push({
|
||
node: tempPair.node.right,
|
||
sum: tempPair.sum + tempPair.node.right.val
|
||
});
|
||
}
|
||
if (tempPair.node.left !== null) {
|
||
helperStack.push({
|
||
node: tempPair.node.left,
|
||
sum: tempPair.sum + tempPair.node.left.val
|
||
});
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和 ii
|
||
|
||
**递归法:**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, targetSum: number): number[][] {
|
||
function recur(node: TreeNode, sumGap: number, routeArr: number[]): void {
|
||
if (
|
||
node.left === null &&
|
||
node.right === null &&
|
||
sumGap === 0
|
||
) resArr.push([...routeArr]);
|
||
if (node.left !== null) {
|
||
sumGap -= node.left.val;
|
||
routeArr.push(node.left.val);
|
||
recur(node.left, sumGap, routeArr);
|
||
sumGap += node.left.val;
|
||
routeArr.pop();
|
||
}
|
||
if (node.right !== null) {
|
||
sumGap -= node.right.val;
|
||
routeArr.push(node.right.val);
|
||
recur(node.right, sumGap, routeArr);
|
||
sumGap += node.right.val;
|
||
routeArr.pop();
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
const resArr: number[][] = [];
|
||
if (root === null) return resArr;
|
||
const routeArr: number[] = [];
|
||
routeArr.push(root.val);
|
||
recur(root, targetSum - root.val, routeArr);
|
||
return resArr;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Swift
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
|
||
guard let root = root else {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return traversal(root, targetSum - root.val)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, _ count: Int) -> Bool {
|
||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil && count == 0 {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
|
||
if traversal(leftNode, count - leftNode.val) {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
|
||
if traversal(rightNode, count - rightNode.val) {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代**
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
func hasPathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> Bool {
|
||
guard let root = root else {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
var stack = Array<(TreeNode, Int)>()
|
||
stack.append((root, root.val))
|
||
|
||
while !stack.isEmpty {
|
||
let node = stack.removeLast()
|
||
|
||
if node.0.left == nil && node.0.right == nil && targetSum == node.1 {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let rightNode = node.0.right {
|
||
stack.append((rightNode, node.1 + rightNode.val))
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let leftNode = node.0.left {
|
||
stack.append((leftNode, node.1 + leftNode.val))
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和 II
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
var result = [[Int]]()
|
||
var path = [Int]()
|
||
func pathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ targetSum: Int) -> [[Int]] {
|
||
result.removeAll()
|
||
path.removeAll()
|
||
guard let root = root else {
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
path.append(root.val)
|
||
traversal(root, count: targetSum - root.val)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func traversal(_ cur: TreeNode?, count: Int) {
|
||
var count = count
|
||
// 遇到了叶子节点且找到了和为targetSum的路径
|
||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil && count == 0 {
|
||
result.append(path)
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 遇到叶子节点而没有找到合适的边,直接返回
|
||
if cur?.left == nil && cur?.right == nil{
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let leftNode = cur?.left {
|
||
path.append(leftNode.val)
|
||
count -= leftNode.val
|
||
traversal(leftNode, count: count)// 递归
|
||
count += leftNode.val// 回溯
|
||
path.removeLast()// 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if let rightNode = cur?.right {
|
||
path.append(rightNode.val)
|
||
count -= rightNode.val
|
||
traversal(rightNode, count: count)// 递归
|
||
count += rightNode.val// 回溯
|
||
path.removeLast()// 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### C
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
递归法:
|
||
|
||
```c
|
||
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
||
// 递归结束条件:若当前节点不存在,返回false
|
||
if(!root)
|
||
return false;
|
||
// 若当前节点为叶子节点,且targetSum-root的值为0。(当前路径上的节点值的和满足条件)返回true
|
||
if(!root->right && !root->left && targetSum == root->val)
|
||
return true;
|
||
|
||
// 查看左子树和右子树的所有节点是否满足条件
|
||
return hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代法:
|
||
|
||
```c
|
||
// 存储一个节点以及当前的和
|
||
struct Pair {
|
||
struct TreeNode* node;
|
||
int sum;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
|
||
struct Pair stack[1000];
|
||
int stackTop = 0;
|
||
|
||
// 若root存在,则将节点和值封装成一个pair入栈
|
||
if(root) {
|
||
struct Pair newPair = {root, root->val};
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 当栈不为空时
|
||
while(stackTop) {
|
||
// 出栈栈顶元素
|
||
struct Pair topPair = stack[--stackTop];
|
||
// 若栈顶元素为叶子节点,且和为targetSum时,返回true
|
||
if(!topPair.node->left && !topPair.node->right && topPair.sum == targetSum)
|
||
return true;
|
||
|
||
// 若当前栈顶节点有左右孩子,计算和并入栈
|
||
if(topPair.node->left) {
|
||
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->left, topPair.sum + topPair.node->left->val};
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||
}
|
||
if(topPair.node->right) {
|
||
struct Pair newPair = {topPair.node->right, topPair.sum + topPair.node->right->val};
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = newPair;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和 II
|
||
|
||
```c
|
||
int** ret;
|
||
int* path;
|
||
int* colSize;
|
||
int retTop;
|
||
int pathTop;
|
||
|
||
void traversal(const struct TreeNode* const node, int count) {
|
||
// 若当前节点为叶子节点
|
||
if(!node->right && !node->left) {
|
||
// 若当前path上的节点值总和等于targetSum。
|
||
if(count == 0) {
|
||
// 复制当前path
|
||
int *curPath = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pathTop);
|
||
memcpy(curPath, path, sizeof(int) * pathTop);
|
||
// 记录当前path的长度为pathTop
|
||
colSize[retTop] = pathTop;
|
||
// 将当前path加入到ret数组中
|
||
ret[retTop++] = curPath;
|
||
}
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 若节点有左/右孩子
|
||
if(node->left) {
|
||
// 将左孩子的值加入path中
|
||
path[pathTop++] = node->left->val;
|
||
traversal(node->left, count - node->left->val);
|
||
// 回溯
|
||
pathTop--;
|
||
}
|
||
if(node->right) {
|
||
// 将右孩子的值加入path中
|
||
path[pathTop++] = node->right->val;
|
||
traversal(node->right, count - node->right->val);
|
||
// 回溯
|
||
--pathTop;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||
// 初始化数组
|
||
ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 1000);
|
||
path = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 1000);
|
||
colSize = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
|
||
retTop = pathTop = 0;
|
||
*returnSize = 0;
|
||
|
||
// 若根节点不存在,返回空的ret
|
||
if(!root)
|
||
return ret;
|
||
// 将根节点加入到path中
|
||
path[pathTop++] = root->val;
|
||
traversal(root, targetSum - root->val);
|
||
|
||
// 设置返回ret数组大小,以及其中每个一维数组元素的长度
|
||
*returnSize = retTop;
|
||
*returnColumnSizes = colSize;
|
||
|
||
return ret;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Scala
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
**递归:**
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
|
||
if(root == null) return false
|
||
var res = false
|
||
|
||
def traversal(curNode: TreeNode, sum: Int): Unit = {
|
||
if (res) return // 如果直接标记为true了,就没有往下递归的必要了
|
||
if (curNode.left == null && curNode.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
|
||
res = true
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
// 往下递归
|
||
if (curNode.left != null) traversal(curNode.left, sum + curNode.left.value)
|
||
if (curNode.right != null) traversal(curNode.right, sum + curNode.right.value)
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
traversal(root, root.value)
|
||
res // return关键字可以省略
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代:**
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||
def hasPathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): Boolean = {
|
||
if (root == null) return false
|
||
val stack = mutable.Stack[(TreeNode, Int)]()
|
||
stack.push((root, root.value)) // 将根节点元素放入stack
|
||
while (!stack.isEmpty) {
|
||
val curNode = stack.pop() // 取出栈顶元素
|
||
// 如果遇到叶子节点,看当前的值是否等于targetSum,等于则返回true
|
||
if (curNode._1.left == null && curNode._1.right == null && curNode._2 == targetSum) {
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
if (curNode._1.right != null) stack.push((curNode._1.right, curNode._2 + curNode._1.right.value))
|
||
if (curNode._1.left != null) stack.push((curNode._1.left, curNode._2 + curNode._1.left.value))
|
||
}
|
||
false //如果没有返回true,即可返回false,return关键字可以省略
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和 II
|
||
|
||
**递归:**
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
|
||
def pathSum(root: TreeNode, targetSum: Int): List[List[Int]] = {
|
||
val res = ListBuffer[List[Int]]()
|
||
if (root == null) return res.toList
|
||
val path = ListBuffer[Int]();
|
||
|
||
def traversal(cur: TreeNode, count: Int): Unit = {
|
||
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null && count == 0) {
|
||
res.append(path.toList)
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur.left != null) {
|
||
path.append(cur.left.value)
|
||
traversal(cur.left, count - cur.left.value)
|
||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||
}
|
||
if (cur.right != null) {
|
||
path.append(cur.right.value)
|
||
traversal(cur.right, count - cur.right.value)
|
||
path.remove(path.size - 1)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
path.append(root.value)
|
||
traversal(root, targetSum - root.value)
|
||
res.toList
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Rust
|
||
|
||
0112.路径总和
|
||
|
||
递归:
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::rc::Rc;
|
||
use std::cell::RefCell;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn has_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
|
||
if root.is_none() {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
let node = root.unwrap();
|
||
if node.borrow().left.is_none() && node.borrow().right.is_none() {
|
||
return node.borrow().val == target_sum;
|
||
}
|
||
return Self::has_path_sum(node.borrow().left.clone(), target_sum - node.borrow().val)
|
||
|| Self::has_path_sum(node.borrow().right.clone(), target_sum - node.borrow().val);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代:
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::rc::Rc;
|
||
use std::cell::RefCell;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn has_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> bool {
|
||
let mut stack = vec![];
|
||
if let Some(node) = root {
|
||
stack.push((node.borrow().val, node.to_owned()));
|
||
}
|
||
while !stack.is_empty() {
|
||
let (value, node) = stack.pop().unwrap();
|
||
if node.borrow().left.is_none() && node.borrow().right.is_none() && value == target_sum
|
||
{
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
if node.borrow().left.is_some() {
|
||
if let Some(r) = node.borrow().left.as_ref() {
|
||
stack.push((r.borrow().val + value, r.to_owned()));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if node.borrow().right.is_some() {
|
||
if let Some(r) = node.borrow().right.as_ref() {
|
||
stack.push((r.borrow().val + value, r.to_owned()));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
false
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
0113.路径总和-ii
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
|
||
let mut res = vec![];
|
||
let mut route = vec![];
|
||
if root.is_none() {
|
||
return res;
|
||
} else {
|
||
route.push(root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val);
|
||
}
|
||
Self::recur(
|
||
&root,
|
||
target_sum - root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val,
|
||
&mut res,
|
||
&mut route,
|
||
);
|
||
res
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
pub fn recur(
|
||
root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
|
||
sum: i32,
|
||
res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>,
|
||
route: &mut Vec<i32>,
|
||
) {
|
||
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
|
||
if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() && sum == 0 {
|
||
res.push(route.to_vec());
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
if node.left.is_some() {
|
||
let left = node.left.as_ref().unwrap();
|
||
route.push(left.borrow().val);
|
||
Self::recur(&node.left, sum - left.borrow().val, res, route);
|
||
route.pop();
|
||
}
|
||
if node.right.is_some() {
|
||
let right = node.right.as_ref().unwrap();
|
||
route.push(right.borrow().val);
|
||
Self::recur(&node.right, sum - right.borrow().val, res, route);
|
||
route.pop();
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
### C#
|
||
```csharp
|
||
// 0112.路径总和
|
||
// 递归
|
||
public bool HasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum)
|
||
{
|
||
if (root == null) return false;
|
||
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == root.val) return true;
|
||
return HasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || HasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
0113.路径总和:
|
||
```csharp
|
||
/*
|
||
* @lc app=leetcode id=113 lang=csharp
|
||
* 0113.路径总和 II
|
||
* [113] Path Sum II
|
||
* 递归法
|
||
*/
|
||
public class Solution {
|
||
private List<List<int>> result = new List<List<int>>();
|
||
private List<int> path = new List<int>();
|
||
|
||
// Main function to find paths with the given sum
|
||
public IList<IList<int>> PathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
|
||
result.Clear();
|
||
path.Clear();
|
||
if (root == null) return result.Select(list => list as IList<int>).ToList();
|
||
path.Add(root.val); // Add the root node to the path
|
||
traversal(root, targetSum - root.val); // Start the traversal
|
||
return result.Select(list => list as IList<int>).ToList();
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Recursive function to traverse the tree and find paths
|
||
private void traversal(TreeNode node, int count) {
|
||
// If a leaf node is reached and the target sum is achieved
|
||
if (node.left == null && node.right == null && count == 0) {
|
||
result.Add(new List<int>(path)); // Add a copy of the path to the result
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// If a leaf node is reached and the target sum is not achieved, or if it's not a leaf node
|
||
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return;
|
||
|
||
// Traverse the left subtree
|
||
if (node.left != null) {
|
||
path.Add(node.left.val);
|
||
count -= node.left.val;
|
||
traversal(node.left, count); // Recursive call
|
||
count += node.left.val; // Backtrack
|
||
path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); // Backtrack
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Traverse the right subtree
|
||
if (node.right != null) {
|
||
path.Add(node.right.val);
|
||
count -= node.right.val;
|
||
traversal(node.right, count); // Recursive call
|
||
count += node.right.val; // Backtrack
|
||
path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); // Backtrack
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// @lc code=end
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|