249 lines
8.5 KiB
Markdown
249 lines
8.5 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 200. 岛屿数量
|
||
|
||
[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-islands/)
|
||
|
||
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
|
||
|
||
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
|
||
|
||
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
提示:
|
||
|
||
* m == grid.length
|
||
* n == grid[i].length
|
||
* 1 <= m, n <= 300
|
||
* grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
注意题目中每座岛屿只能由**水平方向和/或竖直方向上**相邻的陆地连接形成。
|
||
|
||
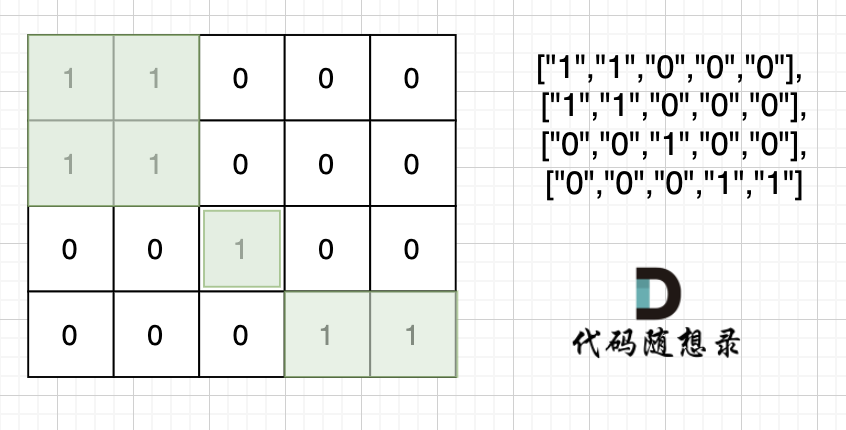
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
|
||
|
||
本题思路,是用遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
|
||
|
||
在遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
|
||
|
||
那么如果把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
|
||
|
||
### 广度优先搜索
|
||
|
||
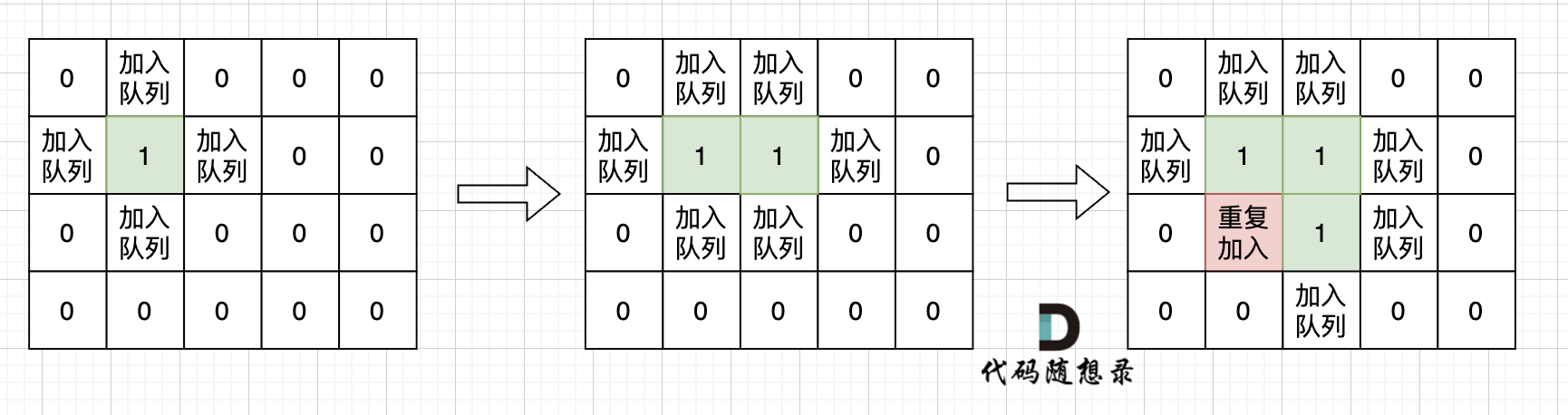
不少同学用广搜做这道题目的时候,超时了。 这里有一个广搜中很重要的细节:
|
||
|
||
根本原因是**只要 加入队列就代表 走过,就需要标记,而不是从队列拿出来的时候再去标记走过**。
|
||
|
||
很多同学可能感觉这有区别吗?
|
||
|
||
如果从队列拿出节点,再去标记这个节点走过,就会发生下图所示的结果,会导致很多节点重复加入队列。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
超时写法 (从队列中取出节点再标记)
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||
que.push({x, y});
|
||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||
visited[curx][cury] = true; // 从队列中取出在标记走过
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
加入队列 就代表走过,立刻标记,正确写法:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||
que.push({x, y});
|
||
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
以上两个版本其实,其实只有细微区别,就是 `visited[x][y] = true;` 放在的地方,着去取决于我们对 代码中队列的定义,队列中的节点就表示已经走过的节点。 **所以只要加入队列,立即标记该节点走过**。
|
||
|
||
本题完整广搜代码:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
|
||
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
|
||
que.push({x, y});
|
||
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
|
||
while(!que.empty()) {
|
||
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
|
||
int curx = cur.first;
|
||
int cury = cur.second;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
|
||
que.push({nextx, nexty});
|
||
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
public:
|
||
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
|
||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
|
||
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
|
||
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
|
||
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
|
||
boolean[][] visited;
|
||
int[][] move = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
|
||
|
||
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
|
||
int res = 0;
|
||
visited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
|
||
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
|
||
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
|
||
if(!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == '1') {
|
||
bfs(grid, i, j);
|
||
res++;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//将这片岛屿上的所有陆地都访问到
|
||
public void bfs(char[][] grid, int y, int x) {
|
||
Deque<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
|
||
queue.offer(new int[]{y, x});
|
||
visited[y][x] = true;
|
||
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
|
||
int[] cur = queue.poll();
|
||
int m = cur[0];
|
||
int n = cur[1];
|
||
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nexty = m + move[i][0];
|
||
int nextx = n + move[i][1];
|
||
if(nextx < 0 || nexty == grid.length || nexty < 0 || nextx == grid[0].length) continue;
|
||
if(!visited[nexty][nextx] && grid[nexty][nextx] == '1') {
|
||
queue.offer(new int[]{nexty, nextx});
|
||
visited[nexty][nextx] = true; //只要加入队列就标记为访问
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
BFS solution
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
self.dirs = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
|
||
|
||
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
|
||
m = len(grid)
|
||
n = len(grid[0])
|
||
visited = [[False]*n for _ in range(m)]
|
||
res = 0
|
||
for i in range(m):
|
||
for j in range(n):
|
||
if visited[i][j] == False and grid[i][j] == '1':
|
||
res += 1
|
||
self.bfs(grid, i, j, visited) # Call bfs within this condition
|
||
return res
|
||
|
||
def bfs(self, grid, i, j, visited):
|
||
q = deque()
|
||
q.append((i,j))
|
||
visited[i][j] = True
|
||
while q:
|
||
x, y = q.popleft()
|
||
for k in range(4):
|
||
next_i = x + self.dirs[k][0]
|
||
next_j = y + self.dirs[k][1]
|
||
|
||
if next_i < 0 or next_i >= len(grid):
|
||
continue
|
||
if next_j < 0 or next_j >= len(grid[0]):
|
||
continue
|
||
if visited[next_i][next_j]:
|
||
continue
|
||
if grid[next_i][next_j] == '0':
|
||
continue
|
||
q.append((next_i, next_j))
|
||
visited[next_i][next_j] = True
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
```
|
||
|