225 lines
7.9 KiB
Markdown
225 lines
7.9 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 797.所有可能的路径
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/all-paths-from-source-to-target/)
|
||
|
||
给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序)
|
||
|
||
graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
|
||
|
||
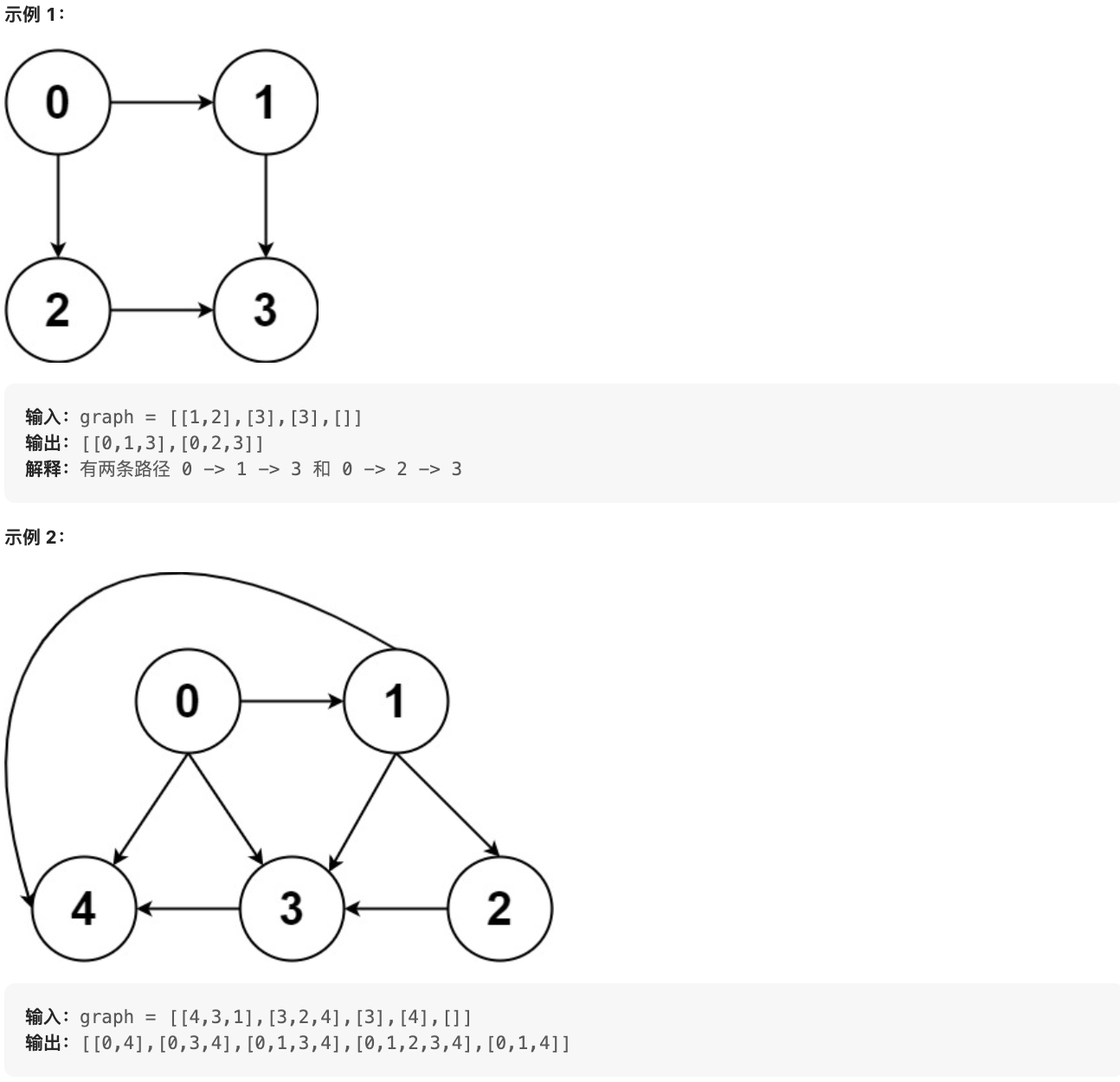
|
||
|
||
提示:
|
||
|
||
* n == graph.length
|
||
* 2 <= n <= 15
|
||
* 0 <= graph[i][j] < n
|
||
* graph[i][j] != i(即不存在自环)
|
||
* graph[i] 中的所有元素 互不相同
|
||
* 保证输入为 有向无环图(DAG)
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
这道题目是深度优先搜索,比较好的入门题。
|
||
|
||
如果对深度优先搜索还不够了解,可以先看这里:[深度优先搜索的理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/图论深搜理论基础.html)
|
||
|
||
我依然总结了深搜三部曲,如果按照代码随想录刷题的录友,应该刷过 二叉树的递归三部曲,回溯三部曲。
|
||
|
||
**大家可能有疑惑,深搜 和 二叉树和回溯算法 有什么区别呢**? 什么时候用深搜 什么时候用回溯?
|
||
|
||
我在讲解[二叉树理论基础](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树理论基础.html)的时候,提到过,**二叉树的前中后序遍历其实就是深搜在二叉树这种数据结构上的应用**。
|
||
|
||
那么回溯算法呢,**其实 回溯算法就是 深搜,只不过 我们给他一个更细分的定义,叫做回溯算法**。
|
||
|
||
那有的录友可能说:那我以后称回溯算法为深搜,是不是没毛病?
|
||
|
||
理论上来说,没毛病,但 就像是 二叉树 你不叫它二叉树,叫它数据结构,有问题不? 也没问题对吧。
|
||
|
||
建议是 有细分的场景,还是称其细分场景的名称。 所以回溯算法可以独立出来,但回溯确实就是深搜。
|
||
|
||
接下来我们使用深搜三部曲来分析题目:
|
||
|
||
1. 确认递归函数,参数
|
||
|
||
首先我们dfs函数一定要存一个图,用来遍历的,还要存一个目前我们遍历的节点,定义为x
|
||
|
||
至于 单一路径,和路径集合可以放在全局变量,那么代码是这样的:
|
||
|
||
```c++
|
||
vector<vector<int>> result; // 收集符合条件的路径
|
||
vector<int> path; // 0节点到终点的路径
|
||
// x:目前遍历的节点
|
||
// graph:存当前的图
|
||
void dfs (vector<vector<int>>& graph, int x)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
2. 确认终止条件
|
||
|
||
什么时候我们就找到一条路径了?
|
||
|
||
当目前遍历的节点 为 最后一个节点的时候,就找到了一条,从 出发点到终止点的路径。
|
||
|
||
当前遍历的节点,我们定义为x,最后一点节点,就是 graph.size() - 1(因为题目描述是找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出)。
|
||
|
||
所以 但 x 等于 graph.size() - 1 的时候就找到一条有效路径。 代码如下:
|
||
|
||
|
||
```c++
|
||
// 要求从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出,所以是 graph.size() - 1
|
||
if (x == graph.size() - 1) { // 找到符合条件的一条路径
|
||
result.push_back(path); // 收集有效路径
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
3. 处理目前搜索节点出发的路径
|
||
|
||
接下来是走 当前遍历节点x的下一个节点。
|
||
|
||
首先是要找到 x节点链接了哪些节点呢? 遍历方式是这样的:
|
||
|
||
```c++
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) { // 遍历节点n链接的所有节点
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
接下来就是将 选中的x所连接的节点,加入到 单一路劲来。
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
path.push_back(graph[x][i]); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
一些录友可以疑惑这里如果找到x 链接的节点的,例如如果x目前是节点0,那么目前的过程就是这样的:
|
||
|
||
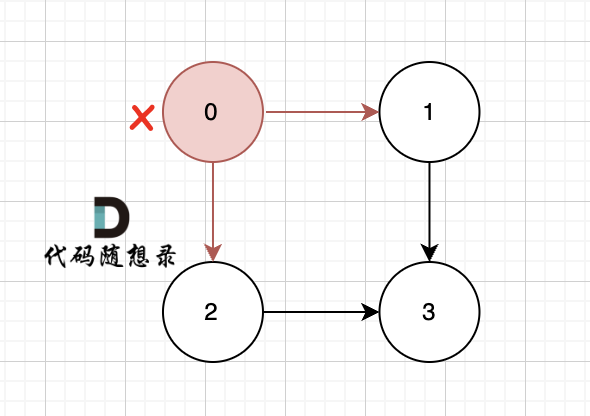
|
||
|
||
二维数组中,graph[x][i] 都是x链接的节点,当前遍历的节点就是 `graph[x][i]` 。
|
||
|
||
进入下一层递归
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
dfs(graph, graph[x][i]); // 进入下一层递归
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
最后就是回溯的过程,撤销本次添加节点的操作。 该过程整体代码:
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) { // 遍历节点n链接的所有节点
|
||
path.push_back(graph[x][i]); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
|
||
dfs(graph, graph[x][i]); // 进入下一层递归
|
||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销本节点
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
本题整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```c++
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
vector<vector<int>> result; // 收集符合条件的路径
|
||
vector<int> path; // 0节点到终点的路径
|
||
// x:目前遍历的节点
|
||
// graph:存当前的图
|
||
void dfs (vector<vector<int>>& graph, int x) {
|
||
// 要求从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出,所以是 graph.size() - 1
|
||
if (x == graph.size() - 1) { // 找到符合条件的一条路径
|
||
result.push_back(path);
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) { // 遍历节点n链接的所有节点
|
||
path.push_back(graph[x][i]); // 遍历到的节点加入到路径中来
|
||
dfs(graph, graph[x][i]); // 进入下一层递归
|
||
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,撤销本节点
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
|
||
path.push_back(0); // 无论什么路径已经是从0节点出发
|
||
dfs(graph, 0); // 开始遍历
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
# 总结
|
||
|
||
本题是比较基础的深度优先搜索模板题,这种有向图路径问题,最合适使用深搜,当然本题也可以使用广搜,但广搜相对来说就麻烦了一些,需要记录一下路径。
|
||
|
||
而深搜和广搜都适合解决颜色类的问题,例如岛屿系列,其实都是 遍历+标记,所以使用哪种遍历都是可以的。
|
||
|
||
至于广搜理论基础,我们在下一篇在好好讲解,敬请期待!
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
## Java
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
// 深度优先遍历
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
List<List<Integer>> ans; // 用来存放满足条件的路径
|
||
List<Integer> cnt; // 用来保存 dfs 过程中的节点值
|
||
|
||
public void dfs(int[][] graph, int node) {
|
||
if (node == graph.length - 1) { // 如果当前节点是 n - 1,那么就保存这条路径
|
||
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(cnt));
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
for (int index = 0; index < graph[node].length; index++) {
|
||
int nextNode = graph[node][index];
|
||
cnt.add(nextNode);
|
||
dfs(graph, nextNode);
|
||
cnt.remove(cnt.size() - 1); // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
|
||
ans = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
cnt = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
cnt.add(0); // 注意,0 号节点要加入 cnt 数组中
|
||
dfs(graph, 0);
|
||
return ans;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## Python
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def __init__(self):
|
||
self.result = []
|
||
self.path = [0]
|
||
|
||
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
|
||
if not graph: return []
|
||
|
||
self.dfs(graph, 0)
|
||
return self.result
|
||
|
||
def dfs(self, graph, root: int):
|
||
if root == len(graph) - 1: # 成功找到一条路径时
|
||
# ***Python的list是mutable类型***
|
||
# ***回溯中必须使用Deep Copy***
|
||
self.result.append(self.path[:])
|
||
return
|
||
|
||
for node in graph[root]: # 遍历节点n的所有后序节点
|
||
self.path.append(node)
|
||
self.dfs(graph, node)
|
||
self.path.pop() # 回溯
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
|