288 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
288 lines
8.0 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20210924105952.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
## 674. 最长连续递增序列
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-continuous-increasing-subsequence/)
|
||
|
||
给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且 连续递增的子序列,并返回该序列的长度。
|
||
|
||
连续递增的子序列 可以由两个下标 l 和 r(l < r)确定,如果对于每个 l <= i < r,都有 nums[i] < nums[i + 1] ,那么子序列 [nums[l], nums[l + 1], ..., nums[r - 1], nums[r]] 就是连续递增子序列。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
输入:nums = [1,3,5,4,7]
|
||
输出:3
|
||
解释:最长连续递增序列是 [1,3,5], 长度为3。
|
||
尽管 [1,3,5,7] 也是升序的子序列, 但它不是连续的,因为 5 和 7 在原数组里被 4 隔开。
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
输入:nums = [2,2,2,2,2]
|
||
输出:1
|
||
解释:最长连续递增序列是 [2], 长度为1。
|
||
|
||
提示:
|
||
|
||
* 0 <= nums.length <= 10^4
|
||
* -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
本题相对于昨天的[动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](https://programmercarl.com/0300.最长上升子序列.html)最大的区别在于“连续”。
|
||
|
||
本题要求的是最长**连续**递增序列
|
||
|
||
### 动态规划
|
||
|
||
动规五部曲分析如下:
|
||
|
||
1. 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
|
||
|
||
**dp[i]:以下标i为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度为dp[i]**。
|
||
|
||
注意这里的定义,一定是以下标i为结尾,并不是说一定以下标0为起始位置。
|
||
|
||
2. 确定递推公式
|
||
|
||
如果 nums[i + 1] > nums[i],那么以 i+1 为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度 一定等于 以i为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度 + 1 。
|
||
|
||
即:dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1;
|
||
|
||
**注意这里就体现出和[动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](https://programmercarl.com/0300.最长上升子序列.html)的区别!**
|
||
|
||
因为本题要求连续递增子序列,所以就必要比较nums[i + 1]与nums[i],而不用去比较nums[j]与nums[i] (j是在0到i之间遍历)。
|
||
|
||
既然不用j了,那么也不用两层for循环,本题一层for循环就行,比较nums[i + 1] 和 nums[i]。
|
||
|
||
这里大家要好好体会一下!
|
||
|
||
3. dp数组如何初始化
|
||
|
||
以下标i为结尾的数组的连续递增的子序列长度最少也应该是1,即就是nums[i]这一个元素。
|
||
|
||
所以dp[i]应该初始1;
|
||
|
||
4. 确定遍历顺序
|
||
|
||
从递推公式上可以看出, dp[i + 1]依赖dp[i],所以一定是从前向后遍历。
|
||
|
||
本文在确定递推公式的时候也说明了为什么本题只需要一层for循环,代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
|
||
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { // 连续记录
|
||
dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1; // 递推公式
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
5. 举例推导dp数组
|
||
|
||
已输入nums = [1,3,5,4,7]为例,dp数组状态如下:
|
||
|
||
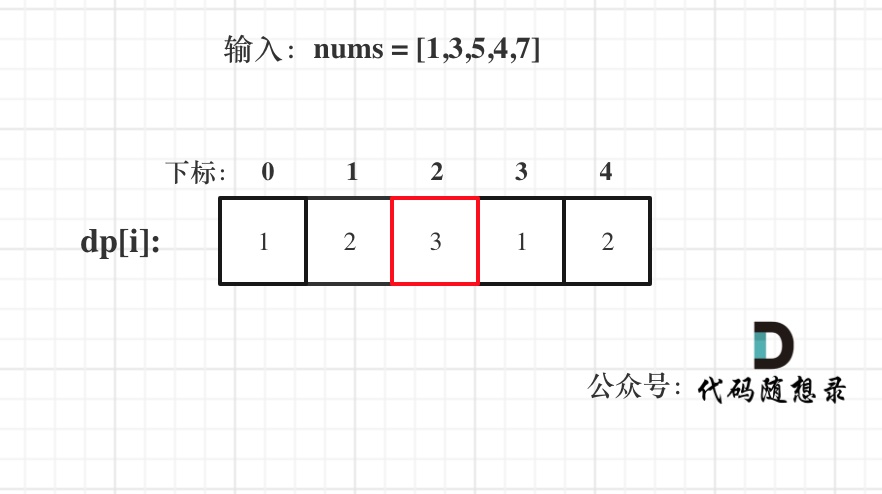
|
||
|
||
**注意这里要取dp[i]里的最大值,所以dp[2]才是结果!**
|
||
|
||
以上分析完毕,C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
|
||
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
|
||
int result = 1;
|
||
vector<int> dp(nums.size() ,1);
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
|
||
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { // 连续记录
|
||
dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1;
|
||
}
|
||
if (dp[i + 1] > result) result = dp[i + 1];
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||
* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||
|
||
### 贪心
|
||
|
||
这道题目也可以用贪心来做,也就是遇到nums[i + 1] > nums[i]的情况,count就++,否则count为1,记录count的最大值就可以了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
|
||
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
|
||
int result = 1; // 连续子序列最少也是1
|
||
int count = 1;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
|
||
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { // 连续记录
|
||
count++;
|
||
} else { // 不连续,count从头开始
|
||
count = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
if (count > result) result = count;
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
本题也是动规里子序列问题的经典题目,但也可以用贪心来做,大家也会发现贪心好像更简单一点,而且空间复杂度仅是$O(1)$。
|
||
|
||
在动规分析中,关键是要理解和[动态规划:300.最长递增子序列](https://programmercarl.com/0300.最长上升子序列.html)的区别。
|
||
|
||
**要联动起来,才能理解递增子序列怎么求,递增连续子序列又要怎么求**。
|
||
|
||
概括来说:不连续递增子序列的跟前0-i 个状态有关,连续递增的子序列只跟前一个状态有关
|
||
|
||
本篇我也把区别所在之处重点介绍了,关键在递推公式和遍历方法上,大家可以仔细体会一波!
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
|
||
Java:
|
||
|
||
> 动态规划:
|
||
```java
|
||
/**
|
||
* 1.dp[i] 代表当前下标最大连续值
|
||
* 2.递推公式 if(nums[i+1]>nums[i]) dp[i+1] = dp[i]+1
|
||
* 3.初始化 都为1
|
||
* 4.遍历方向,从其那往后
|
||
* 5.结果推导 。。。。
|
||
* @param nums
|
||
* @return
|
||
*/
|
||
public static int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
|
||
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++) {
|
||
dp[i] = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
int res = 1;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
|
||
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) {
|
||
dp[i + 1] = dp[i] + 1;
|
||
}
|
||
res = res > dp[i + 1] ? res : dp[i + 1];
|
||
}
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 贪心法:
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
public static int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
|
||
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
|
||
int res = 1; // 连续子序列最少也是1
|
||
int count = 1;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
|
||
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) { // 连续记录
|
||
count++;
|
||
} else { // 不连续,count从头开始
|
||
count = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
if (count > res) res = count;
|
||
}
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Python:
|
||
|
||
> 动态规划:
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
if len(nums) == 0:
|
||
return 0
|
||
result = 1
|
||
dp = [1] * len(nums)
|
||
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
|
||
if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录
|
||
dp[i+1] = dp[i] + 1
|
||
result = max(result, dp[i+1])
|
||
return result
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 贪心法:
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def findLengthOfLCIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
if len(nums) == 0:
|
||
return 0
|
||
result = 1 #连续子序列最少也是1
|
||
count = 1
|
||
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
|
||
if nums[i+1] > nums[i]: #连续记录
|
||
count += 1
|
||
else: #不连续,count从头开始
|
||
count = 1
|
||
result = max(result, count)
|
||
return result
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Go:
|
||
|
||
Javascript:
|
||
|
||
> 动态规划:
|
||
```javascript
|
||
const findLengthOfLCIS = (nums) => {
|
||
let dp = Array(nums.length).fill(1);
|
||
|
||
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
|
||
if(nums[i+1] > nums[i]) {
|
||
dp[i+1] = dp[i]+ 1;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return Math.max(...dp);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 贪心法:
|
||
```javascript
|
||
const findLengthOfLCIS = (nums) => {
|
||
if(nums.length === 1) {
|
||
return 1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let maxLen = 1;
|
||
let curMax = 1;
|
||
let cur = nums[0];
|
||
|
||
for(let num of nums) {
|
||
if(num > cur) {
|
||
curMax += 1;
|
||
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, curMax);
|
||
} else {
|
||
curMax = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
cur = num;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return maxLen;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
-----------------------
|
||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|