692 lines
19 KiB
Markdown
692 lines
19 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://www.programmercarl.com/xunlian/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="./qita/join.md">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 404.左叶子之和
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/)
|
||
|
||
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
|
||
|
||
示例:
|
||
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
## 算法公开课
|
||
|
||
**[《代码随想录》算法视频公开课](https://programmercarl.com/other/gongkaike.html)::[二叉树的题目中,总有一些规则让你找不到北 | LeetCode:404.左叶子之和](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1GY4y1K7z8),相信结合视频在看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解**。
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
**首先要注意是判断左叶子,不是二叉树左侧节点,所以不要上来想着层序遍历。**
|
||
|
||
因为题目中其实没有说清楚左叶子究竟是什么节点,那么我来给出左叶子的明确定义:**节点A的左孩子不为空,且左孩子的左右孩子都为空(说明是叶子节点),那么A节点的左孩子为左叶子节点**
|
||
|
||
大家思考一下如下图中二叉树,左叶子之和究竟是多少?
|
||
|
||
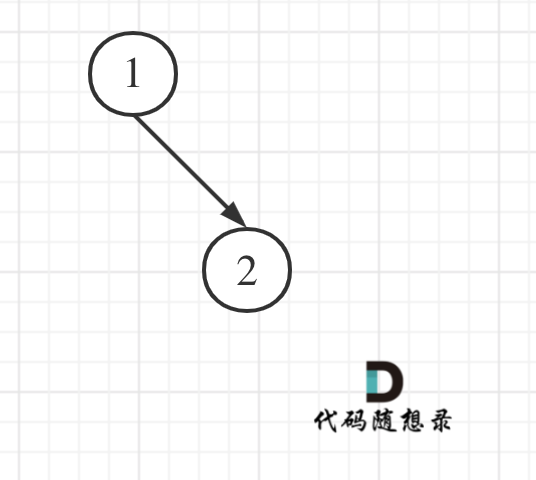
|
||
**其实是0,因为这棵树根本没有左叶子!**
|
||
|
||
但看这个图的左叶子之和是多少?
|
||
|
||
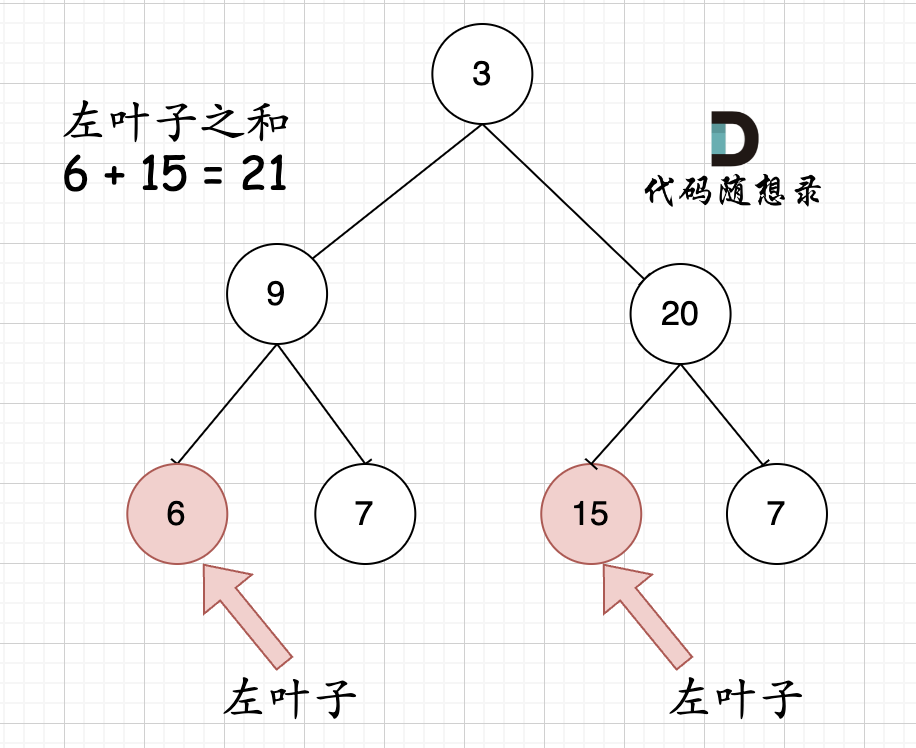
|
||
|
||
相信通过这两个图,大家对最左叶子的定义有明确理解了。
|
||
|
||
那么**判断当前节点是不是左叶子是无法判断的,必须要通过节点的父节点来判断其左孩子是不是左叶子。**
|
||
|
||
|
||
如果该节点的左节点不为空,该节点的左节点的左节点为空,该节点的左节点的右节点为空,则找到了一个左叶子,判断代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->left == NULL && node->left->right == NULL) {
|
||
左叶子节点处理逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 递归法
|
||
|
||
递归的遍历顺序为后序遍历(左右中),是因为要通过递归函数的返回值来累加求取左叶子数值之和。
|
||
|
||
递归三部曲:
|
||
|
||
1. 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
|
||
|
||
判断一个树的左叶子节点之和,那么一定要传入树的根节点,递归函数的返回值为数值之和,所以为int
|
||
|
||
使用题目中给出的函数就可以了。
|
||
|
||
2. 确定终止条件
|
||
|
||
如果遍历到空节点,那么左叶子值一定是0
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
if (root == NULL) return 0;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
注意,只有当前遍历的节点是父节点,才能判断其子节点是不是左叶子。 所以如果当前遍历的节点是叶子节点,那其左叶子也必定是0,那么终止条件为:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
if (root == NULL) return 0;
|
||
if (root->left == NULL && root->right== NULL) return 0; //其实这个也可以不写,如果不写不影响结果,但就会让递归多进行了一层。
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
|
||
|
||
当遇到左叶子节点的时候,记录数值,然后通过递归求取左子树左叶子之和,和 右子树左叶子之和,相加便是整个树的左叶子之和。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left); // 左
|
||
if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right) {
|
||
leftValue = root->left->val;
|
||
}
|
||
int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right); // 右
|
||
|
||
int sum = leftValue + rightValue; // 中
|
||
return sum;
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
整体递归代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
if (root == NULL) return 0;
|
||
if (root->left == NULL && root->right== NULL) return 0;
|
||
|
||
int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left); // 左
|
||
if (root->left && !root->left->left && !root->left->right) { // 左子树就是一个左叶子的情况
|
||
leftValue = root->left->val;
|
||
}
|
||
int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right); // 右
|
||
|
||
int sum = leftValue + rightValue; // 中
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
以上代码精简之后如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
if (root == NULL) return 0;
|
||
int leftValue = 0;
|
||
if (root->left != NULL && root->left->left == NULL && root->left->right == NULL) {
|
||
leftValue = root->left->val;
|
||
}
|
||
return leftValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
精简之后的代码其实看不出来用的是什么遍历方式了,对于算法初学者以上根据第一个版本来学习。
|
||
|
||
### 迭代法
|
||
|
||
本题迭代法使用前中后序都是可以的,只要把左叶子节点统计出来,就可以了,那么参考文章 [二叉树:听说递归能做的,栈也能做!](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的迭代遍历.html)和[二叉树:迭代法统一写法](https://programmercarl.com/二叉树的统一迭代法.html)中的写法,可以写出一个前序遍历的迭代法。
|
||
|
||
判断条件都是一样的,代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
if (root == NULL) return 0;
|
||
st.push(root);
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
TreeNode* node = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->left == NULL && node->left->right == NULL) {
|
||
result += node->left->val;
|
||
}
|
||
if (node->right) st.push(node->right);
|
||
if (node->left) st.push(node->left);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
这道题目要求左叶子之和,其实是比较绕的,因为不能判断本节点是不是左叶子节点。
|
||
|
||
此时就要通过节点的父节点来判断其左孩子是不是左叶子了。
|
||
|
||
**平时我们解二叉树的题目时,已经习惯了通过节点的左右孩子判断本节点的属性,而本题我们要通过节点的父节点判断本节点的属性。**
|
||
|
||
希望通过这道题目,可以扩展大家对二叉树的解题思路。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java:
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
|
||
if (root == null) return 0;
|
||
int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); // 左
|
||
int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); // 右
|
||
|
||
int midValue = 0;
|
||
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) {
|
||
midValue = root.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
int sum = midValue + leftValue + rightValue; // 中
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代**
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
|
||
if (root == null) return 0;
|
||
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<> ();
|
||
stack.add(root);
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
|
||
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
|
||
if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null) {
|
||
result += node.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
if (node.right != null) stack.add(node.right);
|
||
if (node.left != null) stack.add(node.left);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
```java
|
||
// 层序遍历迭代法
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
|
||
int sum = 0;
|
||
if (root == null) return 0;
|
||
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
|
||
queue.offer(root);
|
||
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
|
||
int size = queue.size();
|
||
while (size -- > 0) {
|
||
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
|
||
if (node.left != null) { // 左节点不为空
|
||
queue.offer(node.left);
|
||
if (node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null){ // 左叶子节点
|
||
sum += node.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Python:
|
||
递归
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root):
|
||
if root is None:
|
||
return 0
|
||
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
|
||
return 0
|
||
|
||
leftValue = self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) # 左
|
||
if root.left and not root.left.left and not root.left.right: # 左子树是左叶子的情况
|
||
leftValue = root.left.val
|
||
|
||
rightValue = self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right) # 右
|
||
|
||
sum_val = leftValue + rightValue # 中
|
||
return sum_val
|
||
```
|
||
递归精简版
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root):
|
||
if root is None:
|
||
return 0
|
||
leftValue = 0
|
||
if root.left is not None and root.left.left is None and root.left.right is None:
|
||
leftValue = root.left.val
|
||
return leftValue + self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代法
|
||
```python
|
||
# Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||
# class TreeNode:
|
||
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
|
||
# self.val = val
|
||
# self.left = left
|
||
# self.right = right
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root):
|
||
if root is None:
|
||
return 0
|
||
st = [root]
|
||
result = 0
|
||
while st:
|
||
node = st.pop()
|
||
if node.left and node.left.left is None and node.left.right is None:
|
||
result += node.left.val
|
||
if node.right:
|
||
st.append(node.right)
|
||
if node.left:
|
||
st.append(node.left)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go:
|
||
|
||
**递归法**
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
|
||
if root == nil {
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
leftValue := sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) // 左
|
||
|
||
if root.Left != nil && root.Left.Left == nil && root.Left.Right == nil {
|
||
leftValue = root.Left.Val // 中
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
rightValue := sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right) // 右
|
||
|
||
return leftValue + rightValue
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**递归精简版**
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
|
||
if root == nil {
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
leftValue := 0
|
||
if root.Left != nil && root.Left.Left == nil && root.Left.Right == nil {
|
||
leftValue = root.Left.Val
|
||
}
|
||
return leftValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代法(前序遍历)**
|
||
|
||
```go
|
||
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
|
||
st := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
|
||
if root == nil {
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
st = append(st, root)
|
||
result := 0
|
||
|
||
for len(st) != 0 {
|
||
node := st[len(st)-1]
|
||
st = st[:len(st)-1]
|
||
if node.Left != nil && node.Left.Left == nil && node.Left.Right == nil {
|
||
result += node.Left.Val
|
||
}
|
||
if node.Right != nil {
|
||
st = append(st, node.Right)
|
||
}
|
||
if node.Left != nil {
|
||
st = append(st, node.Left)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### JavaScript:
|
||
|
||
**递归法**
|
||
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {
|
||
//采用后序遍历 递归遍历
|
||
// 1. 确定递归函数参数
|
||
const nodesSum = function(node) {
|
||
// 2. 确定终止条件
|
||
if(node === null) {
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
let leftValue = nodesSum(node.left);
|
||
let rightValue = nodesSum(node.right);
|
||
// 3. 单层递归逻辑
|
||
let midValue = 0;
|
||
if(node.left && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {
|
||
midValue = node.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
let sum = midValue + leftValue + rightValue;
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
return nodesSum(root);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代法**
|
||
```javascript
|
||
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function(root) {
|
||
//采用层序遍历
|
||
if(root === null) {
|
||
return null;
|
||
}
|
||
let queue = [];
|
||
let sum = 0;
|
||
queue.push(root);
|
||
while(queue.length) {
|
||
let node = queue.shift();
|
||
if(node.left !== null && node.left.left === null && node.left.right === null) {
|
||
sum+=node.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
node.left && queue.push(node.left);
|
||
node.right && queue.push(node.right);
|
||
}
|
||
return sum;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### TypeScript:
|
||
|
||
> 递归法
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||
if (root === null) return 0;
|
||
let midVal: number = 0;
|
||
if (
|
||
root.left !== null &&
|
||
root.left.left === null &&
|
||
root.left.right === null
|
||
) {
|
||
midVal = root.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
let leftVal: number = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
|
||
let rightVal: number = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
|
||
return midVal + leftVal + rightVal;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 迭代法
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode | null): number {
|
||
let helperStack: TreeNode[] = [];
|
||
let tempNode: TreeNode;
|
||
let sum: number = 0;
|
||
if (root !== null) helperStack.push(root);
|
||
while (helperStack.length > 0) {
|
||
tempNode = helperStack.pop()!;
|
||
if (
|
||
tempNode.left !== null &&
|
||
tempNode.left.left === null &&
|
||
tempNode.left.right === null
|
||
) {
|
||
sum += tempNode.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
if (tempNode.right !== null) helperStack.push(tempNode.right);
|
||
if (tempNode.left !== null) helperStack.push(tempNode.left);
|
||
}
|
||
return sum;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Swift:
|
||
|
||
**递归法**
|
||
```swift
|
||
func sumOfLeftLeaves(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||
guard let root = root else {
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left)
|
||
let rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
|
||
|
||
var midValue: Int = 0
|
||
if root.left != nil && root.left?.left == nil && root.left?.right == nil {
|
||
midValue = root.left!.val
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let sum = midValue + leftValue + rightValue
|
||
return sum
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
**迭代法**
|
||
```swift
|
||
func sumOfLeftLeaves(_ root: TreeNode?) -> Int {
|
||
guard let root = root else {
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
var stack = Array<TreeNode>()
|
||
stack.append(root)
|
||
var sum = 0
|
||
|
||
while !stack.isEmpty {
|
||
let lastNode = stack.removeLast()
|
||
|
||
if lastNode.left != nil && lastNode.left?.left == nil && lastNode.left?.right == nil {
|
||
sum += lastNode.left!.val
|
||
}
|
||
if let right = lastNode.right {
|
||
stack.append(right)
|
||
}
|
||
if let left = lastNode.left {
|
||
stack.append(left)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return sum
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### C:
|
||
递归法:
|
||
```c
|
||
int sumOfLeftLeaves(struct TreeNode* root){
|
||
// 递归结束条件:若当前结点为空,返回0
|
||
if(!root)
|
||
return 0;
|
||
|
||
// 递归取左子树的左结点和和右子树的左结点和
|
||
int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);
|
||
int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
|
||
|
||
// 若当前结点的左结点存在,且其为叶子结点。取它的值
|
||
int midValue = 0;
|
||
if(root->left && (!root->left->left && !root->left->right))
|
||
midValue = root->left->val;
|
||
|
||
return leftValue + rightValue + midValue;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
迭代法:
|
||
```c
|
||
int sumOfLeftLeaves(struct TreeNode* root){
|
||
struct TreeNode* stack[1000];
|
||
int stackTop = 0;
|
||
|
||
// 若传入root结点不为空,将其入栈
|
||
if(root)
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = root;
|
||
|
||
int sum = 0;
|
||
//若栈不为空,进行循环
|
||
while(stackTop) {
|
||
// 出栈栈顶元素
|
||
struct TreeNode *topNode = stack[--stackTop];
|
||
// 若栈顶元素的左孩子为左叶子结点,将其值加入sum中
|
||
if(topNode->left && (!topNode->left->left && !topNode->left->right))
|
||
sum += topNode->left->val;
|
||
|
||
// 若当前栈顶结点有左右孩子。将他们加入栈中进行遍历
|
||
if(topNode->right)
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = topNode->right;
|
||
if(topNode->left)
|
||
stack[stackTop++] = topNode->left;
|
||
}
|
||
return sum;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Scala:
|
||
|
||
**递归:**
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||
if(root == null) return 0
|
||
var midValue = 0
|
||
if(root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null){
|
||
midValue = root.left.value
|
||
}
|
||
// return关键字可以省略
|
||
midValue + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代:**
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||
def sumOfLeftLeaves(root: TreeNode): Int = {
|
||
val stack = mutable.Stack[TreeNode]()
|
||
if (root == null) return 0
|
||
stack.push(root)
|
||
var sum = 0
|
||
while (!stack.isEmpty) {
|
||
val curNode = stack.pop()
|
||
if (curNode.left != null && curNode.left.left == null && curNode.left.right == null) {
|
||
sum += curNode.left.value // 如果满足条件就累加
|
||
}
|
||
if (curNode.right != null) stack.push(curNode.right)
|
||
if (curNode.left != null) stack.push(curNode.left)
|
||
}
|
||
sum
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Rust:
|
||
|
||
**递归**
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::cell::RefCell;
|
||
use std::rc::Rc;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn sum_of_left_leaves(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
|
||
let mut res = 0;
|
||
if let Some(node) = root {
|
||
if let Some(left) = &node.borrow().left {
|
||
if left.borrow().right.is_none() && left.borrow().right.is_none() {
|
||
res += left.borrow().val;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
res + Self::sum_of_left_leaves(node.borrow().left.clone())
|
||
+ Self::sum_of_left_leaves(node.borrow().right.clone())
|
||
} else {
|
||
0
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**迭代:**
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::cell::RefCell;
|
||
use std::rc::Rc;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn sum_of_left_leaves(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
|
||
let mut res = 0;
|
||
let mut stack = vec![root];
|
||
while !stack.is_empty() {
|
||
if let Some(node) = stack.pop().unwrap() {
|
||
if let Some(left) = &node.borrow().left {
|
||
if left.borrow().left.is_none() && left.borrow().right.is_none() {
|
||
res += left.borrow().val;
|
||
}
|
||
stack.push(Some(left.to_owned()));
|
||
}
|
||
if let Some(right) = &node.borrow().right {
|
||
stack.push(Some(right.to_owned()));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
res
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### C#
|
||
```csharp
|
||
// 递归
|
||
public int SumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root)
|
||
{
|
||
if (root == null) return 0;
|
||
|
||
int leftValue = SumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
|
||
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null)
|
||
{
|
||
leftValue += root.left.val;
|
||
}
|
||
int rightValue = SumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
|
||
return leftValue + rightValue;
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|