688 lines
18 KiB
Markdown
688 lines
18 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="https://code-thinking-1253855093.file.myqcloud.com/pics/20210924105952.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 第51题. N皇后
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/)
|
||
|
||
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
|
||
|
||
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
|
||
|
||
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
|
||
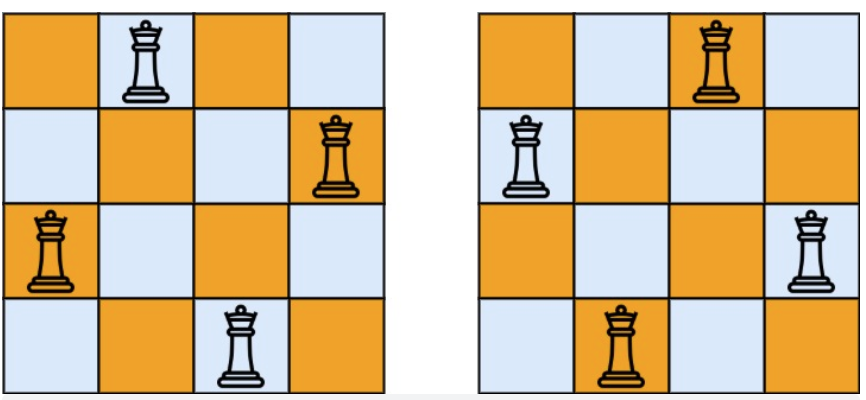
|
||
|
||
* 输入:n = 4
|
||
* 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
|
||
* 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
|
||
* 输入:n = 1
|
||
* 输出:[["Q"]]
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
**如果对回溯算法基础还不了解的话,我还特意录制了一期视频:[带你学透回溯算法(理论篇)](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cy4y167mM/)** 可以结合题解和视频一起看,希望对大家理解回溯算法有所帮助。
|
||
|
||
|
||
都知道n皇后问题是回溯算法解决的经典问题,但是用回溯解决多了组合、切割、子集、排列问题之后,遇到这种二维矩阵还会有点不知所措。
|
||
|
||
首先来看一下皇后们的约束条件:
|
||
|
||
1. 不能同行
|
||
2. 不能同列
|
||
3. 不能同斜线
|
||
|
||
确定完约束条件,来看看究竟要怎么去搜索皇后们的位置,其实搜索皇后的位置,可以抽象为一棵树。
|
||
|
||
下面我用一个 3 * 3 的棋盘,将搜索过程抽象为一棵树,如图:
|
||
|
||
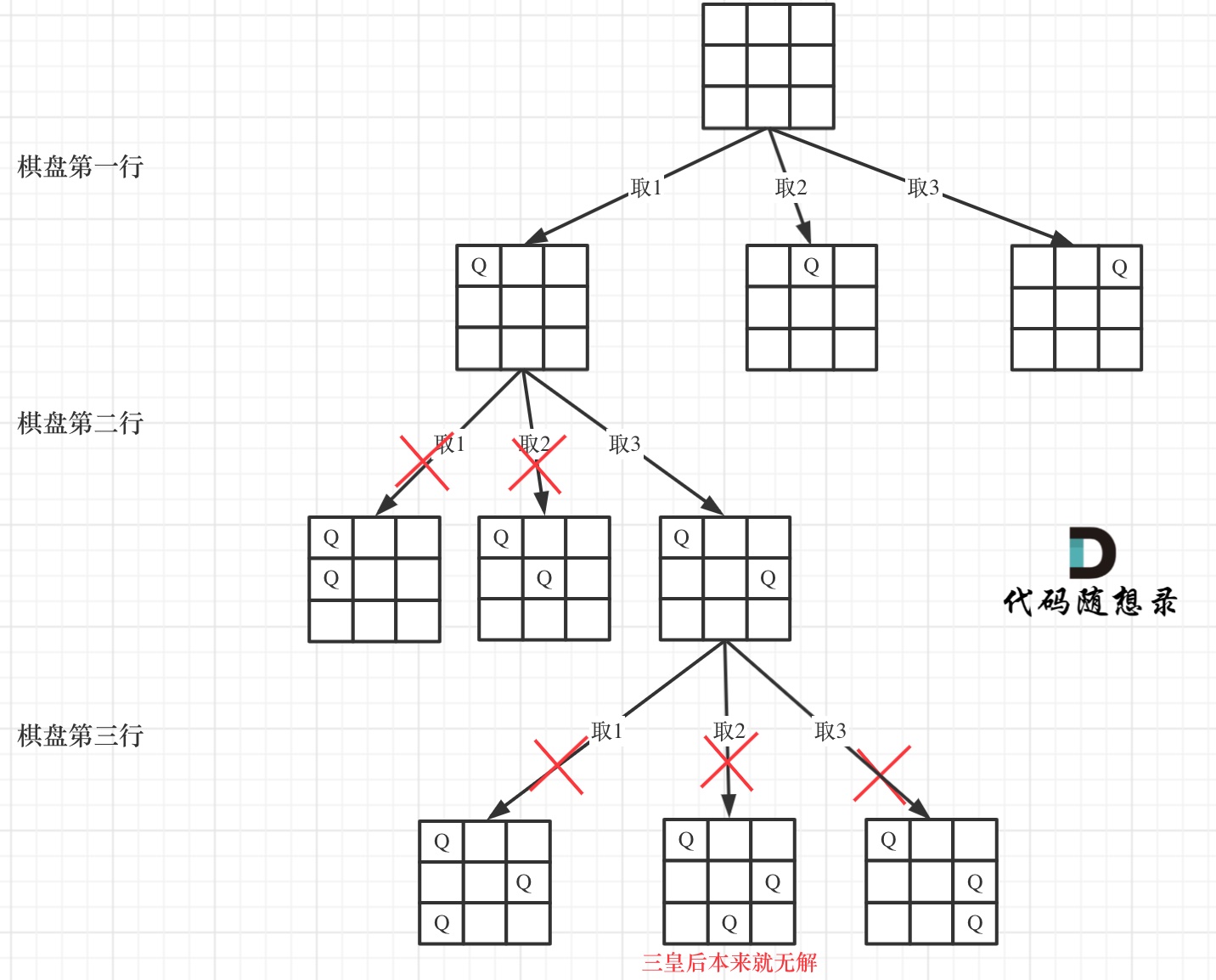
|
||
|
||
从图中,可以看出,二维矩阵中矩阵的高就是这棵树的高度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每一个节点的宽度。
|
||
|
||
那么我们用皇后们的约束条件,来回溯搜索这棵树,**只要搜索到了树的叶子节点,说明就找到了皇后们的合理位置了**。
|
||
|
||
### 回溯三部曲
|
||
|
||
按照我总结的如下回溯模板,我们来依次分析:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
void backtracking(参数) {
|
||
if (终止条件) {
|
||
存放结果;
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
|
||
处理节点;
|
||
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
|
||
回溯,撤销处理结果
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 递归函数参数
|
||
|
||
我依然是定义全局变量二维数组result来记录最终结果。
|
||
|
||
参数n是棋盘的大小,然后用row来记录当前遍历到棋盘的第几层了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
vector<vector<string>> result;
|
||
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 递归终止条件
|
||
|
||
在如下树形结构中:
|
||

|
||
|
||
|
||
可以看出,当递归到棋盘最底层(也就是叶子节点)的时候,就可以收集结果并返回了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
if (row == n) {
|
||
result.push_back(chessboard);
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 单层搜索的逻辑
|
||
|
||
递归深度就是row控制棋盘的行,每一层里for循环的col控制棋盘的列,一行一列,确定了放置皇后的位置。
|
||
|
||
每次都是要从新的一行的起始位置开始搜,所以都是从0开始。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
|
||
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
|
||
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 验证棋盘是否合法
|
||
|
||
按照如下标准去重:
|
||
|
||
1. 不能同行
|
||
2. 不能同列
|
||
3. 不能同斜线 (45度和135度角)
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
|
||
// 检查列
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
|
||
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
|
||
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
|
||
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在这份代码中,细心的同学可以发现为什么没有在同行进行检查呢?
|
||
|
||
因为在单层搜索的过程中,每一层递归,只会选for循环(也就是同一行)里的一个元素,所以不用去重了。
|
||
|
||
那么按照这个模板不难写出如下C++代码:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
vector<vector<string>> result;
|
||
// n 为输入的棋盘大小
|
||
// row 是当前递归到棋盘的第几行了
|
||
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
|
||
if (row == n) {
|
||
result.push_back(chessboard);
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
|
||
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
|
||
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
|
||
// 检查列
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是一个剪枝
|
||
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查 45度角是否有皇后
|
||
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查 135度角是否有皇后
|
||
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
|
||
result.clear();
|
||
std::vector<std::string> chessboard(n, std::string(n, '.'));
|
||
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
可以看出,除了验证棋盘合法性的代码,省下来部分就是按照回溯法模板来的。
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
本题是我们解决棋盘问题的第一道题目。
|
||
|
||
如果从来没有接触过N皇后问题的同学看着这样的题会感觉无从下手,可能知道要用回溯法,但也不知道该怎么去搜。
|
||
|
||
**这里我明确给出了棋盘的宽度就是for循环的长度,递归的深度就是棋盘的高度,这样就可以套进回溯法的模板里了**。
|
||
|
||
大家可以在仔细体会体会!
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言补充
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
|
||
if not n: return []
|
||
board = [['.'] * n for _ in range(n)]
|
||
res = []
|
||
def isVaild(board,row, col):
|
||
#判断同一列是否冲突
|
||
for i in range(len(board)):
|
||
if board[i][col] == 'Q':
|
||
return False
|
||
# 判断左上角是否冲突
|
||
i = row -1
|
||
j = col -1
|
||
while i>=0 and j>=0:
|
||
if board[i][j] == 'Q':
|
||
return False
|
||
i -= 1
|
||
j -= 1
|
||
# 判断右上角是否冲突
|
||
i = row - 1
|
||
j = col + 1
|
||
while i>=0 and j < len(board):
|
||
if board[i][j] == 'Q':
|
||
return False
|
||
i -= 1
|
||
j += 1
|
||
return True
|
||
|
||
def backtracking(board, row, n):
|
||
# 如果走到最后一行,说明已经找到一个解
|
||
if row == n:
|
||
temp_res = []
|
||
for temp in board:
|
||
temp_str = "".join(temp)
|
||
temp_res.append(temp_str)
|
||
res.append(temp_res)
|
||
for col in range(n):
|
||
if not isVaild(board, row, col):
|
||
continue
|
||
board[row][col] = 'Q'
|
||
backtracking(board, row+1, n)
|
||
board[row][col] = '.'
|
||
backtracking(board, 0, n)
|
||
return res
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
|
||
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
|
||
char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];
|
||
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
|
||
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
|
||
}
|
||
backTrack(n, 0, chessboard);
|
||
return res;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
public void backTrack(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard) {
|
||
if (row == n) {
|
||
res.add(Array2List(chessboard));
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for (int col = 0;col < n; ++col) {
|
||
if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) {
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
|
||
backTrack(n, row+1, chessboard);
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard) {
|
||
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
|
||
|
||
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
|
||
list.add(String.copyValueOf(c));
|
||
}
|
||
return list;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
public boolean isValid(int row, int col, int n, char[][] chessboard) {
|
||
// 检查列
|
||
for (int i=0; i<row; ++i) { // 相当于剪枝
|
||
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 检查45度对角线
|
||
for (int i=row-1, j=col-1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 检查135度对角线
|
||
for (int i=row-1, j=col+1; i>=0 && j<=n-1; i--, j++) {
|
||
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Go
|
||
```Go
|
||
func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string {
|
||
var res [][]string
|
||
chessboard := make([][]string, n)
|
||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||
chessboard[i] = make([]string, n)
|
||
}
|
||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
|
||
chessboard[i][j] = "."
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
var backtrack func(int)
|
||
backtrack = func(row int) {
|
||
if row == n {
|
||
temp := make([]string, n)
|
||
for i, rowStr := range chessboard {
|
||
temp[i] = strings.Join(rowStr, "")
|
||
}
|
||
res = append(res, temp)
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||
if isValid(n, row, i, chessboard) {
|
||
chessboard[row][i] = "Q"
|
||
backtrack(row + 1)
|
||
chessboard[row][i] = "."
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
backtrack(0)
|
||
return res
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
func isValid(n, row, col int, chessboard [][]string) bool {
|
||
for i := 0; i < row; i++ {
|
||
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
for i, j := row-1, col-1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i, j = i-1, j-1 {
|
||
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
for i, j := row-1, col+1; i >= 0 && j < n; i, j = i-1, j+1 {
|
||
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### Javascript
|
||
```Javascript
|
||
var solveNQueens = function(n) {
|
||
function isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n) {
|
||
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
|
||
if(chessBoard[i][col] === 'Q') {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for(let i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
|
||
if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for(let i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
|
||
if(chessBoard[i][j] === 'Q') {
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
function transformChessBoard(chessBoard) {
|
||
let chessBoardBack = []
|
||
chessBoard.forEach(row => {
|
||
let rowStr = ''
|
||
row.forEach(value => {
|
||
rowStr += value
|
||
})
|
||
chessBoardBack.push(rowStr)
|
||
})
|
||
|
||
return chessBoardBack
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let result = []
|
||
function backtracing(row,chessBoard) {
|
||
if(row === n) {
|
||
result.push(transformChessBoard(chessBoard))
|
||
return
|
||
}
|
||
for(let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
|
||
if(isValid(row, col, chessBoard, n)) {
|
||
chessBoard[row][col] = 'Q'
|
||
backtracing(row + 1,chessBoard)
|
||
chessBoard[row][col] = '.'
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
let chessBoard = new Array(n).fill([]).map(() => new Array(n).fill('.'))
|
||
backtracing(0,chessBoard)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## TypeScript
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function solveNQueens(n: number): string[][] {
|
||
const board: string[][] = new Array(n).fill(0).map(_ => new Array(n).fill('.'));
|
||
const resArr: string[][] = [];
|
||
backTracking(n, 0, board);
|
||
return resArr;
|
||
function backTracking(n: number, rowNum: number, board: string[][]): void {
|
||
if (rowNum === n) {
|
||
resArr.push(transformBoard(board));
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
if (isValid(i, rowNum, board) === true) {
|
||
board[rowNum][i] = 'Q';
|
||
backTracking(n, rowNum + 1, board);
|
||
board[rowNum][i] = '.';
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
function isValid(col: number, row: number, board: string[][]): boolean {
|
||
const n: number = board.length;
|
||
if (col < 0 || col >= n || row < 0 || row >= n) return false;
|
||
// 检查列
|
||
for (let row of board) {
|
||
if (row[col] === 'Q') return false;
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查45度方向
|
||
let x: number = col,
|
||
y: number = row;
|
||
while (y >= 0 && x < n) {
|
||
if (board[y--][x++] === 'Q') return false;
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查135度方向
|
||
x = col;
|
||
y = row;
|
||
while (x >= 0 && y >= 0) {
|
||
if (board[y--][x--] === 'Q') return false;
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
function transformBoard(board: string[][]): string[] {
|
||
const resArr = [];
|
||
for (let row of board) {
|
||
resArr.push(row.join(''));
|
||
}
|
||
return resArr;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Swift
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
func solveNQueens(_ n: Int) -> [[String]] {
|
||
var result = [[String]]()
|
||
// 棋盘,使用Character的二维数组,以便于更新元素
|
||
var chessboard = [[Character]](repeating: [Character](repeating: ".", count: n), count: n)
|
||
// 检查棋盘是否符合N皇后
|
||
func isVaild(row: Int, col: Int) -> Bool {
|
||
// 检查列
|
||
for i in 0 ..< row {
|
||
if chessboard[i][col] == "Q" { return false }
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
var i, j: Int
|
||
// 检查45度
|
||
i = row - 1
|
||
j = col - 1
|
||
while i >= 0, j >= 0 {
|
||
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
|
||
i -= 1
|
||
j -= 1
|
||
}
|
||
// 检查135度
|
||
i = row - 1
|
||
j = col + 1
|
||
while i >= 0, j < n {
|
||
if chessboard[i][j] == "Q" { return false }
|
||
i -= 1
|
||
j += 1
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
func backtracking(row: Int) {
|
||
if row == n {
|
||
result.append(chessboard.map { String($0) })
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for col in 0 ..< n {
|
||
guard isVaild(row: row, col: col) else { continue }
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = "Q" // 放置皇后
|
||
backtracking(row: row + 1)
|
||
chessboard[row][col] = "." // 回溯
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
backtracking(row: 0)
|
||
return result
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### C
|
||
```c
|
||
char ***ans;
|
||
char **path;
|
||
int ansTop, pathTop;
|
||
//将path中元素复制到ans中
|
||
void copyPath(int n) {
|
||
char **tempPath = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * pathTop);
|
||
int i;
|
||
for(i = 0; i < pathTop; ++i) {
|
||
tempPath[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
|
||
int j;
|
||
for(j = 0; j < n; ++j)
|
||
tempPath[i][j] = path[i][j];
|
||
tempPath[i][j] = '\0';
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
ans[ansTop++] = tempPath;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//判断当前位置是否有效(是否不被其它皇后影响)
|
||
int isValid(int x, int y, int n) {
|
||
int i, j;
|
||
//检查同一行以及同一列是否有效
|
||
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||
if(path[y][i] == 'Q' || path[i][x] == 'Q')
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
//下面两个for循环检查斜角45度是否有效
|
||
i = y - 1;
|
||
j = x - 1;
|
||
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
|
||
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
|
||
return 0;
|
||
--i, --j;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
i = y + 1;
|
||
j = x + 1;
|
||
while(i < n && j < n) {
|
||
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
|
||
return 0;
|
||
++i, ++j;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//下面两个for循环检查135度是否有效
|
||
i = y - 1;
|
||
j = x + 1;
|
||
while(i >= 0 && j < n) {
|
||
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
|
||
return 0;
|
||
--i, ++j;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
i = y + 1;
|
||
j = x -1;
|
||
while(j >= 0 && i < n) {
|
||
if(path[i][j] == 'Q')
|
||
return 0;
|
||
++i, --j;
|
||
}
|
||
return 1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
void backTracking(int n, int depth) {
|
||
//若path中有四个元素,将其拷贝到ans中。从当前层返回
|
||
if(pathTop == n) {
|
||
copyPath(n);
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//遍历横向棋盘
|
||
int i;
|
||
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
|
||
//若当前位置有效
|
||
if(isValid(i, depth, n)) {
|
||
//在当前位置放置皇后
|
||
path[depth][i] = 'Q';
|
||
//path中元素数量+1
|
||
++pathTop;
|
||
|
||
backTracking(n, depth + 1);
|
||
//进行回溯
|
||
path[depth][i] = '.';
|
||
//path中元素数量-1
|
||
--pathTop;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//初始化存储char*数组path,将path中所有元素设为'.'
|
||
void initPath(int n) {
|
||
int i, j;
|
||
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
//为path中每个char*开辟空间
|
||
path[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * n + 1);
|
||
//将path中所有字符设为'.'
|
||
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
|
||
path[i][j] = '.';
|
||
//在每个字符串结尾加入'\0'
|
||
path[i][j] = '\0';
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
char *** solveNQueens(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
|
||
//初始化辅助变量
|
||
ans = (char***)malloc(sizeof(char**) * 400);
|
||
path = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * n);
|
||
ansTop = pathTop = 0;
|
||
|
||
//初始化path数组
|
||
initPath(n);
|
||
backTracking(n, 0);
|
||
|
||
//设置返回数组大小
|
||
*returnSize = ansTop;
|
||
int i;
|
||
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * ansTop);
|
||
for(i = 0; i < ansTop; ++i) {
|
||
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = n;
|
||
}
|
||
return ans;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
-----------------------
|
||
<div align="center"><img src=https://code-thinking.cdn.bcebos.com/pics/01二维码一.jpg width=500> </img></div>
|