355 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
355 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
# 827.最大人工岛
|
||
|
||
[力扣链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/making-a-large-island/)
|
||
|
||
给你一个大小为 n x n 二进制矩阵 grid 。最多 只能将一格 0 变成 1 。
|
||
|
||
返回执行此操作后,grid 中最大的岛屿面积是多少?
|
||
|
||
岛屿 由一组上、下、左、右四个方向相连的 1 形成。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
* 输入: grid = [[1, 0], [0, 1]]
|
||
* 输出: 3
|
||
* 解释: 将一格0变成1,最终连通两个小岛得到面积为 3 的岛屿。
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
* 输入: grid = [[1, 1], [1, 0]]
|
||
* 输出: 4
|
||
* 解释: 将一格0变成1,岛屿的面积扩大为 4。
|
||
|
||
示例 3:
|
||
* 输入: grid = [[1, 1], [1, 1]]
|
||
* 输出: 4
|
||
* 解释: 没有0可以让我们变成1,面积依然为 4。
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
本题的一个暴力想法,应该是遍历地图尝试 将每一个 0 改成1,然后去搜索地图中的最大的岛屿面积。
|
||
|
||
计算地图的最大面积:遍历地图 + 深搜岛屿,时间复杂度为 n * n。
|
||
|
||
(其实使用深搜还是广搜都是可以的,其目的就是遍历岛屿做一个标记,相当于染色,那么使用哪个遍历方式都行,以下我用深搜来讲解)
|
||
|
||
每改变一个0的方格,都需要重新计算一个地图的最大面积,所以 整体时间复杂度为:n^4。
|
||
|
||
如果对深度优先搜索不了解的录友,可以看这里:[深度优先搜索精讲](https://programmercarl.com/图论深搜理论基础.html)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 优化思路
|
||
|
||
其实每次深搜遍历计算最大岛屿面积,我们都做了很多重复的工作。
|
||
|
||
只要用一次深搜把每个岛屿的面积记录下来就好。
|
||
|
||
第一步:一次遍历地图,得出各个岛屿的面积,并做编号记录。可以使用map记录,key为岛屿编号,value为岛屿面积
|
||
第二步:在遍历地图,遍历0的方格(因为要将0变成1),并统计该1(由0变成的1)周边岛屿面积,将其相邻面积相加在一起,遍历所有 0 之后,就可以得出 选一个0变成1 之后的最大面积。
|
||
|
||
拿如下地图的岛屿情况来举例: (1为陆地)
|
||
|
||
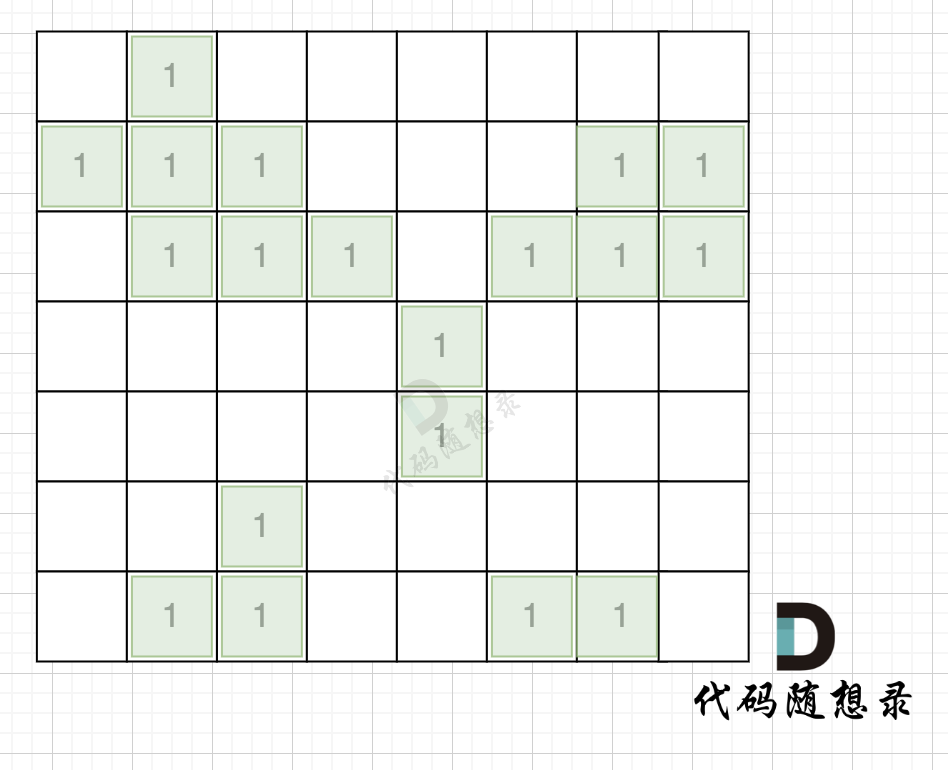
|
||
|
||
第一步,则遍历题目,并将岛屿到编号和面积上的统计,过程如图所示:
|
||
|
||
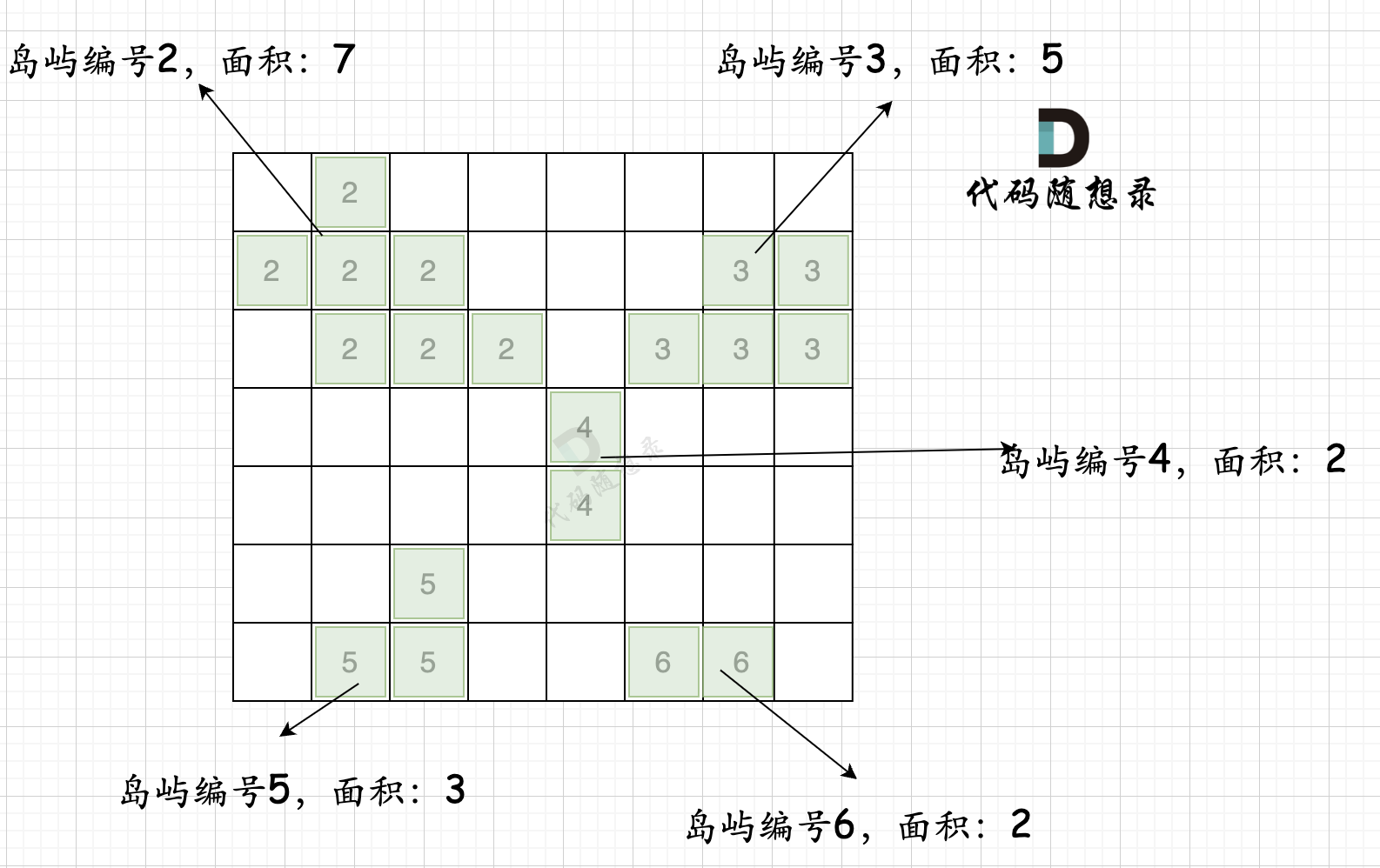
|
||
|
||
|
||
本过程代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
|
||
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
|
||
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过
|
||
grid[x][y] = mark; // 给陆地标记新标签
|
||
count++;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty, mark);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
|
||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); // 标记访问过的点
|
||
unordered_map<int ,int> gridNum;
|
||
int mark = 2; // 记录每个岛屿的编号
|
||
bool isAllGrid = true; // 标记是否整个地图都是陆地
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
|
||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
|
||
count = 0;
|
||
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||
gridNum[mark] = count; // 记录每一个岛屿的面积
|
||
mark++; // 记录下一个岛屿编号
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
这个过程时间复杂度 n * n 。可能有录友想:分明是两个for循环下面套这一个dfs,时间复杂度怎么回事 n * n呢?
|
||
|
||
其实大家可以仔细看一下代码,**n * n这个方格地图中,每个节点我们就遍历一次,并不会重复遍历**。
|
||
|
||
第二步过程如图所示:
|
||
|
||
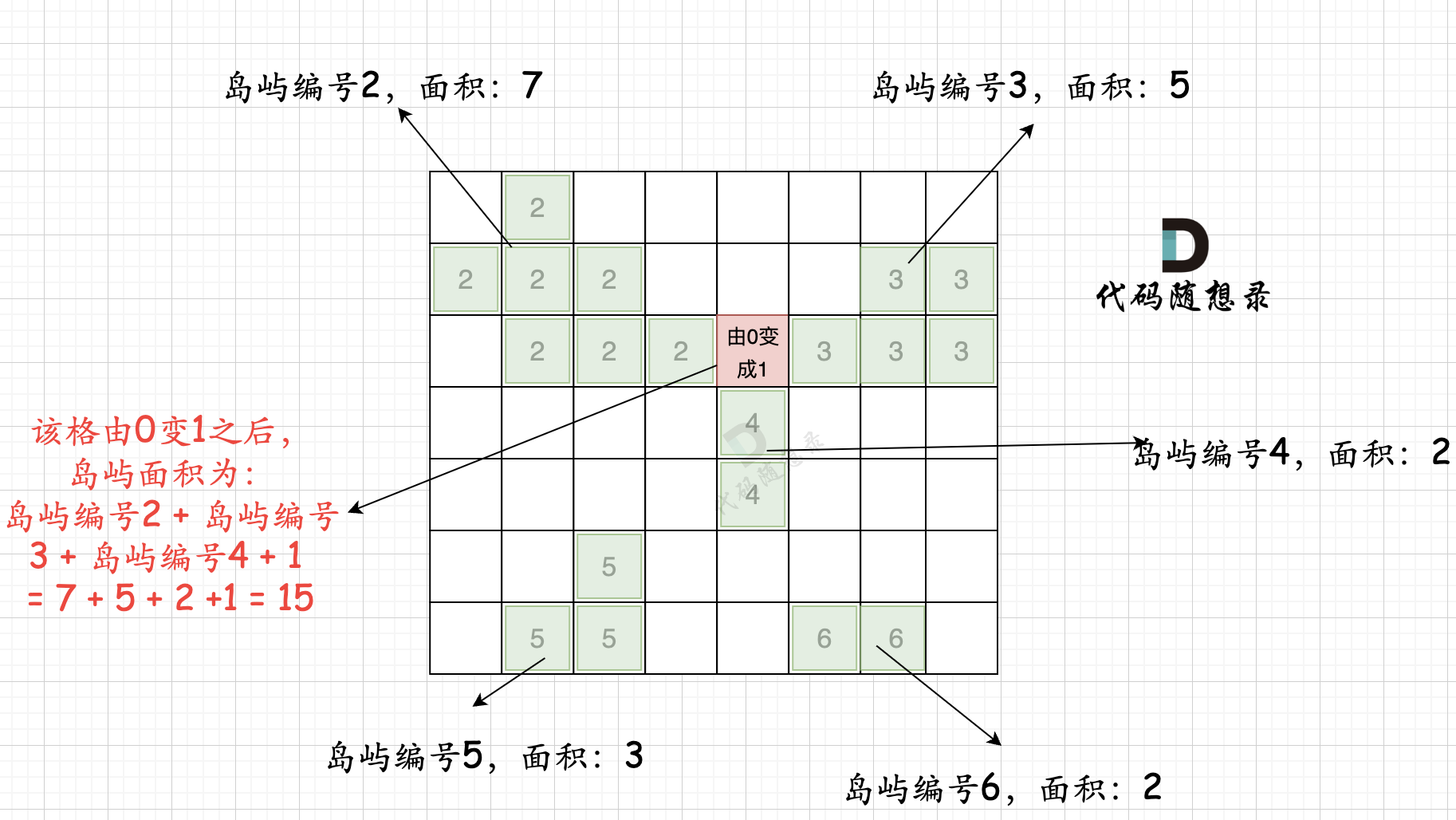
|
||
|
||
也就是遍历每一个0的方格,并统计其相邻岛屿面积,最后取一个最大值。
|
||
|
||
这个过程的时间复杂度也为 n * n。
|
||
|
||
所以整个解法的时间复杂度,为 n * n + n * n 也就是 n^2。
|
||
|
||
当然这里还有一个优化的点,就是 可以不用 visited数组,因为有mark来标记,所以遍历过的grid[i][j]是不等于1的。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y, int mark) {
|
||
if (grid[x][y] != 1 || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
|
||
grid[x][y] = mark; // 给陆地标记新标签
|
||
count++;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
dfs(grid, nextx, nexty, mark);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
|
||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||
unordered_map<int ,int> gridNum;
|
||
int mark = 2; // 记录每个岛屿的编号
|
||
bool isAllGrid = true; // 标记是否整个地图都是陆地
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
|
||
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
|
||
count = 0;
|
||
dfs(grid, i, j, mark); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||
gridNum[mark] = count; // 记录每一个岛屿的面积
|
||
mark++; // 记录下一个岛屿编号
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
不过为了让各个变量各司其事,代码清晰一些,完整代码还是使用visited数组来标记。
|
||
|
||
最后,整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
int count;
|
||
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
|
||
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
|
||
if (visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return; // 终止条件:访问过的节点 或者 遇到海水
|
||
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问过
|
||
grid[x][y] = mark; // 给陆地标记新标签
|
||
count++;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
|
||
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
|
||
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
|
||
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
|
||
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty, mark);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
int largestIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
|
||
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
|
||
vector<vector<bool>> visited = vector<vector<bool>>(n, vector<bool>(m, false)); // 标记访问过的点
|
||
unordered_map<int ,int> gridNum;
|
||
int mark = 2; // 记录每个岛屿的编号
|
||
bool isAllGrid = true; // 标记是否整个地图都是陆地
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
|
||
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
|
||
count = 0;
|
||
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
|
||
gridNum[mark] = count; // 记录每一个岛屿的面积
|
||
mark++; // 记录下一个岛屿编号
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (isAllGrid) return n * m; // 如果都是陆地,返回全面积
|
||
|
||
// 以下逻辑是根据添加陆地的位置,计算周边岛屿面积之和
|
||
int result = 0; // 记录最后结果
|
||
unordered_set<int> visitedGrid; // 标记访问过的岛屿
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
|
||
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
|
||
int count = 1; // 记录连接之后的岛屿数量
|
||
visitedGrid.clear(); // 每次使用时,清空
|
||
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
|
||
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
|
||
int neari = i + dir[k][1]; // 计算相邻坐标
|
||
int nearj = j + dir[k][0];
|
||
if (neari < 0 || neari >= grid.size() || nearj < 0 || nearj >= grid[0].size()) continue;
|
||
if (visitedGrid.count(grid[neari][nearj])) continue; // 添加过的岛屿不要重复添加
|
||
// 把相邻四面的岛屿数量加起来
|
||
count += gridNum[grid[neari][nearj]];
|
||
visitedGrid.insert(grid[neari][nearj]); // 标记该岛屿已经添加过
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
result = max(result, count);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; // 四个方向
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param grid 矩阵数组
|
||
* @param row 当前遍历的节点的行号
|
||
* @param col 当前遍历的节点的列号
|
||
* @param mark 当前区域的标记
|
||
* @return 返回当前区域内 1 的数量
|
||
*/
|
||
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int row, int col, int mark) {
|
||
int ans = 0;
|
||
grid[row][col] = mark;
|
||
for (int[] current: position) {
|
||
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
|
||
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= grid.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= grid.length) continue; // 越界
|
||
if (grid[curRow][curCol] == 1)
|
||
ans += 1 + dfs(grid, curRow, curCol, mark);
|
||
}
|
||
return ans;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) {
|
||
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE, size = grid.length, mark = 2;
|
||
Map<Integer, Integer> getSize = new HashMap<>();
|
||
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
|
||
for (int col = 0; col < size; col++) {
|
||
if (grid[row][col] == 1) {
|
||
int areaSize = 1 + dfs(grid, row, col, mark);
|
||
getSize.put(mark++, areaSize);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
for (int row = 0; row < size; row++) {
|
||
for (int col = 0; col < size; col++) {
|
||
// 当前位置如果不是 0 那么直接跳过,因为我们只能把 0 变成 1
|
||
if (grid[row][col] != 0) continue;
|
||
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); // 防止同一个区域被重复计算
|
||
// 计算从当前位置开始获取的 1 的数量,初始化 1 是因为把当前位置的 0 转换成了 1
|
||
int curSize = 1;
|
||
for (int[] current: position) {
|
||
int curRow = row + current[0], curCol = col + current[1];
|
||
if (curRow < 0 || curRow >= grid.length || curCol < 0 || curCol >= grid.length) continue;
|
||
int curMark = grid[curRow][curCol]; // 获取对应位置的标记
|
||
// 如果标记存在 hashSet 中说明该标记被记录过一次,如果不存在 getSize 中说明该标记是无效标记(此时 curMark = 0)
|
||
if (hashSet.contains(curMark) || !getSize.containsKey(curMark)) continue;
|
||
hashSet.add(curMark);
|
||
curSize += getSize.get(curMark);
|
||
}
|
||
ans = Math.max(ans, curSize);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
// 当 ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE 说明矩阵数组中不存在 0,全都是有效区域,返回数组大小即可
|
||
return ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? size * size : ans;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def largestIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
|
||
visited = set() #标记访问过的位置
|
||
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
|
||
res = 0
|
||
island_size = 0 #用于保存当前岛屿的尺寸
|
||
directions = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]] #四个方向
|
||
islands_size = defaultdict(int) #保存每个岛屿的尺寸
|
||
|
||
def dfs(island_num, r, c):
|
||
visited.add((r, c))
|
||
grid[r][c] = island_num #访问过的位置标记为岛屿编号
|
||
nonlocal island_size
|
||
island_size += 1
|
||
for i in range(4):
|
||
nextR = r + directions[i][0]
|
||
nextC = c + directions[i][1]
|
||
if (nextR not in range(m) or #行坐标越界
|
||
nextC not in range(n) or #列坐标越界
|
||
(nextR, nextC) in visited): #坐标已访问
|
||
continue
|
||
if grid[nextR][nextC] == 1: #遇到有效坐标,进入下一个层搜索
|
||
dfs(island_num, nextR, nextC)
|
||
|
||
island_num = 2 #初始岛屿编号设为2, 因为grid里的数据有0和1, 所以从2开始编号
|
||
all_land = True #标记是否整个地图都是陆地
|
||
for r in range(m):
|
||
for c in range(n):
|
||
if grid[r][c] == 0:
|
||
all_land = False #地图里不全是陆地
|
||
if (r, c) not in visited and grid[r][c] == 1:
|
||
island_size = 0 #遍历每个位置前重置岛屿尺寸为0
|
||
dfs(island_num, r, c)
|
||
islands_size[island_num] = island_size #保存当前岛屿尺寸
|
||
island_num += 1 #下一个岛屿编号加一
|
||
if all_land:
|
||
return m * n #如果全是陆地, 返回地图面积
|
||
|
||
count = 0 #某个位置0变成1后当前岛屿尺寸
|
||
#因为后续计算岛屿面积要往四个方向遍历,但某2个或3个方向的位置可能同属于一个岛,
|
||
#所以为避免重复累加,把已经访问过的岛屿编号加入到这个集合
|
||
visited_island = set() #保存访问过的岛屿
|
||
for r in range(m):
|
||
for c in range(n):
|
||
if grid[r][c] == 0:
|
||
count = 1 #把由0转换为1的位置计算到面积里
|
||
visited_island.clear() #遍历每个位置前清空集合
|
||
for i in range(4):
|
||
nearR = r + directions[i][0]
|
||
nearC = c + directions[i][1]
|
||
if nearR not in range(m) or nearC not in range(n): #周围位置越界
|
||
continue
|
||
if grid[nearR][nearC] in visited_island: #岛屿已访问
|
||
continue
|
||
count += islands_size[grid[nearR][nearC]] #累加连在一起的岛屿面积
|
||
visited_island.add(grid[nearR][nearC]) #标记当前岛屿已访问
|
||
res = max(res, count)
|
||
return res
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|