472 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
472 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
> 如果哈希值比较少、特别分散、跨度非常大,使用数组就造成空间的极大浪费!
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 349. 两个数组的交集
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/)
|
||
|
||
题意:给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
**说明:**
|
||
输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的。
|
||
我们可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
|
||
|
||
## 思路
|
||
|
||
关于本题,我录制了讲解视频:[学透哈希表,set使用有技巧!Leetcode:349. 两个数组的交集](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ba411S7wu),看视频配合题解,事半功倍。
|
||
|
||
这道题目,主要要学会使用一种哈希数据结构:unordered_set,这个数据结构可以解决很多类似的问题。
|
||
|
||
注意题目特意说明:**输出结果中的每个元素一定是唯一的,也就是说输出的结果的去重的, 同时可以不考虑输出结果的顺序**
|
||
|
||
这道题用暴力的解法时间复杂度是O(n^2),那来看看使用哈希法进一步优化。
|
||
|
||
那么用数组来做哈希表也是不错的选择,例如[242. 有效的字母异位词](https://programmercarl.com/0242.有效的字母异位词.html)
|
||
|
||
但是要注意,**使用数组来做哈希的题目,是因为题目都限制了数值的大小。**
|
||
|
||
而这道题目没有限制数值的大小,就无法使用数组来做哈希表了。
|
||
|
||
**而且如果哈希值比较少、特别分散、跨度非常大,使用数组就造成空间的极大浪费。**
|
||
|
||
此时就要使用另一种结构体了,set ,关于set,C++ 给提供了如下三种可用的数据结构:
|
||
|
||
* std::set
|
||
* std::multiset
|
||
* std::unordered_set
|
||
|
||
std::set和std::multiset底层实现都是红黑树,std::unordered_set的底层实现是哈希表, 使用unordered_set 读写效率是最高的,并不需要对数据进行排序,而且还不要让数据重复,所以选择unordered_set。
|
||
|
||
思路如图所示:
|
||
|
||
|
||
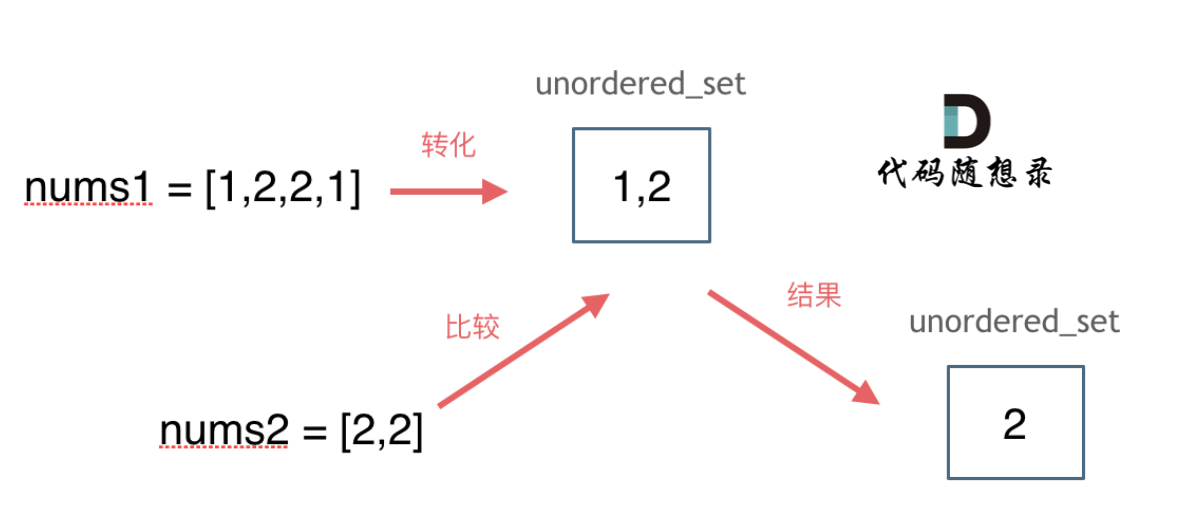
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
|
||
unordered_set<int> result_set; // 存放结果,之所以用set是为了给结果集去重
|
||
unordered_set<int> nums_set(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
|
||
for (int num : nums2) {
|
||
// 发现nums2的元素 在nums_set里又出现过
|
||
if (nums_set.find(num) != nums_set.end()) {
|
||
result_set.insert(num);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return vector<int>(result_set.begin(), result_set.end());
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 时间复杂度: O(mn)
|
||
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
|
||
|
||
## 拓展
|
||
|
||
那有同学可能问了,遇到哈希问题我直接都用set不就得了,用什么数组啊。
|
||
|
||
直接使用set 不仅占用空间比数组大,而且速度要比数组慢,set把数值映射到key上都要做hash计算的。
|
||
|
||
不要小瞧 这个耗时,在数据量大的情况,差距是很明显的。
|
||
|
||
## 后记
|
||
|
||
本题后面 力扣改了 题目描述 和 后台测试数据,增添了 数值范围:
|
||
|
||
* 1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 1000
|
||
* 0 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000
|
||
|
||
所以就可以 使用数组来做哈希表了, 因为数组都是 1000以内的。
|
||
|
||
对应C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
|
||
unordered_set<int> result_set; // 存放结果,之所以用set是为了给结果集去重
|
||
int hash[1005] = {0}; // 默认数值为0
|
||
for (int num : nums1) { // nums1中出现的字母在hash数组中做记录
|
||
hash[num] = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
for (int num : nums2) { // nums2中出现话,result记录
|
||
if (hash[num] == 1) {
|
||
result_set.insert(num);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return vector<int>(result_set.begin(), result_set.end());
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 时间复杂度: O(m + n)
|
||
* 空间复杂度: O(n)
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
|
||
Java:
|
||
|
||
```Java
|
||
import java.util.HashSet;
|
||
import java.util.Set;
|
||
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
|
||
if (nums1 == null || nums1.length == 0 || nums2 == null || nums2.length == 0) {
|
||
return new int[0];
|
||
}
|
||
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
|
||
Set<Integer> resSet = new HashSet<>();
|
||
//遍历数组1
|
||
for (int i : nums1) {
|
||
set1.add(i);
|
||
}
|
||
//遍历数组2的过程中判断哈希表中是否存在该元素
|
||
for (int i : nums2) {
|
||
if (set1.contains(i)) {
|
||
resSet.add(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//方法1:将结果集合转为数组
|
||
|
||
return resSet.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray();
|
||
|
||
//方法2:另外申请一个数组存放setRes中的元素,最后返回数组
|
||
int[] arr = new int[resSet.size()];
|
||
int j = 0;
|
||
for(int i : resSet){
|
||
arr[j++] = i;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return arr;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Python3:
|
||
(版本一) 使用字典和集合
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
|
||
# 使用哈希表存储一个数组中的所有元素
|
||
table = {}
|
||
for num in nums1:
|
||
table[num] = table.get(num, 0) + 1
|
||
|
||
# 使用集合存储结果
|
||
res = set()
|
||
for num in nums2:
|
||
if num in table:
|
||
res.add(num)
|
||
del table[num]
|
||
|
||
return list(res)
|
||
```
|
||
(版本二) 使用数组
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
|
||
count1 = [0]*1001
|
||
count2 = [0]*1001
|
||
result = []
|
||
for i in range(len(nums1)):
|
||
count1[nums1[i]]+=1
|
||
for j in range(len(nums2)):
|
||
count2[nums2[j]]+=1
|
||
for k in range(1001):
|
||
if count1[k]*count2[k]>0:
|
||
result.append(k)
|
||
return result
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
(版本三) 使用集合
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def intersection(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
|
||
return list(set(nums1) & set(nums2))
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Go:
|
||
```go
|
||
func intersection(nums1 []int, nums2 []int) []int {
|
||
set:=make(map[int]struct{},0) // 用map模拟set
|
||
res:=make([]int,0)
|
||
for _,v:=range nums1{
|
||
if _,ok:=set[v];!ok{
|
||
set[v]=struct{}{}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
for _,v:=range nums2{
|
||
//如果存在于上一个数组中,则加入结果集,并清空该set值
|
||
if _,ok:=set[v];ok{
|
||
res=append(res,v)
|
||
delete(set, v)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return res
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
javaScript:
|
||
|
||
```js
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param {number[]} nums1
|
||
* @param {number[]} nums2
|
||
* @return {number[]}
|
||
*/
|
||
var intersection = function(nums1, nums2) {
|
||
// 根据数组大小交换操作的数组
|
||
if(nums1.length < nums2.length) {
|
||
const _ = nums1;
|
||
nums1 = nums2;
|
||
nums2 = _;
|
||
}
|
||
const nums1Set = new Set(nums1);
|
||
const resSet = new Set();
|
||
// for(const n of nums2) {
|
||
// nums1Set.has(n) && resSet.add(n);
|
||
// }
|
||
// 循环 比 迭代器快
|
||
for(let i = nums2.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
nums1Set.has(nums2[i]) && resSet.add(nums2[i]);
|
||
}
|
||
return Array.from(resSet);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
TypeScript:
|
||
|
||
版本一(正常解法):
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function intersection(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number[] {
|
||
let resSet: Set<number> = new Set(),
|
||
nums1Set: Set<number> = new Set(nums1);
|
||
for (let i of nums2) {
|
||
if (nums1Set.has(i)) {
|
||
resSet.add(i);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return Array.from(resSet);
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
版本二(秀操作):
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function intersection(nums1: number[], nums2: number[]): number[] {
|
||
return Array.from(new Set(nums1.filter(i => nums2.includes(i))))
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Swift:
|
||
|
||
```swift
|
||
func intersection(_ nums1: [Int], _ nums2: [Int]) -> [Int] {
|
||
var set1 = Set<Int>()
|
||
var set2 = Set<Int>()
|
||
for num in nums1 {
|
||
set1.insert(num)
|
||
}
|
||
for num in nums2 {
|
||
if set1.contains(num) {
|
||
set2.insert(num)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return Array(set2)
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
PHP:
|
||
```php
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
/**
|
||
* @param Integer[] $nums1
|
||
* @param Integer[] $nums2
|
||
* @return Integer[]
|
||
*/
|
||
function intersection($nums1, $nums2) {
|
||
if (count($nums1) == 0 || count($nums2) == 0) {
|
||
return [];
|
||
}
|
||
$counts = [];
|
||
$res = [];
|
||
foreach ($nums1 as $num) {
|
||
$counts[$num] = 1;
|
||
}
|
||
foreach ($nums2 as $num) {
|
||
if (isset($counts[$num])) {
|
||
$res[] = $num;
|
||
}
|
||
unset($counts[$num]);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return $res;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Rust:
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn intersection(nums1: Vec<i32>, nums2: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
|
||
let mut resultSet: HashSet<i32> = HashSet::with_capacity(1000);
|
||
let nums1Set: HashSet<i32> = nums1.into_iter().collect();
|
||
|
||
for num in nums2.iter() {
|
||
if nums1Set.contains(num) {
|
||
resultSet.insert(*num);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
let ret: Vec<i32> = resultSet.into_iter().collect();
|
||
ret
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
解法2:
|
||
|
||
```rust
|
||
use std::collections::HashSet;
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn intersection(nums1: Vec<i32>, nums2: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
|
||
nums1
|
||
.into_iter()
|
||
.collect::<HashSet<_>>()
|
||
.intersection(&nums2.into_iter().collect::<HashSet<_>>())
|
||
.copied()
|
||
.collect()
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
C:
|
||
```C
|
||
int* intersection1(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* returnSize){
|
||
|
||
int nums1Cnt[1000] = {0};
|
||
int lessSize = nums1Size < nums2Size ? nums1Size : nums2Size;
|
||
int * result = (int *) calloc(lessSize, sizeof(int));
|
||
int resultIndex = 0;
|
||
int* tempNums;
|
||
|
||
int i;
|
||
|
||
/* Calculate the number's counts for nums1 array */
|
||
for(i = 0; i < nums1Size; i ++) {
|
||
nums1Cnt[nums1[i]]++;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/* Check if the value in nums2 is existing in nums1 count array */
|
||
for(i = 0; i < nums2Size; i ++) {
|
||
if(nums1Cnt[nums2[i]] > 0) {
|
||
result[resultIndex] = nums2[i];
|
||
resultIndex ++;
|
||
/* Clear this count to avoid duplicated value */
|
||
nums1Cnt[nums2[i]] = 0;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
* returnSize = resultIndex;
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Scala:
|
||
|
||
正常解法:
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def intersection(nums1: Array[Int], nums2: Array[Int]): Array[Int] = {
|
||
// 导入mutable
|
||
import scala.collection.mutable
|
||
// 临时Set,用于记录数组1出现的每个元素
|
||
val tmpSet: mutable.HashSet[Int] = new mutable.HashSet[Int]()
|
||
// 结果Set,存储最终结果
|
||
val resSet: mutable.HashSet[Int] = new mutable.HashSet[Int]()
|
||
// 遍历nums1,把每个元素添加到tmpSet
|
||
nums1.foreach(tmpSet.add(_))
|
||
// 遍历nums2,如果在tmpSet存在就添加到resSet
|
||
nums2.foreach(elem => {
|
||
if (tmpSet.contains(elem)) {
|
||
resSet.add(elem)
|
||
}
|
||
})
|
||
// 将结果转换为Array返回,return可以省略
|
||
resSet.toArray
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
骚操作1:
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def intersection(nums1: Array[Int], nums2: Array[Int]): Array[Int] = {
|
||
// 先转为Set,然后取交集,最后转换为Array
|
||
(nums1.toSet).intersect(nums2.toSet).toArray
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
骚操作2:
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def intersection(nums1: Array[Int], nums2: Array[Int]): Array[Int] = {
|
||
// distinct去重,然后取交集
|
||
(nums1.distinct).intersect(nums2.distinct)
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
C#:
|
||
```csharp
|
||
public int[] Intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
|
||
if(nums1==null||nums1.Length==0||nums2==null||nums1.Length==0)
|
||
return new int[0]; //注意数组条件
|
||
HashSet<int> one = Insert(nums1);
|
||
HashSet<int> two = Insert(nums2);
|
||
one.IntersectWith(two);
|
||
return one.ToArray();
|
||
}
|
||
public HashSet<int> Insert(int[] nums){
|
||
HashSet<int> one = new HashSet<int>();
|
||
foreach(int num in nums){
|
||
one.Add(num);
|
||
}
|
||
return one;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
## 相关题目
|
||
|
||
* 350.两个数组的交集 II
|
||
|
||
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
|