594 lines
17 KiB
Markdown
594 lines
17 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/xunlianying.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/训练营.png" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong><a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tqCxrMEU-ajQumL1i8im9A">参与本项目</a>,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 134. 加油站
|
||
|
||
[力扣题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/gas-station/)
|
||
|
||
在一条环路上有 N 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。
|
||
|
||
你有一辆油箱容量无限的的汽车,从第 i 个加油站开往第 i+1 个加油站需要消耗汽油 cost[i] 升。你从其中的一个加油站出发,开始时油箱为空。
|
||
|
||
如果你可以绕环路行驶一周,则返回出发时加油站的编号,否则返回 -1。
|
||
|
||
说明:
|
||
|
||
* 如果题目有解,该答案即为唯一答案。
|
||
* 输入数组均为非空数组,且长度相同。
|
||
* 输入数组中的元素均为非负数。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
输入:
|
||
* gas = [1,2,3,4,5]
|
||
* cost = [3,4,5,1,2]
|
||
|
||
输出: 3
|
||
解释:
|
||
* 从 3 号加油站(索引为 3 处)出发,可获得 4 升汽油。此时油箱有 = 0 + 4 = 4 升汽油
|
||
* 开往 4 号加油站,此时油箱有 4 - 1 + 5 = 8 升汽油
|
||
* 开往 0 号加油站,此时油箱有 8 - 2 + 1 = 7 升汽油
|
||
* 开往 1 号加油站,此时油箱有 7 - 3 + 2 = 6 升汽油
|
||
* 开往 2 号加油站,此时油箱有 6 - 4 + 3 = 5 升汽油
|
||
* 开往 3 号加油站,你需要消耗 5 升汽油,正好足够你返回到 3 号加油站。
|
||
* 因此,3 可为起始索引。
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
输入:
|
||
* gas = [2,3,4]
|
||
* cost = [3,4,3]
|
||
|
||
* 输出: -1
|
||
* 解释:
|
||
你不能从 0 号或 1 号加油站出发,因为没有足够的汽油可以让你行驶到下一个加油站。我们从 2 号加油站出发,可以获得 4 升汽油。 此时油箱有 = 0 + 4 = 4 升汽油。开往 0 号加油站,此时油箱有 4 - 3 + 2 = 3 升汽油。开往 1 号加油站,此时油箱有 3 - 3 + 3 = 3 升汽油。你无法返回 2 号加油站,因为返程需要消耗 4 升汽油,但是你的油箱只有 3 升汽油。因此,无论怎样,你都不可能绕环路行驶一周。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 暴力方法
|
||
|
||
暴力的方法很明显就是$O(n^2)$的,遍历每一个加油站为起点的情况,模拟一圈。
|
||
|
||
如果跑了一圈,中途没有断油,而且最后油量大于等于0,说明这个起点是ok的。
|
||
|
||
暴力的方法思路比较简单,但代码写起来也不是很容易,关键是要模拟跑一圈的过程。
|
||
|
||
**for循环适合模拟从头到尾的遍历,而while循环适合模拟环形遍历,要善于使用while!**
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < cost.size(); i++) {
|
||
int rest = gas[i] - cost[i]; // 记录剩余油量
|
||
int index = (i + 1) % cost.size();
|
||
while (rest > 0 && index != i) { // 模拟以i为起点行驶一圈
|
||
rest += gas[index] - cost[index];
|
||
index = (index + 1) % cost.size();
|
||
}
|
||
// 如果以i为起点跑一圈,剩余油量>=0,返回该起始位置
|
||
if (rest >= 0 && index == i) return i;
|
||
}
|
||
return -1;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
* 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
|
||
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 贪心算法(方法一)
|
||
|
||
直接从全局进行贪心选择,情况如下:
|
||
|
||
* 情况一:如果gas的总和小于cost总和,那么无论从哪里出发,一定是跑不了一圈的
|
||
* 情况二:rest[i] = gas[i]-cost[i]为一天剩下的油,i从0开始计算累加到最后一站,如果累加没有出现负数,说明从0出发,油就没有断过,那么0就是起点。
|
||
|
||
* 情况三:如果累加的最小值是负数,汽车就要从非0节点出发,从后向前,看哪个节点能这个负数填平,能把这个负数填平的节点就是出发节点。
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
|
||
int curSum = 0;
|
||
int min = INT_MAX; // 从起点出发,油箱里的油量最小值
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < gas.size(); i++) {
|
||
int rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
curSum += rest;
|
||
if (curSum < min) {
|
||
min = curSum;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (curSum < 0) return -1; // 情况1
|
||
if (min >= 0) return 0; // 情况2
|
||
// 情况3
|
||
for (int i = gas.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
int rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
min += rest;
|
||
if (min >= 0) {
|
||
return i;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return -1;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||
|
||
**其实我不认为这种方式是贪心算法,因为没有找出局部最优,而是直接从全局最优的角度上思考问题**。
|
||
|
||
但这种解法又说不出是什么方法,这就是一个从全局角度选取最优解的模拟操作。
|
||
|
||
所以对于本解法是贪心,我持保留意见!
|
||
|
||
但不管怎么说,解法毕竟还是巧妙的,不用过于执着于其名字称呼。
|
||
|
||
## 贪心算法(方法二)
|
||
|
||
可以换一个思路,首先如果总油量减去总消耗大于等于零那么一定可以跑完一圈,说明 各个站点的加油站 剩油量rest[i]相加一定是大于等于零的。
|
||
|
||
每个加油站的剩余量rest[i]为gas[i] - cost[i]。
|
||
|
||
i从0开始累加rest[i],和记为curSum,一旦curSum小于零,说明[0, i]区间都不能作为起始位置,起始位置从i+1算起,再从0计算curSum。
|
||
|
||
如图:
|
||
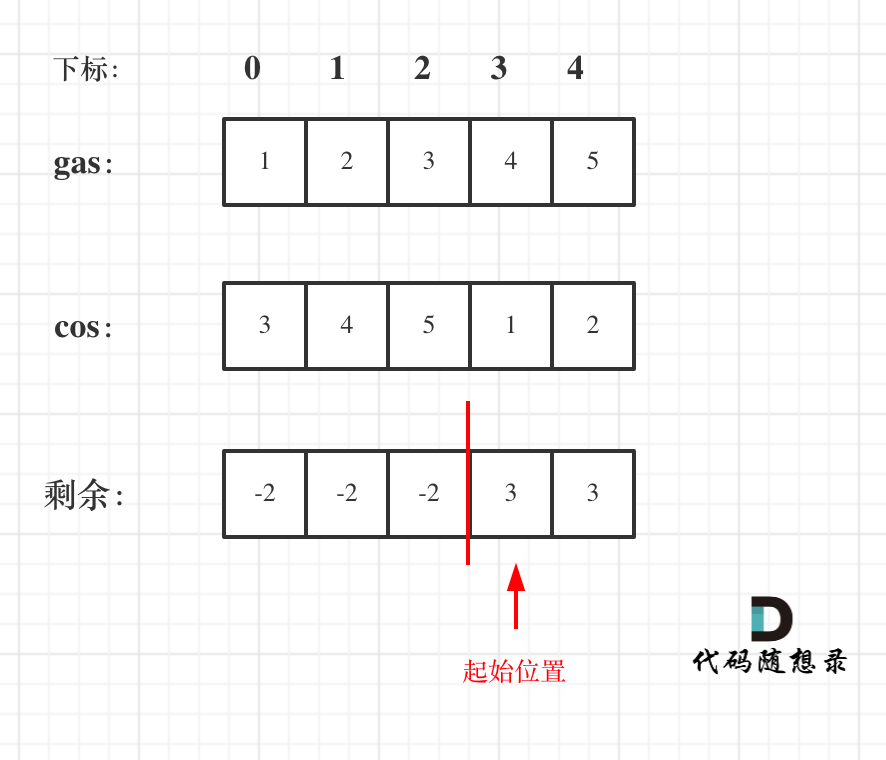
|
||
|
||
那么为什么一旦[i,j] 区间和为负数,起始位置就可以是j+1呢,j+1后面就不会出现更大的负数?
|
||
|
||
如果出现更大的负数,就是更新j,那么起始位置又变成新的j+1了。
|
||
|
||
而且j之前出现了多少负数,j后面就会出现多少正数,因为耗油总和是大于零的(前提我们已经确定了一定可以跑完全程)。
|
||
|
||
**那么局部最优:当前累加rest[j]的和curSum一旦小于0,起始位置至少要是j+1,因为从j开始一定不行。全局最优:找到可以跑一圈的起始位置**。
|
||
|
||
局部最优可以推出全局最优,找不出反例,试试贪心!
|
||
|
||
C++代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```CPP
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
|
||
int curSum = 0;
|
||
int totalSum = 0;
|
||
int start = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < gas.size(); i++) {
|
||
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
if (curSum < 0) { // 当前累加rest[i]和 curSum一旦小于0
|
||
start = i + 1; // 起始位置更新为i+1
|
||
curSum = 0; // curSum从0开始
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (totalSum < 0) return -1; // 说明怎么走都不可能跑一圈了
|
||
return start;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
* 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
|
||
* 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
|
||
|
||
**说这种解法为贪心算法,才是是有理有据的,因为全局最优解是根据局部最优推导出来的**。
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
对于本题首先给出了暴力解法,暴力解法模拟跑一圈的过程其实比较考验代码技巧的,要对while使用的很熟练。
|
||
|
||
然后给出了两种贪心算法,对于第一种贪心方法,其实我认为就是一种直接从全局选取最优的模拟操作,思路还是好巧妙的,值得学习一下。
|
||
|
||
对于第二种贪心方法,才真正体现出贪心的精髓,用局部最优可以推出全局最优,进而求得起始位置。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Java
|
||
```java
|
||
// 解法1
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
|
||
int sum = 0;
|
||
int min = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
|
||
sum += (gas[i] - cost[i]);
|
||
min = Math.min(sum, min);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if (sum < 0) return -1;
|
||
if (min >= 0) return 0;
|
||
|
||
for (int i = gas.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
|
||
min += (gas[i] - cost[i]);
|
||
if (min >= 0) return i;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return -1;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
```java
|
||
// 解法2
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
|
||
int curSum = 0;
|
||
int totalSum = 0;
|
||
int index = 0;
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
|
||
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
if (curSum < 0) {
|
||
index = (i + 1) % gas.length ;
|
||
curSum = 0;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (totalSum < 0) return -1;
|
||
return index;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Python
|
||
```python
|
||
# 解法1
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
n = len(gas)
|
||
cur_sum = 0
|
||
min_sum = float('inf')
|
||
|
||
for i in range(n):
|
||
cur_sum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
min_sum = min(min_sum, cur_sum)
|
||
|
||
if cur_sum < 0: return -1
|
||
if min_sum >= 0: return 0
|
||
|
||
for j in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
|
||
min_sum += gas[j] - cost[j]
|
||
if min_sum >= 0:
|
||
return j
|
||
|
||
return -1
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
# 解法2
|
||
class Solution:
|
||
def canCompleteCircuit(self, gas: List[int], cost: List[int]) -> int:
|
||
start = 0
|
||
curSum = 0
|
||
totalSum = 0
|
||
for i in range(len(gas)):
|
||
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
if curSum < 0:
|
||
curSum = 0
|
||
start = i + 1
|
||
if totalSum < 0: return -1
|
||
return start
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Go
|
||
```go
|
||
func canCompleteCircuit(gas []int, cost []int) int {
|
||
curSum := 0
|
||
totalSum := 0
|
||
start := 0
|
||
for i := 0; i < len(gas); i++ {
|
||
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
if curSum < 0 {
|
||
start = i+1
|
||
curSum = 0
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if totalSum < 0 {
|
||
return -1
|
||
}
|
||
return start
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Javascript
|
||
暴力:
|
||
```js
|
||
var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) {
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
|
||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i] //记录剩余油量
|
||
// 以i为起点行驶一圈,index为下一个目的地
|
||
let index = (i + 1) % cost.length
|
||
while(rest > 0 && index !== i) {
|
||
rest += gas[index] - cost[index]
|
||
index = (index + 1) % cost.length
|
||
}
|
||
if(rest >= 0 && index === i) return i
|
||
}
|
||
return -1
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
解法一:
|
||
```js
|
||
var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) {
|
||
let curSum = 0
|
||
let min = Infinity
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
|
||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
curSum += rest
|
||
if(curSum < min) {
|
||
min = curSum
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if(curSum < 0) return -1 //1.总油量 小于 总消耗量
|
||
if(min >= 0) return 0 //2. 说明油箱里油没断过
|
||
//3. 从后向前,看哪个节点能这个负数填平,能把这个负数填平的节点就是出发节点
|
||
for(let i = gas.length -1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
min += rest
|
||
if(min >= 0) {
|
||
return i
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return -1
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
解法二:
|
||
```Javascript
|
||
var canCompleteCircuit = function(gas, cost) {
|
||
const gasLen = gas.length
|
||
let start = 0
|
||
let curSum = 0
|
||
let totalSum = 0
|
||
|
||
for(let i = 0; i < gasLen; i++) {
|
||
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i]
|
||
if(curSum < 0) {
|
||
curSum = 0
|
||
start = i + 1
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if(totalSum < 0) return -1
|
||
|
||
return start
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### TypeScript
|
||
|
||
**暴力法:**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function canCompleteCircuit(gas: number[], cost: number[]): number {
|
||
for (let i = 0, length = gas.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||
let curSum: number = 0;
|
||
let index: number = i;
|
||
while (curSum >= 0 && index < i + length) {
|
||
let tempIndex: number = index % length;
|
||
curSum += gas[tempIndex] - cost[tempIndex];
|
||
index++;
|
||
}
|
||
if (index === i + length && curSum >= 0) return i;
|
||
}
|
||
return -1;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**解法二:**
|
||
|
||
```typescript
|
||
function canCompleteCircuit(gas: number[], cost: number[]): number {
|
||
let total: number = 0;
|
||
let curGas: number = 0;
|
||
let tempDiff: number = 0;
|
||
let resIndex: number = 0;
|
||
for (let i = 0, length = gas.length; i < length; i++) {
|
||
tempDiff = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
total += tempDiff;
|
||
curGas += tempDiff;
|
||
if (curGas < 0) {
|
||
resIndex = i + 1;
|
||
curGas = 0;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (total < 0) return -1;
|
||
return resIndex;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Rust
|
||
|
||
贪心算法:方法一
|
||
|
||
```Rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn can_complete_circuit(gas: Vec<i32>, cost: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||
let mut cur_sum = 0;
|
||
let mut min = i32::MAX;
|
||
for i in 0..gas.len() {
|
||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
cur_sum += rest;
|
||
if cur_sum < min { min = cur_sum; }
|
||
}
|
||
if cur_sum < 0 { return -1; }
|
||
if min > 0 { return 0; }
|
||
for i in (0..gas.len()).rev() {
|
||
let rest = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
min += rest;
|
||
if min >= 0 { return i as i32; }
|
||
}
|
||
-1
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
贪心算法:方法二
|
||
|
||
```Rust
|
||
impl Solution {
|
||
pub fn can_complete_circuit(gas: Vec<i32>, cost: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
|
||
let mut cur_sum = 0;
|
||
let mut total_sum = 0;
|
||
let mut start = 0;
|
||
for i in 0..gas.len() {
|
||
cur_sum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
total_sum += gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
if cur_sum < 0 {
|
||
start = i + 1;
|
||
cur_sum = 0;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if total_sum < 0 { return -1; }
|
||
start as i32
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
### C
|
||
|
||
贪心算法:方法一
|
||
|
||
|
||
```c
|
||
int canCompleteCircuit(int* gas, int gasSize, int* cost, int costSize){
|
||
int curSum = 0;
|
||
int i;
|
||
int min = INT_MAX;
|
||
//遍历整个数组。计算出每站的用油差。并将其与最小累加量比较
|
||
for(i = 0; i < gasSize; i++) {
|
||
int diff = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
curSum += diff;
|
||
if(curSum < min)
|
||
min = curSum;
|
||
}
|
||
//若汽油总数为负数,代表无法跑完一环。返回-1
|
||
if(curSum < 0)
|
||
return -1;
|
||
//若min大于等于0,说明每一天加油量比用油量多。因此从0出发即可
|
||
if(min >= 0)
|
||
return 0;
|
||
//若累加最小值为负,则找到一个非零元素(加油量大于出油量)出发。返回坐标
|
||
for(i = gasSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
|
||
min+=(gas[i]-cost[i]);
|
||
if(min >= 0)
|
||
return i;
|
||
}
|
||
//逻辑上不会返回这个0
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
贪心算法:方法二
|
||
```c
|
||
int canCompleteCircuit(int* gas, int gasSize, int* cost, int costSize){
|
||
int curSum = 0;
|
||
int totalSum = 0;
|
||
int start = 0;
|
||
|
||
int i;
|
||
for(i = 0; i < gasSize; ++i) {
|
||
// 当前i站中加油量与耗油量的差
|
||
int diff = gas[i] - cost[i];
|
||
|
||
curSum += diff;
|
||
totalSum += diff;
|
||
|
||
// 若0到i的加油量都为负,则开始位置应为i+1
|
||
if(curSum < 0) {
|
||
curSum = 0;
|
||
// 当i + 1 == gasSize时,totalSum < 0(此时i为gasSize - 1),油车不可能返回原点
|
||
start = i + 1;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 若总和小于0,加油车无论如何都无法返回原点。返回-1
|
||
if(totalSum < 0)
|
||
return -1;
|
||
|
||
return start;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Scala
|
||
|
||
暴力解法:
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||
for (i <- cost.indices) {
|
||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||
var index = (i + 1) % cost.length // index为i的下一个节点
|
||
while (rest > 0 && i != index) {
|
||
rest += (gas(index) - cost(index))
|
||
index = (index + 1) % cost.length
|
||
}
|
||
if (rest >= 0 && index == i) return i
|
||
}
|
||
-1
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
贪心算法,方法一:
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||
var curSum = 0
|
||
var min = Int.MaxValue
|
||
for (i <- gas.indices) {
|
||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||
curSum += rest
|
||
min = math.min(min, curSum)
|
||
}
|
||
if (curSum < 0) return -1 // 情况1: gas的总和小于cost的总和,不可能到达终点
|
||
if (min >= 0) return 0 // 情况2: 最小值>=0,从0号出发可以直接到达
|
||
// 情况3: min为负值,从后向前看,能把min填平的节点就是出发节点
|
||
for (i <- gas.length - 1 to 0 by -1) {
|
||
var rest = gas(i) - cost(i)
|
||
min += rest
|
||
if (min >= 0) return i
|
||
}
|
||
-1
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
贪心算法,方法二:
|
||
|
||
```scala
|
||
object Solution {
|
||
def canCompleteCircuit(gas: Array[Int], cost: Array[Int]): Int = {
|
||
var curSum = 0
|
||
var totalSum = 0
|
||
var start = 0
|
||
for (i <- gas.indices) {
|
||
curSum += (gas(i) - cost(i))
|
||
totalSum += (gas(i) - cost(i))
|
||
if (curSum < 0) {
|
||
start = i + 1 // 起始位置更新
|
||
curSum = 0 // curSum从0开始
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
if (totalSum < 0) return -1 // 说明怎么走不可能跑一圈
|
||
start
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://programmercarl.com/other/kstar.html" target="_blank">
|
||
<img src="../pics/网站星球宣传海报.jpg" width="1000"/>
|
||
</a>
|