404 lines
13 KiB
Markdown
404 lines
13 KiB
Markdown
<p align="center">
|
||
<a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/知识星球-代码随想录-blue" alt=""></a>
|
||
<a href="https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/刷题-微信群-green" alt=""></a>
|
||
<a href="https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201210231711160.png"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/公众号-代码随想录-brightgreen" alt=""></a>
|
||
<a href="https://space.bilibili.com/525438321"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/B站-代码随想录-orange" alt=""></a>
|
||
</p>
|
||
<p align="center"><strong>欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!</strong></p>
|
||
|
||
|
||
> 求高度还是求深度,你搞懂了不?
|
||
|
||
## 110.平衡二叉树
|
||
|
||
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
|
||
|
||
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
|
||
|
||
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
|
||
|
||
示例 1:
|
||
|
||
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
返回 true 。
|
||
|
||
示例 2:
|
||
|
||
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
返回 false 。
|
||
|
||
## 题外话
|
||
|
||
咋眼一看这道题目和[二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/guKwV-gSNbA1CcbvkMtHBg)很像,其实有很大区别。
|
||
|
||
这里强调一波概念:
|
||
|
||
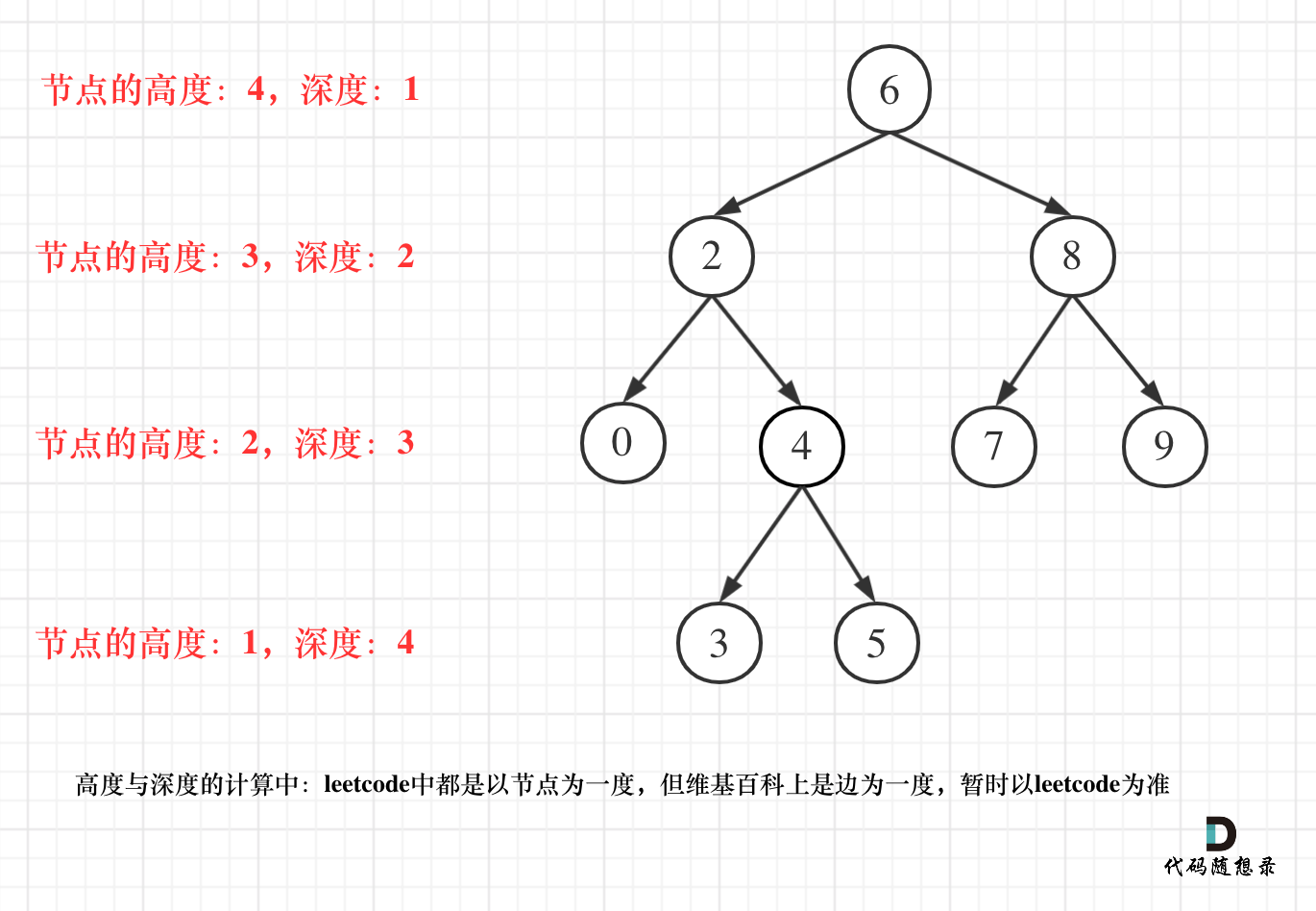
* 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
|
||
* 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数。
|
||
|
||
但leetcode中强调的深度和高度很明显是按照节点来计算的,如图:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
关于根节点的深度究竟是1 还是 0,不同的地方有不一样的标准,leetcode的题目中都是以节点为一度,即根节点深度是1。但维基百科上定义用边为一度,即根节点的深度是0,我们暂时以leetcode为准(毕竟要在这上面刷题)。
|
||
|
||
因为求深度可以从上到下去查 所以需要前序遍历(中左右),而高度只能从下到上去查,所以只能后序遍历(左右中)
|
||
|
||
有的同学一定疑惑,为什么[二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/guKwV-gSNbA1CcbvkMtHBg)中求的是二叉树的最大深度,也用的是后序遍历。
|
||
|
||
**那是因为代码的逻辑其实是求的根节点的高度,而根节点的高度就是这颗树的最大深度,所以才可以使用后序遍历。**
|
||
|
||
在[二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/guKwV-gSNbA1CcbvkMtHBg)中,如果真正求取二叉树的最大深度,代码应该写成如下:(前序遍历)
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int result;
|
||
void getDepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
|
||
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
|
||
|
||
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
|
||
|
||
if (node->left) { // 左
|
||
depth++; // 深度+1
|
||
getDepth(node->left, depth);
|
||
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
|
||
}
|
||
if (node->right) { // 右
|
||
depth++; // 深度+1
|
||
getDepth(node->right, depth);
|
||
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
|
||
}
|
||
return ;
|
||
}
|
||
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
result = 0;
|
||
if (root == 0) return result;
|
||
getDepth(root, 1);
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
**可以看出使用了前序(中左右)的遍历顺序,这才是真正求深度的逻辑!**
|
||
|
||
注意以上代码是为了把细节体现出来,简化一下代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
int result;
|
||
void getDepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
|
||
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
|
||
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
|
||
if (node->left) { // 左
|
||
getDepth(node->left, depth + 1);
|
||
}
|
||
if (node->right) { // 右
|
||
getDepth(node->right, depth + 1);
|
||
}
|
||
return ;
|
||
}
|
||
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
result = 0;
|
||
if (root == 0) return result;
|
||
getDepth(root, 1);
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 本题思路
|
||
|
||
### 递归
|
||
|
||
此时大家应该明白了既然要求比较高度,必然是要后序遍历。
|
||
|
||
递归三步曲分析:
|
||
|
||
1. 明确递归函数的参数和返回值
|
||
|
||
参数的话为传入的节点指针,就没有其他参数需要传递了,返回值要返回传入节点为根节点树的深度。
|
||
|
||
那么如何标记左右子树是否差值大于1呢。
|
||
|
||
如果当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树已经不是二叉平衡树了,还返回高度的话就没有意义了。
|
||
|
||
所以如果已经不是二叉平衡树了,可以返回-1 来标记已经不符合平衡树的规则了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
// -1 表示已经不是平衡二叉树了,否则返回值是以该节点为根节点树的高度
|
||
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
2. 明确终止条件
|
||
|
||
递归的过程中依然是遇到空节点了为终止,返回0,表示当前节点为根节点的书高度为0
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
if (node == NULL) {
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
3. 明确单层递归的逻辑
|
||
|
||
如何判断当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树是否是平衡二叉树呢,当然是左子树高度和右子树高度相差。
|
||
|
||
分别求出左右子树的高度,然后如果差值小于等于1,则返回当前二叉树的高度,否则则返回-1,表示已经不是二叉树了。
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int leftDepth = depth(node->left); // 左
|
||
if (leftDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
int rightDepth = depth(node->right); // 右
|
||
if (rightDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
|
||
int result;
|
||
if (abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1) { // 中
|
||
result = -1;
|
||
} else {
|
||
result = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth); // 以当前节点为根节点的最大高度
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return result;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
代码精简之后如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
|
||
if (leftDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
|
||
if (rightDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
return abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
此时递归的函数就已经写出来了,这个递归的函数传入节点指针,返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是二叉平衡树,则返回-1。
|
||
|
||
getDepth整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
|
||
if (node == NULL) {
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
|
||
if (leftDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
|
||
if (rightDepth == -1) return -1;
|
||
return abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
最后本题整体递归代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是二叉搜索树了则返回-1
|
||
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
|
||
if (node == NULL) {
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left);
|
||
if (leftDepth == -1) return -1; // 说明左子树已经不是二叉平衡树
|
||
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right);
|
||
if (rightDepth == -1) return -1; // 说明右子树已经不是二叉平衡树
|
||
return abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth);
|
||
}
|
||
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
return getDepth(root) == -1 ? false : true;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 迭代
|
||
|
||
在[二叉树:看看这些树的最大深度](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/guKwV-gSNbA1CcbvkMtHBg)中我们可以使用层序遍历来求深度,但是就不能直接用层序遍历来求高度了,这就体现出求高度和求深度的不同。
|
||
|
||
本题的迭代方式可以先定义一个函数,专门用来求高度。
|
||
|
||
这个函数通过栈模拟的后序遍历找每一个节点的高度(其实是通过求传入节点为根节点的最大深度来求的高度)
|
||
|
||
代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```C++
|
||
// cur节点的最大深度,就是cur的高度
|
||
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
if (cur != NULL) st.push(cur);
|
||
int depth = 0; // 记录深度
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
TreeNode* node = st.top();
|
||
if (node != NULL) {
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
st.push(node); // 中
|
||
st.push(NULL);
|
||
depth++;
|
||
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
|
||
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
|
||
|
||
} else {
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
node = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
depth--;
|
||
}
|
||
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
然后再用栈来模拟前序遍历,遍历每一个节点的时候,再去判断左右孩子的高度是否符合,代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
if (root == NULL) return true;
|
||
st.push(root);
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
if (abs(getDepth(node->left) - getDepth(node->right)) > 1) { // 判断左右孩子高度是否符合
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
|
||
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
整体代码如下:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
private:
|
||
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
if (cur != NULL) st.push(cur);
|
||
int depth = 0; // 记录深度
|
||
int result = 0;
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
TreeNode* node = st.top();
|
||
if (node != NULL) {
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
st.push(node); // 中
|
||
st.push(NULL);
|
||
depth++;
|
||
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
|
||
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
|
||
|
||
} else {
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
node = st.top();
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
depth--;
|
||
}
|
||
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
|
||
stack<TreeNode*> st;
|
||
if (root == NULL) return true;
|
||
st.push(root);
|
||
while (!st.empty()) {
|
||
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
|
||
st.pop();
|
||
if (abs(getDepth(node->left) - getDepth(node->right)) > 1) {
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
|
||
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
|
||
}
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
当然此题用迭代法,其实效率很低,因为没有很好的模拟回溯的过程,所以迭代法有很多重复的计算。
|
||
|
||
虽然理论上所有的递归都可以用迭代来实现,但是有的场景难度可能比较大。
|
||
|
||
**例如:都知道回溯法其实就是递归,但是很少人用迭代的方式去实现回溯算法!**
|
||
|
||
因为对于回溯算法已经是非常复杂的递归了,如果在用迭代的话,就是自己给自己找麻烦,效率也并不一定高。
|
||
|
||
## 总结
|
||
|
||
通过本题可以了解求二叉树深度 和 二叉树高度的差异,求深度适合用前序遍历,而求高度适合用后序遍历。
|
||
|
||
本题迭代法其实有点复杂,大家可以有一个思路,也不一定说非要写出来。
|
||
|
||
但是递归方式是一定要掌握的!
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 其他语言版本
|
||
|
||
Java:
|
||
|
||
|
||
Python:
|
||
|
||
|
||
Go:
|
||
```Go
|
||
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
|
||
if root==nil{
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
if !isBalanced(root.Left) || !isBalanced(root.Right){
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
LeftH:=maxdepth(root.Left)+1
|
||
RightH:=maxdepth(root.Right)+1
|
||
if abs(LeftH-RightH)>1{
|
||
return false
|
||
}
|
||
return true
|
||
}
|
||
func maxdepth(root *TreeNode)int{
|
||
if root==nil{
|
||
return 0
|
||
}
|
||
return max(maxdepth(root.Left),maxdepth(root.Right))+1
|
||
}
|
||
func max(a,b int)int{
|
||
if a>b{
|
||
return a
|
||
}
|
||
return b
|
||
}
|
||
func abs(a int)int{
|
||
if a<0{
|
||
return -a
|
||
}
|
||
return a
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
-----------------------
|
||
* 作者微信:[程序员Carl](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b66DFkOp8OOxdZC_xLZxfw)
|
||
* B站视频:[代码随想录](https://space.bilibili.com/525438321)
|
||
* 知识星球:[代码随想录](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/QVF6upVMSbgvZy8lHZS3CQ)
|
||
<div align="center"><img src=../pics/公众号.png width=450 alt=> </img></div> |